Monosaccharides: Structure, Classification, and Functions in Biology
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What are monosaccharides?
The simplest form of carbohydrates, consisting of single sugar units.
What is the general formula for carbohydrates?
Cn(H2O)m
Name three examples of monosaccharides.
Glucose, cellulose, sucrose.
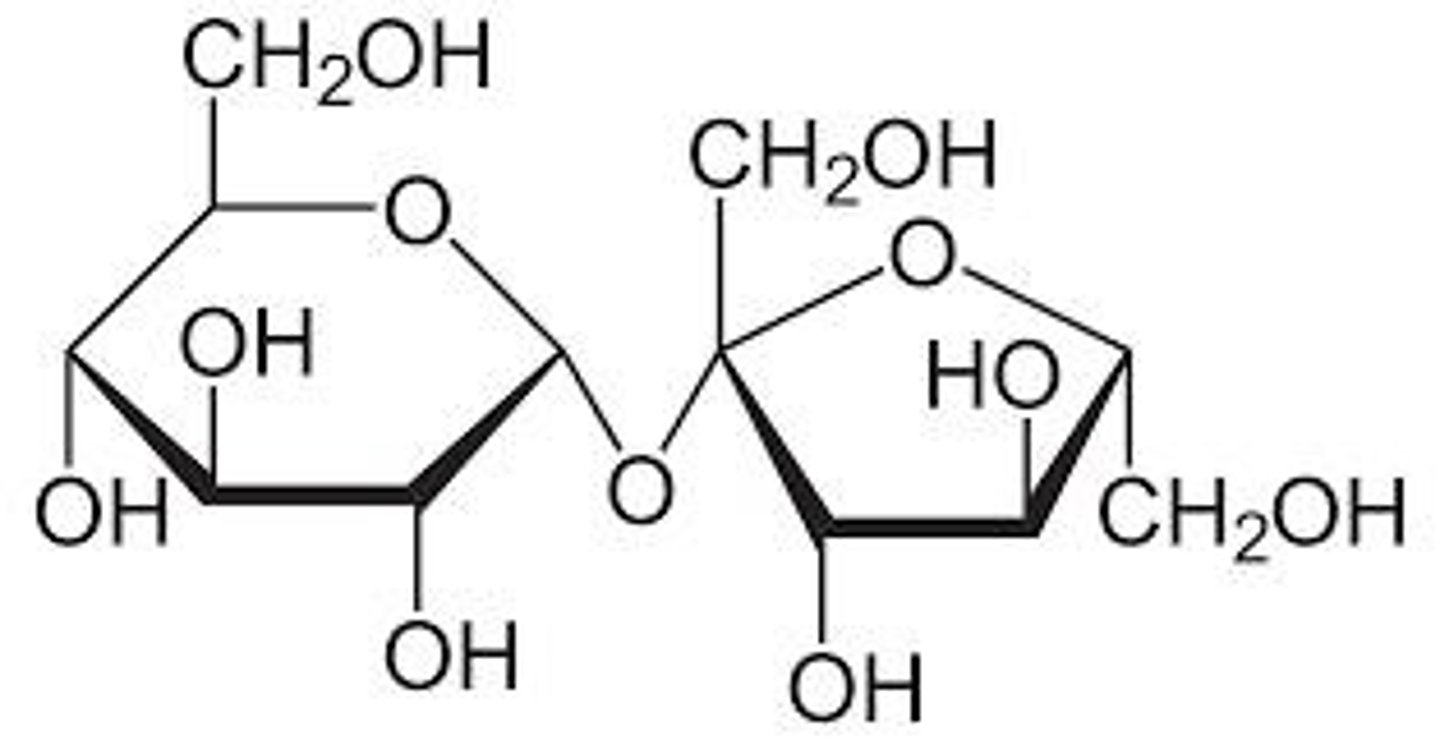
What functional groups do carbohydrates contain?
Multiple hydroxyl (OH) groups.
What is the molecular weight range for monosaccharides?
From as small as glyceraldehyde (90 g/mol) to as large as amylopectin (over 200,000,000 g/mol).
What are glycoproteins?
Covalently linked carbohydrates with proteins.
What are glycolipids?
Covalently linked carbohydrates with lipids.
What are the primary functions of carbohydrates?
Energy source and storage, structural components, informational molecules.
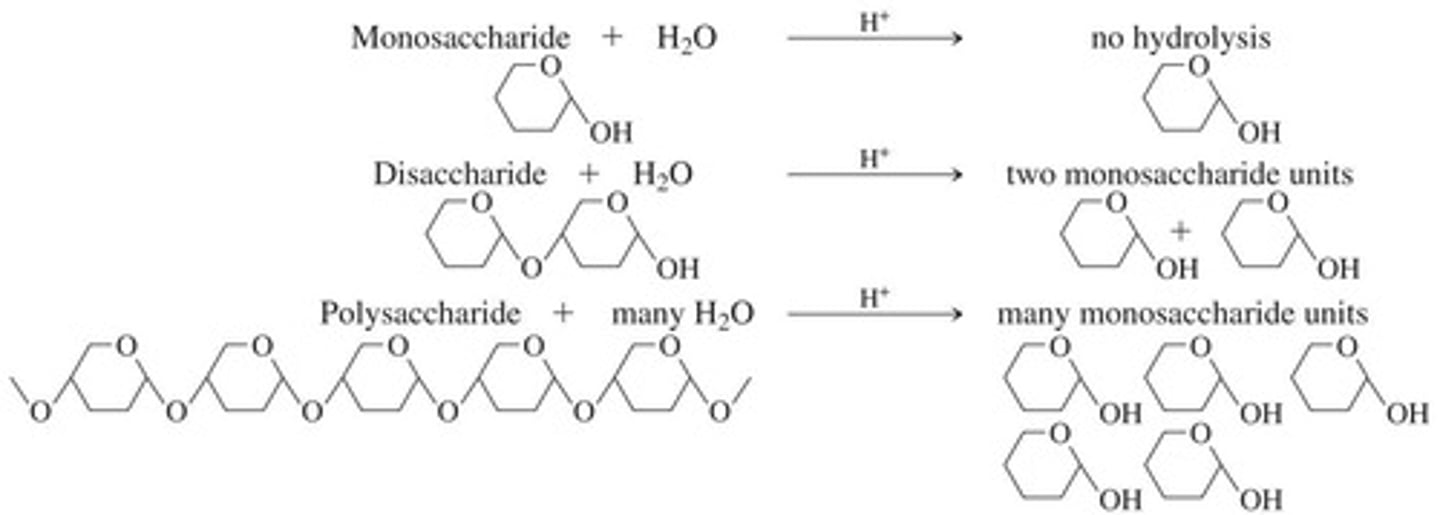
What are the three types of carbohydrates?
Monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides.
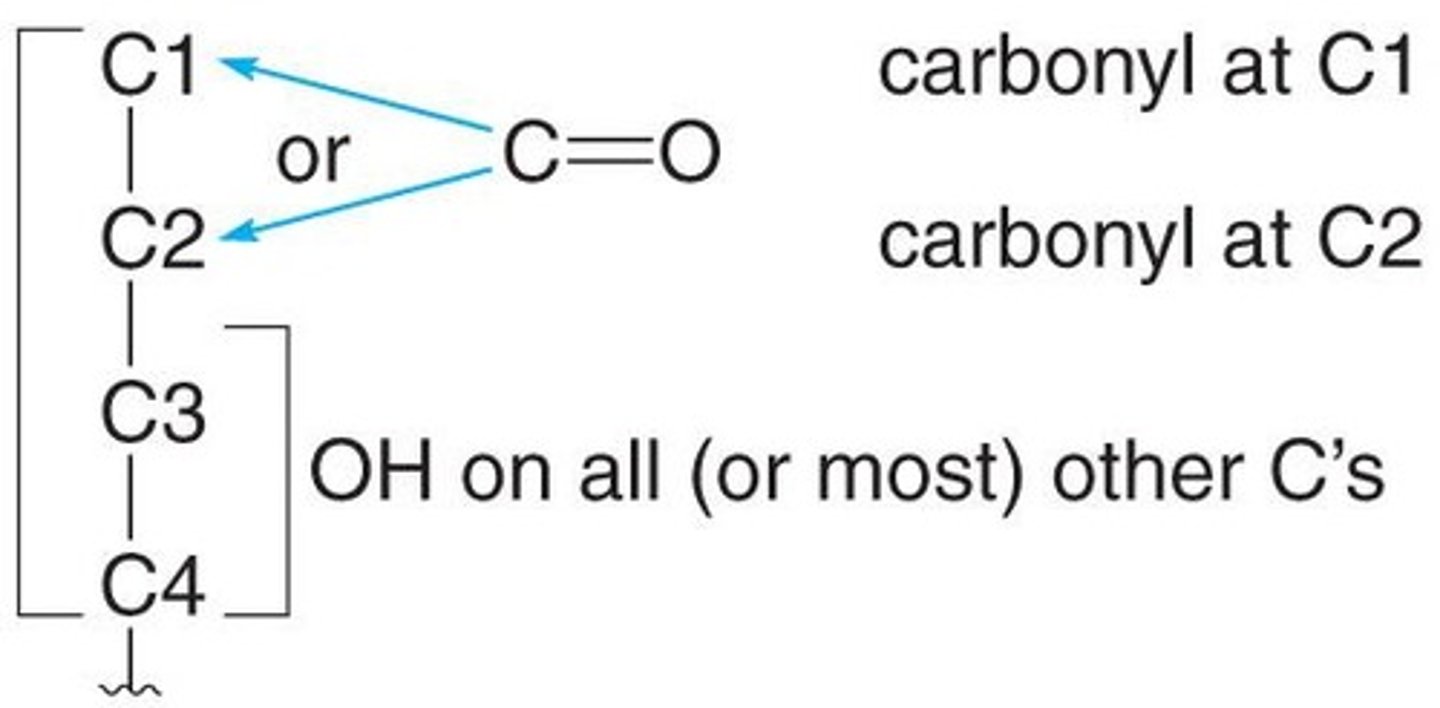
How are monosaccharides classified?
Based on the number of carbons (triose, tetrose, pentose, hexose) and the carbonyl functional group (aldose or ketose).
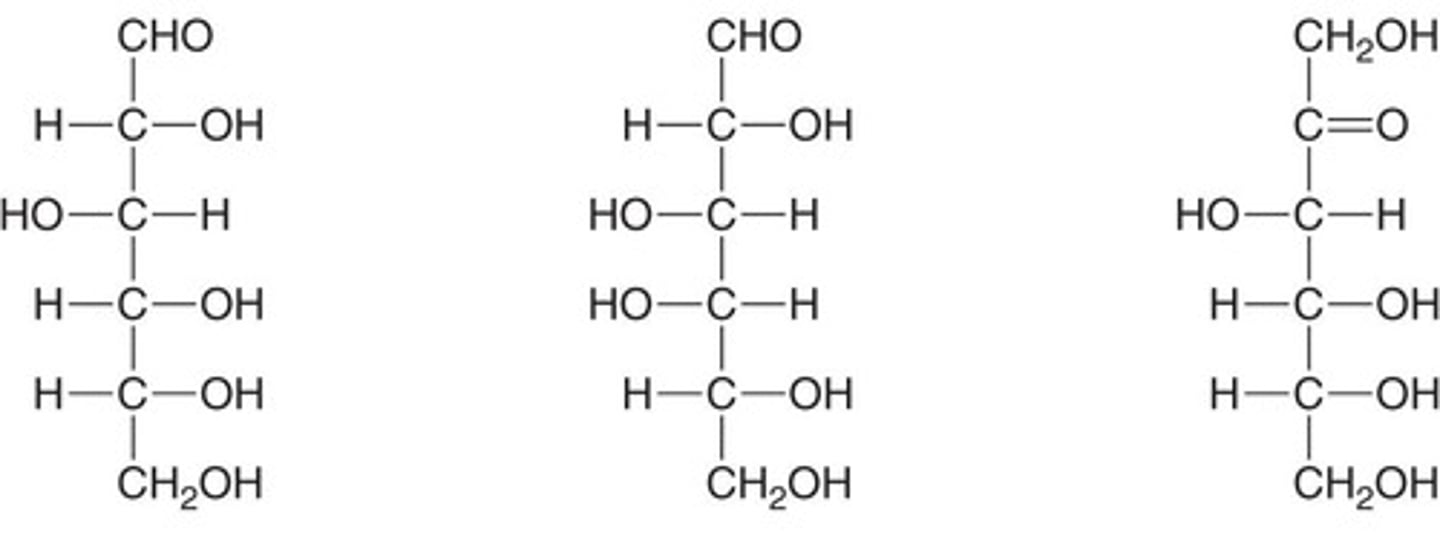
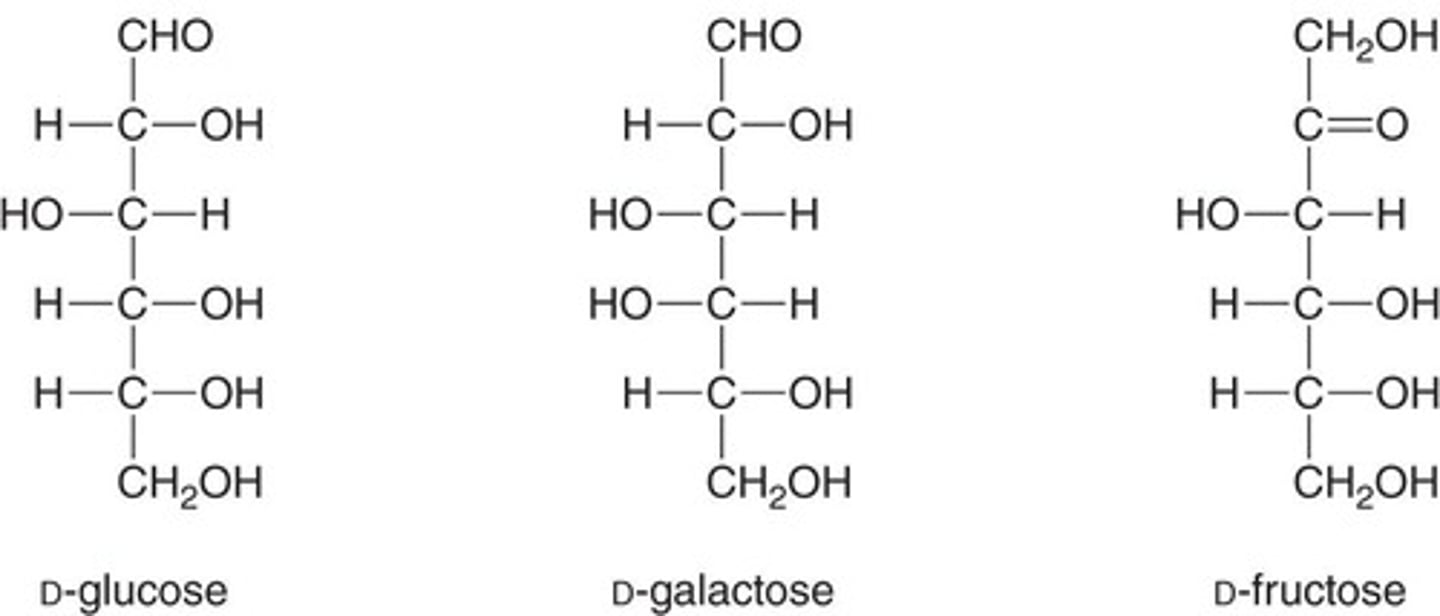
What distinguishes aldoses from ketoses?
Aldoses have an aldehyde group, while ketoses have a ketone group.
What are enantiomers?
Isomers that are nonsuperimposable mirror images of each other.
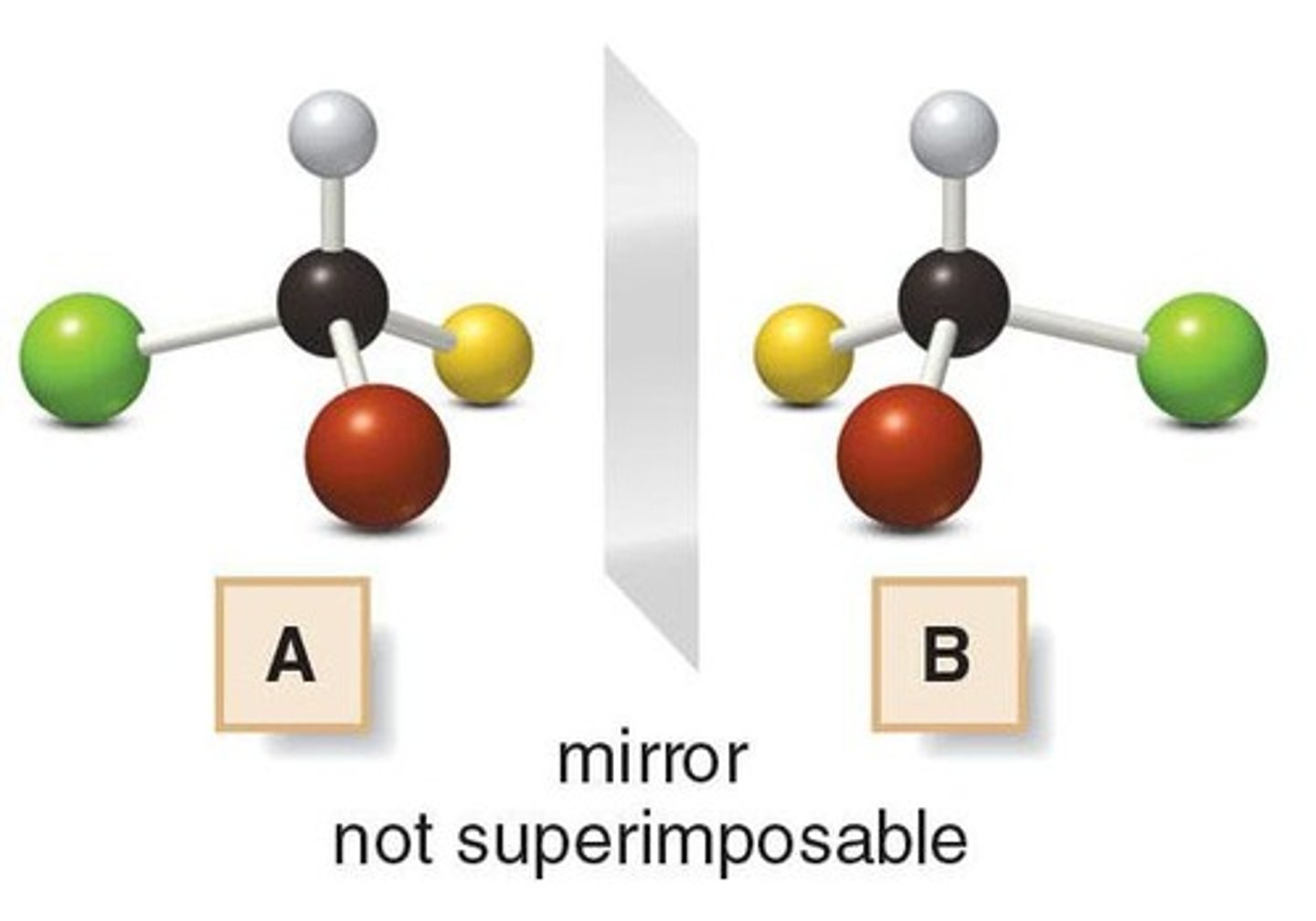
What is a chiral carbon?
A carbon atom bonded to four different groups.
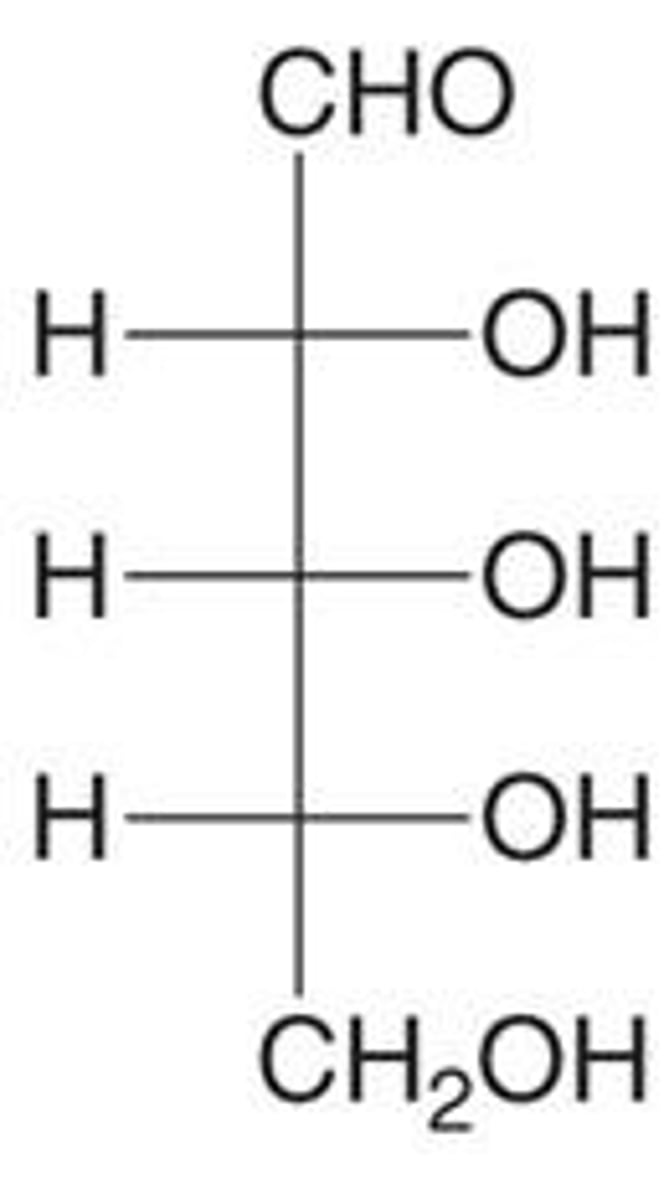
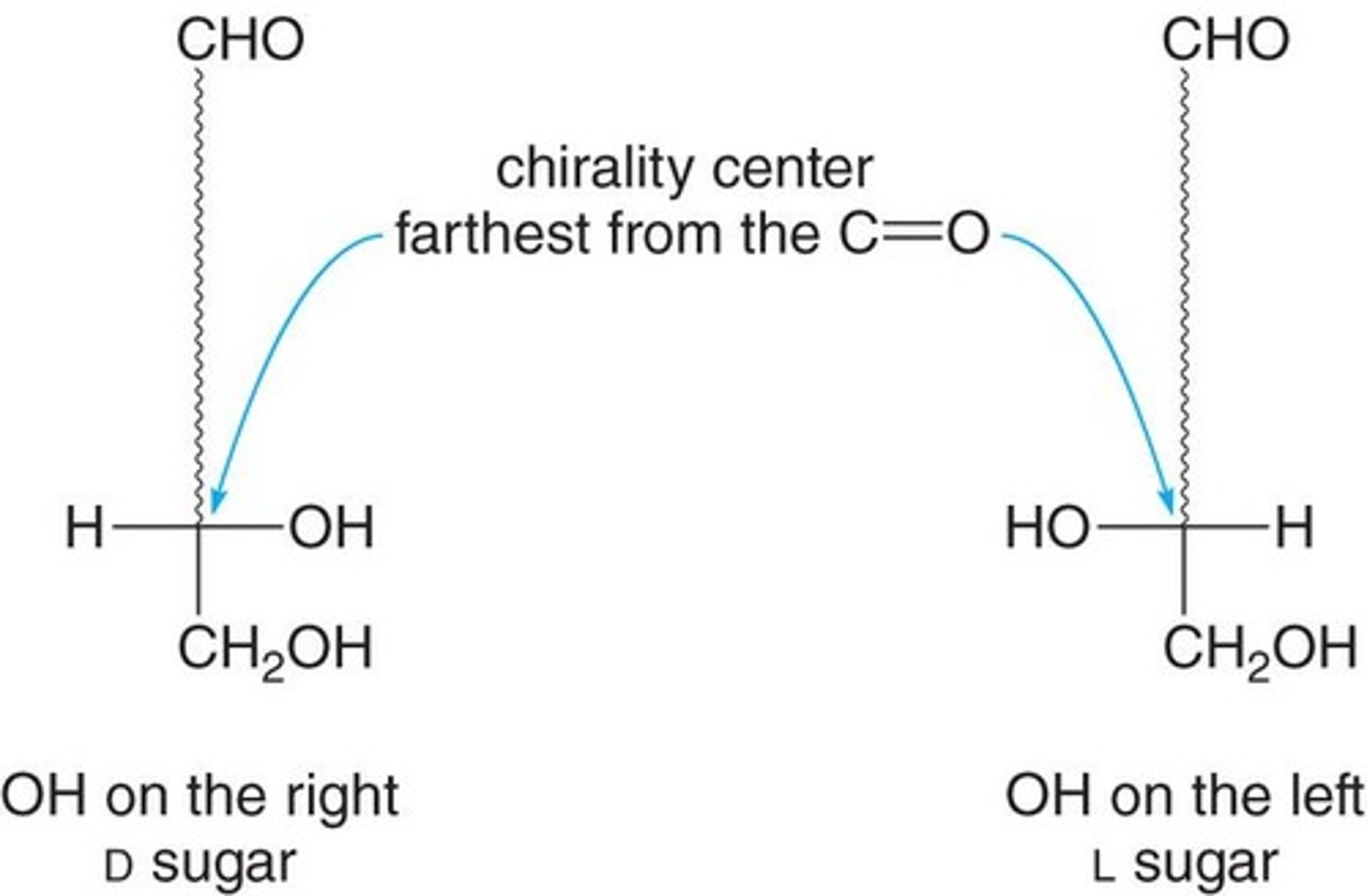
What is the D and L notation in sugars?
D-sugars have the -OH group on the right, while L-sugars have it on the left.
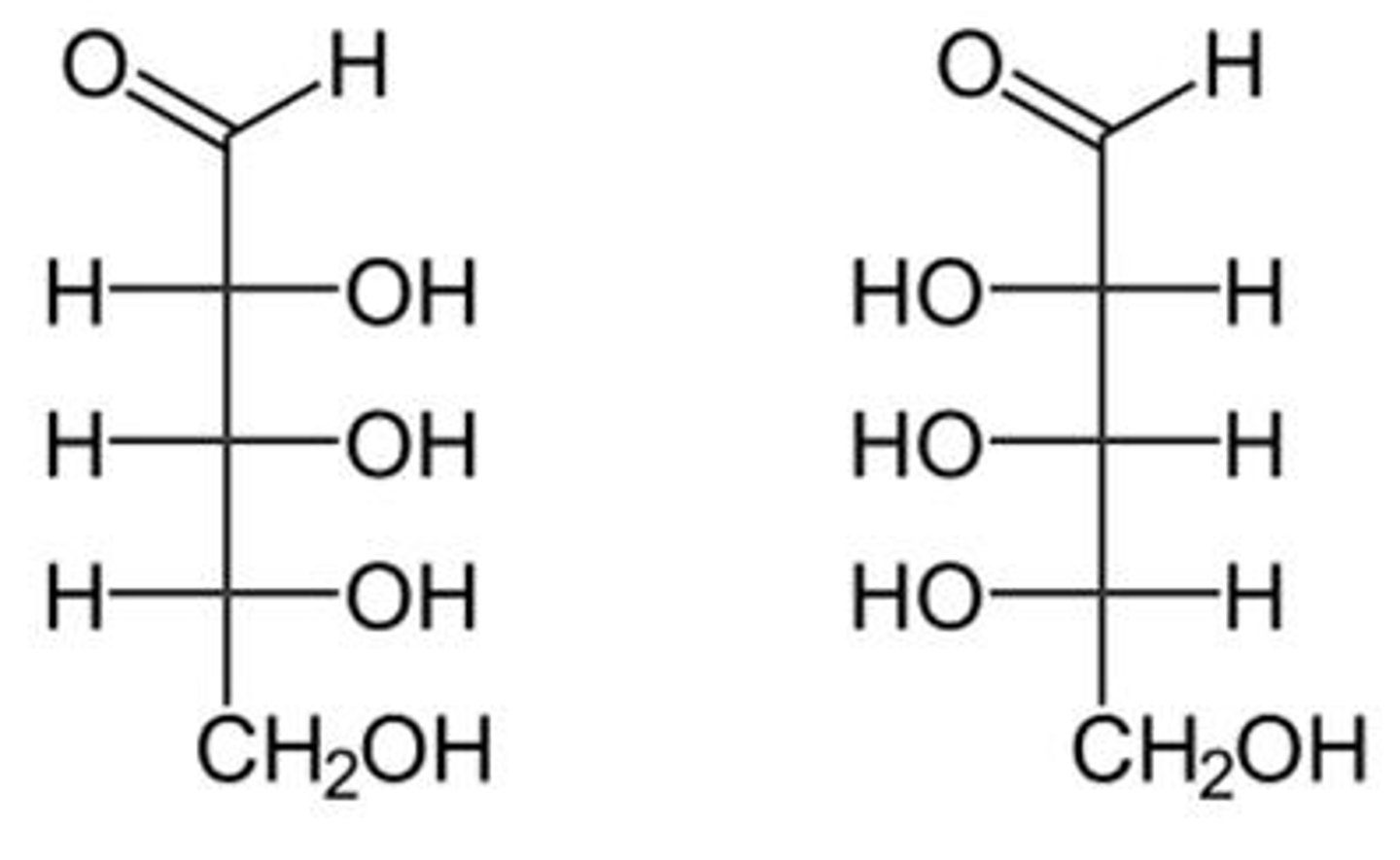
What are epimers?
Stereoisomers that differ at only one chiral carbon.
What is D-Glucose also known as?
Dextrose or blood sugar.
What is the cyclic form of D-Glucose?
A 6-membered ring formed through cyclization.
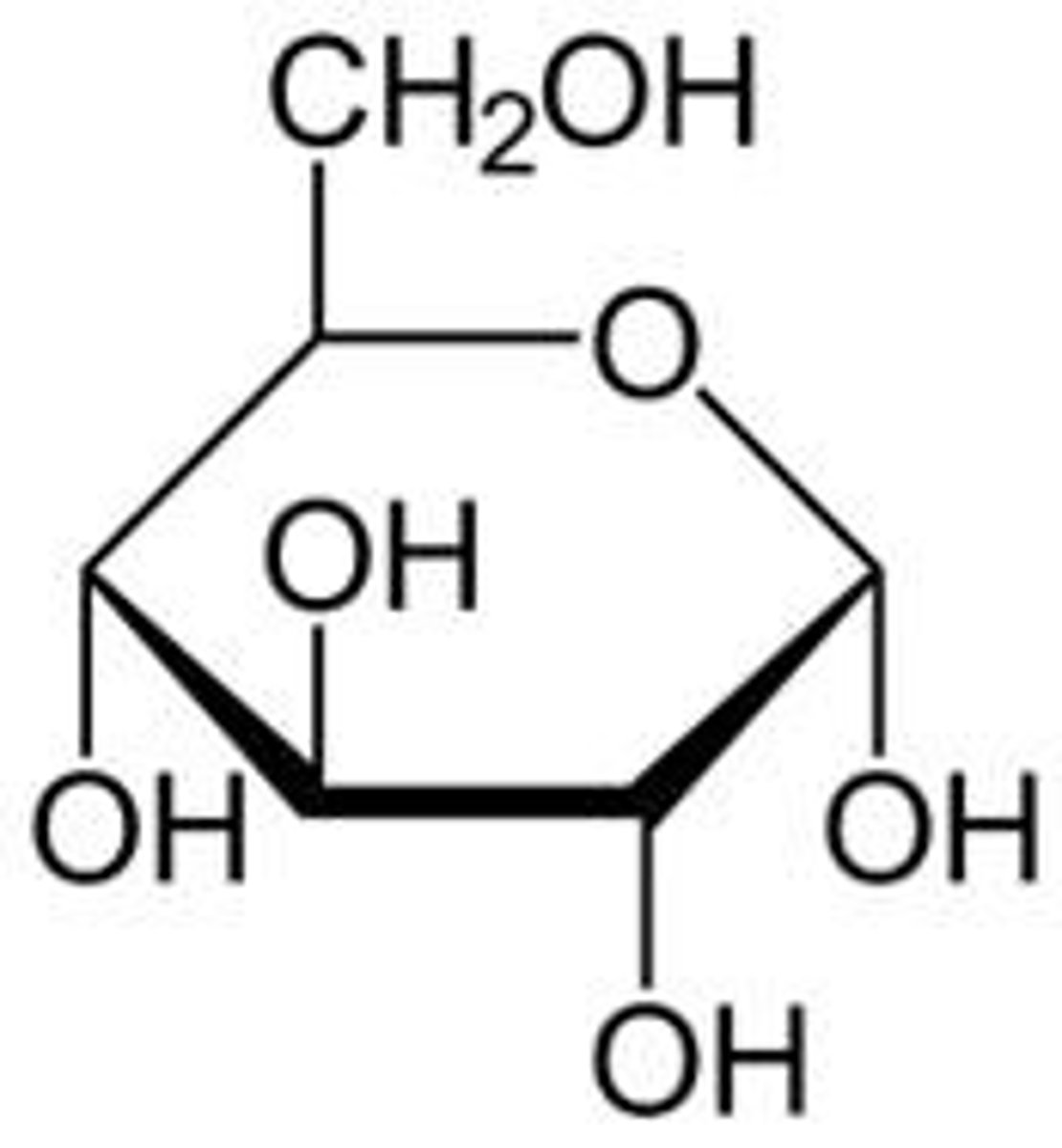
What is D-Ribose important for?
It is a key component of RNA.
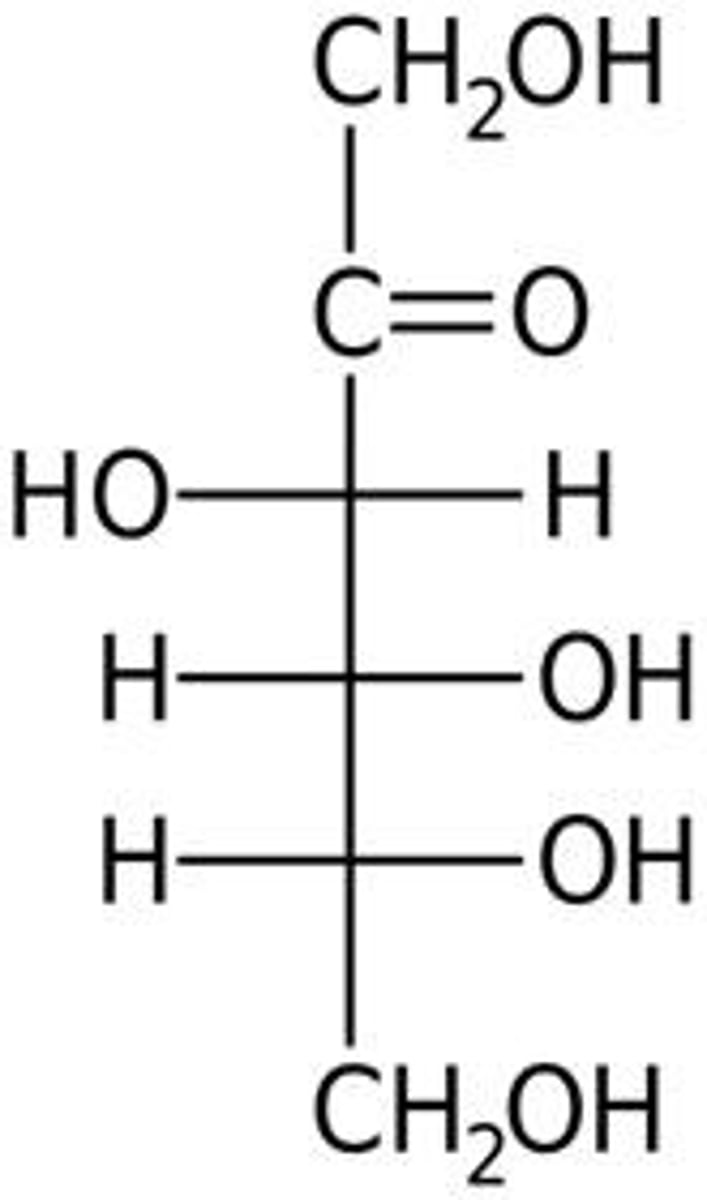
What is D-Fructose known for?
It is the sweetest naturally occurring carbohydrate.
What happens during the oxidation of monosaccharides?
The aldehyde group can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid.
What are reducing sugars?
Sugars that can be oxidized, such as D-glucose and D-fructose.
What occurs during the reduction of monosaccharides?
The carbonyl group is converted into a hydroxyl group, producing sugar alcohols.
What is xylitol?
A sugar alcohol derived from xylose, known for being sweet and low-calorie.