Fine Motor, Cognitive, Language, Social-Emotional, Adaptive Development
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
somatosensory
vision
msk
regulation
cognition
social and culture
what are the factors contributing to fine motor skill development
precision, accuracy
for fine motor skills, _______ and ______ come from children coordinating visual and somatosensory info guiding hand and finger movements while maintaining stable posture
visual system
______ is the last to develop
rudimentary
at birth, there is ______ visual fixation with brief tracking ability
light
newborns’ vision adjusts to ______ and focus — they can see light and dark ranges
clearer, binocular vision, cross midline
3-6 month vision:
separate
6 month vision: fully developed visual control, eyes move ______ from head, color vision developing
judge distance well
1 year vision:
3-5 years
_____ vision: figure ground improves, enhanced fine motor skills
ALL PLANES
5 year vision: tracking in _______ and disassociate eye-head movements
6-7 years
_______ vision: figure ground stabilizes, perception improves
form constancy, ten
8-9 years vision: position in space, stabilization of ______, continued improvement in spatial relations until _____ y.o.
parent
5-8 months vision: child can recognize ______ across the room
palmar grasp reflex
0-3 months grasp:
palmar
4-5 month grasp:
radial digital
7-9 month grasp:
raking
7-8 month grasp:
inferior pincer
7-10 month grasp:
neat pincer (pad-to-pad)
9-10 month grasp:
tip (superior) pincer
10-12 month grasp:
refinement and varied power grasps
1-3 years grasp:
FALSE — wrist EXTENSION
T/F: at 9-10 months, wrist flexion becomes more prominent during grasping
ULNAR
When babies start grasping, they use the _____ side of their hand
ATNR
______ sets babies up for reaching by allowing them to look at objects with extended arms
ulnar, radial
Grasp progresses from ______ to _______….once crawling and creeping, babies start to dissociate hand pressure for even better grasp and support
hook or snap grip
8-12 months power grasp:
cylindrical
12 months power grasp:
spherical
18 months power grasp:
lateral pretension
toddlerhood power grasp:
go look at development of pencil grasp (slide 8/26)!!!!!
go look at development of pencil grasp (slide 8/26)!!!!!
radial cross palmar
palmar supinate
digital pronate (extended index)
brush
extended fingers
cross thumb
static tripod
four fingers
lateral tripod
dynamic tripod
pencil grasp progression: (if you find a way to remember this exact order, lmk!!)
hand + finger strength
cross midline
hand eye coordination
bilateral integration
manipulation
postural stability
key aspects of pencil grasp progression:
Expressive
________ language is the ability to speak and convey thoughts, needs, ideas
Receptive
_______ language is understanding what words are said to you
Speech
_______ includes articulation (fine mov’t of tongue/teeth/lips), voice (inflection, modulation), and fluency (coherency of word patterns)
cooing/gooing
alert to sounds
smiles/quiets when talked to
2-3 month speech/language milestones:
squeals/growls/raspberries
babbling
giggles/laughs
4-6 month speech/language milestones:
babbling
looks when name is called
gestures
7-9 months speech/language milestones:
babbling with more sounds
pointing/waving
says 1-2 words
10-12 month speech/language milestones:
shakes head yes/no
points understands/uses words for common objects
simple directions
1 or more body parts
13-18 months speech/language milestones:
50+ words
asks for help
puts 2+ words together
2-step directions
19-24 months speech/language milestones:
phrases
asks why/how
says name + age when asked
plurals/verbs/past tense
easier to understand
2-3 years (24-30 mo.) speech/language milestones:
Cognition
_______ is the ability to acquire and use information to meet task and environmental demands through experiences, sense, and thought
play is how skills are learned
nurturing, consistent
Children learn best with a ______ environment and secure attachment to a ______ caregiver
TRUE
T/F: we have to pair cognitive learning with motor learning to have the best outcomes
Sensorimotor, 0-2 yo.
what is Piaget’s 1st stage and age range
Preoperational, 2-7 yo.
what is Piaget’s 2nd stage and age range
Concrete Operational, 7-11 yo.
what is Piaget’s 3rd stage and age range
Formal Operational, 11+ yo.
what is Piaget’s 4th stage and age range
sequentially
Piaget’s theory of cognitive development: stages progress ______ and build on the prior stage
Scaffolding
______ allows children to get comfortable with playing before a new challenge is added/increased
challenge point
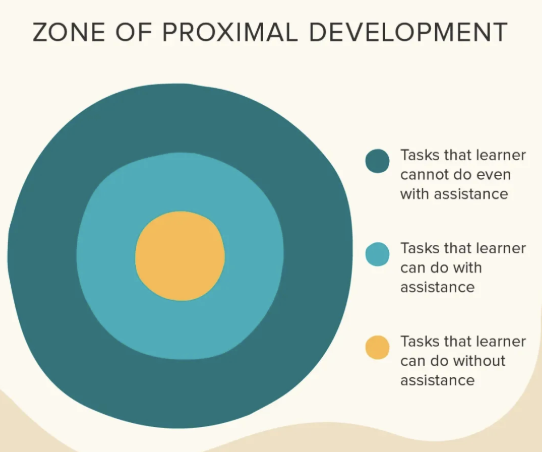
reasoning
Psychosocial development is tied to development of _______, success with the stages of Erikson’s psychosocial development prepares for learning in various environments
go look at Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development chart (slide 18/26) !!!!!
go look at Erikson’s Stages of Psychosocial Development chart (slide 18/26) !!!!!
emotional, regulation
the Attachment theory (Bowlby + Ainsworth) explains that attachment is important for _______ development and ______
secure, cogntiive
Children who develop _____ attachments to caregivers are in a better position to develop _____ skills
TRUE
T/F: Cognitive development begins through motor and sensory experiences and caregiver interactions via proprioception, tactile, and vestibular systems
follows caregiver’s face
1-2 mo. cognitive milestone:
follows object in circle
looks at toys and hands
reaches for faces
3 mo. cognitive milestones:
interacts with toys
object permanence — parent leaves room
6 mo. cognitive milestones:
search for hidden objects
peek-a-boo
9 mo. cognitive milestones:
points
first words
finds toys in containers
12 mo. cognitive milestones:
turns pages
uses items in correct manner
stacks 2 blocks
15 mo. cognitive milestones:
copies caregiver’s routines
18 mo. cognitive milestone:
plays with 2+ at same time
pretend play
2 yo. cognitive milestones:
cries to show feelings
1 mo. S-E milestone:
spontaneous smiling
4 mo. S-E milestone:
knows familiar people
6 mo. S-E milestone:
has preferences for people/toys
enjoys simple games
12 mo. S-E milestones:
imitates behaviors
initiates play
points to show things
18 mo. S-E milestones:
more independence
2 yo. S-E milestones:
more range of feelings
takes turns
copies others
3 yo. S-E milestones:
negotiates
prefers playing with others
likes and dislikes
4 yo. S-E milestones:
agrees to rules
wants to please
demanding and cooperative behaviors
5 yo. S-E milestones:
holds bottle with both hands
uses cup with help
plays with spoon
6-9 mo. Adaptive milestones:
holds cup and sips with help
finger feeding
spoon to mouth
takes off socks
helps with dressing (takes off before putting on)
12-15 mo. Adaptive milestones:
scoops food and feeds self
15-18 mo. Adaptive milestones:
drinks from cup w/out spills
wants to feed self
fork and spoon w/out spills
picks up toys
takes off shoe/socks/pants
2-3 yr. Adaptive milestones:
independent eating
help with fasteners
takes off/puts on clothes
understands safety
gets snacks from kitchen
3-5 yr. Adaptive milestones: