Animal Nutrition Exam 1 Study Guide
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
Nutrition
Numerous chemical reactions and physiological processes which transform food into body tissues and activities
Nutrient
Chemicals in the diet
element or compound (simple as. copper)
Supports normal
reproduction
growth
lactation
Essential Nutrient
Cannot be made
not in sufficient amount
needed in diet
Nonessential Nutrient
vitamin C essential in dogs and cats but not in all an animals
can be made
not needed in diet
Fistulation
Carnivores
Herbivores
Pre-gastric fermentors
Hindgut Fermentors
Omnivores
Crop
Proventriculus
Ventriculus
Papillae
Digestion
Prehension
Mastication
Deglutition
Absorption
Villi
Microvilli
Passive Diffution
Facilitated Diffusion
Active Transport
Phagocytosis
Metabolism
Catabolism
Anabolism
Gastrin
GIP
CCK
Secretin
Somatostain
Pancreatic Polypeptide
VIP
Ghrelin
Leptin
Esophageal groove
Regurgitation
Activation Energy
Catalyst
Zymogen
Cofactors
Coenzymes
Inhibitors
Allosteric Modifers
Importance of Nutrition
Involves:
Ingestion, digestion, and absorption of nutrients
Transport of nutrients to body cells
Removal of waste
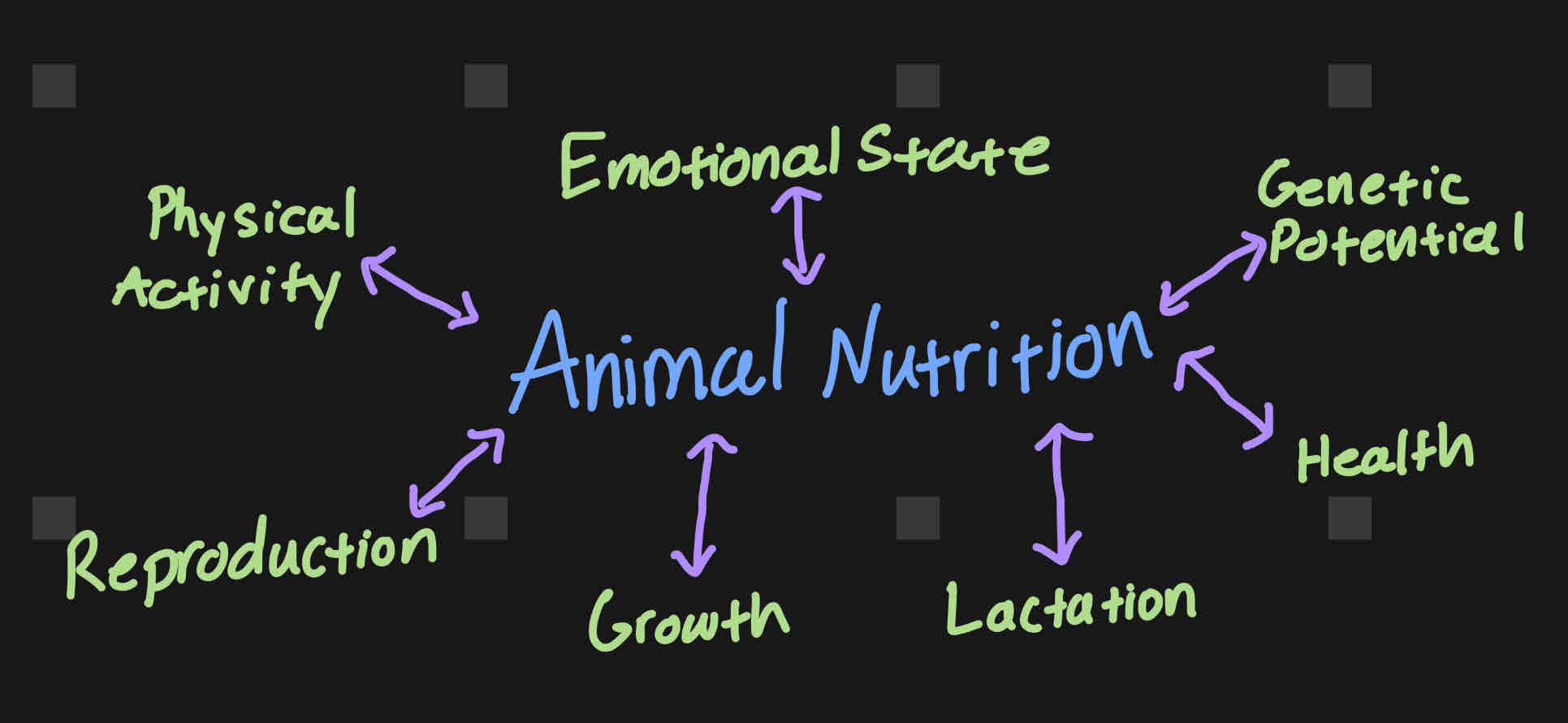
Important of Nutrition to Producers
nutrition is involved in every aspect of life
nutrition costs over ½ of all costs on an animal
Relationship between chemical composition of plants and animals
Essential vs. Nonessential Nutrients
Classes of nutrients
Water
most limiting
the most essential nutrient of all
animals can learn to starve
Carbohydrates
NRG
Fats
NRG
Proteins
can provide some NRG
relatively expensive
Minerals
not going to provide NRG
Vitamins
not going to provide NRG
Functions of Nutrients
Water
Carbohydrates
Fats
Proteins
Minerals
Vitamins
Anatomical differences b/w species (compare and contrast)
Importance of structures within the ruminant stomach
Regions of the gastric stomach (importance of each)
4 methods of digestion
Mechanical
Physical breakdown of food
Chemical
Chemical breakdown of food
Enzymatic
Catalyze the breakdown of food
Microbial
Microorganisms breakdown food
Steps of digestion
Regulation of digestion (hormones, etc.)
Saliva (where from, composition, functions)
stomach (functions, regions, secretions)
Parts of the small intestine
Microanatomy of the intestine (importance of each)
How to increase. surface area for absorption
Describe the 4 types of absorption
Describe the 3 processes involved in metabolism
compare/contrast young and adult ruminants
Describe ruminant stomach and its function
Describe microbes found int he rumen and relationship with the animal
Describe the advantages and disadvantages of pre-gastric fermentation
Differences between young and adult ruminants
Different compartments of the ruminant stomach and their functions
Microbes found in the rumen and the symbiotic relationship they have with the animal
Advantages and disadvantages of fermentation
Differences/similarities between post gastric fermentation of a horse vs. a cow.
Water’s importance compared to other nutrients
Functions of water in the body
Influences of water requirements
Source of Water
Water loss and regulation
Functions of enzymes and coenzymes
Enzyme specificity for substrates
Factors that affect enzyme activity