Aquatic Biomes: Freshwater
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
What are the factors affecting aquatic ecosystems?
water depth
Temperature
Current
Nutrient availability
pH, Salinity and dissolved oxygen
What are the components of water depth?
photic zone
Aphotic zone
Benthic zone
the sunlit region near the surface in which photosynthesis can occur
Photosynthetic organisms live in this zone
Photic zone
at depths greater than 200 m where light cannot penetrate
Most organisms that live here are larger animals like sharks squids, etc
Aphotic zone
the bottom zone like the ocean floor or bottom of a lake
Benthos are organisms living in this zone
Benthic zone
Water depth (ocean) zones
Euphotic zone
Disphotic zone
Aphotic zone
the sunlit zone where algae and phytoplankton are abundant
Most of the life in the ocean is found in this layer due to the abundance of food source
Euphotic zone
barely-lit ocean layer (twilight zone)
This receives faint and filtered sunlight during daytime which is not enough for photosynthesis to take place
Food is not abundant
Disphotic zone
the deepest layer also known as midnight zone where temperature is low and pressure is high
Bioluminescent organisms are thriving in this layer
Aphotic zone
Temperature in aquatic habitats also often varies with?
temperature in aquatic habitats also often varies with depth
The deepest parts of lakes and oceans are often colder than surface waters
can dramatically affect water temperature because they can carry water that is significantly warmer or cooler than would be typical for any given latitude, depth, or distance from shore
Currents
Organisms need certain substances to live such as?
such as oxygen, nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus
The type of availability of these dissolved substances vary within and between bodies of water, greatly affecting the types of organisms that can survive there
Why is pH an issue with corals and coral reefs?
pH is now an issue with corals and coral reefs as lower pH decreases coral’s ability to form structure
Freshwater intrusion in clam beds can stress the organisms leading to disease and mortality
Low DO influenced by eutrophication and low flushing rates have caused massive fish kills
Coral reefs could be in an irreversible decline by 2040 due to?
Ocean acidification
What are the aquatic ecosystems
freshwater
Marine
What are the components of freshwater
ice sheets
Ice caps
Glaciers
Bogs
Ponds
Lakes
Rivers
Streams
Groundwater (aquifer and underground streams)
What are the of marine ecosystems
coral reefs
Estuaries
Open ocean
Mangrove
Swamps
Seagrass meadows
What are the types of freshwater habitat
lentic habitat
lotic habitat
calm freshwater habitat or standing water
Lentic habitat
Washed or the running water
Lotic habitat
large and open
Deeper with photic and aphotic zones
Sunlight doesn’t reach the bottom, temperature is not uniform
Freshwater ecosystems: Lakes
small and enclosed
Shallow, photic zone only
Sunlight reaches bottom temperature is uniform
Freshwater ecosystems: pond
The surface layer of water that is constantly mixed by wind and waves and is warmed by the sun, from late spring to late fall
Epilimnion
The middle layer characterized by a steep gradient in temperature and demarcated by the regions above (epilimnion) and below (hypolimnion)
Metalimnion
What is the function of Metalimnion?
The Metalimnion is the barrier that prevents mixing and heat exchange between the epilimnion and hypolimnion
The deepest layer of uniformly cold water that does not mix with the upper layers and has low circulation. The colder water within the _____ is at its maximum density at a temperature of 39.2 F (4C)
Hypolimnion
Is a seasonal phenomenon that occurs from late spring to late fall in temperate regions.
Thermal stratification
in the summer, the upper layer of water in the Great Lakes (epilimnion) is warmed significantly by the sun. Cooler water separates, forming two additional layers (Metalimnion and hypolimnion) that are heavier or denser. During the winter, there is no stratification as the lake cools, and the overall temperature of the lake is more uniform
What are the lake tropic classifications?
oligotrophic
mesotrophic
eutrophic
are generally deep and clear with little aquatic plant growth. These lakes maintain sufficient dissolved oxygen in the cool, deep bottom waters during late summer to support cold water fish such as trout and whitefish
Oligotrophic lakes
Lakes that fall between the two extremes of oligotrophic and eutrophication are called?
Mesotrophic lakes
Lakes have poor clarity, and support abundant aquatic plant growth
the cool bottom waters usually contain little or no dissolved oxygen
these lakes can only support warm water fish such as bass and pike
Eutrophic lakes
What are characteristics of Oligotrophic lake?
low nutrient levels
Good light penetration
High dissolved oxygen
Deep waters
Low algal growth
Small mouth bass, lake trout, pike, sturgeon, whitefish
What are the characteristics of eutrophication lake
high nutrient levels
Poor light penetration
Low dissolved oxygen
Shallow waters
High algal growth
Carp, bullhead, catfish
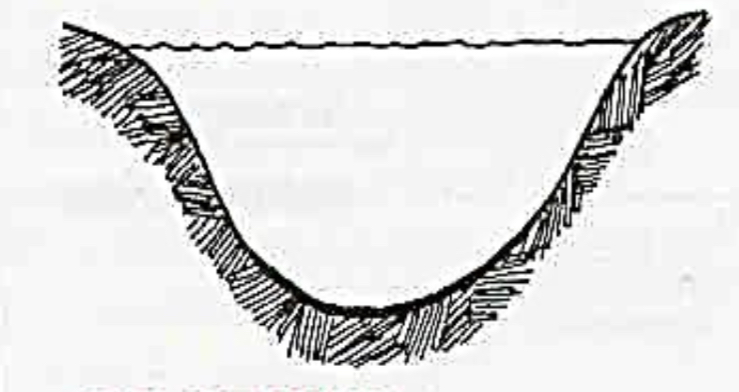
Oligotrophic
clear water, low productivity
Very desirable fishery of large game fish
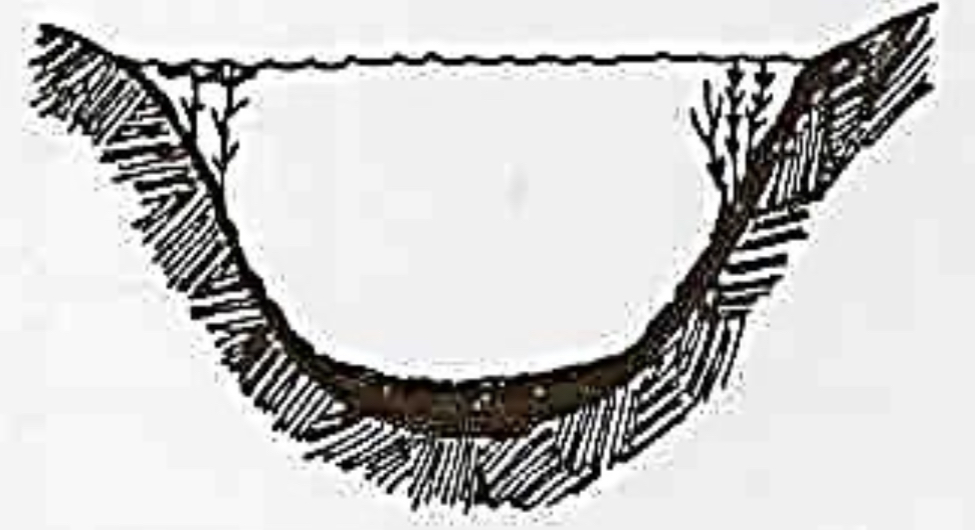
Mesotrophic
increased production
Accumulated organic matter
Occasional algal bloom
Good fishery
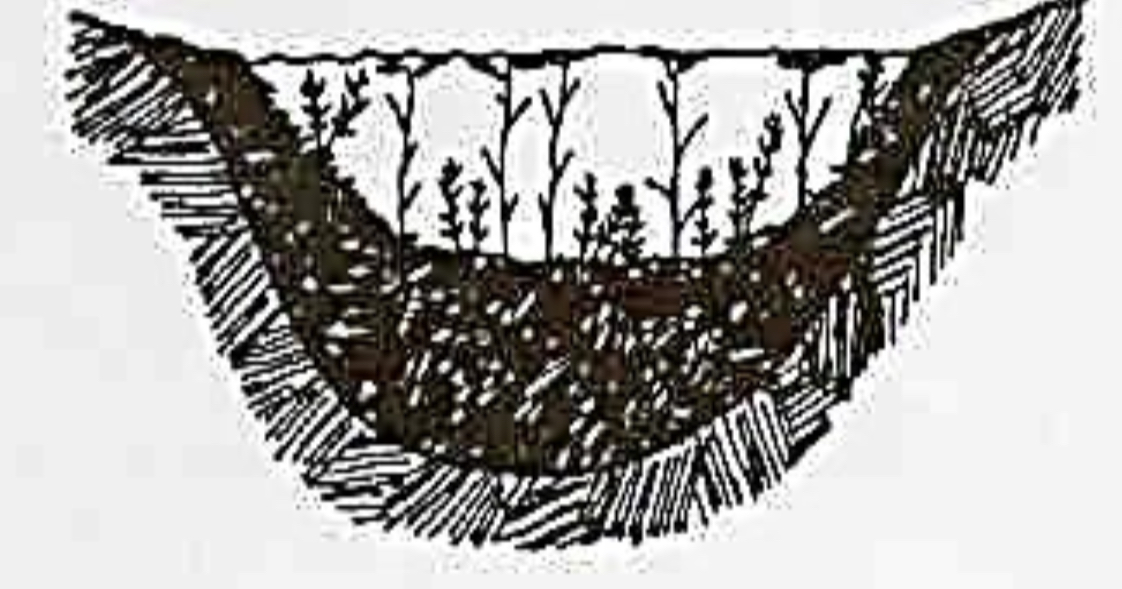
Eutrophic
very productive
May experience oxygen depletion
Rough fish common
Small channels of freshwater that contains flowing water. they can be both natural and artificial
Streams
flow all year long while seasonal streams are only seen at certain times of year, usually in wet season or as a result of snow or ice melting
Perennial streams
flow without stopping until they reach an endpoint or another body of water
continuous streams
on the other hand, may have breaks or different reaches depending on seasonality, barriers and other factors
Interrupted steams
a ribbon-like body of water that flows downhill due to the force of gravity. This is a larger stream
Rivers

mountain headwater streams flow swiftly down steep slopes and cut a deep V-shaped valley. Rapids and waterfalls are common
Zone 1: Headwaters
low elevation streams merge and flow down gentler slopes. The valley broadens and the river begins to meander
Zone 2: Transfer zone
at even lower elevation a river wanders and meanders slowly across a broad, nearly flat valley
At its mouth it may divide into many separate channels as it flows across a delta built up of riverborne sediment and into the sea
Zone 3: Depositional Zone
an area of land that is covered by water or saturated with water. It is entirely covered by water at least part of the year. This is a transition zone
wetlands
what are the three major kinds of wetlands?
swamps, marshes and bogs
often form on flat land around lakes or streams, where the water table is high and runoff is slow
swamps
are dominated by grasses and aquatic plants
often develop around lakes and streams
Marshes
swamps and marshes are generally found where?
swamps and marshes are generally found in warm climates
develop in areas where the water table, or the upper surface of underground water is high
They often begin in glacial depression called kettle lakes, which are deeper than prairie potholes. this commonly is found in cold or even artic areas in north america, europe and asia
bogs
this is an area where freshwater river or streams meet in the ocean
the salty ocean mixes with a freshwater river resulting in BRACKISH WATER
are among the most productive ecosystems in the world. Many animals rely on for food, places to breed, and migration stopovers
Estuaries

what are the four major types of estuaries?
The four major types of estuaries classified by their geology are:
drowned river valley
bar-built
tectonic
fjords