J 201 Midterm
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:23 PM on 11/28/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
1
New cards
media
mass communication regarded collectively
2
New cards
medium
point between any two things
3
New cards
society
something that holds us together; groups/communities despite the size
4
New cards
why we look at media and society
- observe how it shapes our lives
- respond to culture
- reflect on our role as media producers and consumers
- demand social justice
- form relationships
- collecting parts of history
- respond to culture
- reflect on our role as media producers and consumers
- demand social justice
- form relationships
- collecting parts of history
5
New cards
ideology
a set of ideas (often unconscious) that consists of a particular worldview
6
New cards
dominant ideology
broader set of values that we learn to see as shared and universal
7
New cards
hegemony
the dominance or leadership of one social group or nation over others through dominant ideologies
8
New cards
the banking method
Freire (1968) introduced the 'banking' concept of education whereby he equated teachers with bank clerks and saw them as 'depositing' information into students rather than drawing out knowledge from individual students or creating inquisitive beings with a thirst for knowledge.
9
New cards
interpellation
the constitutive process where individuals acknowledge and respond to ideologies, thereby recognizing themselves as subjects
10
New cards
incorporation
criticism and resistance are acknowledged, but nothing fundamentally changes
11
New cards
hypodermic needle/magic bullet
the period of time we receive/consume media (shannon-weaver's model of communication)
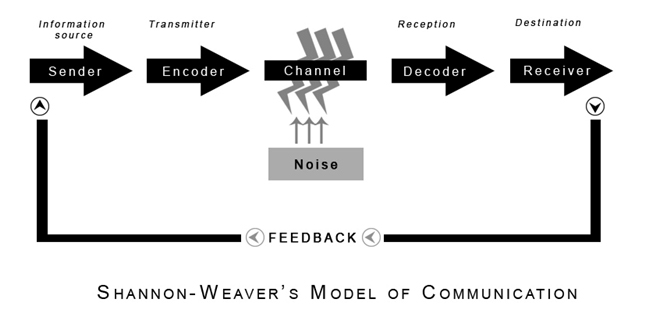
12
New cards
technology and skeptism
fear surrounding new technology; scholars focused on the role of media to persuade and recruit (aka propaganda)
13
New cards
payne fund studies
a series of studies conducted to determine the effects of movies on the behavior of children and adolescents
- the sleeper effect: seeing something but don't process it until later and forget where it came from
- children are susceptible to content and can get obsess with it
- love, sex, and crime were the main categories that appealed to audience (still are)
- the sleeper effect: seeing something but don't process it until later and forget where it came from
- children are susceptible to content and can get obsess with it
- love, sex, and crime were the main categories that appealed to audience (still are)
14
New cards
parasocial relationships
a relationship that a person imagines having with someone they see from the media (eg movie character)
15
New cards
uses and gratification theory
media consumers are passive consumers of mass communications; rather, they play an active role in media consumption
16
New cards
uncertainty reduction theory
there is uncertainty with new things/people and it hades over time with interactions. a good first impression can reduce uncertainty faster
17
New cards
encoding/decoding
a communication model that offers a theoretical approach to how messages in media, particularly mass media, are produced, disseminated, and understood
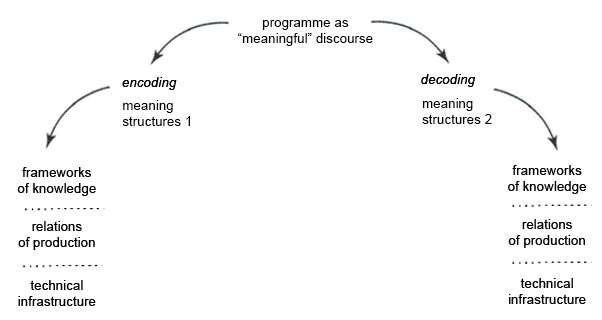
18
New cards
dominant reading
reader accepts and reproduces the intended (encoded) meaning
19
New cards
negotiated reading
reader broadly accepts message of the text but adjusts certain aspects to reflect their own position and experience
20
New cards
oppositional reading
reader understands dominant message and rejects it
21
New cards
stereotyping
reducing people to a few, simple, essential characteristics that are represented as fixed by nature; oversimplifying
22
New cards
representation
the social process of making and exchanging meaning
23
New cards
semiotics
studies how meaning is created; uses parts to understand more about the whole (signified + signifier -> sign)

24
New cards
connotative vs denotative
connotative is the flexible relationships between the signified and signifier while denotative is the literal relationship between the signified and signifier
25
New cards
difference and othering
difference is meaning-making. othering can rely on binaries and power, where one side is preferred; othering is also when everyone else is considered the "other" while one dominant group is perceived as "normal"
26
New cards
naturalization
presenting difference (amongst people and groups) as rooted in nature
27
New cards
marshall mcluhan - medium is the message
for the “message” of any medium or technology is the change of scale or pace or pattern that it introduces into human affairs
28
New cards
global village
The world viewed as a community in which distance and isolation have dramatically reduced by electronic media
29
New cards
trans-coding
taking an existing meaning and re-appropriating it to create new meanings
30
New cards
reverse stereotypes
revalue negative stereotypes and reverse expectations
31
New cards
positive images
substuting positive images for negative ones
32
New cards
critique from within
Make stereotypes work against themselves
33
New cards
mediatization
the process by which media becomes more a part of how social, political and cultural processes operate
34
New cards
moral panics
amplified fears (eg. AI, abortion rights)
35
New cards
celebratory media events
monopolistic, replanned; contests, conquests, and coronations; aims for reconciliation, national collectivism (eg. olympics, red carpet events)
36
New cards
conflicted media events
sites of antagonism (eg. andrew tate, johnny vs amber court)
37
New cards
media disaster
unexpected events (eg. 9/11, school shootings)
38
New cards
media scandals
a breach in moral conduct and authority; often notable people but regs with particularly notable acts too (eg. adam levine, kanye west)
39
New cards
mediatized public crisis
unfold over a period of time; social drama; big net, more story than event
40
New cards
spectacle
an event of scene regarded in terms of its visual impact
41
New cards
identity politics
Solidarity, political mobilization around identity; conflicts around different identity groups
42
New cards
identity groups
gender, disability, sexuality, nationality, race, ethnicity, social class
43
New cards
intersectionality
how different identities interact with each other when someone identifies with multiple minority communities; interlocking systems of oppression
44
New cards
structural intersectionality
how the experiences of people within a particular identity category are qualitatively different from each other depending on their other intersecting identities; privilege of certain identities
45
New cards
political intersectionality
how inequalities and their intersections are relevant to policies and political strategies of groups of people who occupy multiple subordinate identities; undermining inequalities faced by certain groups
46
New cards
representational intersectionality
the depiction of individuals and groups in dominant culture and society through media, texts, language, and images; how both the dominant and marginalized groups are represented in society
47
New cards
critical race theory
Core idea is that race is a social construct and that racism is not merey a product of individual bias or prejudice, but also something embedded in legal systems and policies
48
New cards
trans representation
Trans people are never really represented in a neutral way. A lot of them are seen as crazy or unreal rather than human. Media identifies them as sex workers
49
New cards
Symbolic Annihilation
proposed as a concept by Gerbner and Gross (1976) to describe the absence of representation, or underrepresentation, of a group of people in the media
50
New cards
Disidentification
Involves looking for specific aspects of a character and extracting that in order to see yourself reflect in the media. Often used by marginalized populations because they are rarely present. Allows people to find “identities in difference”
51
New cards
The first wave Feminism (1848-1920)
Focused on the right to vote, so it had an end date. Margaret Sanger start birth control clinic in 1917 become basis of Planned Parenthood
52
New cards
Second wave feminism (1963-1990s)
Right to birth control for married and unmarried women.1973 Roe V. Wade - safe abortion access. Education equality under Title IX in 1973. Women strove to get bank accounts and credit cards under their own names.
53
New cards
Third wave feminism (mid 1990s-)
An embrace of girliness, saying its a power. Recognizing dangers and pleasure of patriarchy. Lacks the type of policy chang of the prior waves.
54
New cards
cultural studies
Theories and practices from a range of humanities and social science disciplines. Investigate the ways in which culture produce and are produced
55
New cards
Medicalization
which medical authority annexes bodies, actions, attitudes, and behaviors ranging from the everyday to the “deviant” as medical conditions
56
New cards
Pathologization
negagtive medicalization, making it into a problem
57
New cards
Deficit model
persons with disabilities are viewed as having a problem that needs “fixing” through medicine, rehabilitation, or education
58
New cards
Supercrip
a disabled person, particularly an athlete, who achieves exceptional success in spite of the challenges they face, serving as an inspiration