MARKETING Exam I (Chp. 3)
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ethics and Social Responsibility
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Six modes of Social Control = Societal Order
ethics
laws
formal groups
informal groups
self-regulation
media
An informed and engaged society can help mold individual and corporate behavior.
Ethics
Moral principles that govern a group or individual's conduct, acting as a guide for "right" action.
Laws
Codified ethical rules and guidelines that create legal requirements for business behavior.
Formal & Informal Groups
Organizations (like the American Marketing Association) and groups that establish codes of conduct.
Self Regulation
Voluntary acceptance of standards by non-governmental entities to curb, for example, deceptive advertising.
The Media
Plays a crucial role in informing the public about both positive and negative actions of companies.
Active Civil Society
Engaged citizens who influence marketing practices.
social control
any means used to maintain behavioral norms and regulate conflict
behavioral norms
standards of proper or acceptable behavior. Several modes of social control are important to marketing
Concept of Ethical Behavior
Standards that are legal may not always be ethical
An ethics violation offends a person’s sense of justice or fairness
Constitutes the unwritten rules developed to guide interactions
Many ethical questions arise from balancing a business’s need to produce profit for shareholders against its desire to operate honestly and with concern for environmental and social issues.
Ethical Theories
Deontological
Utilitarian ethical
Casuist ethical
Moral Relativism
Virtue
Deontological theory
people should adhere to their obligations and duties when analyzing an ethical dilemma
Utilitarian theory
founded on the ability to predict the consequences of an action
Casuist ethical theory
compares a current ethical dilemma with examples of similar ethical dilemmas and their outcomes
apply past cases to current (downside: not always a similarity)
Moral Relativism
time-and-place ethics; the belief that ethical truths depend on the individuals and groups holding them
Virtue
a character trait valued as being good
The ethical conduct of businesspeople is shaped by what societal elements?
family
education
religious institutions
3 Approaches of Ethical Decision Making
examine the consequences of decisions
relies on rules and laws to guide decision making
based on theory of moral development: places indiv./groups in 1/3 developmental stages of Morality
Preconventional
Conventional
Postconventional
Business Influences on decision making?
extent of ethical problems within the organization
top managment’s actions on ethics
probability of a harmful outcome
length of time between the decision and onset of consequences
number of people affected
social consensus
Social Consensus (decision making influence)
a psychological phenomenon where individuals look to the behaviors and actions of others to determine their own, particularly in uncertain situations. showing that a majority of similar people already approve of or use a product.
conformity
“herd mentality”
validation
reduced uncertainty
Code of Ethics
guideline to help marketing managers and other employees make better decisions. (Cultural differences like practice of bribery or gift giving.)
identify acceptable business practices
be an effective internal control on behavior
help avoid confusion when determining ethicality of decisions
facilitate discussion between right vs. wrong
Morals
the rules people develop as a result of cultural values and norms
Foreign Corrupt Practices (FCPA)
a law that prohibits U.S. corporations from making illegal payments to public officials of foreign governments to obtain business rights or to enhance their business dealings in those countries
Corporate Social Responsibility
a business’s concern for society’s welfare
Stakeholder (ethical) Theory
social responsibility is paying attention to the interest of every affected stakeholder in every aspect of a firm’s operation
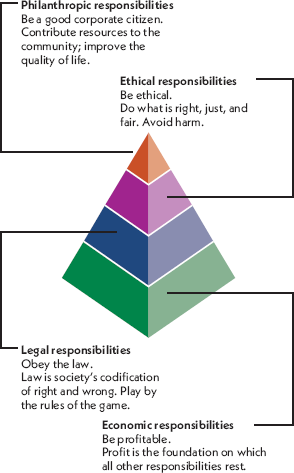
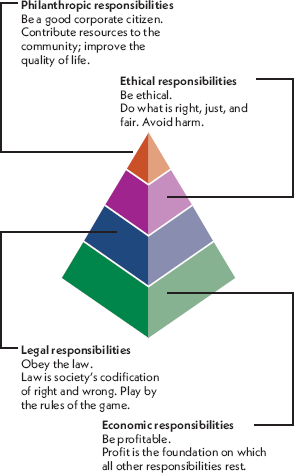
Pyramid of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
a model that suggests CSR is composed of {economic, legal, ethical, and philanthropic responsibilities} and that a firm’s economic performance supports the entire structure
Arguments for Social Responsibility
Arguments against Social Responsibility
Sustainability
the idea that socially responsible companies will outperform their peers by focusing on the world’s social problems and viewing them as opportunities to build profits and help the world at the same time
environmental
economic
financial
social
Green Marketing (branch of social responsibility)
the development and marketing of products designed to minimize negative effects on the physical environment or to improve the environment.
often bottom line of a business
Greenwashing (negative)
Adding a minimal number of green product attributes to promote a product as green
Cause-Related Marketing
the cooperative marketing efforts between a for-profit firm and a nonprofit organization.
popular; can enhance the reputation of the corporation
make additional profit for the company
consumers sometimes come to believe that every company is tied to a cause = consumer cause fatigue.
(different from philanthropy, which is a specific, tax-deductible donation)
The for-profit firm hopes to generate extra sales, and the nonprofit firm, in turn, hopes to receive money, goods, and/or services.
Company Stakeholders
B Corps
for-profit companies certified by the non-profit B Lab for meeting high, verified standards of social and environmental performance, transparency, and accountability.
To become a B Corp Certified company, a firm must pass a 200-point assessment.