Unit 4 Genetics Vocabulary (ADV)
1/42
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
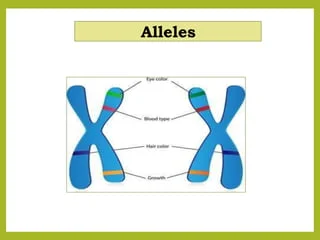
Alleles
Alternative forms of a gene that result in different traits.
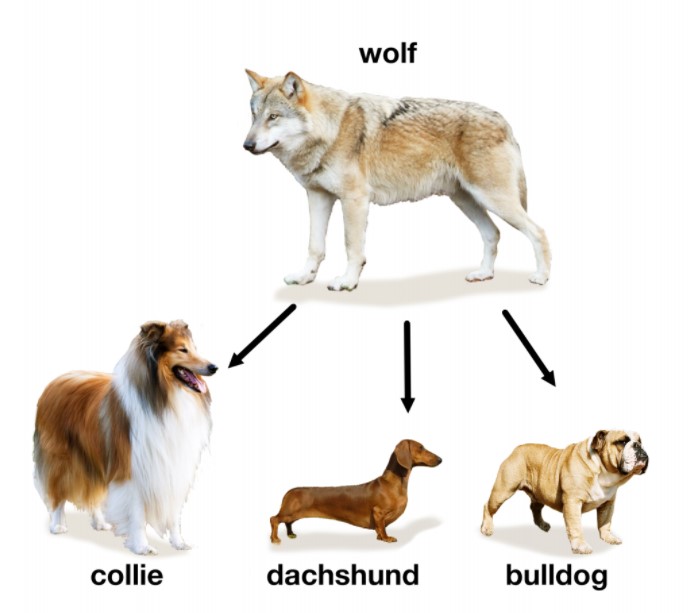
Artificial selection (selective breeding)
The process of intentionally choosing and breeding organisms with desirable traits to produce offspring with those traits.
Asexual reproduction
Type of reproduction that involves only one parent, and the offspring are genetically identical to the parent.
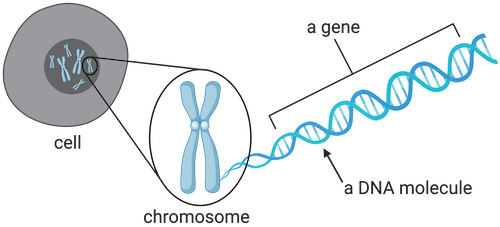
Chromosomes
Thread-like structures found in the nucleus of cells that carry genetic information in the form of DNA.
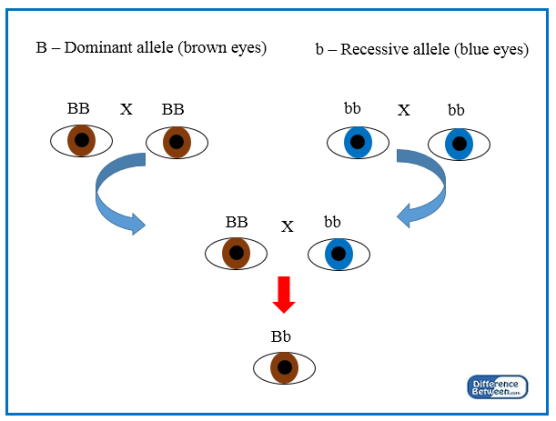
Dominant allele
An allele that is expressed or observed as a trait when present in either one or both copies in an individual's genotype.
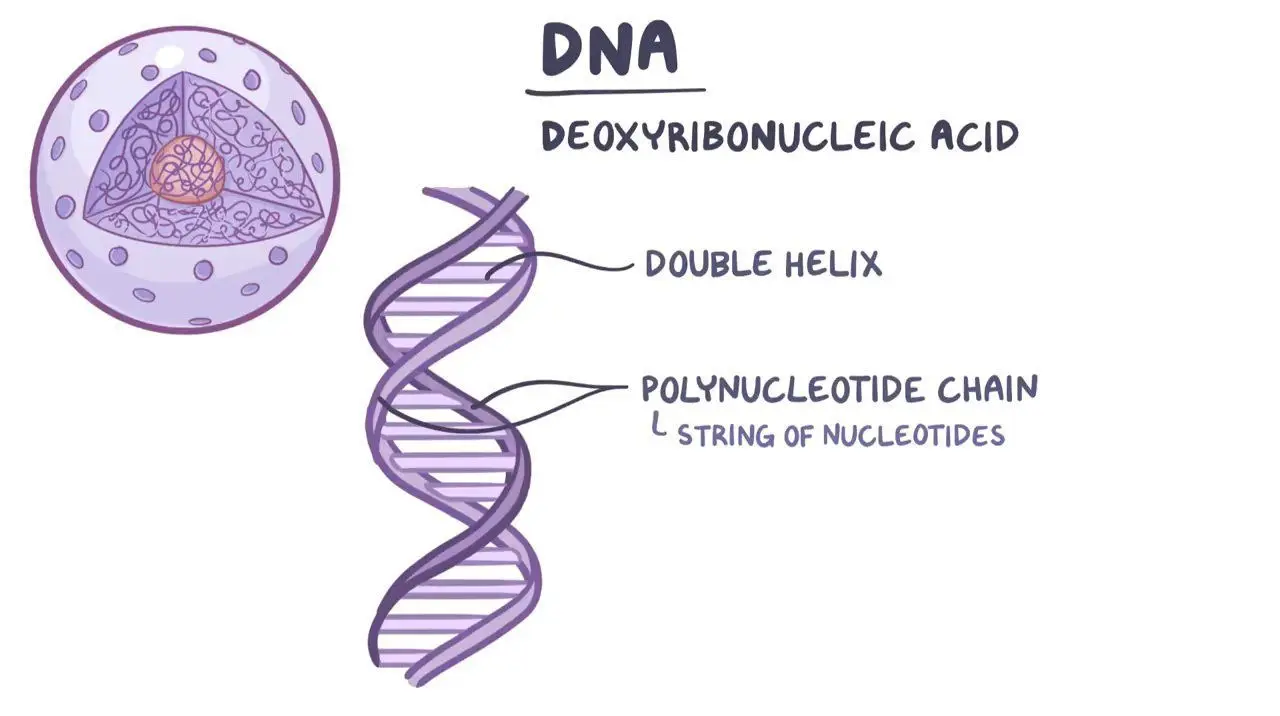
DNA
Molecule present in all living things; contains the genetic information that determines the traits that an organism inherits.
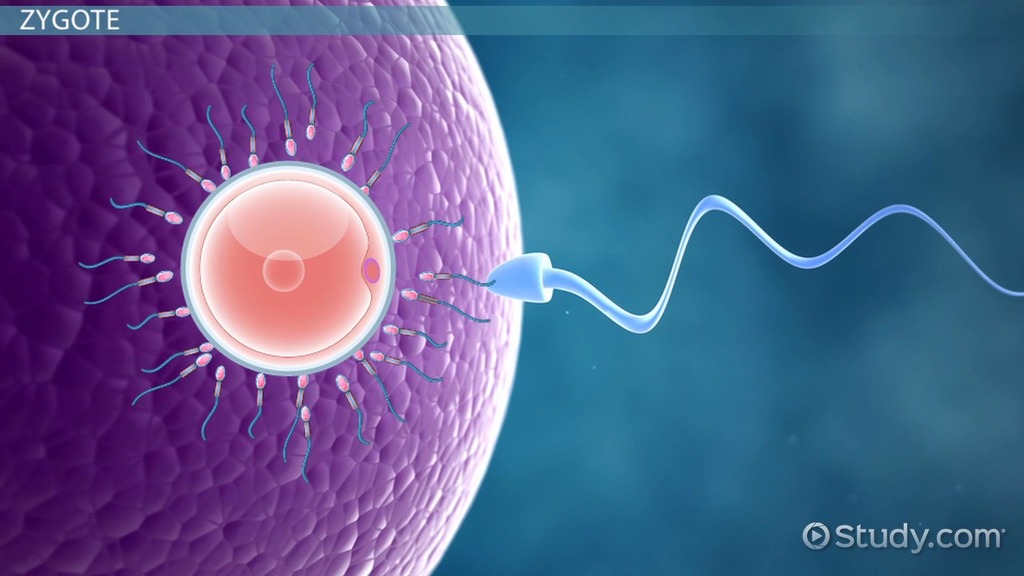
Fertilization
Fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote.
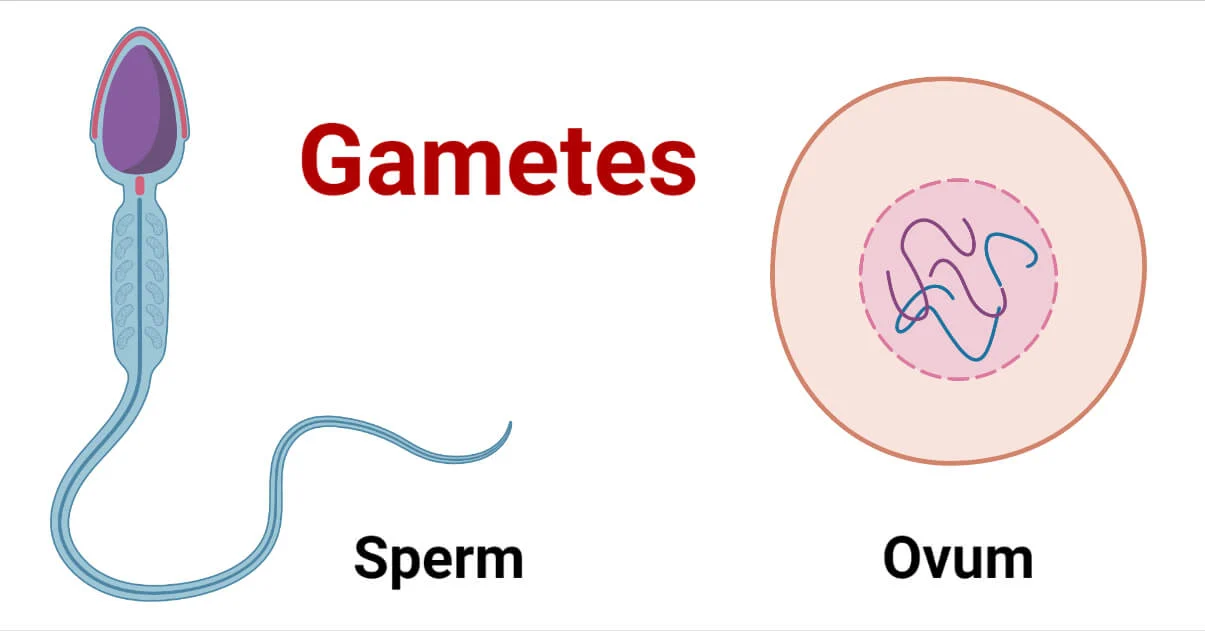
Gametes
Reproductive cells, such as sperm and eggs, that carry half the number of chromosomes found in other cells of an organism.
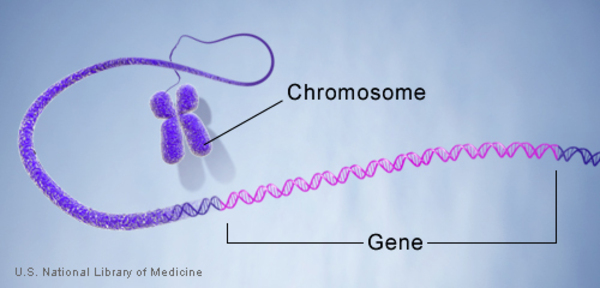
Gene
A segment of DNA and the basic units of heredity that determine the traits and characteristics of an organism.
Genetics
The branch of biology that studies how traits are inherited from one generation to the next.

Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism, which includes the combination of alleles present for a particular trait.
Heredity
The passing on of traits from parents to offspring through genetic information.

Heterozygous
Having two different alleles for a particular gene.

Homozygous
Having two identical alleles for a particular gene.

Hybrid
Offspring resulting from the breeding of two different individuals or varieties.
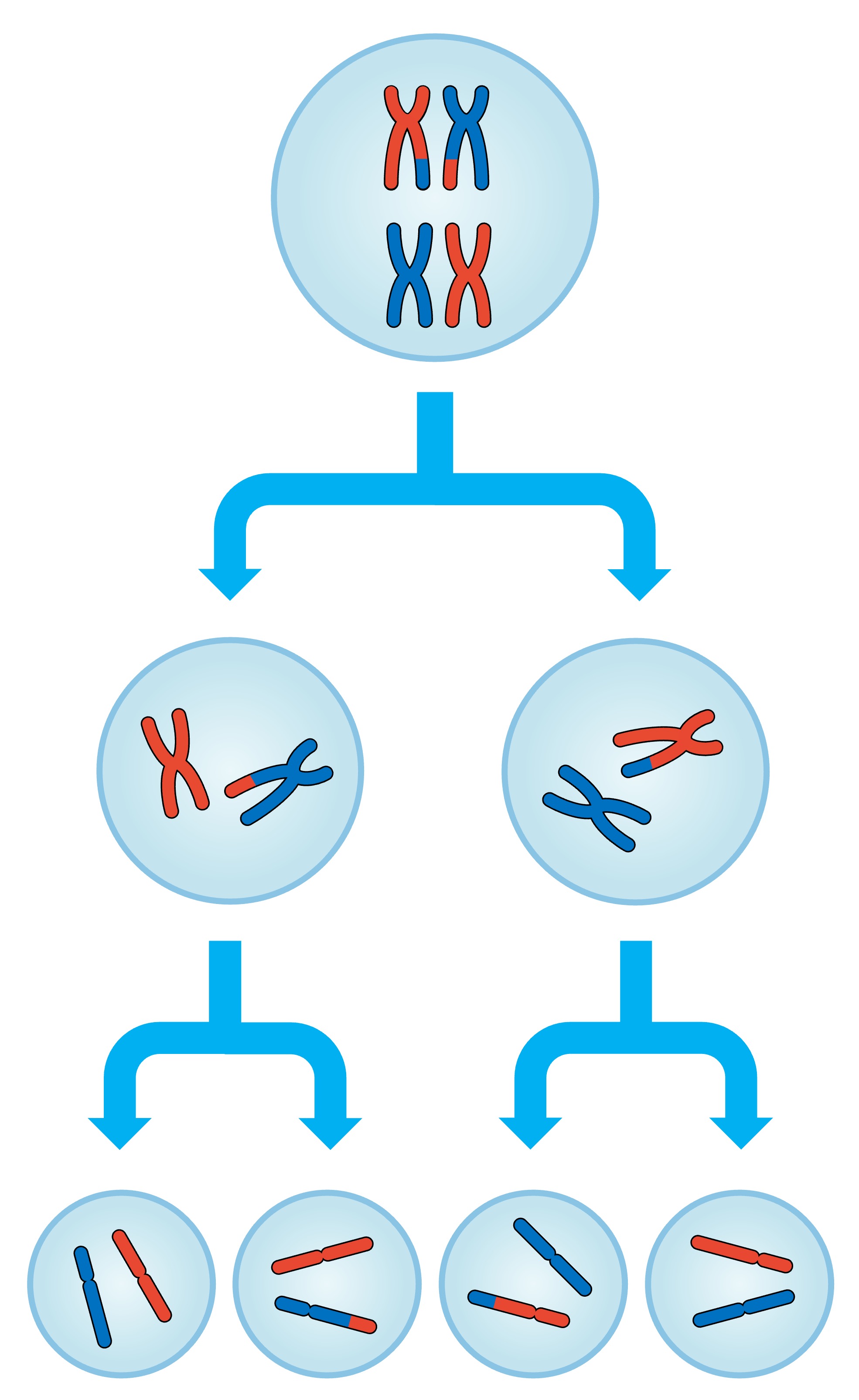
Meiosis
Cell division which produces gametes with half the number of chromosomes.
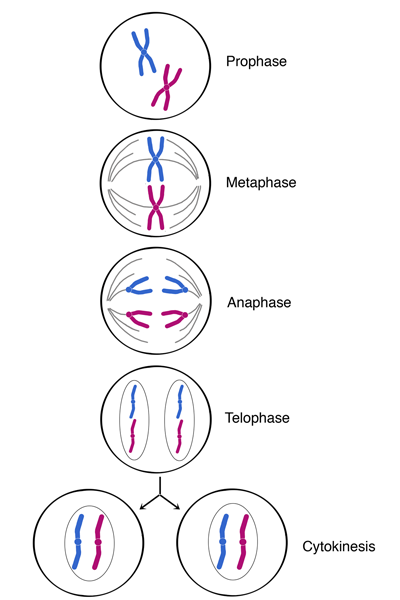
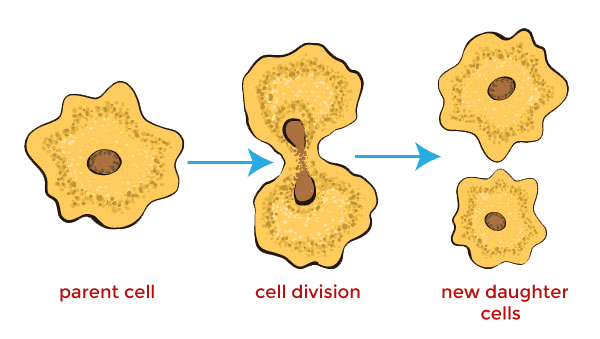
Mitosis
Cell division that results in the formation of two identical daughter cells.
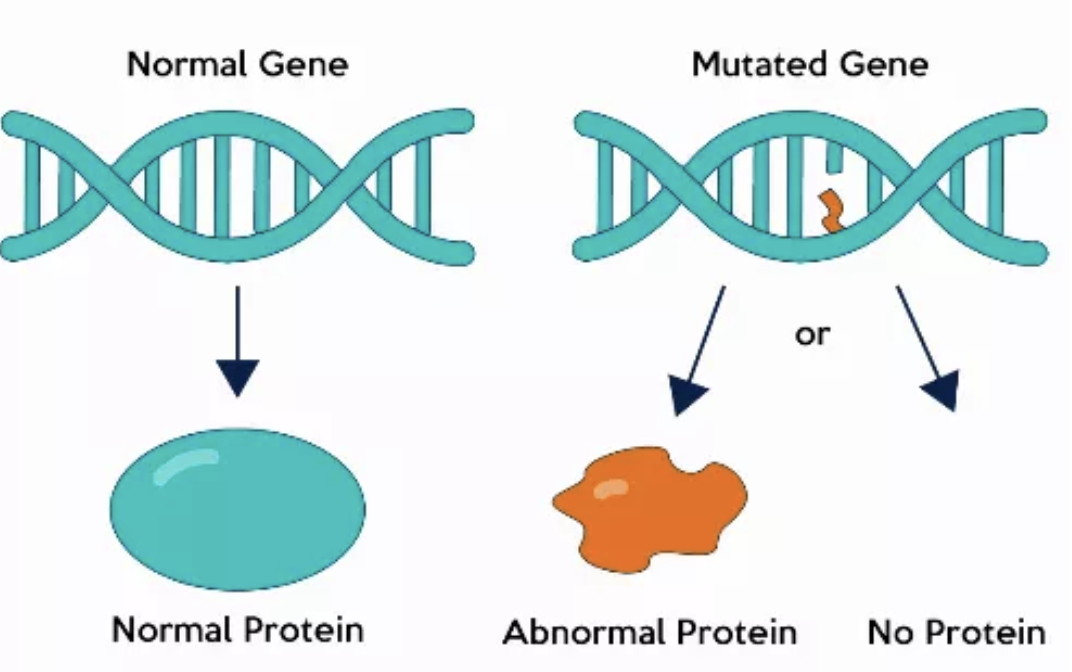
Mutation
A change in the DNA sequence of a gene or chromosome.

Phenotype
The observable physical characteristics of an organism.

Purebred
An organism that has a homozygous genotype for a particular trait.
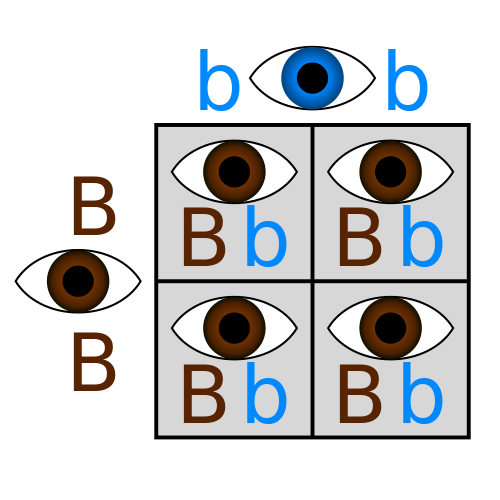
Punnett Square
Diagram used to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring resulting from a cross between two individuals.
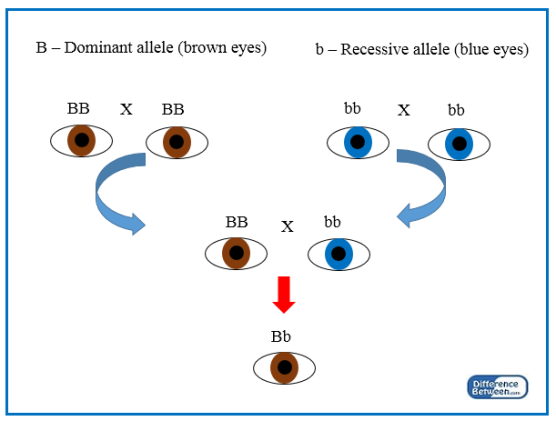
Recessive Allele
An allele that is expressed as a trait only when present in two copies in an individual's genotype.

Sexual reproduction
Type of reproduction that involves the fusion of gametes from two parents.
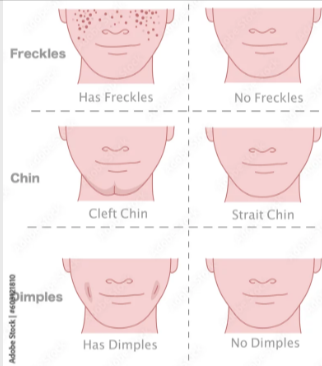
Trait
A specific characteristic or feature of an organism that can be inherited or acquired.
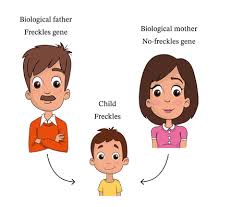
Inherited trait
A trait that is passed down from parents to offspring through genetic information.
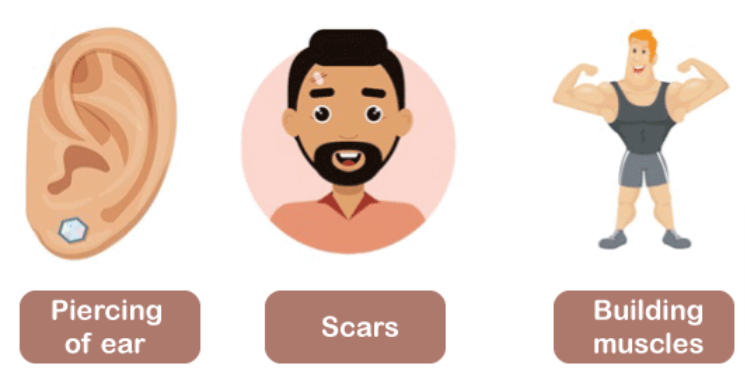
Acquired trait
A trait that is not inherited but is developed or acquired during an individual's lifetime.

Variation
Differences or diversity among individuals of the same species.
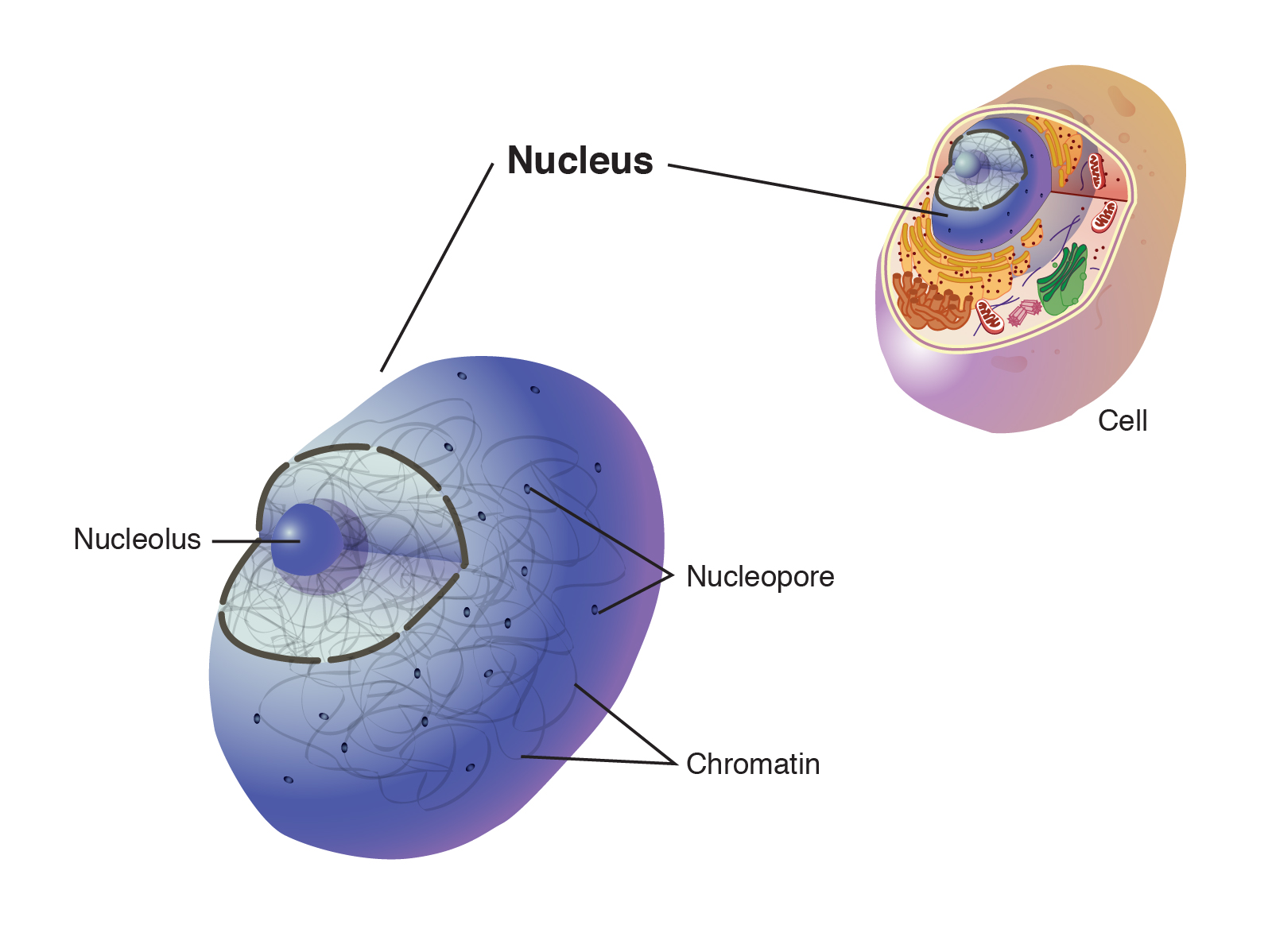
Nucleus
A membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell’s DNA.
Offspring
The new individuals that are produced as a result of reproduction.

Clone/Cloning
The process of creating an identical copy of an organism or a specific gene.
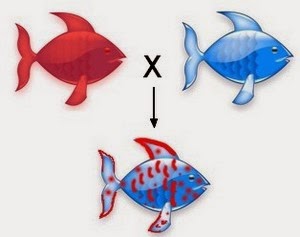
Codominance
When both alleles of a gene are fully expressed in the phenotype of an individual.
Genome
The complete set of genetic material or DNA present in an organism.

Karyotype
A visual representation of an individual's chromosomes arranged in pairs according to their size and shape.
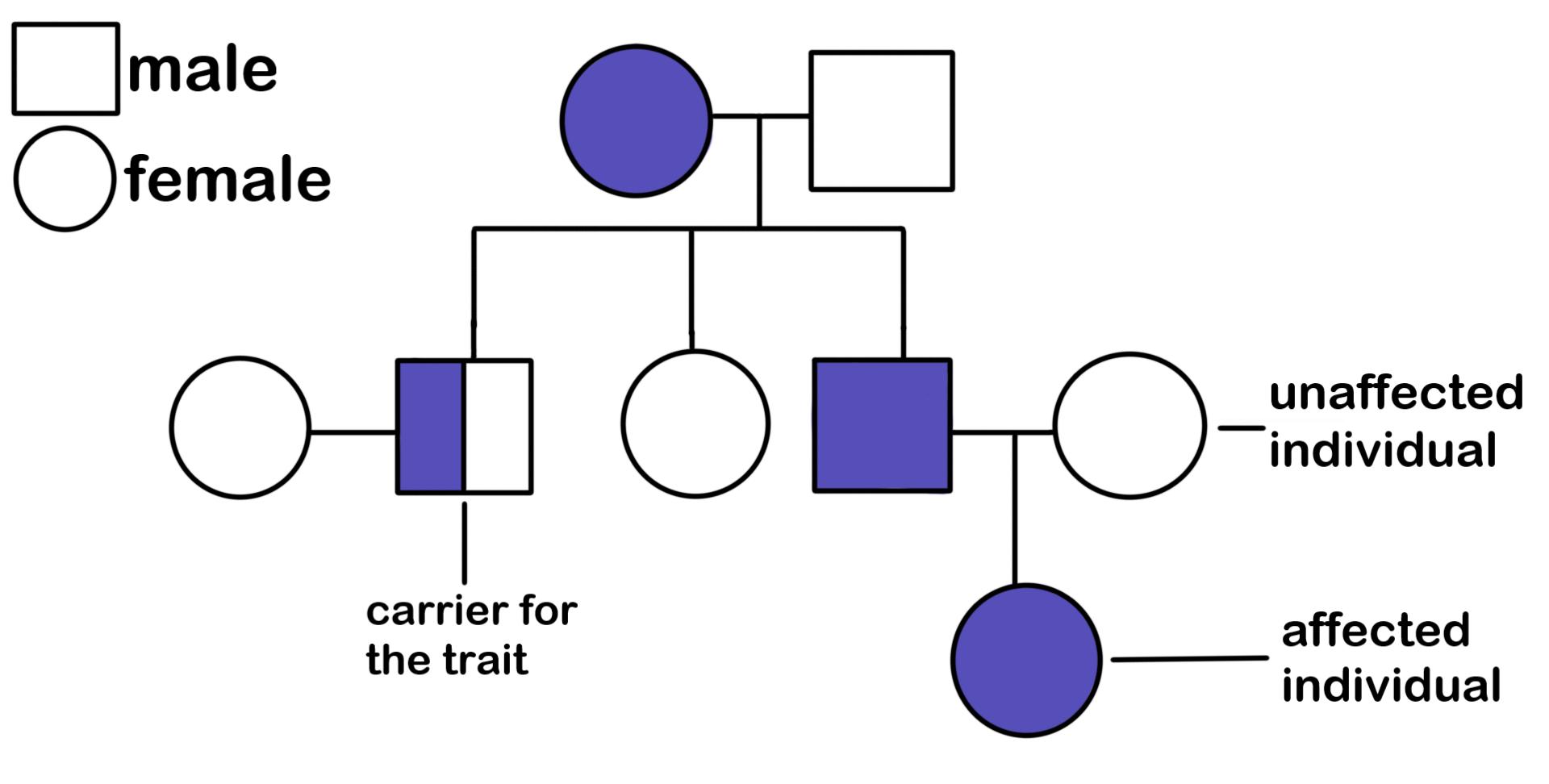
Pedigree
A diagram or chart that shows the genetic relationships within a family over multiple generations.
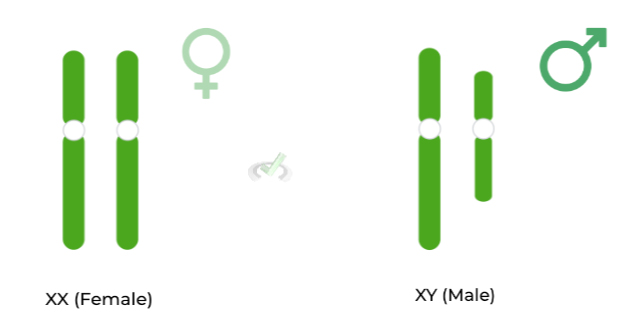
Sex-linked
Traits or genes that are located on the sex chromosomes.
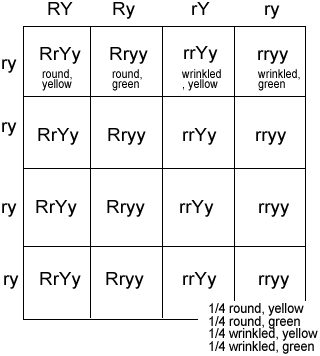
Dihybrid
An individual or a cross involving two different traits or genes.
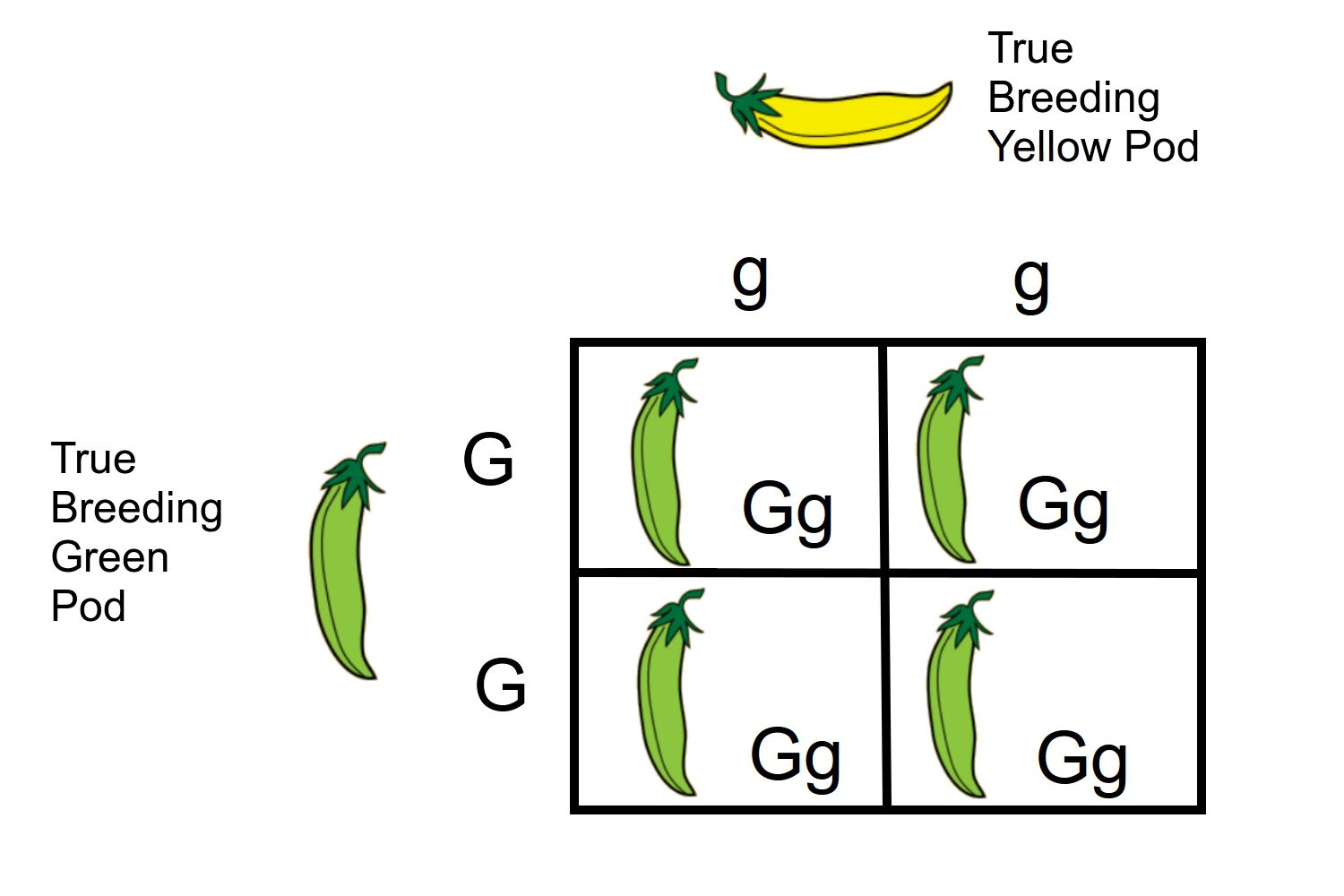
Monohybrid
An individual or a cross involving a single trait or gene.

Gene therapy
A medical technique that involves the modification of genes in an individual's cells to treat or prevent genetic disorders.
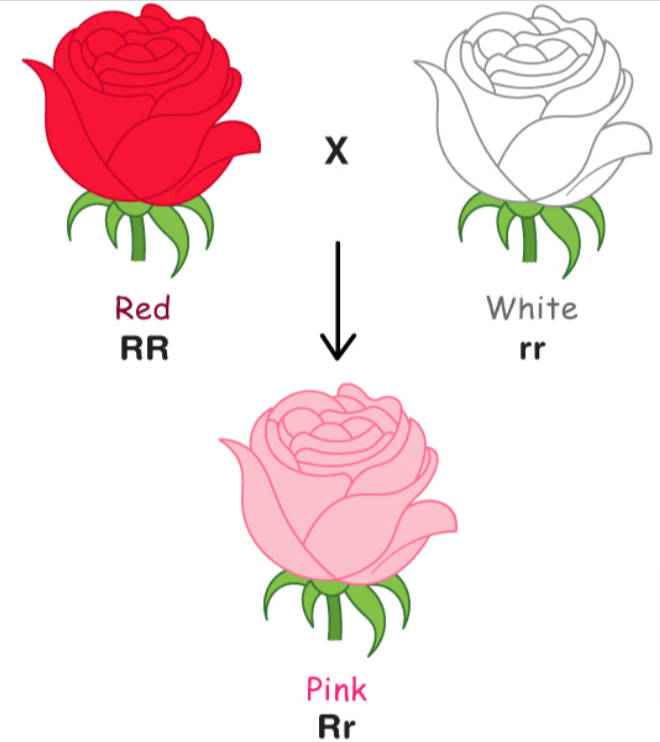
Incomplete dominance
When one allele for a specific trait is not completely expressed over its paired allele.
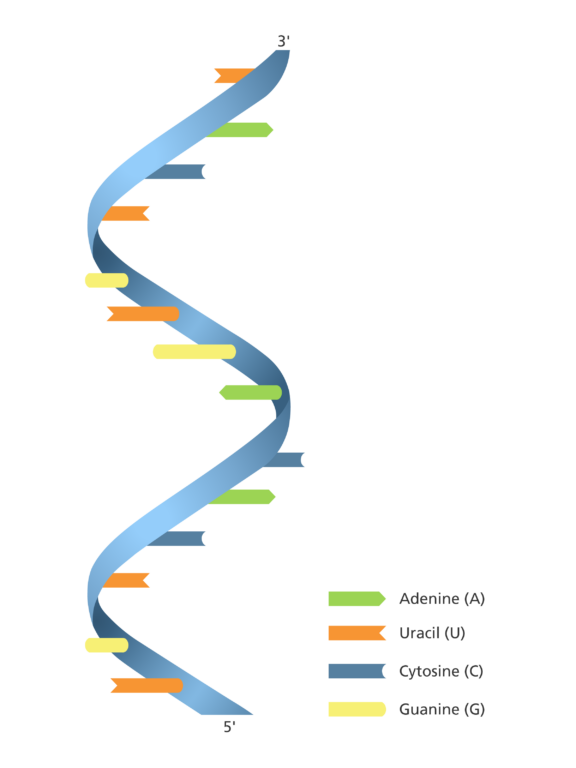
RNA
A nucleic acid present in all living cells that carries instructions from DNA for protein synthesis.
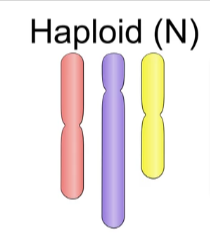
Haploid
Cells that contain one complete set of chromosomes.
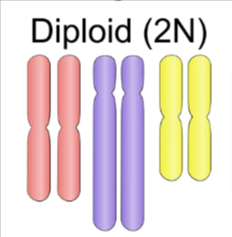
Diploid
Cells that contain two complete sets of chromosomes.
Probability
The likelihood that an event is going to occur.