Chapter 5 Proteins CHEM 136
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Amino acids
______ are the building blocks that form proteins.
Amino group, carboxyl group, side chain, hydrogen
What are parts of an amino acid?
Zwitterions
Amino acids exist as _____.
Zwitterions, positive, negative
These molecules are overall neutral but contain distinct _____ and _____ ion ends.
Nonpolar, polar, acidic, basic
The four classes of amino acids are ____, ____, ____, and _____.
Nonpolar
_____ acids contain either just hydrogen or carbon chains in their R groups.
Polar
_____ amino acids contain alcohols, thiols, and amides in their R groups.
Acidic
_____ amino acids contain a carboxylic acid in their R groups,
Basic
______ amino acids contain an amine in their R groups.
Hydrogen, carbon
Nonpolar amino acids contain either just ______ or ______ chains.
alcohols, thiols, amides
Polar amino acids contain ______, ______, and ______.
Carboxylic acid
Acidic amino acids contain a _______ ______.
Amine
Basic amino acids contain an ______.
Tripeptide
A ______ is formed from the linking of 3 amino acids.
N
The ____ terminus is the side that ends with the amine.
C
The ____ terminus is the side that ends with the carboxylic acid.
4
How many levels are in the protein structure?
3D
The levels of protein structure describe the buildup to the _______ shape that proteins possess.
Order
The _____ that amino acids are in determine the protein.
Sequences, structures
Different _____ will results in different ______ which effect function.
Alpha helix, beta sheets
_____ _____ and _____ ____ are secondary structures.
Secondary structures
_______ are common in many different proteins and organisms.
Tertiary structures
______ _______ are interactions between R groups of the amino acids.
Amino acids, close
Tertiary structures can happen between _____ _____ that are not even ______ together in primary.
Hydrophobic
_________ interactions occur between nonpolar R groups.
Hydrophilic
_________ interactions occur between polar R groups and water.
Hydrophilic
Hydrogen bonding is a special kind of ______ interaction.
NH3, carboxylic acid
A salt Bridge-ionic interaction between charged R groups has a positive _____ and a negative _____.
Disulfide
________ is an oxidation of two thiols in R groups.
Two thiols
What is a disulfide made of?
No
Do all proteins have quaternary structures?
Quaternary
_______ structures are interactions between two or more tertiary structures to form the biologically active protein..
Catalysts
Enzymes are biological ______.
enzymes, life, fast
Without _____ the chemical reactions needed to sustain ____ would not occur at a _____ enough rate.
high degree of specificity
Enzymes are effective without extreme conditions because of their _______.
lock, key
Enzymes are sometimes described as a _____ and ____ model.
Substrate
reactant of an enzyme reaction
Active site
The part of an enzyme where the reaction occurs
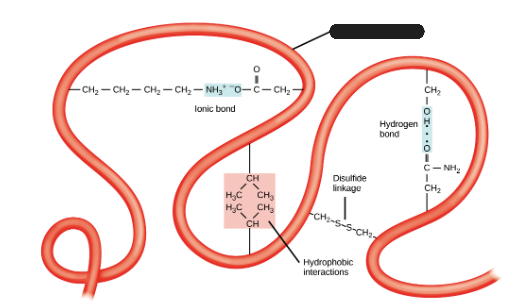
Disulfide linkage
What is being shown in the image?
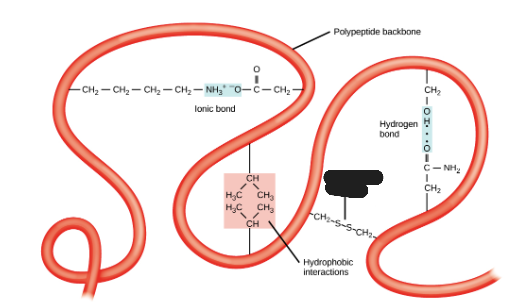
Hydrogen bond
What is being shown in the image?
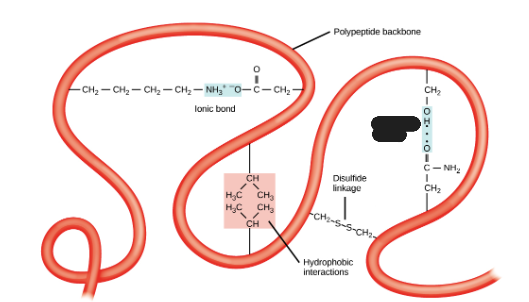
Hydrophobic interactions
What is being shown in the image?
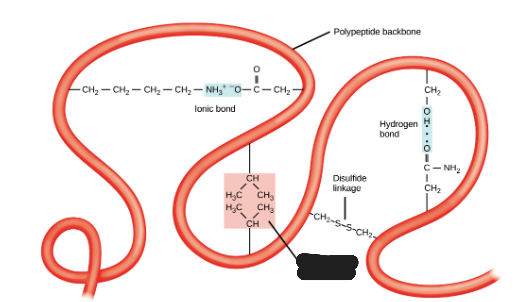
Ionic bond
What is being shown in the image?
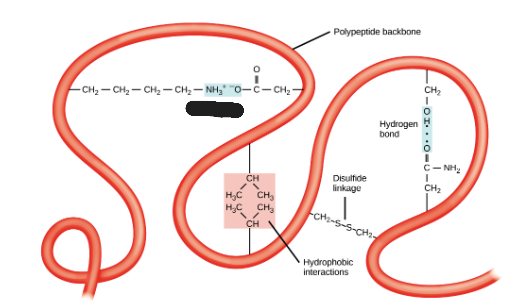
Polypeptide backbone
What is being shown in the image?