Diffusion, Osmosis, Passive and Active Transport || Biology H
1/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Diffusion (movement)
Movement of molecules from high concentration → low until equilibrium is reached. DOES NOT REQUIRE ENERGY
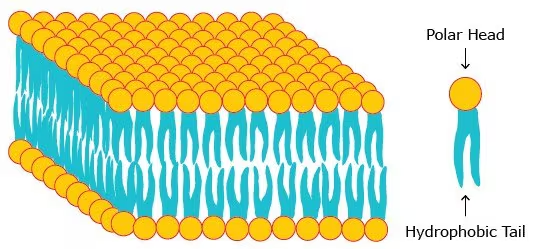
Cell Membrane main functions:
Protects the cell
Controls what enters and leaves
Maintains homeostasis
What is the cell membrane structure called?
Phospholipid Bilayer
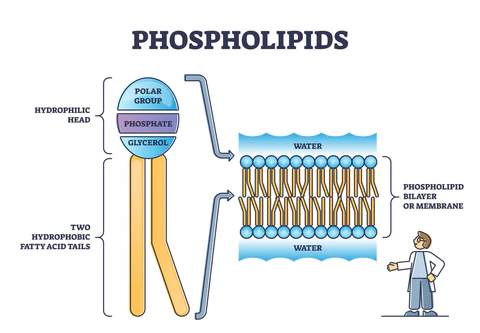
Which one likes water, and which one doesn’t?
Phospholipid Head:
Phospholipid Tail:
Head: Hydrophilic (water-loving)
Tail: Hydrophobic (water-fearing)
Carbs function in a phospholipid bilayer
Helps cells recognize each other (also a protection)
Protein Function in s phospholipid bilayer
Transports molecules
Cell Membranes are, Semipermeable. What does that mean?
They only allow some molecules to pass through. (only allow certain sizes & types of molecules)
What is a Lipid? What are the Key elements?
Long term energy storage, protection, or barrier.
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen (“CHO”)
Chemical structure of a Lipid:
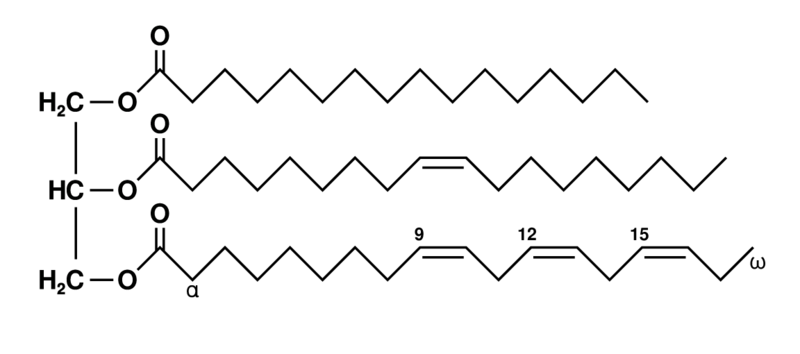
Think Jellyfish
Monomer example:
Polymer Example:
Monomer: Glycerol, Fatty Acid.
Polymer: Lipids
What does a phospholipid look like
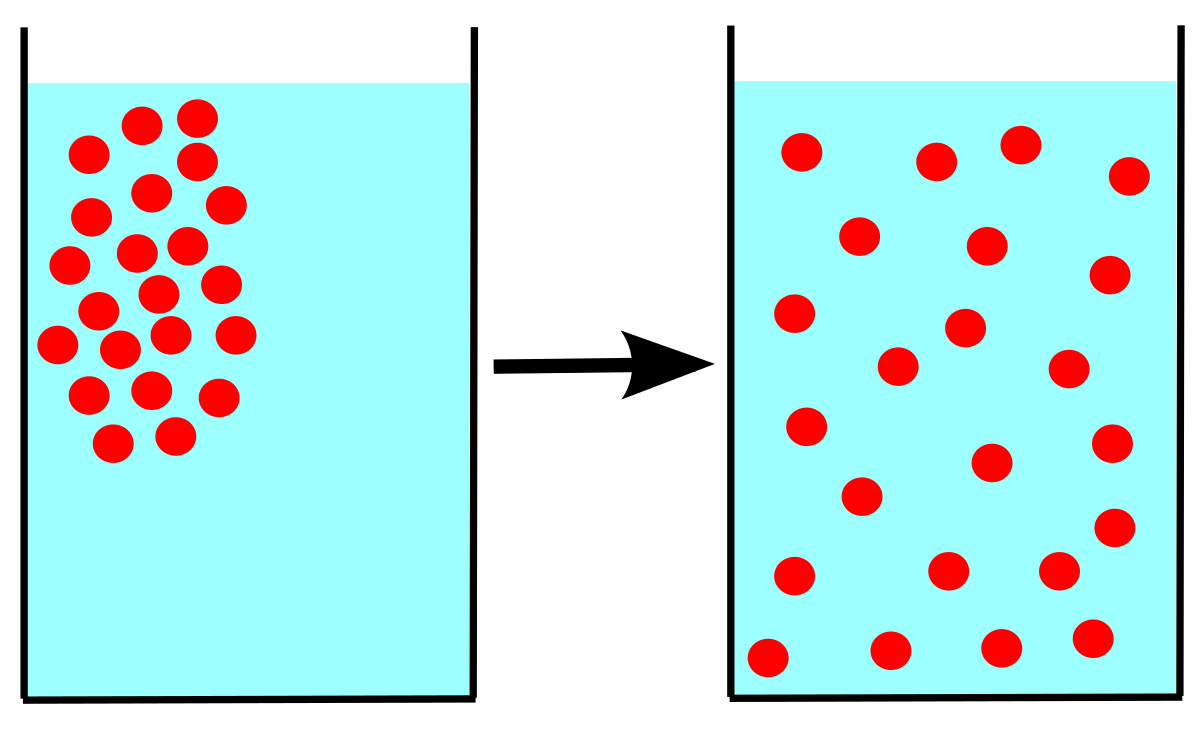
What is diffusion? (occurs, type of molecules)
Diffusion occurs for small & uncharged molecules across a semipermeable membrane.
Osmosis is:
The Diffusion of water across a membrane. (but water)
Water: High → Low concentration
Solvent & Solute: Low → High
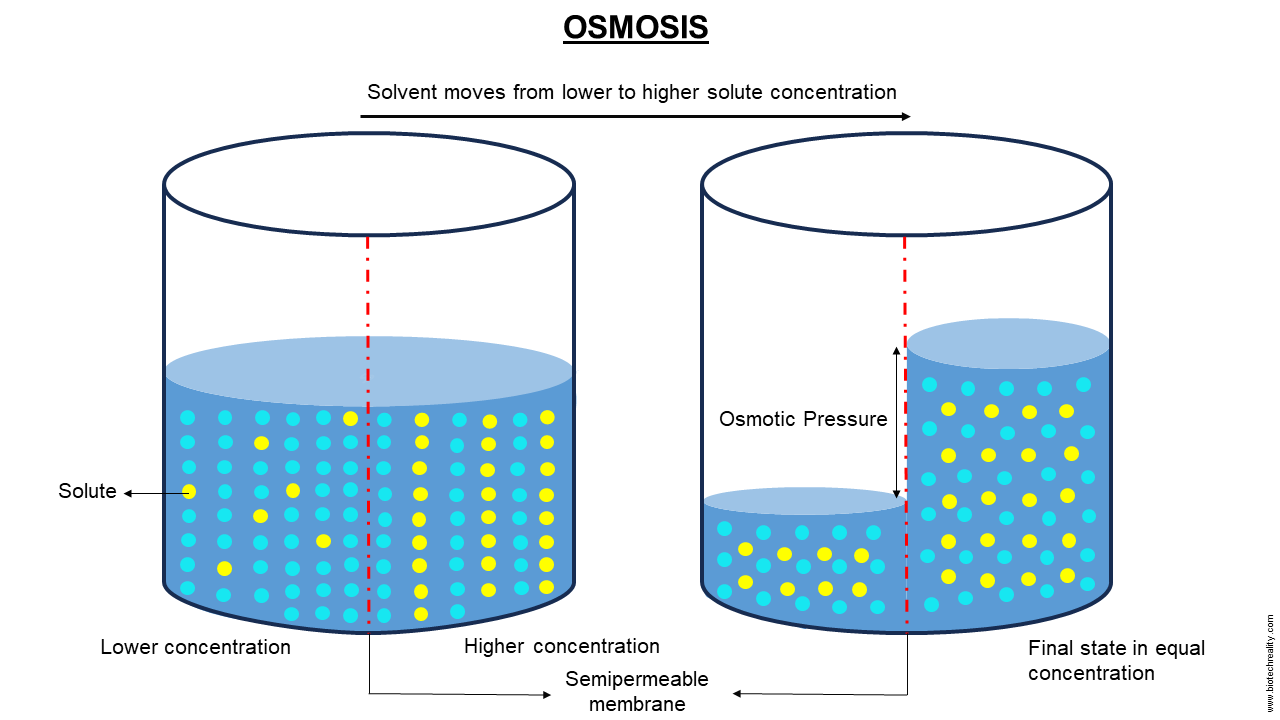
Hypotonic
Water moves into the cell → swelling.
~ Solute concentration higher (inside cell)
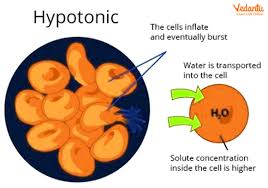
Isotonic
Water moves in and out of the cell, equilibrium.
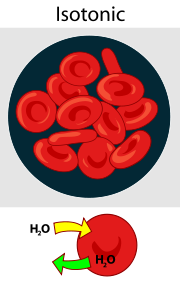
Hypertonic
Water leaver the cell, causing it to shrink.
Which macromolecules make up a cell membrane?
Carbon Dioxide, Oxygen, Water
Passive transport:
Without energy, Simple Diffusion and Facilitated diffusion
Simple diffusion:
diffusion of molecules across the membrane without protein.
Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Facilitated Diffusion
Diffusion of molecules across membrane with the help of transport protein.
Water & Glucose
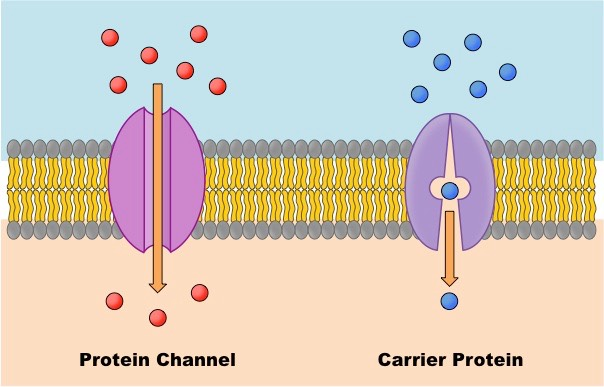
Protein Channel
Passive Transport. Provides an open tunnel through membrane, molecules move across. Choose specific molecules.
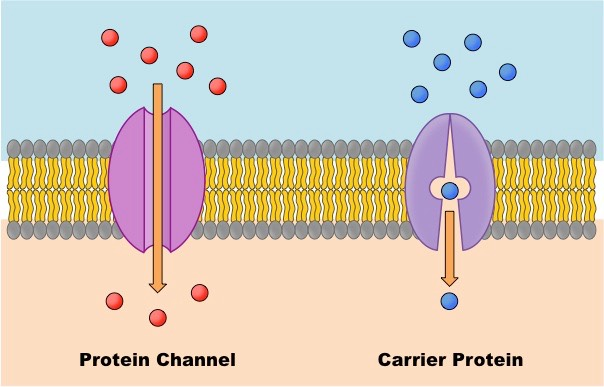
Carrier Proteins
Passive and Active transport. Combine and carry molecules. Transport specific molecules.
Active transport (Type of active transport)
Moves molecules against concentration gradient . Low → High.
ATP/Energy
Needs a carrier
Endocytosis (Type of active transport)
Large molecules/quantities ENTER the cell
Exocytosis (Type of active transport)
Large molecules/quantities EXIT the cell.