2.1 2.2 2.3 Biology Review
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/48
Last updated 9:44 PM on 12/1/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
1
New cards
Covalent bonds
A chemical bond that involves the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.
2
New cards
carbohydrates
In plants and animals, they have a role as a source of energy. Also has structural function in plants. Occurs in different forms - monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. contain C, H and O
3
New cards
lipids
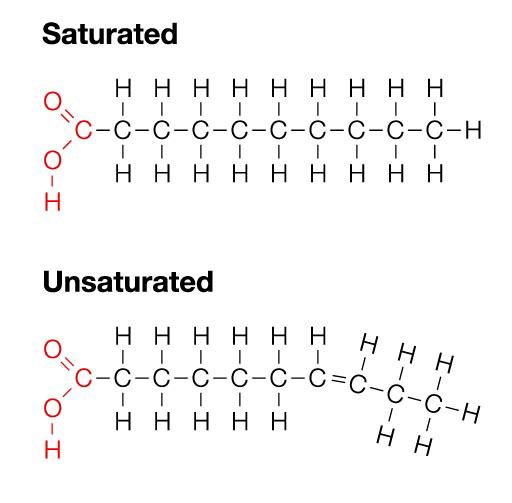
Have a role as energy storage molecules in plants and animals. Triglyceride lipids include fats and oils. Fat is solid and oil is liquid. Animalds store fat whereas plants store oil. contains C, H, and O.
4
New cards
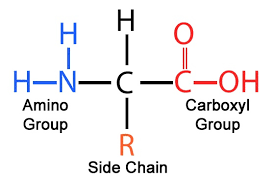
amino acids
building blocks of proteins
5
New cards
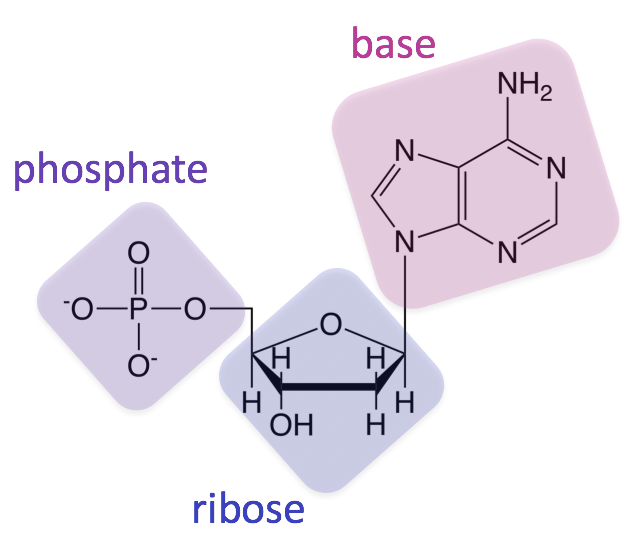
nucleic acid
contains C, H, O, N, and phosphorus. Sub-units are nucleotides, made of a base, sugar, and phosphate group
6
New cards
anabolism
A type of reaction that builds up monomers to form macromolecules.
7
New cards
catabolism
Macromolecules are broken down into monomers.
8
New cards
cohesion
hydrogen bond that makes water molecules stick together. occurs as a result of the polarity of a water molecule and its ability to form hydrogen bonds
9
New cards
adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances. water tends to stick to other molecules (not water) that are charged or polar, occurs because of water's ability to form hydrogen bonds
10
New cards
thermal property of water
the temperature of water remains relatively stable because water has a high specific heat capacity, a high heat of vaporization (liquid to gas), and a high heat of fusion (liquid to ice)
11
New cards
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances. water can dissolve organic and inorganic substances that have charged or polar regions
12
New cards
hydrophilic
substances that are chemically attracted to water
13
New cards
hydrophobic
substances that are insoluble in and dislike water
14
New cards
amino acid
building blocks of proteins, soluble in water, transported through blood plasma
15
New cards
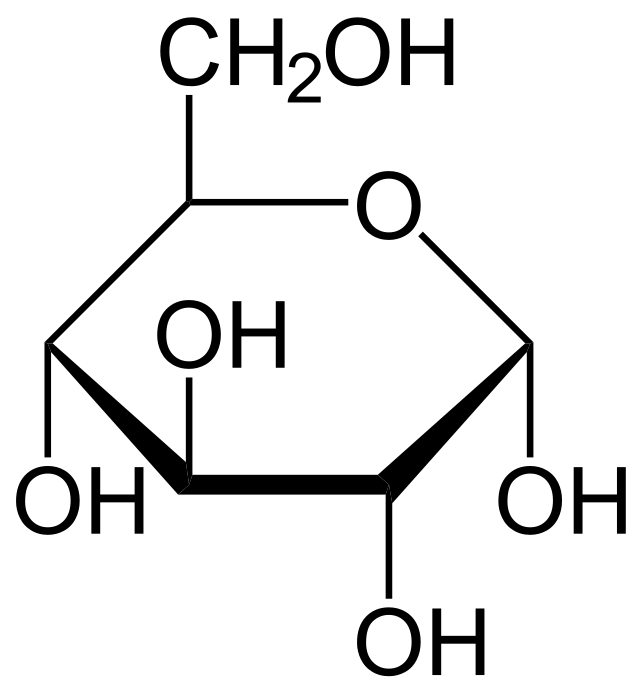
glucose
form of sugar that fuels respiration, found in plants, soluble in water, transported through blood plasma
16
New cards
oxygen
soluble in water, transported in hemoglobin in red blood cells
17
New cards
fats
insoluble in water, transported in blood in lipoprotein complexes
18
New cards
cholesterol
insoluble in water, transported in blood in lipoprotein
19
New cards
sodium chloride
soluble in water, transported in blood plasma
20
New cards
Monosaccharides
A single sugar molecule such as glucose, galactose or fructose, the simplest type of sugar.
21
New cards
Disaccharides
sugars that have two subunits linked together by a condensation reaction. These are held together by a strong covalent bond.
22
New cards
Polysacchrides
Carbohydrates that are made up of more than two monosaccharides such as lactose, sucrose, and maltose
23
New cards
galactose
monosacchride, made by plants and animals, found in milk and some cereals
24
New cards
fructose
monosacchride, made by plants, sweetest naturally occurring carb, found in honey and fruits
25
New cards
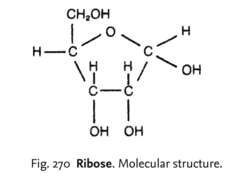
ribose
monosacchride, made by plants and animals, forms the backbone of DNA
26
New cards
maltose
disacchride, made by plants, found in germinating grain and some corn syrup
27
New cards
lactose
disacchride, made by animals, found in milk
28
New cards
sucrose
disacchride, made by plants, table sugar
29
New cards
cellulose
polysacchride, made by plants, makes up the cell wall of plants
30
New cards
starch
A storage polysaccharide in plants, consisting entirely of glucose monomers joined by a glycosidic linkages. amylose = curved chain, amylopectin = branched chain
31
New cards
glycogen
A polysaccharide stored in animals; the storage form of glucose in animals.
32
New cards
saturated fats
Contains fatty acids with no C=C double bonds, only C-C single bonds
33
New cards
polyunsaturated fats
2 or more double bond
34
New cards
monounsaturated fats
A fatty acid whose molecular structure includes only one double carbon bond.
35
New cards
cis-isomers
curved/bent, hydrogen atoms are on the same side of the two carbon atoms, loosely packed
36
New cards
trans-isomers
straight across, hydrogen atoms are on opposite sides of the two carbon atoms, closely packed
37
New cards
BMI formula
mass in kilograms/(height in meters)^2
38
New cards
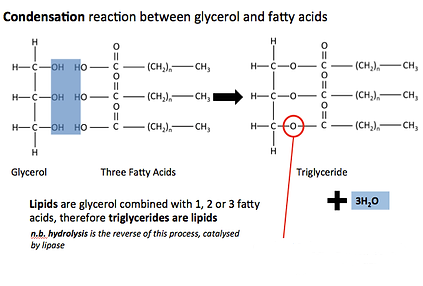
what is the name of the bond formed between three fatty acids and glycerol?
Ester bond
39
New cards
functions of lipids
structure, hormonal signalling, insulation, protection, and storage of energy. Produces 2x more energy than carbs.
40
New cards
organic molecules
Compounds that contain at least two Carbon
41
New cards
Inorganic molecules
Compounds that do not contain Carbon
42
New cards
Polymers
When many monomers are bonded together
43
New cards
Condensation Reaction
Two molecules can be joined to form a larger molecule, held by strong covalent bonds. It is an example of an anabolic reaction.
44
New cards
Hydrolysis Reaction
Involves breaking down polysaccharides, polypeptides and triglycerides into the smaller units of which they are made. It is an example of a catabolic reaction.
45
New cards
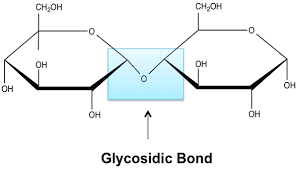
Glycosidic Bond
A type of covalent bond that joins a carbohydrate (sugar) molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate.
46
New cards
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism.
47
New cards
Monomer
Single sub-units in metabolism
48
New cards
Hydrogen bond
when two H2O molecules bond via negative and positive poles
49
New cards
Triglyceride
A molecule made up of three fatty acids covalently bonded to glycerol with an ester bond