Introduction to Psychology: Theories and Approaches
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Behaviourism
Focuses on environmental influences on behavior.
Psychoanalysis
Freud's theory on unconscious mind's influence.
Humanism
Emphasizes individual growth and inherent goodness.
Cognitive Psychology
Studies mental processes and information processing.
Biological Psychology
Examines brain, nervous system, and genetics.
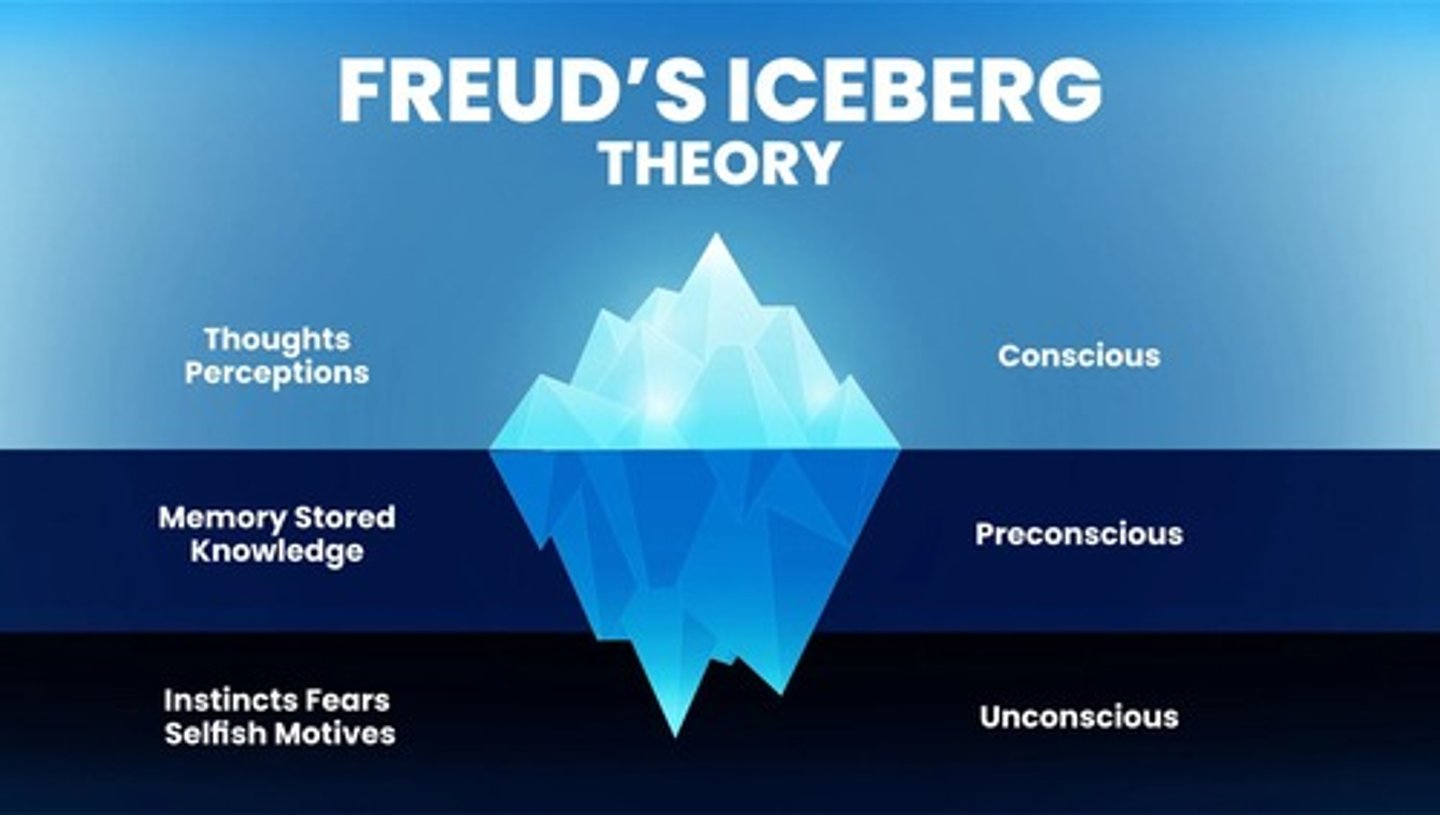
Freud's Iceberg Theory
Describes conscious and unconscious mind structure.
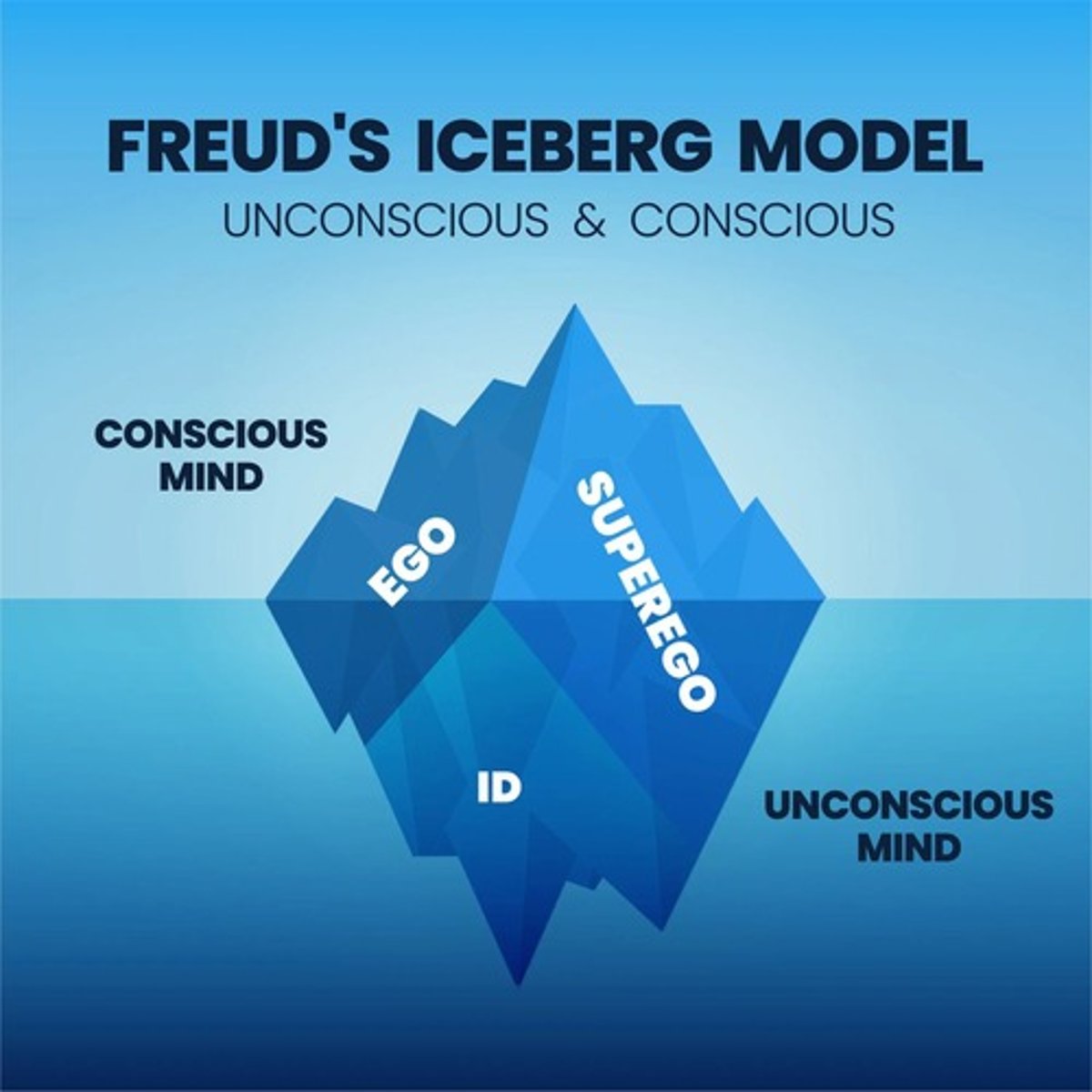
Ego
Rational mind part operating on reality principle.
Id
Instinctual mind part operating on pleasure principle.
Superego
Moral center of the mind regulating behavior.
Defense Mechanisms
Unconscious strategies to protect from anxiety.
Experimental Psychology
Research-focused branch studying various psychological topics.
Applied Psychology
Practical application of psychological theories in real life.
Clinical Psychologists
Professionals diagnosing and treating psychological issues.
Feminist Psychology
Focuses on gender issues in psychological theory.
Cognitive Theory
Explores mental plans affecting behavior and emotions.
Pavlov's Dog
Example of classical conditioning in behaviorism.
Early Childhood Influence
Freud's belief on shaping unconscious behavior.
Carl Jung
Freud's student, expanded on unconscious mind concepts.
Mental Processes
Cognitive psychologists study how information is processed.
Industrial/Organizational Psychology
Applies psychology to workplace settings and issues.
Forensic Psychology
Applies psychological principles within legal contexts.
Conscience
Acts as the mind's moral compass.
Iceberg Model
Freud's analogy for conscious and unconscious mind.
Repression
Unconsciously blocking distressing thoughts.
Denial
Refusal to accept reality or facts.
Projection
Attributing one's own unacceptable feelings to others.
Rationalization
Justifying behaviors with logical reasons.
Intellectualization
Focusing on intellectual aspects to avoid emotional stress.
Reaction Formation
Expressing opposite feelings to conceal true emotions.
Regression
Reverting to earlier developmental stages under stress.
Karen Horney
Neo-Freudian who challenged Freud's views on women.
Feminine Psychology
Focus on women's psychological development and issues.
Neurotic Disorder
Anxiety and fear impacting daily functioning.
Analytic Psychology
Balancing conscious and unconscious aspects of psyche.
Personal Unconscious
Memories unique to the individual.
Collective Unconscious
Shared archetypes and symbols across cultures.
Myers-Briggs Type Indicator
Personality assessment categorizing introversion and extroversion.
Clinical Psychology
Integrates science and theory to address psychological distress.
Personality Psychology
Studies individual patterns of thoughts and behaviors.
Abnormal Psychology
Focuses on unusual behavior patterns and mental disorders.
DSM
Authoritative guide for diagnosing mental disorders.
Developmental Psychology
Study of human change across lifespan.
Stages of Development
Framework for understanding growth patterns.
Psychological Perspectives
Views on thinking, feeling, and acting.
Explicit Attitudes
Conscious beliefs about specific topics.
Implicit Attitudes
Unconscious beliefs influencing behavior.
Cognitive Dissonance
Mental discomfort from conflicting beliefs.
Maslow's Hierarchy
Theory of human motivation and needs.
Reinforcement
Process of encouraging behavior through rewards.
Heredity
Genetic factors influencing development.
Environment
Surroundings affecting individual growth.
Personality
Unique traits influencing behavior and thoughts.
Developmental Stage
Specific period in psychological growth.
Attachment
Emotional bond influencing relationships.
Identity
Sense of self shaped by experiences.
Attitudes
Evaluations that influence behavior and thoughts.
Perception
Interpretation of sensory information.
Consciousness
Awareness of thoughts and surroundings.
Disorders
Mental health issues affecting behavior.
Changing Attitudes
Modifying beliefs to influence behavior changes.
Operant Conditioning
Behavior modification through reinforcement or punishment.
Social Thinking
Automatic judgments made about others during interactions.
Attribution Theory
Explains behavior based on perceived dispositions.
Fundamental Attribution Error
Overemphasis on personality over situational factors.
Stereotypes
Generalized beliefs about groups influencing behavior.
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
Expectations influence behaviors that confirm those expectations.
Opponent-Process Theory
Different neurons respond uniquely to various colors.
Negative Afterimage Effect
Seeing contrasting colors after viewing an image.
Perceptual Constancy
Recognition of objects as unchanged despite view changes.
Amplitude
Wave size measuring sound intensity.
Frequency
Number of sound waves per unit time.
Mental Illness
Broad term for conditions affecting mental health.
Mental Disorder
Conditions causing distress or functional impairment.
Ethics in Psychology
Considerations for validity and reliability in experiments.
Pavlov
Known for classical conditioning with dogs.
Maslow
Developed hierarchy of needs theory.
Jung
Introduced concepts of collective unconscious and archetypes.
Freud
Pioneered psychoanalysis and theories of the unconscious.
B.F. Skinner
Known for behaviorism and operant conditioning.
Binet
Developed first intelligence test for children.
Classical Conditioning
Neutral stimulus elicits response after pairing.
Hierarchy of Needs
Basic needs must be met before higher needs.
Functional Types
Thinking, feeling, sensation, and intuition categories.
Psychometrics
Study measuring personality, ability, and knowledge.
Skinner
Developed behaviorism focusing on observable behaviors.
IQ Test
Measures intelligence through standardized questions.
Asch Conformity Study
Investigated social pressure's effect on judgment.
Little Albert Study
Demonstrated classical conditioning of fear responses.
Monster Study
Tested stuttering theory through labeling normal speech.
Bobo Doll Experiment
Children imitate behavior observed in adults.
Extinction
Conditioned stimulus loses effect without unconditioned stimulus.
Spontaneous Recovery
Reappearance of conditioned response after extinction.
Conditioned Stimulus (CS)
Initially neutral stimulus that elicits response after conditioning.
Unconditioned Stimulus (US)
Stimulus that naturally triggers a response.
Conditioned Response (CR)
Learned response to a previously neutral stimulus.
Social Pressure
Influence from others affecting individual decisions.
Behaviorism
Psychological approach focusing on observable behaviors.