GCSE Physics OCR Gateway - P7
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Name all the energy stores
Thermal, kinetic, gravitational potential, elastic potential, chemical, magnetic, electrostatic, nuclear
How can energy be transferred?
Mechanically, electrically, heating, radiation
What is work done?
the process of transferring energy from one energy store to another
RECALL
Work done equation
Work done (J) = force (N) x distance (m)
What is Gravitational potential energy?
the amount of energy stored in an object due to its height above the ground
RECALL
GPE equations
GPE (J) = mass (kg) x gravity (always 10 N/kg) x height (m)
AND
GPE = weight (N) x height (m)
RECALL!
What is the equation for force with springs?
force (N) = spring constant (N/m) x extension (m)
What is elastic potential energy?
energy stored in an elastic object when work is done on it to change its shape
Equation for EPE
0.5 x spring constant (k) (N/m) x [extension]^2 (x) (m)
What is kinetic energy?
energy of motion
RECALL
kinetic energy equation
0.5 x mass (kg) x (velocity)^2 (m/s)
What is the conservation of energy?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred
What is heat?
Total (random) KE of the particles in a substance
What is temperature?
a measure of average (random) KE in a substance
RECALL
What is specific heat capacity?
The amount of energy required to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1oC
RECALL
equation for SHC
Heat energy (J) = mass (kg) x SHC (J/kg°C) x temp. change (°C)
RECALL
What is Specific Latent Heat?
The amount of energy needed to change 1kg of a substance from one state to another without changing its temperature
RECALL
equation for SLH
Energy (J) = SLH (J/kg) x mass (kg)
Conduction
the transfer of kinetic energy from one particle to the next. Free electrons transfer energy rapidly and make metals good conductors.
Convection
this occurs when liquids and gases are heated and expand (because their particles move further apart) The less dense fluid rises and carries the heat energy with it.
Radiation
this is when IR radiation (an electromagnetic wave) carries heat energy from one place to another. This is the only way heat energy can travel through empty space (which is a vacuum.)
Describe all the ways heat is transferred when boiling a pot of water.
- IR radiation is emitted from the fire
- Energy is transferred to the particles on the bottom of the pot and to the water by conduction
- The water particles gain more kinetic energy and become less dense
- They hotter, less dense water rises to the top and colder water sink which starts a convection current
- Energy is transferred through conduction in the pot itself
- the particles gain more KE and collide with neighbouring particles which transfers thermal energy to the end of the handle
What is power?
the rate of doing work or transferring energy
Equation for power
Power = work done (energy transferred) / time
Equation for power (IVR)
Power (w) = Current (A) (I) x Voltage (v)
OR
Power (w) = [Current]^2 (A) (I) x Resistance (Ω) (R)
OR
Power (w) = [Voltage]^2 (V) / Resistance (Ω) (R)
Equation for electrical energy
Energy (kWh) = Power (kW) x time (h)
Equation of total cost
Total Cost = Units of Energy used x Price per unit of energy
Sankey diagrams
A flow diagram that represents the total energy, the wasted energy and the useful energy of an appliance.
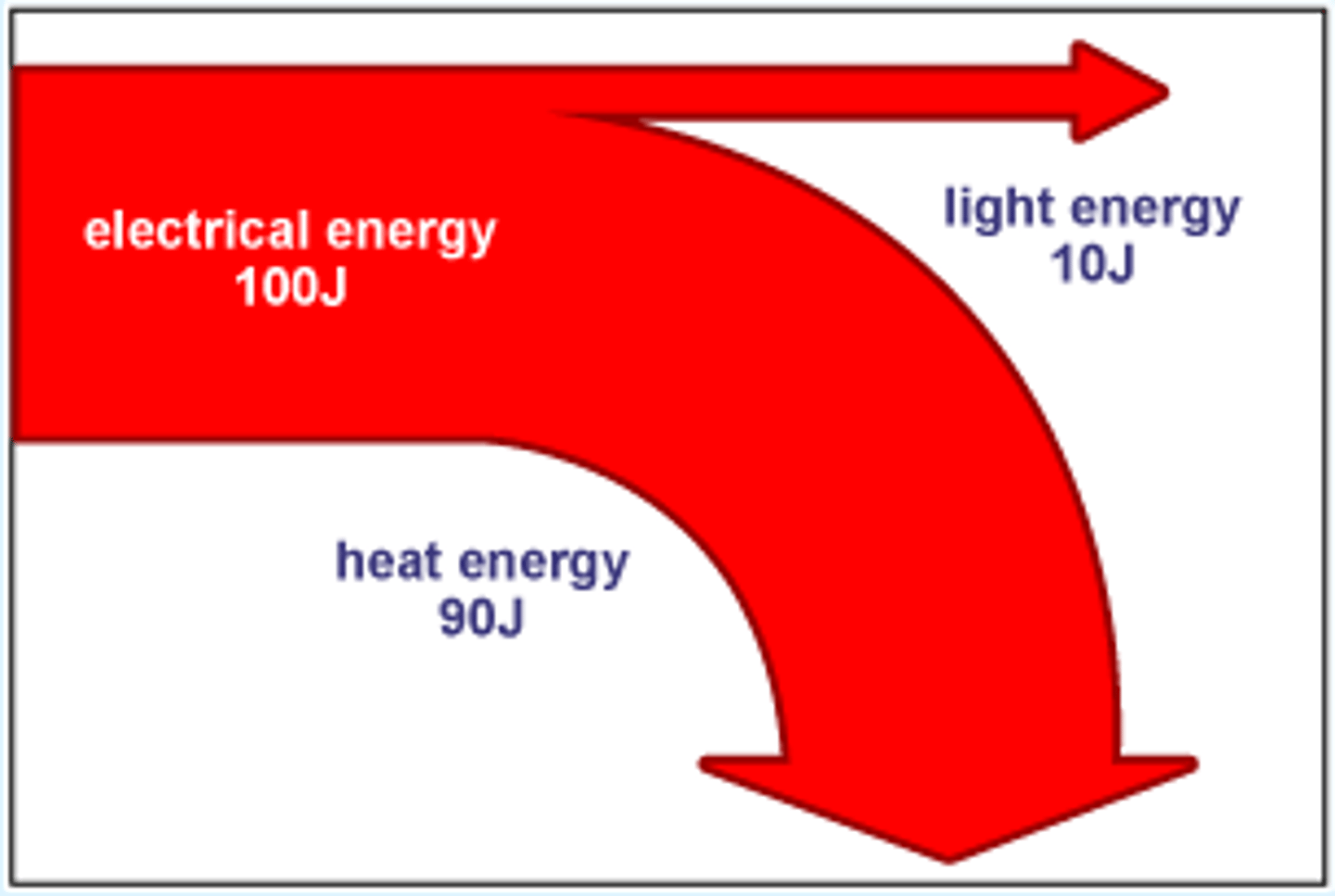
Reduce Heat Transfer in a House
Double Glazing
- Reduces the amount of heat energy that is transferred through windows
* Air is a poor conductor (or a good insulator) so thermal energy through conduction is decreased
* The gap between the window panes is narrow so it is harder for a convection current to start
* Heat will still be transferred via radiation though
Cavity Walls
- Heat is conducted through the solid inner wall to air in the cavity wall
- Heated air will rise carrying heat energy with it (convection)
- Walls can be filled with cavity wall insulation containing many small pockets of trapped air
Equation for efficiency
Efficiency = useful energy output / total energy input x 100