Lecture 2: The Cell
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Sex cells
Germ cells (gametes) for reproduction, including sperm and oocytes.
Somatic cells
Cells that are NOT sex cells; all other cells in the body.
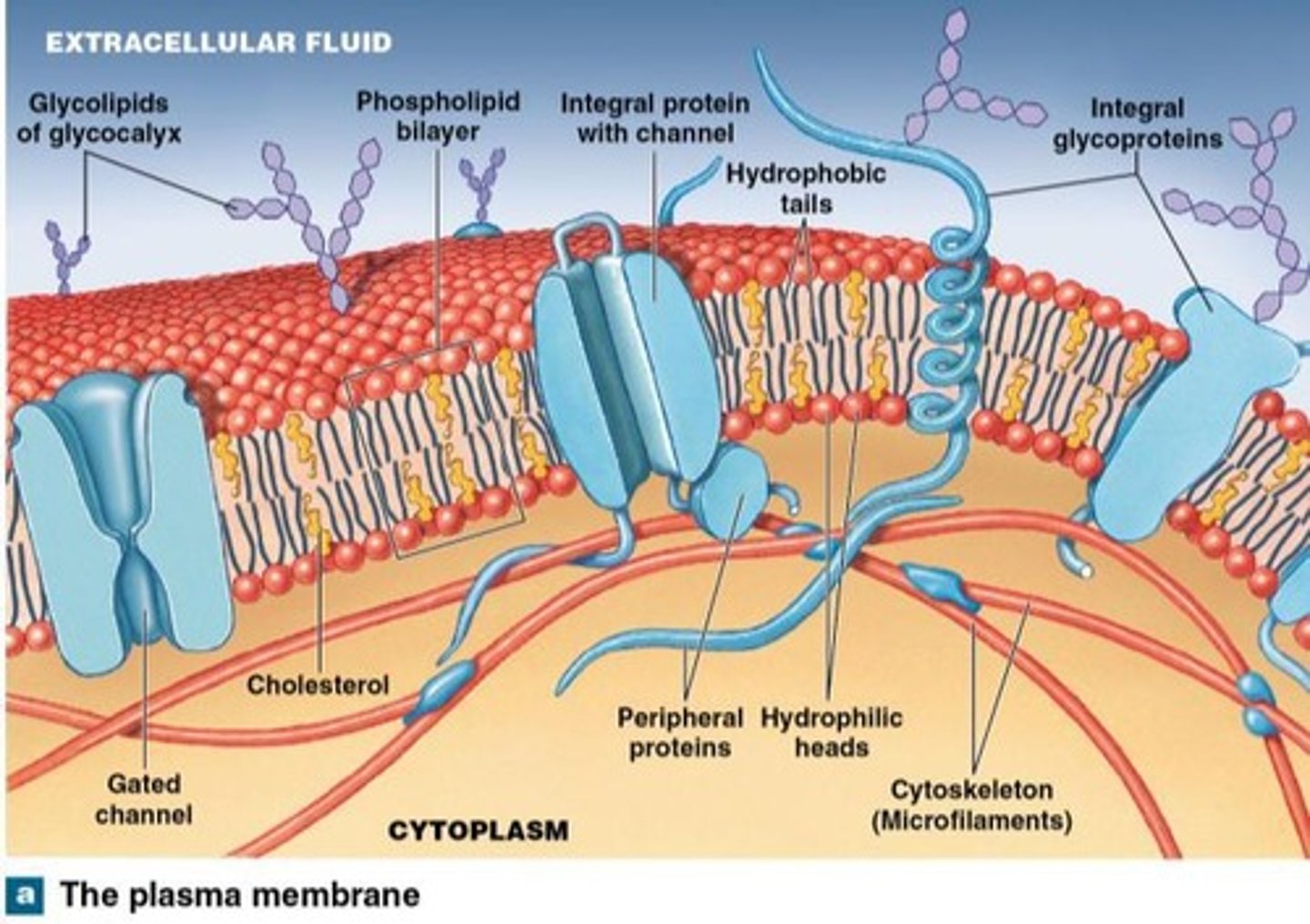
Plasma Membrane
A dynamic structure that consists of a bilayer and multiple components, including phospholipids, glycolipids, and proteins.
Cytoplasm
The material within a cell, excluding the nucleus, consisting of cytosol and organelles.
Cytosol
Intracellular fluid of the cell; gel-like substance inside the cell.
Organelles
Intracellular structures that perform specific functions within the cell.
Membrane Permeability
The ability of the plasma membrane to regulate the exchange of materials with the environment.
Passive processes
Processes where molecules move from high to low concentration without the use of ATP.
Diffusion
Movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
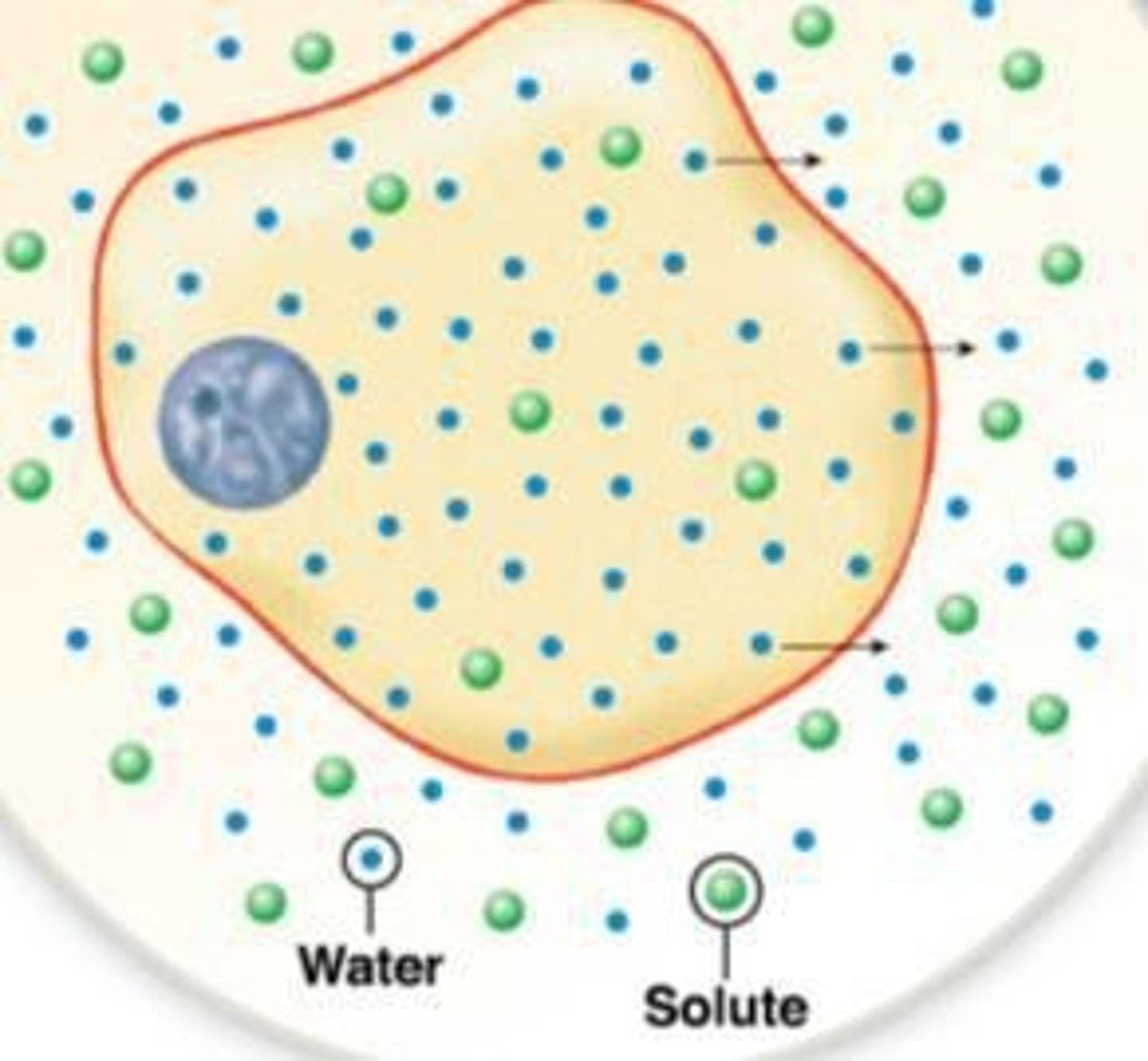
Osmosis
Movement of water across a membrane.
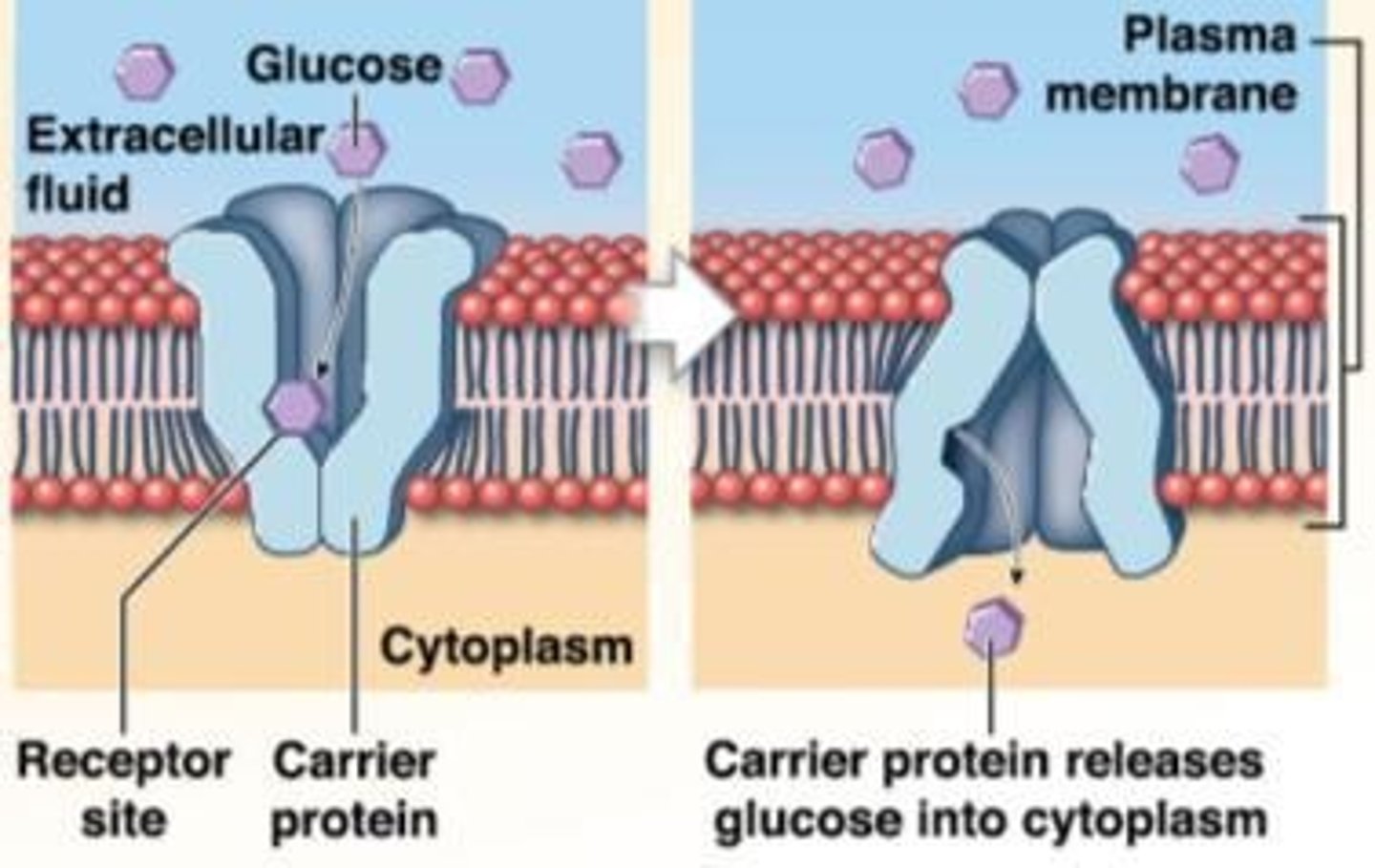
Facilitated diffusion
Movement of molecules across a membrane via protein channels.
Active processes
Processes that require ATP to move molecules from low to high concentration.
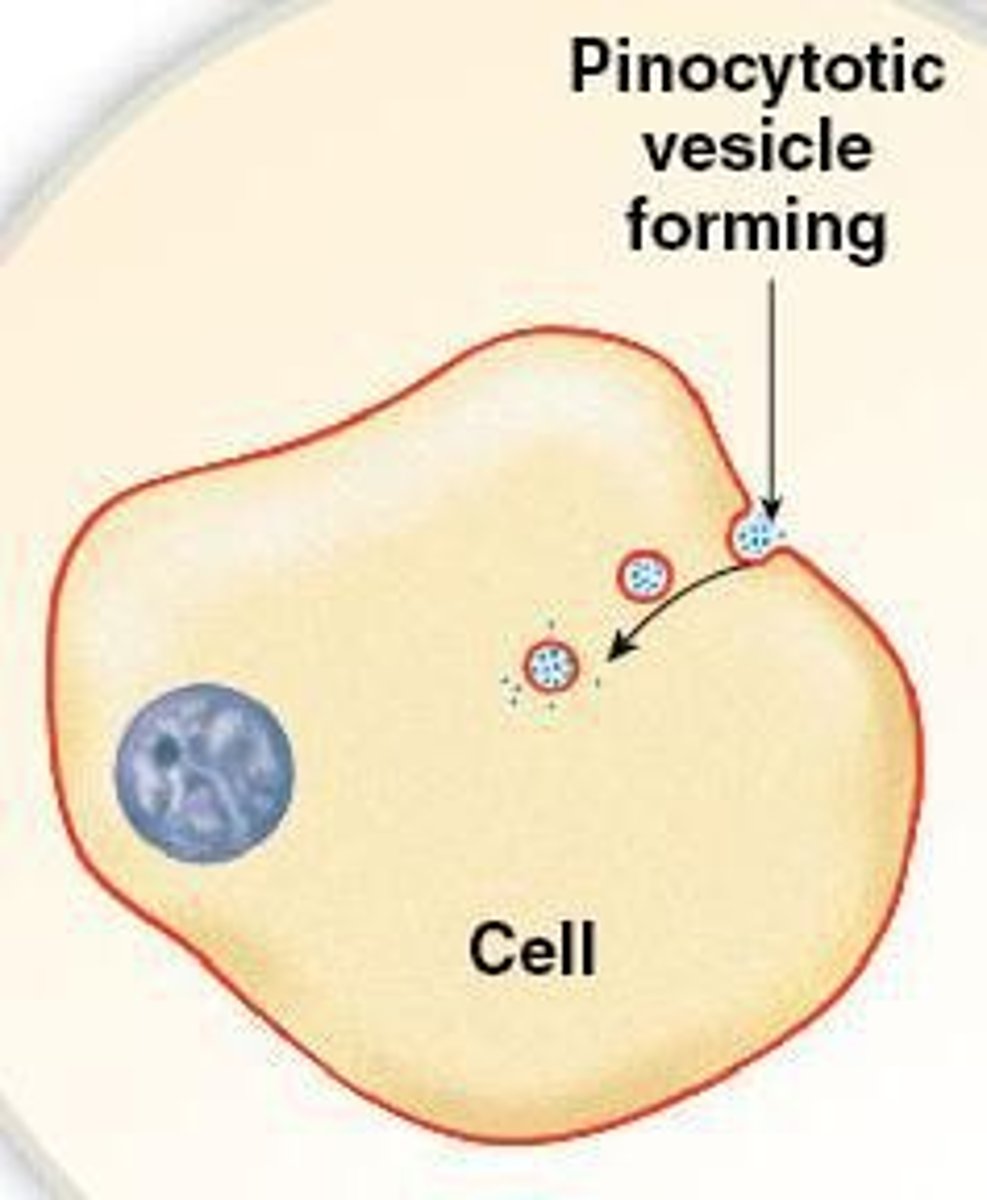
Endocytosis
Process by which cells take in molecules, including cell drinking (pinocytosis) and cell eating (phagocytosis).
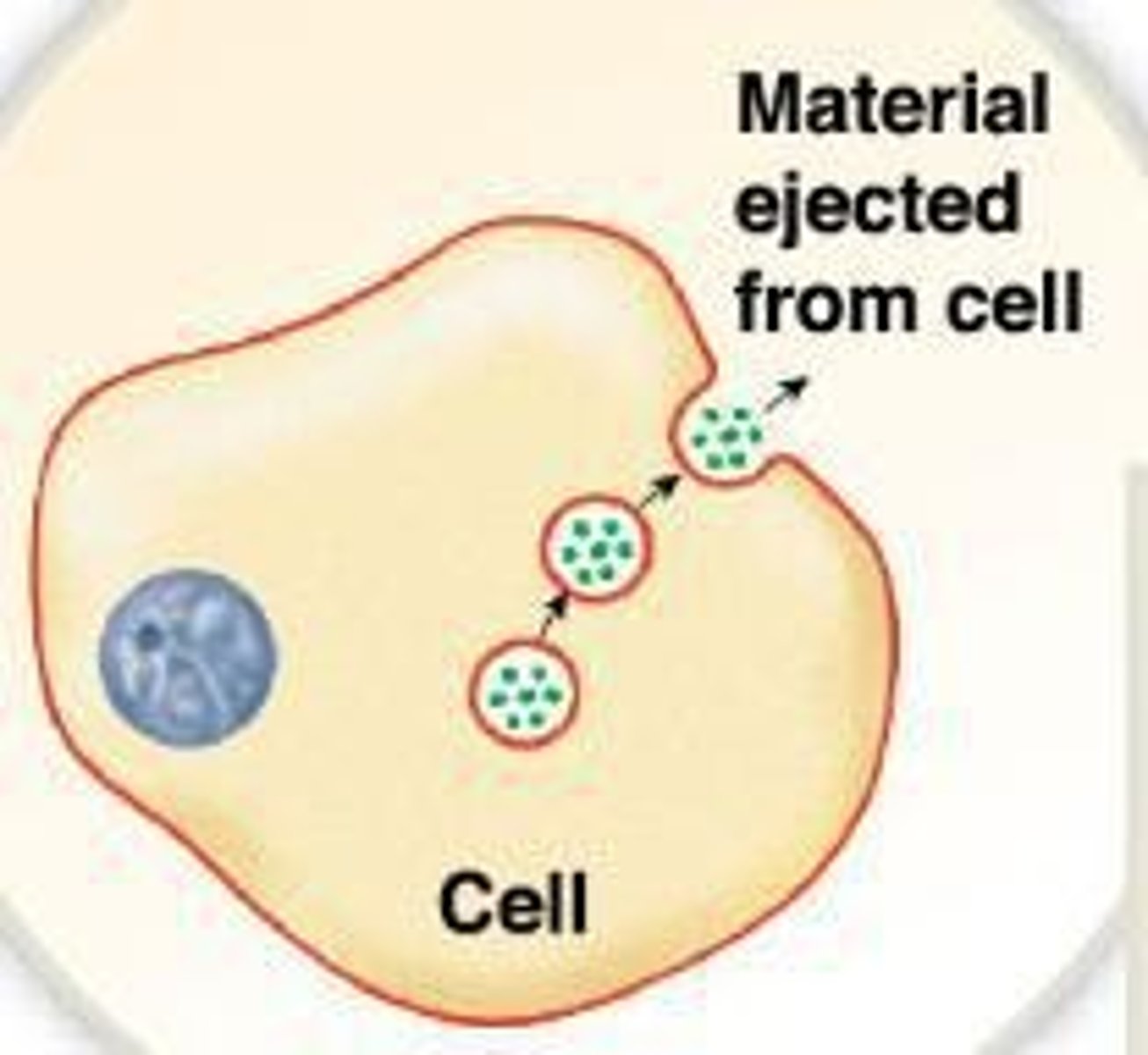
Exocytosis
Process by which cells expel materials.
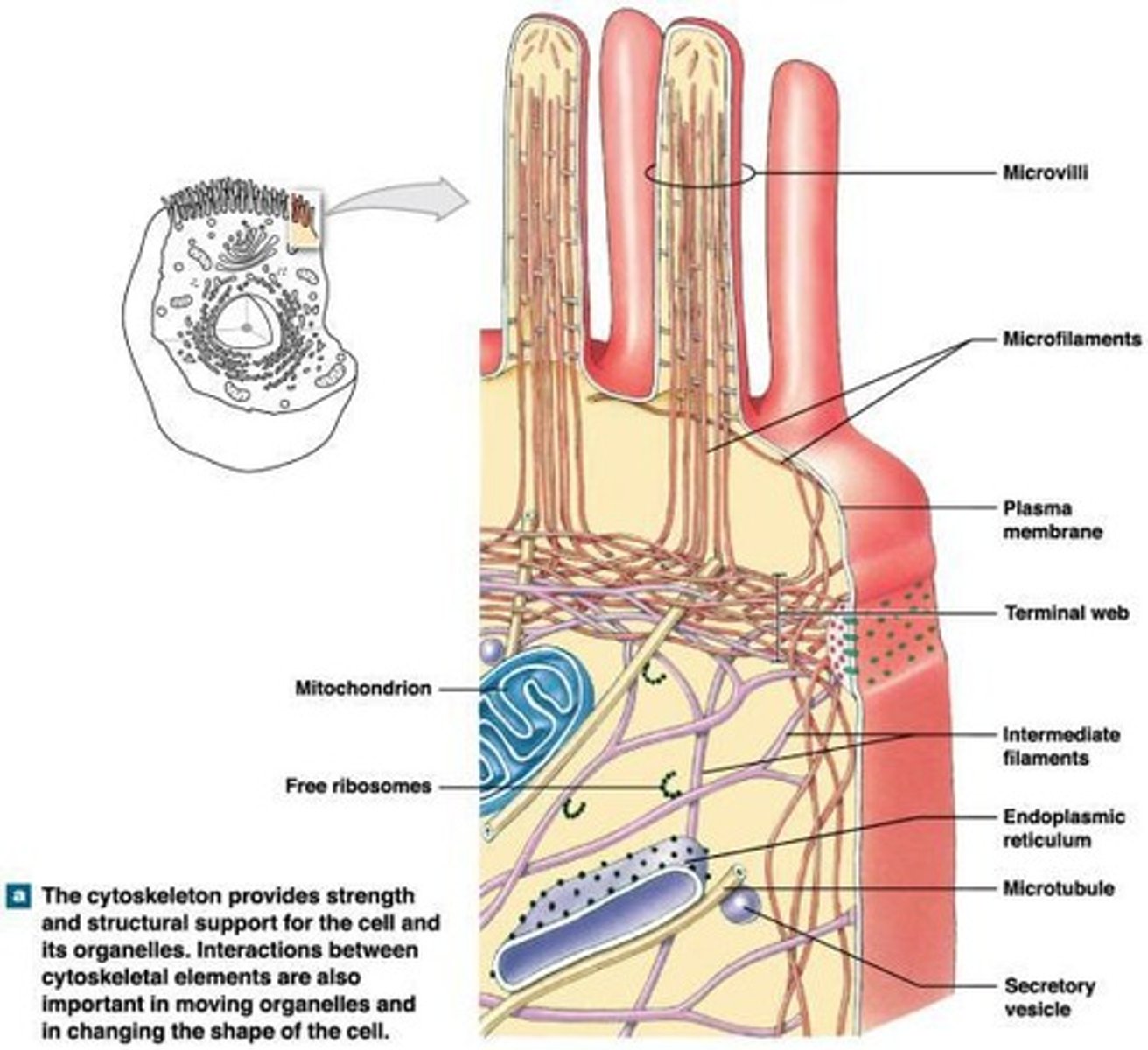
Microvilli
Extensions of the plasma membrane that increase surface area for absorption.
Intracellular fluid (ICF)
Fluid found inside the cell, contributing to the cytosol.
Cell-to-cell communication
The ability of cells to communicate with each other through the plasma membrane.
Structural support
The function of the plasma membrane in providing support to the cell.
Sensitivity to changes
The plasma membrane's ability to respond to changes in the extracellular fluid.
Cholesterol
A component of the plasma membrane that helps maintain its structure.
Peripheral proteins
Proteins located on the outer or inner surface of the plasma membrane.
Integral proteins
Proteins that are embedded within the plasma membrane.
Cytoskeleton
A crucial structure for cell movement, shape maintenance, and endocytosis.
Microfilaments
Thin filaments composed of actin that are involved in cell movement.
Intermediate filaments
Filaments that help maintain cell shape.
Microtubules
Thick filaments composed of tubulin that are involved in intracellular transport and cell division.
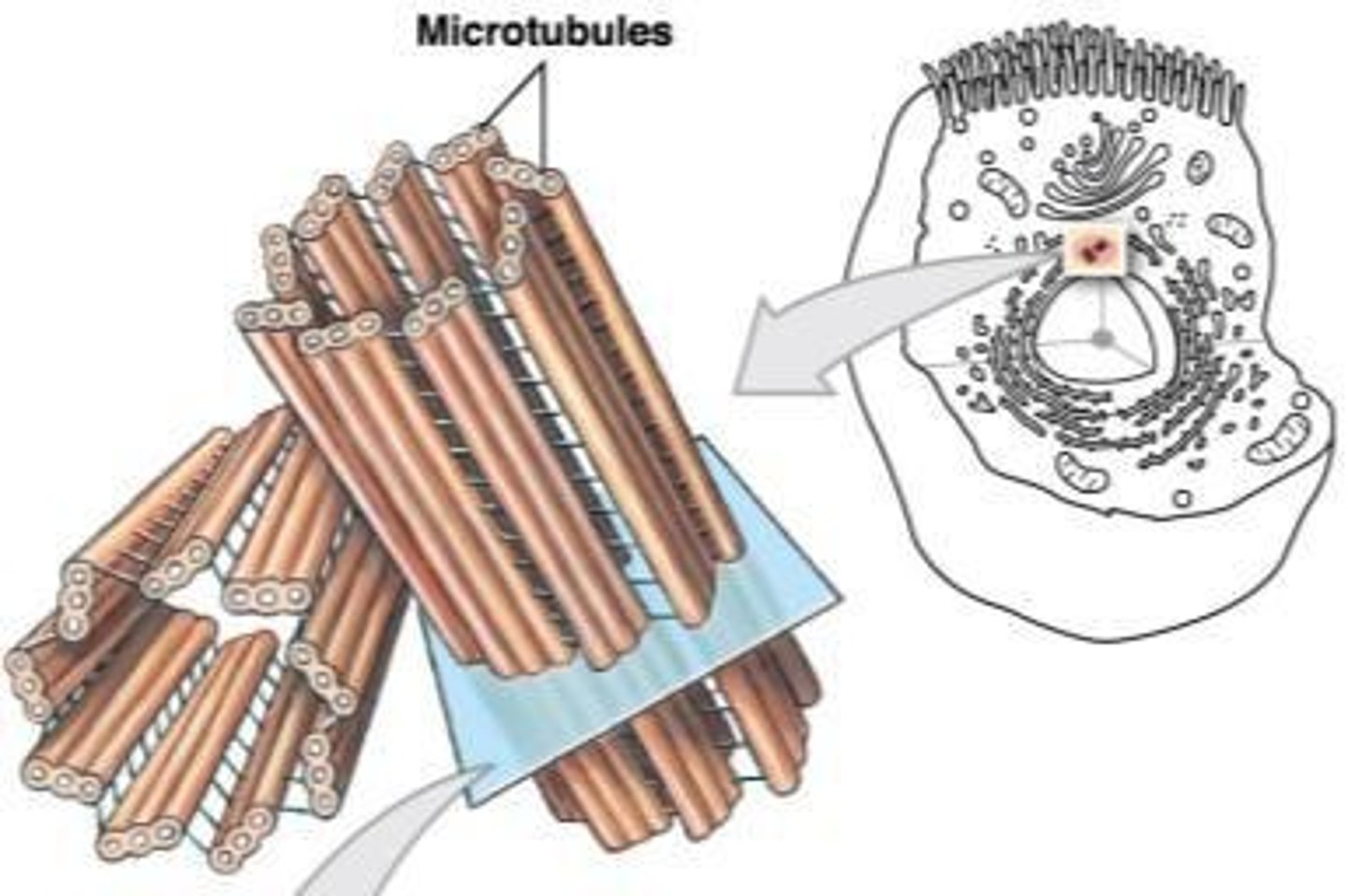
Centriole
An organelle that produces microtubules to move chromosomes during cell division.
Cilia
Short organelles that beat rhythmically to move fluid or secretions across the cell surface.
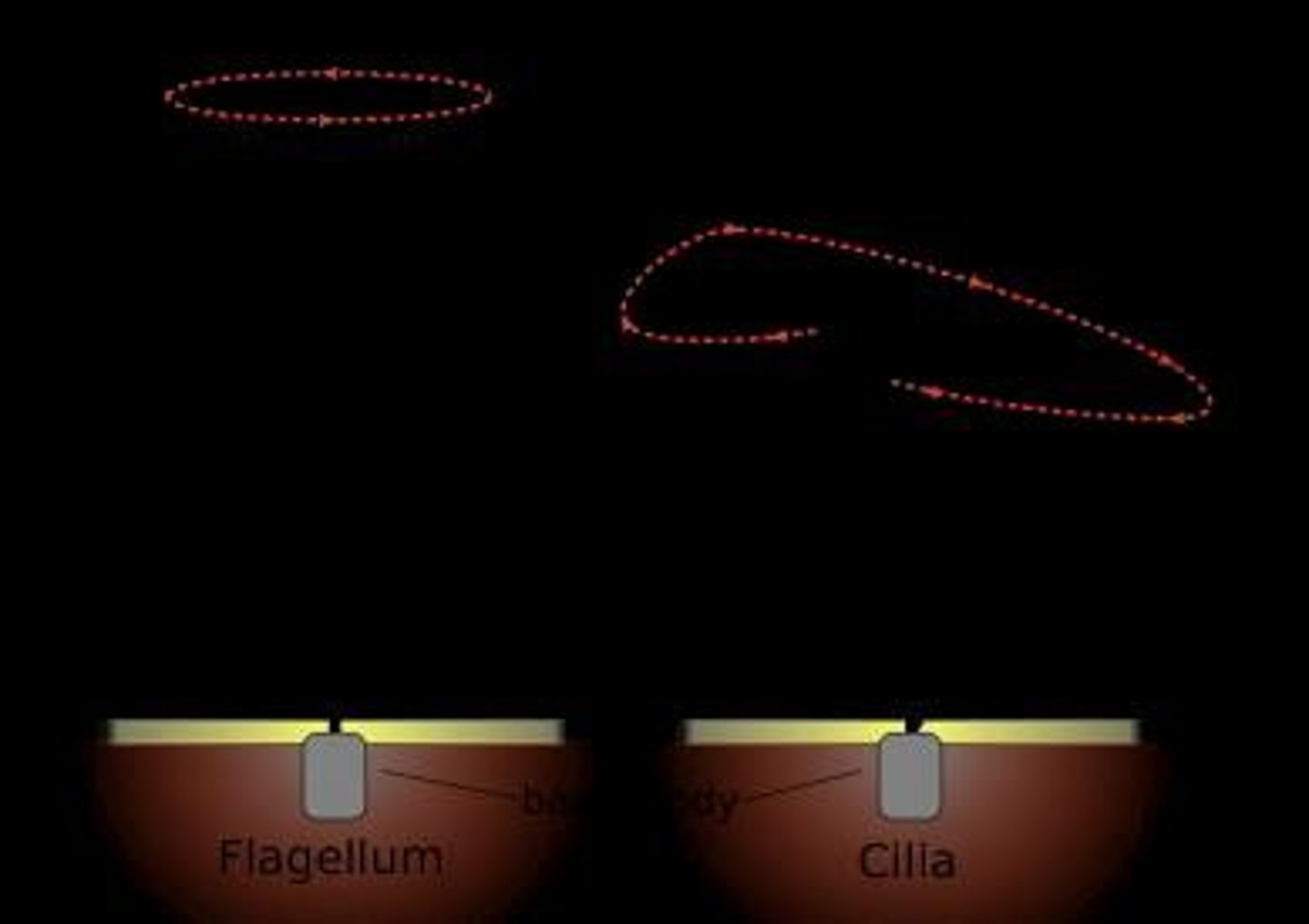
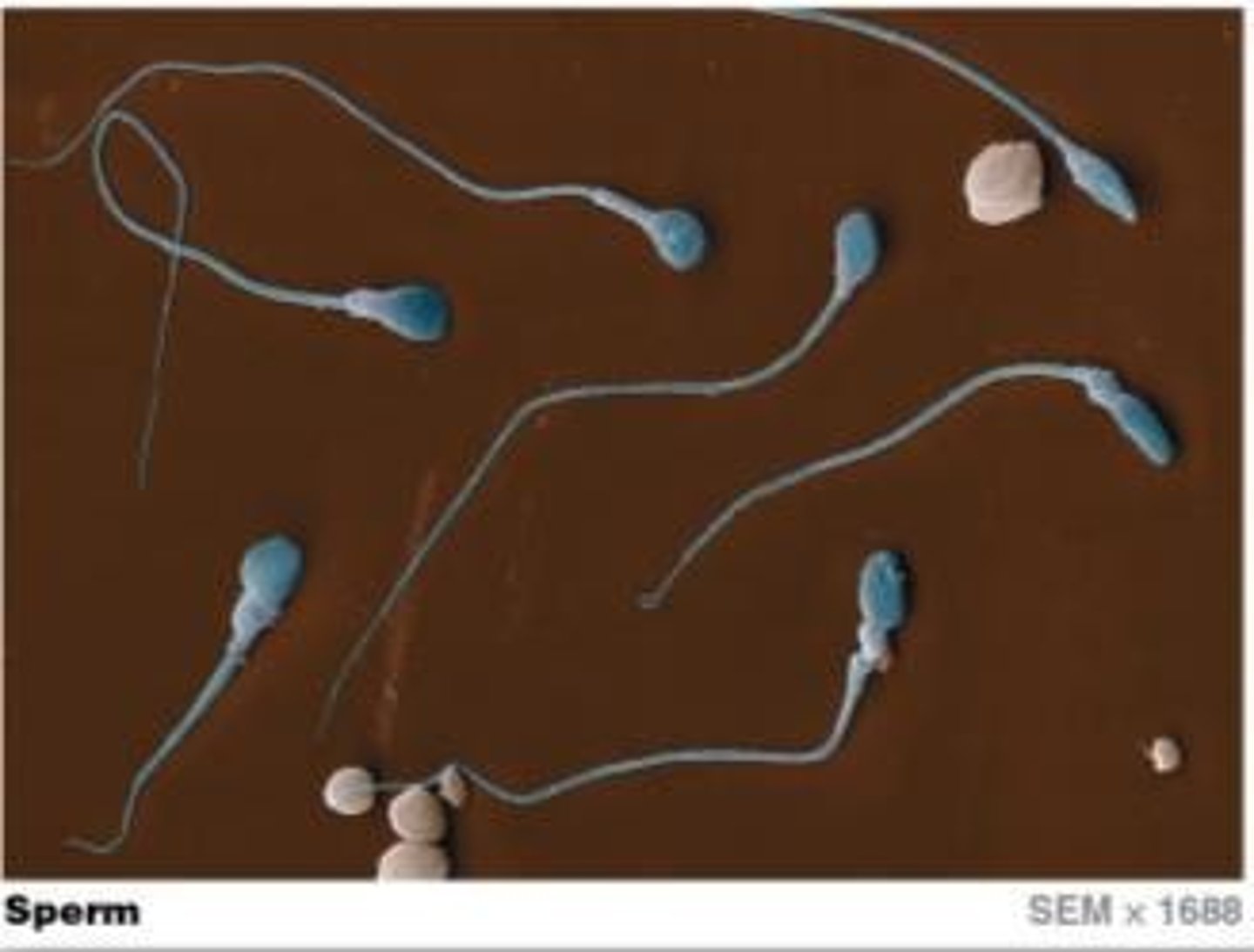
Flagella
Long organelles that propel sperm through fluid.
Ribosomes
Organelles that float in the cytoplasm or are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum, involved in protein production.
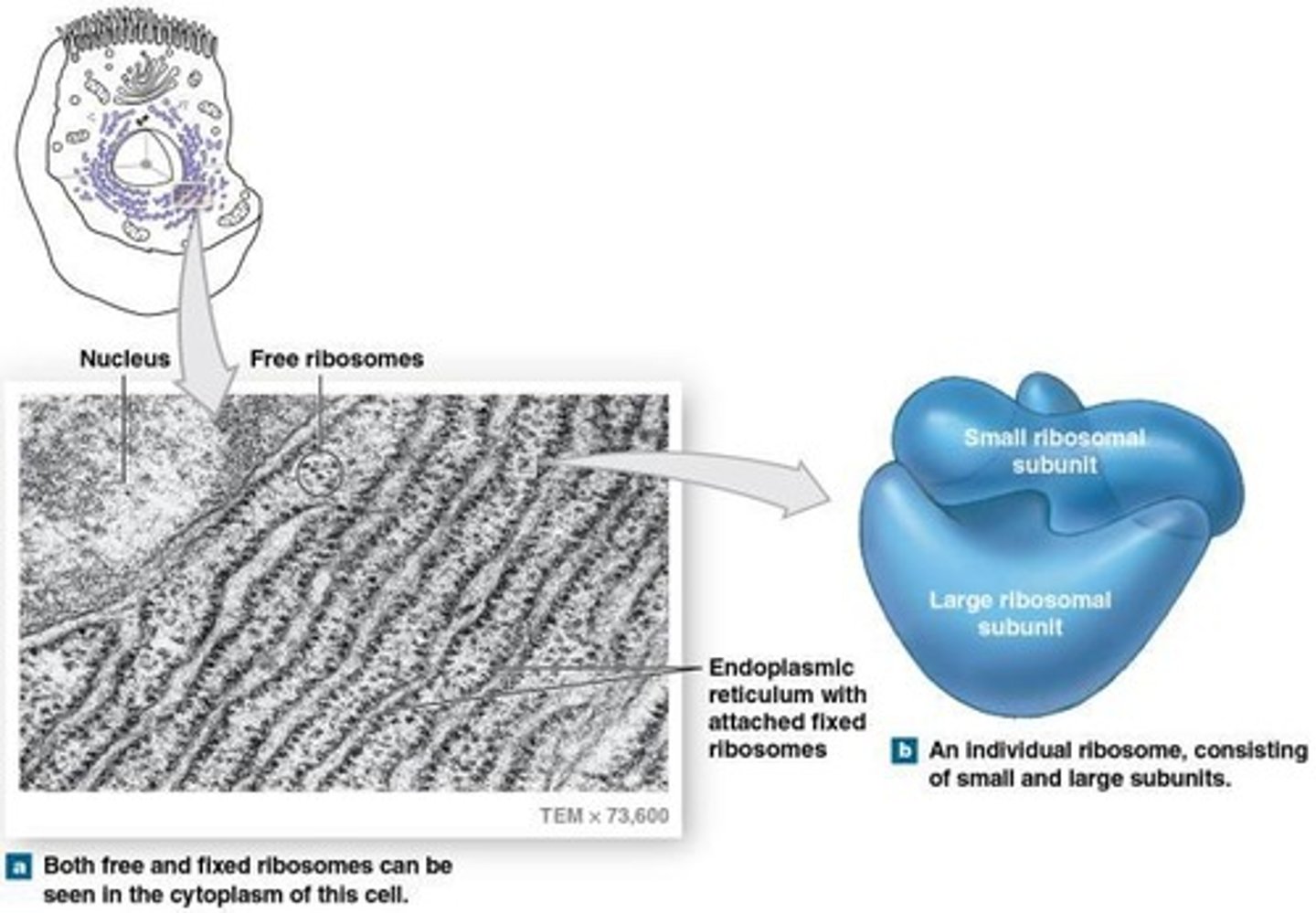
Endoplasmic reticulum
An organelle involved in the production of proteins and lipids.
Mitochondria
Double-layered membraned organelles that produce ATP, the primary energy currency of the cell.
Nucleus
The control center of the cell that contains chromosomes.
Chromatin
Loosely coiled DNA in non-dividing cells that forms a tangled network.
Sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome that are joined at the centromere.
Centromere
The region of a chromosome where sister chromatids are joined and spindle fibers attach during mitosis.
Kinetochores
The region of the centromere where spindle fibers attach during mitosis.
Golgi apparatus
An organelle that functions as the post office of the cell, modifying and packaging proteins.
Lysosome
An organelle that contains enzymes for waste processing and detoxification.
Cell junctions
Structures that connect cells to each other, including gap junctions and tight junctions.
Tight junctions
Cell junctions that prevent leakage of fluids between cells.
Desmosomes
Cell junctions that provide strong adhesion between cells.
Interphase
The phase of the cell cycle where the cell prepares for division.
Mitosis
The process of cell division that results in two identical daughter cells.
Cytokinesis
The division of the cytoplasm that occurs after mitosis.