maternal pelvis
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
function of pelvis
transmits bodyweight to legs which enables mobility
gives flexibility of movement when upright
enables parturition
protects the reproductive organs
how many bones does the pelvis comprise of
4
what are the 4 bones
2 innominate bones
sacrum
coccyx
these bones enclose the pelvic cavity
where are the innominate bones joined
in the front (anteriorly) at the symphysis pubis
where do the four bones connect at
2 sacroiliac joints
symphysis pubis
sacrococcygeal joint
what are the 3 components of each innominate bone
ilium
ischium
pubis
pelvic ligaments
interpubic ligaments
sacroiliac ligaments
sacrococcygeal ligaments
sacrotuberous ligaments
sacrospinous ligaments
where is the ischium
lower part of pelvis (L- shaped)
what does the ischium connect to
the ilium at the back (posteriorly) and the pubis anteriorly
what thickened area of bone does the ischium have
ischial tuberosity
what is the ischial tuberosity
thickened area of bone in ischium
structure that the body rests on when a person is in a seated position
what is behind and slightly above the ischial tuberosity
ischial spine
ischial spine
when assessing a woman’s progress in labour and descent of foetus through the pelvis is estimated in relation to the level of the ischial spines
what are the components of the pubis
main body
2 arm-like structures which protrude out
what are the parts that protrude out in the pubis
rami (on either side)
superior (upper) ramus
inferior (lower) ramus
what does the inferior ramus attach to
ischium
what does the superior ramus attach to
ilium at the iliopectineal eminence
how much of the acetabulum does the superior ramus form
one-fifth
where do the two pubic bones meet
symphysis pubis
what to the two inferior rami form
the pubic arch
what does the suprapubic angle need to be and why
at least 90
in order to allow the baby to pass underneath it
what is the obturator foramen
triangular shaped space enclosed by the body of the pubic bone, rami and ischium
each innominate bone has a large cup shaped socket on it’s surface what’s it called
acetabulum
what is the acetabulum
it is with this that the head of the femur (thigh bone) articulates to form a person’s hip joint
there are 2 curves on the lower aspect of the innominate bone
greater sciatic bone
lesser sciatic bone
describe the greater sciatic notch
wide and rounded extending from the posterior inferior iliac spine up to the ischial spine
what can the size of the notch be used for
assessing the overall shape and size of the pelvis
where is the lesser sciatic notch
between the ischial spine and ischial tuberosity
what does the sacrum form
the back wall of the pelvis
what does the sacrum comprise of
5 vertebrae that are fused together to form a wedge shaped bone
what is the protrusion on the first vertebrae known as
the sacral promontory
what happens if the sacral promontory is too pronounced
it can impede fetal descent through the pelvis
what are on each side of the first sacral vertebra
widened wings of bone- sacral alae
what is the sacral bone perforated by
fur sets of foramina (holes)
how do the four sacral nerves pass
through the perforation
what shape is the anterior surface of the sacrum
concave
what role does the sacrum have
guiding the baby through the maternal pelvis and as part of this navigating around the curve of carus
foetus descends during labour and birth
what is the coccyx
small triangular bone that articulates with the lower end of the sacrum
what does the coccyx comprise of
4 fused vertebrae
what happens with the coccyx during childbirth
moves backwards to help enlarge the pelvic outlet, which assists the baby’s passage to facilitate a vaginal birth
what does the coccyx provide attachment points for
pelvic ligaments, the muscle fibres of the anal sphincter, and the ischiococcygeus muscle of pelvic floor
what is the true pelvis
bony canal that the foetus needs to pass through during the normal mechanism of childbirth (negotiates passage)
what does the true pelvis incorporate
the portions of the pelvis that are below the oblique plane of the pelvic brim
what is the false pelvis
portion of the pelvis that is above the pelvic brim- no impact on birth
what does the true pelvis comprise of
brim, cavity, and an outlet
what does the the pelvic brim separate
the false pelvis, which lies above, from the true pelvis that is below
what is the shape of the brim
round with the exception of the sacral promontory, which protrudes into it posteriorly
what does the pubic bone form
the anterior border of pelvic brim
what is the iliac bones, its lateral borders and the posterior border formed by
the promontory and sacral alae
what are the 3 diameters that are measured (pelvic brim)
anterior posterior diameter
oblique diameter (left and right)
transverse diameter
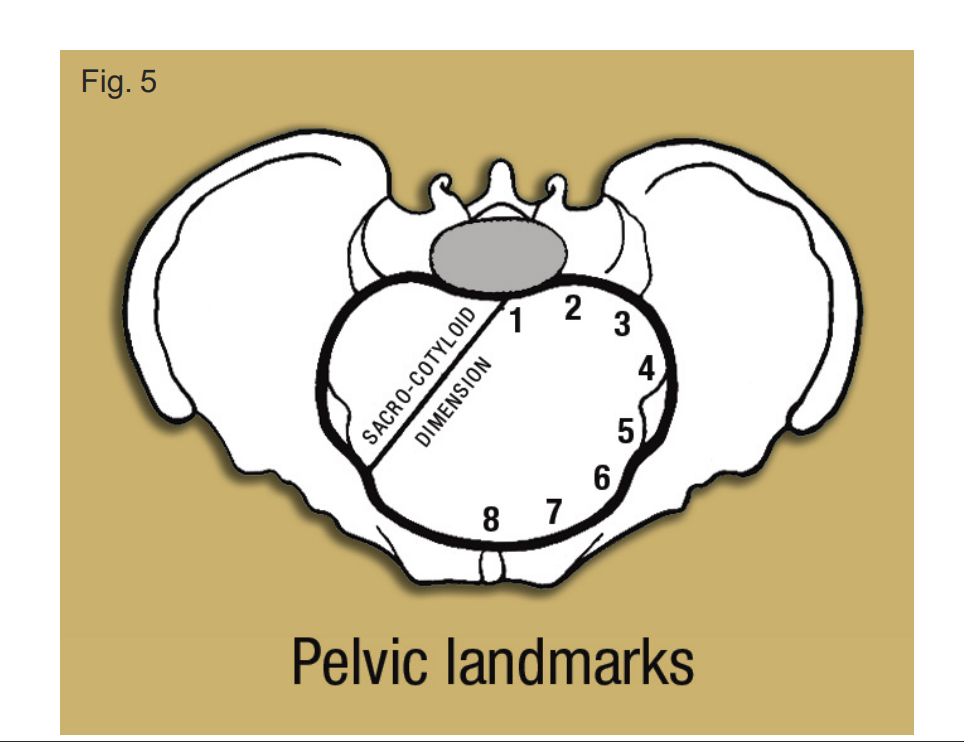
note down all the landmarks 1-8
1) sacral promontory
2) sacral ala
3) sacroiliac joint
4) iliopectineal line
5) iliopectineal eminence
6) superior ramus of pubic bone
7) upper inner border of the body of the pubic bone
8) upper inner border of the symphysis pubis
diameters of pelvic brim
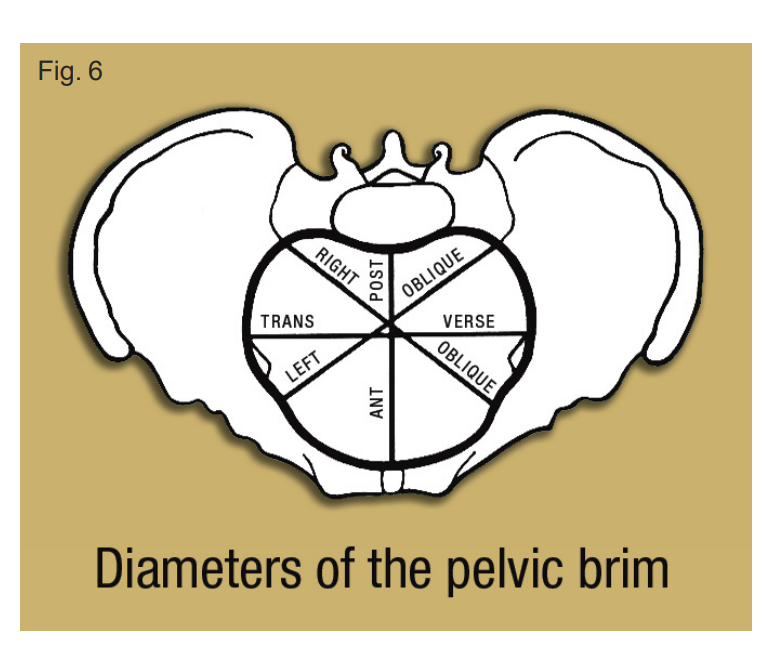
what is the pelvic cavity
extends from the pelvic brim to the pelvic outlet
what does the pelvic cavity form
curve of carus
what is the curve of carus
foetus has to navigate in order to be born and has no specific landmarks
in the anteroposterior view, what does the cavity look like
wedge shaped- shallow at the front and deep at the back
what does the cavity look like if viewed from above in a gynaecoid pelvis
circular in shape and designed to facilitate the descent and rotation of the presenting part
what are the boundaries of the cavity
curve of sacrum
sacroiliac joints
sacrospinous ligaments
ischia
superior pubic ramus
inferior pubic ramus
bodies of the pubes
symphysis pubis
what is the shape of the pelvic outlet
either ovoid or diamond shaped space
what is the perimeter of the pelvic outlet partially comprised of
ligaments
what can the pelvic outlet be described by
anatomical structure
obstetric dimension- space available through which the baby must pass during birth
what are the anatomical boundaries of the pelvic outlet
tip of coccyx
sacrotuberous ligaments
ischial tuberosities
pubic arch
what is the obstetric outlet bounded by
inner border of the base of sacrum- as a result of the coccyx being deflected outwards during childbirth, thus enlarging the outlet
sacrospinous ligaments
ischial spines
lower inner border of the symphysis pubis
the bones of the pelvic outlet are also points of attachment for
the muscles of the pelvic floor and perineum
pelvic measurement of the brim- anteroposterior
11cm
pelvic measurement of brim- right and left oblique
12cm
pelvic measurement of brim- transverse
13cm
pelvic measurement of cavity- anteroposterior
12cm
pelvic measurement of cavity- right and left oblique
12cm
pelvic measurement of cavity- transverse
12cm
pelvic measurement of outlet- anteroposterior
13cm
pelvic measurement of outlet- anteroposterior
13cm
pelvic measurement of outlet- right and left oblique
12cm
pelvic measurement of outlet- transverse
11cm
why are the various diameters significant
help with the successful passage of foetus through the bony pelvic structure
what are pelvic planes
hypothetical flat surfaces on the pelvis, which is located at the brim, cavity and outlet
taking the pelvic brim as our landmark, what’s the plane of the brim
at an angle of 55 degrees to the horizontal
what does the term plane describe
relationship between the pelvis and a flat surface
hypothetical angles are then created in relation to the degree of tilt of a particular individual, which provides a representation of the angles in relation to the planes of the pelvis
curve of carus
imaginary line through which a foetus rotates as it passes through the pelvis
what does the shape of the pelvis determine
the availability of pelvic diameters during childbirth
gynaecoid
classic
inlet is transversely oval
roomier, shallow pelvic cavity with a broad well curved sacrum
sub-pubic angle of 90
blunt ischial spines
android
more masc. in it’s shape and diameters
heart shaped inlet
funnel shaped deep cavity
sacrum is straight—> contracted pelvic outlet
sub-pubic arch has an angle less than 90
ischial spines are prominent—> hinder internal rotation of fetal head—> deep transverse arrest
anthropoid
results from high assimilation i.e the sacral body is assimilated to the fifth lumbar vertebra
pelvic brim is long, narrow and oval in shape
sacrum is long and concave
sub-pubic angle is very wide
ischial spines aren’t prominent
platypelloid
wide pelvis that is characteristically flattened at the brim with the promontory of the sacrum pushed forwards—> forms a kidney shaped pelvic brim
sacrum is flat
pelvic cavity is shallow
sub-pubic angle is greater than 90 degrees
ischial spines are blunt—> fetal descent through cavity is usually unproblematic
gynaecoid- shape of brim
round
gynaecoid- subpubic arch
85-90 degrees
gynaecoid- ischial spines
not prominent, blunt
gynaecoid- sacrum
deep and curved
android- shape of brim
triangular, heart shaped
android- subpubic arch
60-75 degrees (narrow)
android- ischial spines
prominent and narrow interspinous diameter
android- sacrum
straight- flattened and long
anthropoid- shape of brim
oval (widest in the anteroposterior diameter)
anthropoid- subpubic arch
more than 90 degrees
anthropoid- ischial spines
not prominent but may have narrowed interspinous diameter
anthropoid- sacrum
long and narrow- may be slightly curved
platypelloid- shape of brim
bean shaped- flattened
platypelloid- subpubic arch
more than 90 degrees
platypelloid- ischial spines
blunted, usually widely separated- not prominent