APES- chapter 6 (animal populations)
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
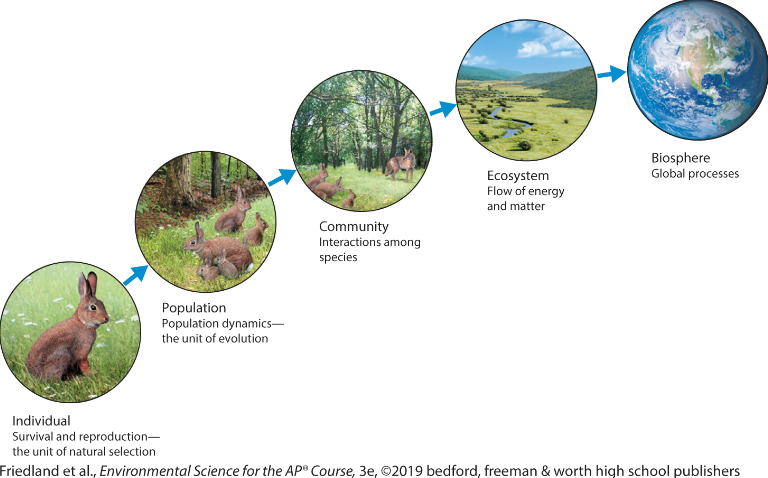
Individual
refers to just one organism
population size
is the total number of individuals within a defined area at a given time
direct count (census)
Count um up! The group is individually counted.
sampling (quadrat method)
Identify an area and multiply by total amount to find the entire area
ex) if a biologist counts 10 squirrels living in a 200 square foot area, she could
predict that there are 100 squirrels living in a 2000 square foot area.
Capture-recapture
In this procedure, biologists use traps to capture the animals alive and mark them in some way. The animals are returned unharmed to their environment. Over a long time period, the animals from the population continue to be trapped and data is taken on how many are captured with tags. A mathematical formula is then used to estimate population size.
ex) California Condor

Population density
Number of individuals per unit area
ex) high density of people in the city low density of people in the country side
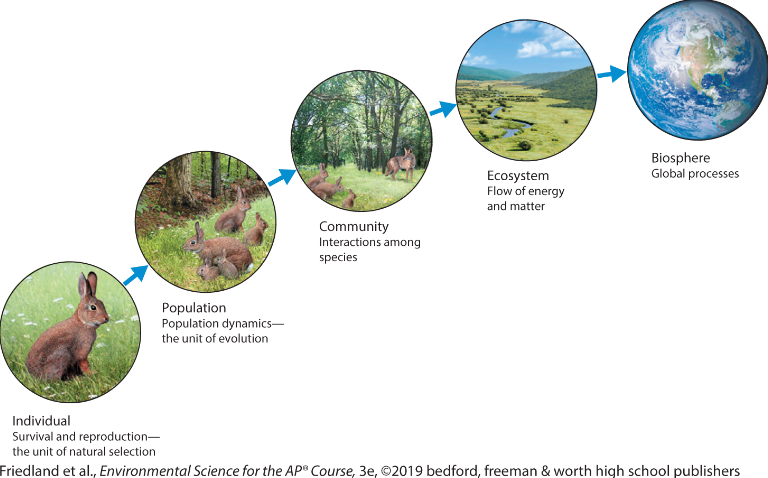
Population
all individuals of a single species living in a given area at a given time
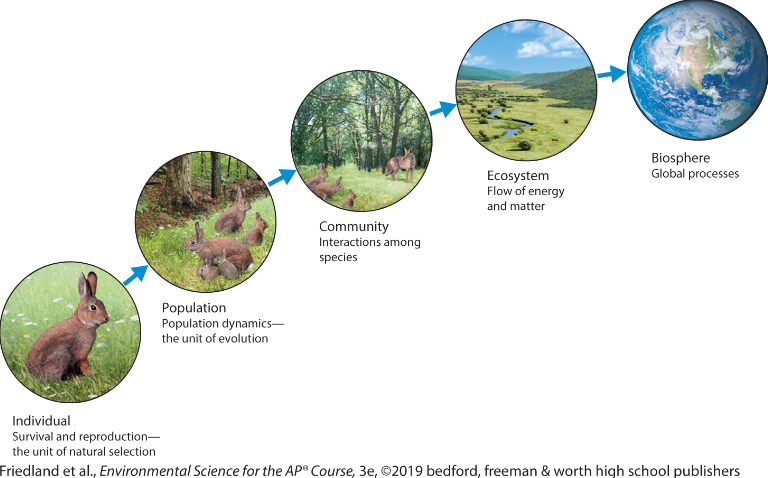
Community
all of the various life forms in an ecosystem
Good things about a high population density
grouped for protection
finding mates
genetic diversity
Bad things about a high population density
spread disease
greater competition
vulnerable to attack (easier to find)
Good things about a low population density
more space
more recorces
Bad things about a low population density
no help from the group
little genetic diversity
hard to find a mate
Population distribution
description of how individuals are distributed to different locations
random population distribution
no particular pattern
typical for many (not all)

uniform population distribution
-organisms spread out very evenly
-Typical of territorial birds
-Helps avoid competition

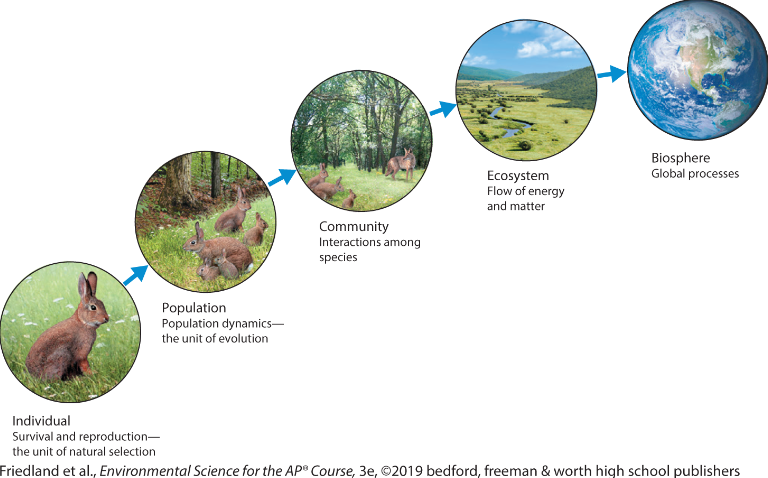
ecosystem
are specific areas that
include abiotic and biotic components
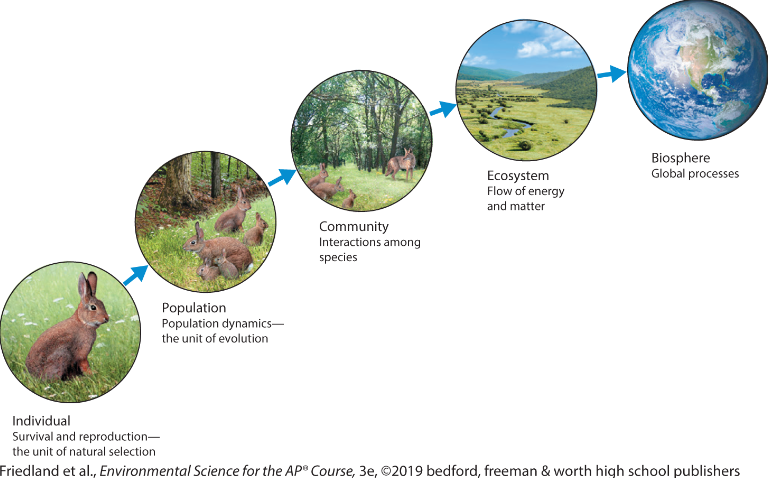
Biosphere
all life on Earth
Clumped population distribution
-grouped near resources
-Good for feeding or protection

Limiting resources
something a population CANT live without, not unlimited (can be dependent or independent)

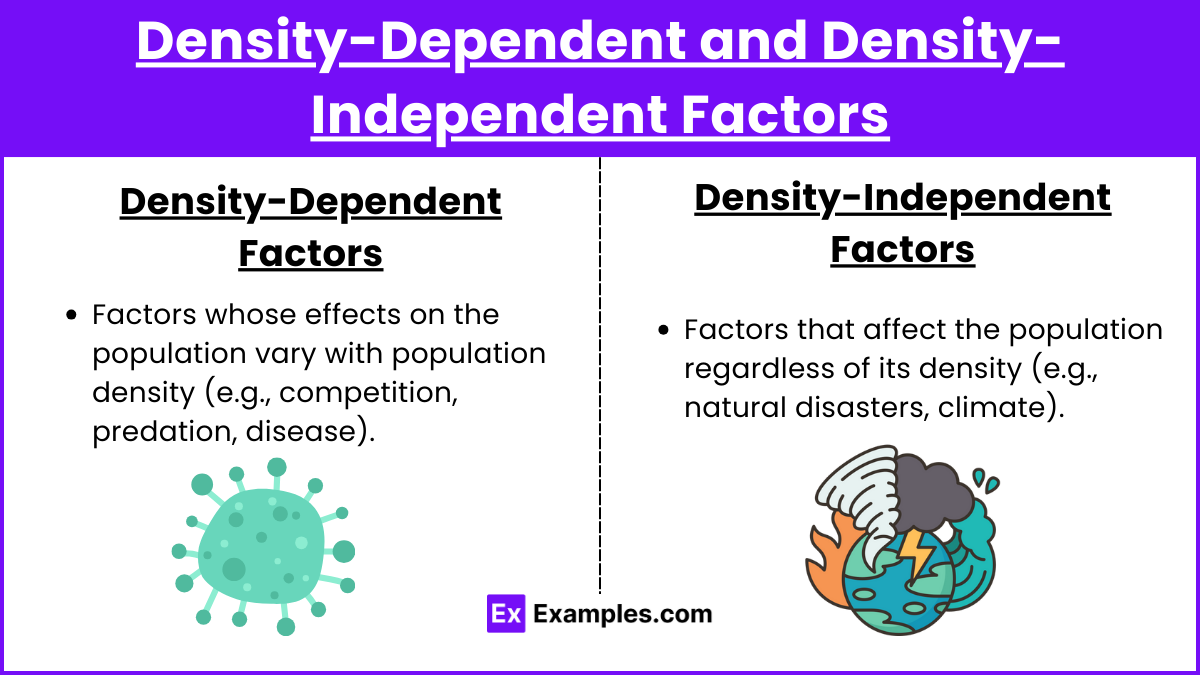
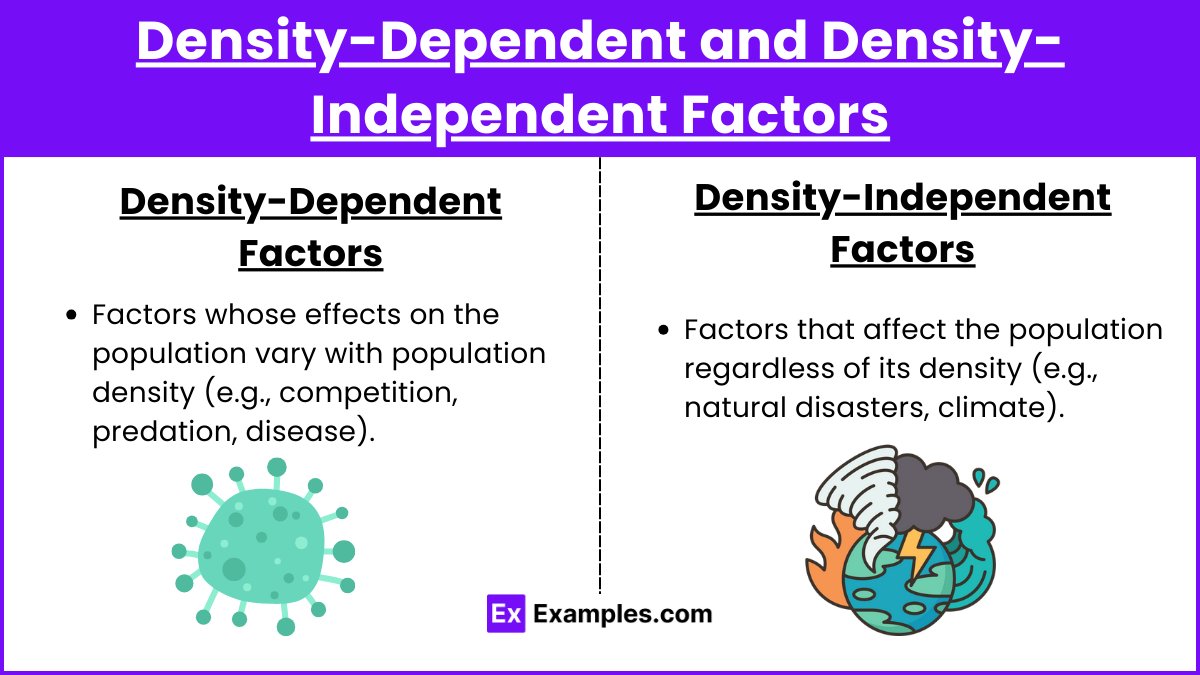
Density-dependent factor
limits on population growth that are directly related to the size of the population
Carrying Capacity (K)
the limit of how many individuals in a population the environment can sustain

Density-independent factors
limits on population growth that are not related to the population size (usually physical or chemical)
ex) tornado over 10 trees or 100 trees…still going to loose a tree
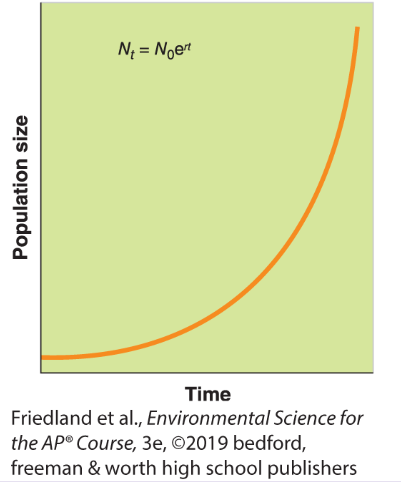
Exponential growth
population grows at a fixed rate
nor limited by recorces, growth is very rapid
density independent growth patern
shown by a J curve
ex) St. Matthew Island, Alaska
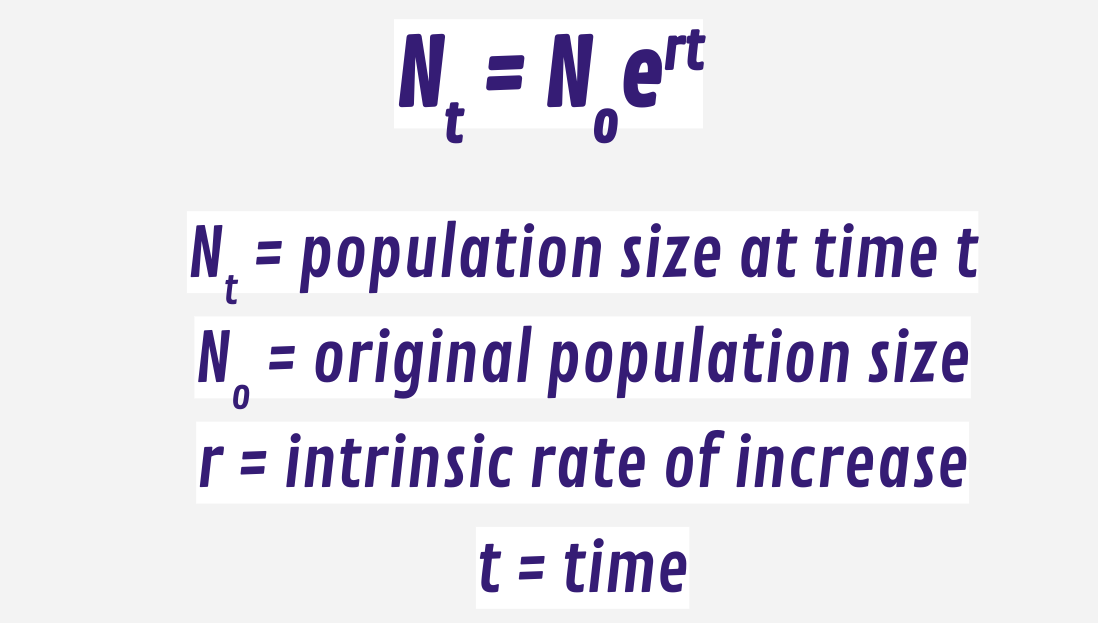
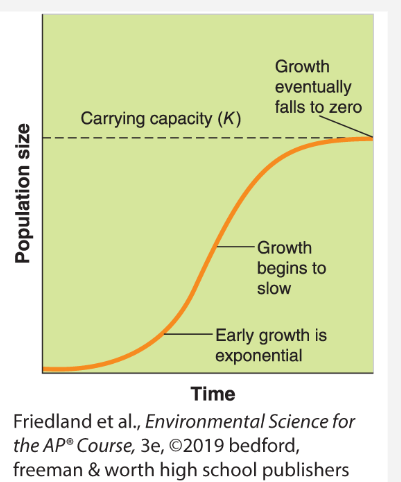
Logistic Growth
exponental growth that slows when it reaches the carrying capacity
turns into an S shaped curve
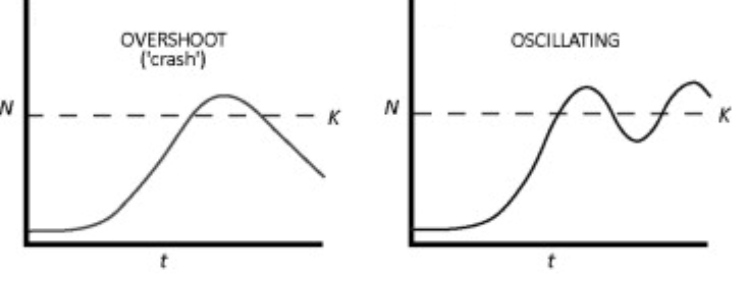
Overshoot
exponental growth then crashes
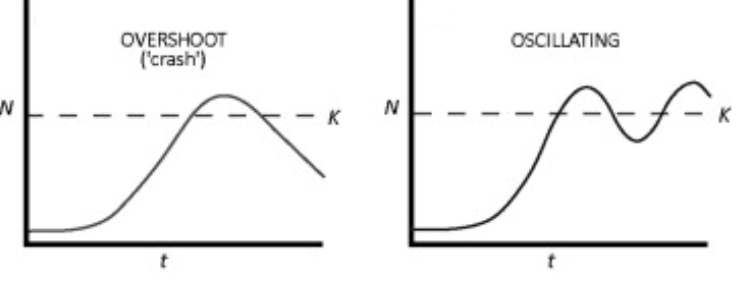
Oscillating
There is a pattern of overshoot from the carrying capacity then dieing off
K-selected species
“quality over quantity”
low growth rate
population size determined by carrying capacity
density-dependent population regulation
slow population growth
Ex) humans

r- selected species
“quantity over quality”
high growth rate
population size determined by large overshoots and rapid die-offs
density independent population regulation
fast population growth
Ex) frogs

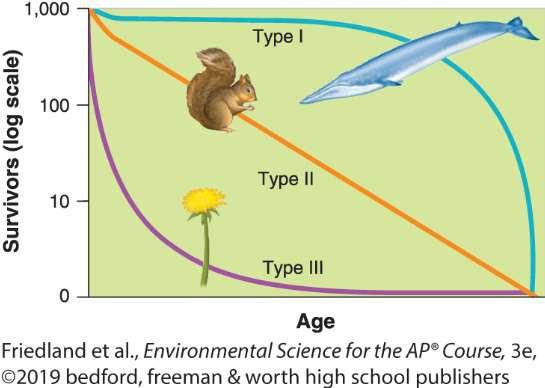
Type I population survivorship growth curves
these live long then die off in large numbers at old age (K-selected species)
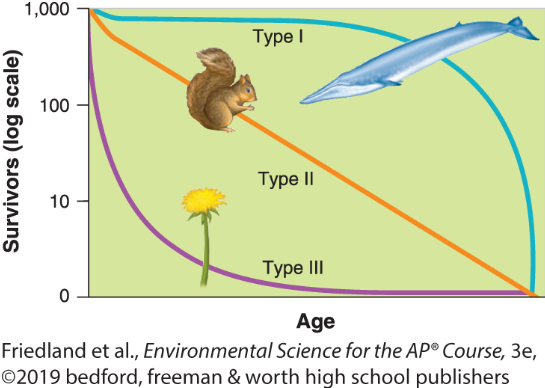
Type II population growth curves
relatively constant decline in survivorship over time
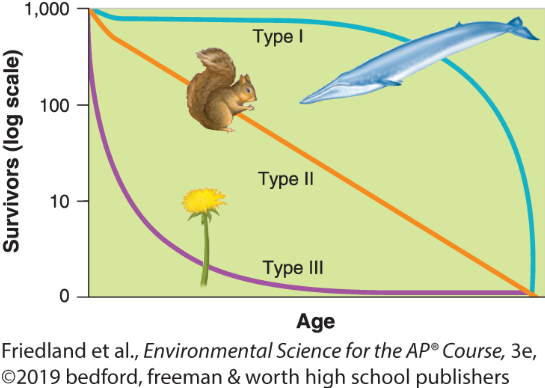
Type III population growth curves
many births, but few survive a long time ( r-selected species)
Provisioning Services
The products directly obtained from ecosystems ex) food
Supporting Services
Indirect services that are necessary for the production of all other ecosystem services. ex)the water cycle

Regulating Services
the benefits obtained from the regulation of ecosystem processes ex)pollination
Cultural Services
non-material benefits that people obtain from ecosystems ex)making recreational parks look nice

competition
individuals competing for a resource
interspecific competition
between different species- both expend energy/cause harm

competitive exclusion principle
adapt or die
Intraspecific Competition
between same species

Resource Partitioning
Two species overlap and must divide a resource based on morphology or behavior
Temporal Partitioning
Collect resources at different times
ex) a nocturnal animal like an owl

Spatial Partitioning
Different areas
ex) Birds eat same insects from top vs. bottom of tree
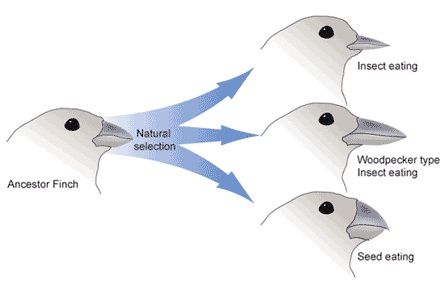
Morphological Partitioning
Adaptive radiation (adapting quickly)
ex) darwin’s fintches
symbiotic relationships
animals interactions with each other, some examples are:
mutralisim
commensalisim
parasitisim

Keystone species
have a PROFOUND affect in the comunity

ecosystem enginer
creates/ maintains a habitat for other species
ex) a beaver

Population sex ratio
how many males to females
population age structure
how many individuals fit into certain age categories
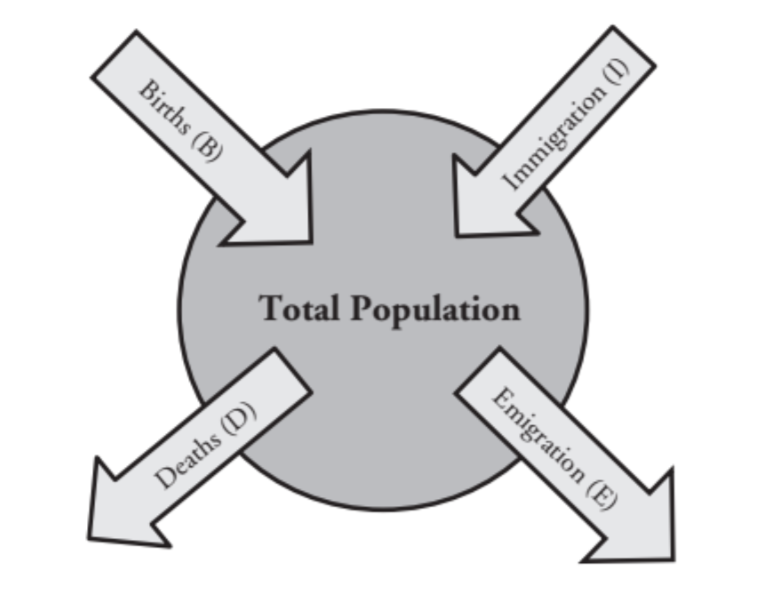
What is a population growth rate?
the number of offspring an individual can produce minus the deaths of the individual/ its offspring during the same time period.
succession
the predictable replacement of one group of species by another group of species over time

primary succession
bare rock. no soil. soil never existed.
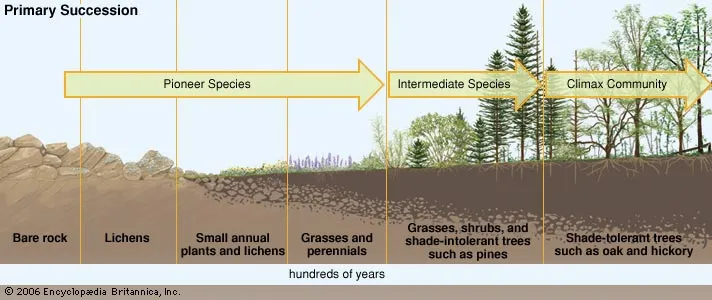
secondary sucession
disturbed area, but has not lost its soil. This is much quicker than primary succession.
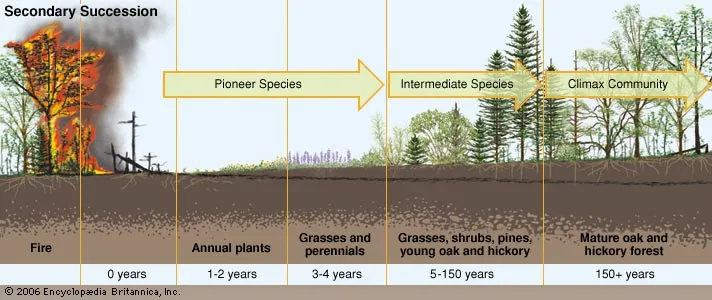
what is the term for populations moving into an area?
immigration
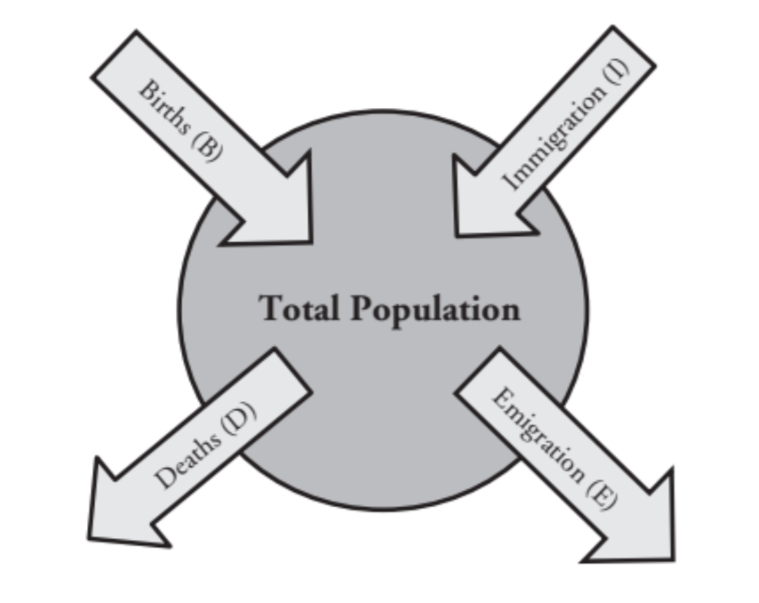
what is the term for populations leaving an area?
emigration