ultimate Ch. 20 study set
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
suffix for monocarboxylic acids
oic acid
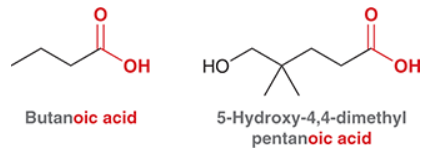
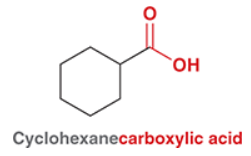
What is the suffix for when carboxylic acid is connected to a ring?
carboxylic acid
What locant does the C atom of COOH take in a monocarboxylic acid?
1
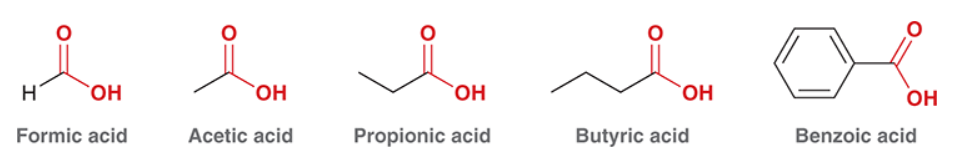
Know the common IUPAC for monocarboxylic acids.
ok
suffix for diacids
dioic acid
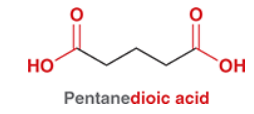
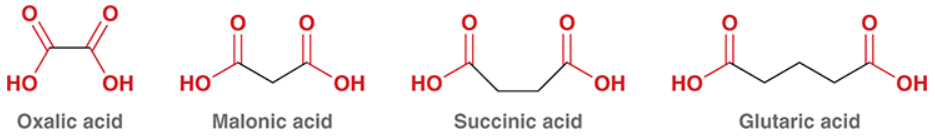
Know the common IUPAC for diacids.
ok
What are deprotonated carboxylic acids?
carboxylate salts
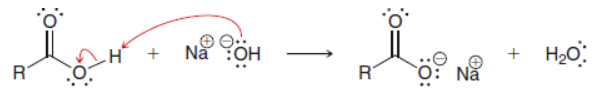
suffix for carboxylate salts
ate
What hybridization are carboxylic acids?
sp3
What geometry are carboxylic acids?
trigonal planar
How many hydrogen bond interactions can COOH form?
2
What is the pKa of most COOH?
4-5
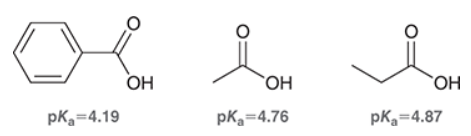
Is the boiling point of carboxylic acids high or low?
relatively high
What forms when COOH is treated with a strong base such as NaOH?
carboxylate salt
Does equilibrium favor carboxylic acid or carboxylate salt?
carboxylic acid
The acidity of carboxylate acid is primarily due to the stability of the_____ _____ which is stabilized how?
conjugate base stabilized by resonance
With the addition of electron-withdrawing substituents, does the pKa of COOH increase or decrease?
decrease
If the conjugate base of a carboxylic acid is resonance stabilized, does acidity increase or decrease?
increase
What is a common electron-withdrawing group that is not a halide?
nitro group NO2
What are the 4 common carboxylic acid derivatives?
acid halide, acid anhydride, ester, amide
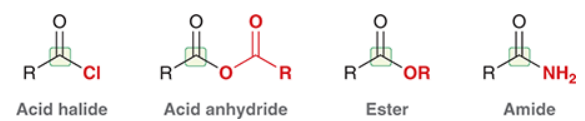
What is the suffix for acid halides? Given acetic acid, what is the acid halide form using Br?
acetyl bromide
What is the suffix for an acid halide group connected to a ring? Given cyclohexanecarboxylic acid, what is the acid halide form using Cl?
Cyclohexane carbonyl chloride
What is the suffix for anhydrides? Given acetic acid, what is the anhydride form?
acetic anhydride
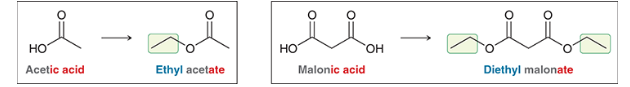
What is the suffix for esters? Give acetic acid, what is the ester form?
ethyl acetate
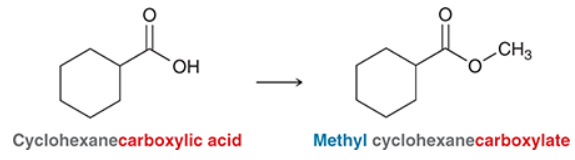
What is the suffix for esters connected to a ring? Given Cyclohexanecarboxylic acid, what is the ester form?
Methyl cyclohexanecarboxylate
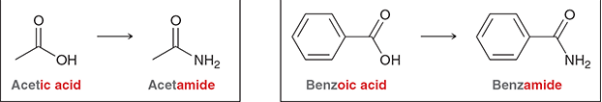
What is the suffix for amides? Given acetic acid, what is the amide form?
acetamide
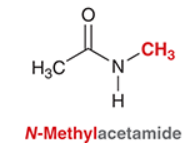
What is the IUPAC of this compound?
N-Methylacetamide
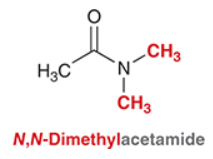
What is the IUPAC of this compound?
N,N-Dimethylacetamide
Which part of a carboxylic acid or derivative can act as a base/nucleophile?
the OH group
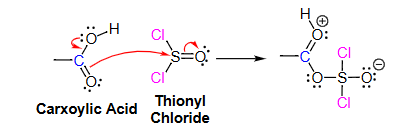
What is a Bronsted-Lowry acid?
any species that can donate a proton
True or False: carboxylic acids can act as Bronsted-Lowry acids.
True
How do you get pKa from Ka?
-log(Ka)
How do you get Ka from pKa?
10^(-pKa)
Rank the reactivity of the 4 common COOH derivatives from least to most reactive:
Amides < Esters < Anhydrides < Acid halides
Do carboxylic acids or carboxylate ions dominate when pH < pKa?
carboxylic acids
Do carboxylic acids or carboxylate ions dominate when pH > pKa?
carboxylate ions
Generally, are carboxylic acids or carboxylate ions more soluble in water? Why?
carboxylate ions because of their charge
Water solubility of carboxylic acids can be increased when they are _____?
ionized
There are 3 oxidation reactions that form carboxylic acids. What are the oxidated reactants in ABC order?
alkylbenzenes, alkynes, primary alcohols
What is the oxidation reagent for alkylbenzenes and primary alcohols to form carboxylic acids?
Na2Cr2O7/H2SO4, H2O
Which reactant undergoes oxidation reaction to form a carboxylic acid via an oxidative cleavage?
alkynes
What are the reagents for oxidative cleavage of alkynes to form carboxylic acids?
1. O3
2. H2O
What is the product when a Grignard reagent is treated with 1. CO2 / 2. H3O+?
carboxylic acid
What are the reagents to treat a Grignard reagent to make carboxylic acids?
1. CO2
2. H3O+
What is the product when nitriles are treated with H3O+ and heat?
carboxylic acids
What are the reagents to treat nitriles to form carboxylic acids?
H3O+ and heat
What is the product when nitriles are treated with OH-/H2O?