CV Anatomy and Physiology
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What makes up the thorax?
spine, ribs, sternum
the body of the sternum is…
flexible - for impact like CPR
the thorax changes…
with development!
triangle to square to rectangle as we get older
What are the muscles of inspiration?
diaphragm, external intercostals, accessory muscles
The diaphragm:
MAIN muscle of innervation
innervated by phrenic nerve - C3, 4, 5
brings in about 2/3 of our tidal volume and ¾ of our air intake when supine
External Intercostals:
lift ribs, increase intrathoracic volume
secondary role to maintain space in between ribs
Accessory muscles:
stabilize ribcage - anything JAW to PELVIC FLOOR
contribute to ventilation and breathing in some way
Quiet expiration is a…
a passive process!!
What happens during quiet expiration?
the inspiratory muscles stop contracting
lungs recoil to resting position
ribs return to resting position
diaphragm rises back into thoracic cavity - increases intrathoracic pressure above atmospheric pressure pushing air out
Forced expiration requires:
abdominals, accessory muscles, postural stabilizers
What are the three ventilatory movements?
pump handle motion
bucket handle motion
combination of movements
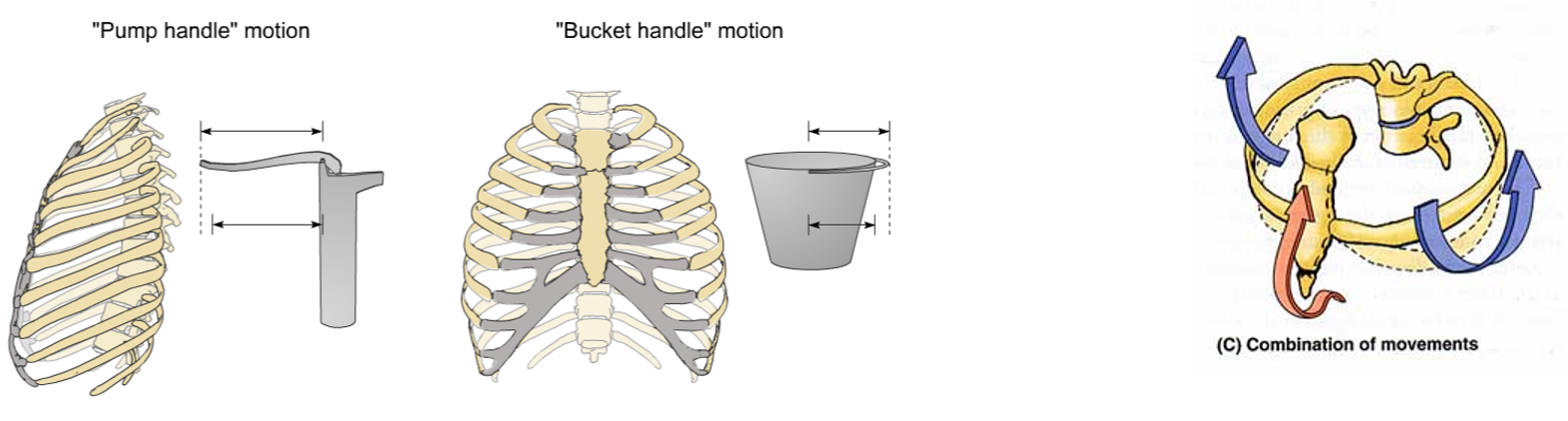
What are the muscle movements of ventilation?
diaphragm - A-P diameter
intercostals - lateral expansion
accessory muscles - sup/inf expansion
What is paradoxical breathing?
chest falls when breathing in and rises when breathing out - seesaw motion of chest
What is inspiration?
expansion of the chest creates negative intrathoracic pressure in relation to the atmosphere
What is expiration?
positive pressure relative to the atmosphere
How does intrathoracic pressure relative atmospheric pressure
intrathoracic is INVERSE to atmospheric
Our drive to breathe is based on…
our need to get rid of CO2
Central control center of breathing:
medulla, pons, chemoreceptors
control of involuntary respiratory activity
maintains normal patterns of breathing
Peripheral control center of breathing:
chemoreceptors, stretch reflex, cough reflex
these chemoreceptors cue you to breathe!
stretch tells your brain if the respiratory muscles are firing correctly or something didn’t feel right
What is compliance?
flexibility - how stretchy our lungs are
What is restrictive lung disease?
can’t get air IN - non-compliant lungs
What is obstructive lung disease?
can’t get air OUT
What is the pressure/volume relationship of breathing?
pressure goes UP, volume of air goes DOWN
Airway resistance of breathing:
more resistance increases amount of work muscles of respiration have to do to get air into the lungs
more resistance = harder to move air
What is laminar flow?
air flows in straight path - low resistance
What is turbulent flow?
coffee stirrer or little straw
What is diffusion?
moving of oxygen out of the alveoli to the circulation
oxygen crosses alveolar membrane and capillary membrane to reach circulation - CO2 does this in OPPOSITE order
Movement of oxygen depends on…
distance between membranes and the diffusion capacity of the gas itself
What is perfusion?
blood flow
gravity dependent - more air and blood to the bases when upright
What is dead space?
if we have an alveolus that is getting air into the lungs but NOT getting blood flow
pulmonary embolus
What is shunting?
blood supply at that capillary, ready to accept oxygen, but NO AIR getting to the alveolus
Sympathetic NS innervation:
autonomic ganglia
bronchodilation
pulmonary artery constriction - raises PA pressure
decreased glandular secretion - dries airway surface
raises heart rate and contractility
coronary artery DILATION
Parasympathetic NS innervation:
vagus N
bronchoconstriction
dilation of pulmonary artery - lowers pressure
increased glandular secretion
coronary artery CONSTRICTION
decreased HR, decreased contractility
Arteries:
thick walls
elastic
handles blood under pressure
Veins:
thin walls
fibrous
holds large amount of blood
Systemic circulation:
large arteries to small capillaries
start in small venule, increase in size to vena cava
distribution, resistance and capacitance vessels
Pulmonary circulation:
colors are switched!
arteries - deoxygenated blood
veins - oxygenated blood
PA pressure decreases, PV pressure goes UP - vice versa
Lymphatic circulation:
returns fluid from interstitial spaces back into systemic circulation
fluid collected by channels and ducts if not collected by veins
Cardiac cycle events:
systole - blood ejects from the chamber
diastole - we relax, blood fills the chamber
S1 - lub
S2 - dub
S3, S4 - abnormality of filling phase