DNA translation
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
define the translation
process of synthesise proteins in cytoplasm using mRNA as a template
what is the genetic codon made from
how many codons DNA have
type of them
why initiation codon is a sense codon
what are non sense codons
3 adjunct nucleotides
64
61 sense codons 3 non sens codons
because it code fro an aa methionine (AUG)3
UAA UGA UAG
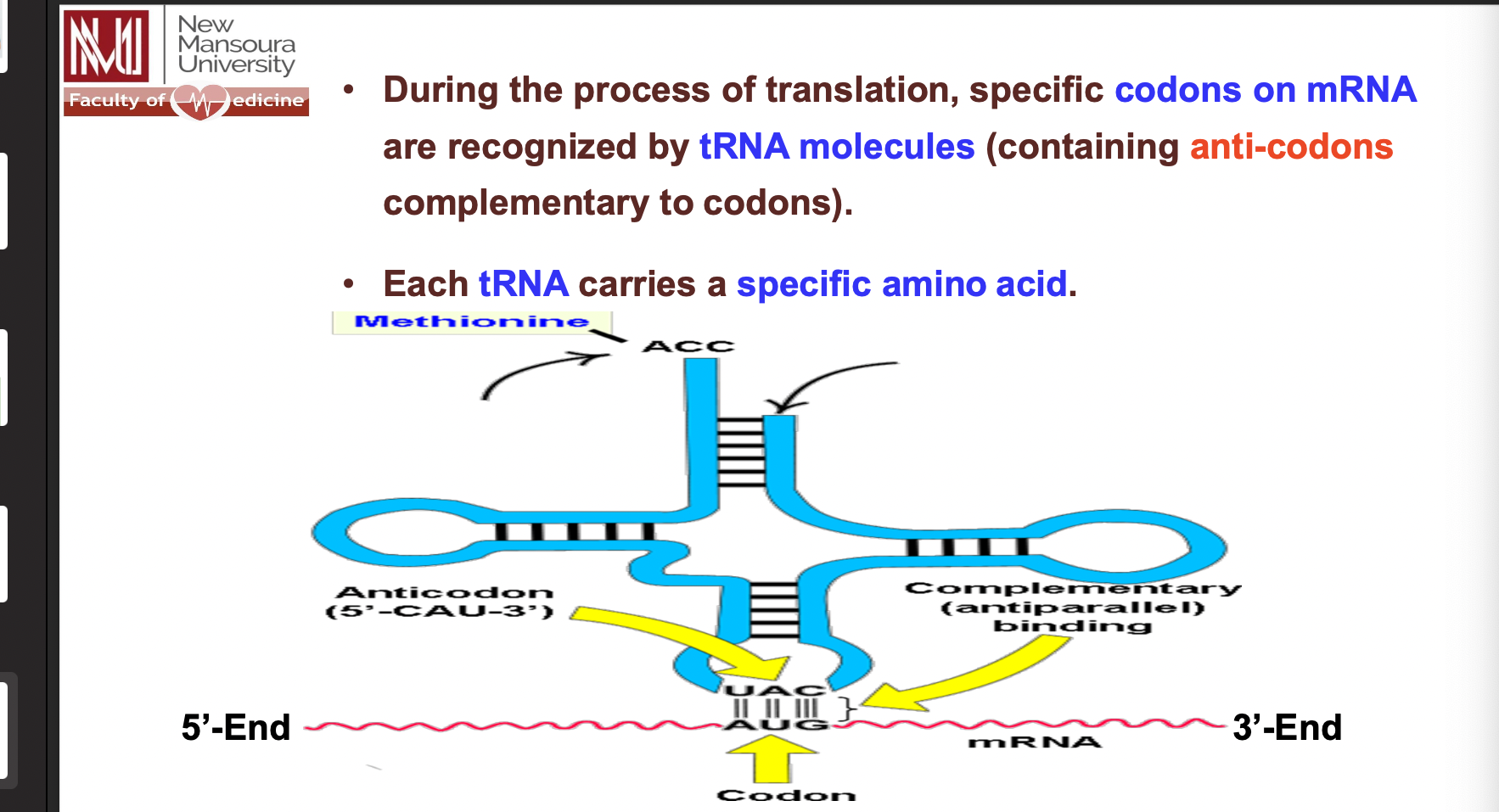
مش عارف بس خايف يجيب حاجة عليها
tuna anticodon are complimenrty for mRNA codons مبهر جدا
what are characters of genetic codon
linear
triplet
specific
universal
degenerate
non overlapping and comma less
explain linear
mRNA codon bases are read from 5>3 end
compare between triplet and specific
triplet codon on mRNA specify certain aa
each codon code for specific aa
explain universal and degenerate
they are the sam in all species
certain aa has more than one codon
what is the defence between codons who code for the same aa
the 3rd base
what is the requirements of translation
ribosome
mRNA
tRNA
aa
aminoacteyl synthesise
protein factors
source of energy
what does the mRNA does
carries the information of arranging the aa in proper order of specific protein
name the steps fro translation and what’s their main event
1 activation of aa: synthesis of aminoactyl tRNA
2 initiation : formation of initiation complex
3elongation: synthesis of polypeptide chain
4termination : release of poly peptide chain
what happens in activation of aa
charging tRNA with its specific aa. on 3 oh end on acceptor arm
how charging OF tRNA done
by amino acetyl tRNA snythetase
does require energy
yes 2 high energy bonds from one ATP molecule
what are the transition machinery made of
ribosome mRNA
initiator tRNA that carries the first amino acid ( you know who it is)
initiation factor
first amino acid is methionine bth
what is the elongation step is catalysed by
is it acyclic process
elongation factors
yes it is
what are the steps
1 binding of new aminactyl tRNA to a site 1 GTP + ef
2 formation of peptide bond between newly and old amino acid catalysed by peptide transferase
3 translocation: ribosome move 1 codon toward 3 end of mRNA using elongation factor 2 and 1 GTP
how many high energy phosphate bonds is needed for one peptide chain
4
2 from 1 ATP molecule
1gtp for adding amino acetyl tRNA
1 GTP for trans location
what happens after translocation
release of uncgcharged tRNA from e site
the peptide trna move from a to p site
A site become free and can be occupied by new aminoacyl tRNA
when does translation ends
when an termination codon is recognise in A site by releasing factors
what does rfs + piptdyl trnasfese+ GTP does
1 hydrolysis of the bond between polypeptide chain and tRNA
2 release both of tRNA and protein
3 dissociation of 80s ribosome into 60 s and 40s subunits
2and 3 results of 1
note the newly synthesised polypeptide chain is objected to post translation modification
name 3 inhibitors of translation
streptomycin : interfere with the initiation step
tetracycline: block A site preventing aminoacy trna from binding
erthromyocin: inhibits trans location step