Physico-Chemical properties and Drug Action
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Functional groups that increase the polarity and dissolution of drugs:
* Very polar groups; each group increases solubility of ____
carbons in a given molecule. This includes:
1. _____ group:
a. _______ (if linked to aliphatic chain)
b. ______(if linked to aromatic ring system)
_____
3. All other functional groups including carboxylic acid, amides,
imides, CN, NO2 , sulfonamide, are weakly polar that can
solubilize only 2-3 carbons.
5-6, Hydroxyl (Alcoholic, Phenolic), primary and secondary amines
Functional groups that increase lipophilicity of drugs:
1. ____ (the bigger the alkyl, the higher the lipophilicity)
2. _____ group
3. _____ groups (I>Br>Cl>F)
4. _____ functions (the more carbons in the group, the more lipophilic the drug will be)
alkyl groups, phenyl, halogen (I> Br, Cl, F), ester
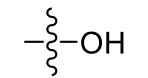
Hydroxyl: very polar, increase solubility of 5-6 carbons
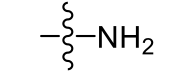
Amino (very polar)
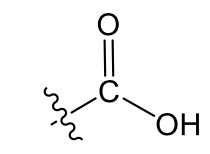
Carboxylic acid: weakly polar, increase solubility of 2-3 carbons, and acidic
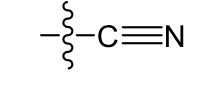
Cyano: weakly polar, increase solubility of 2-3 carbons
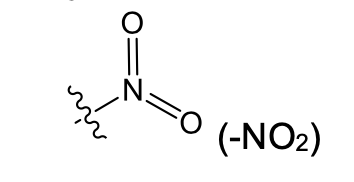
Nitro (weakly polar)
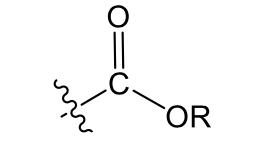
Ester (more carbons= more lipophilic=better absorbed)
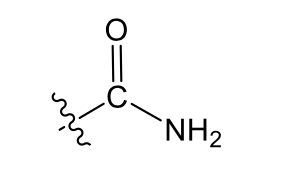
name polarity
Amide (weakly polar)
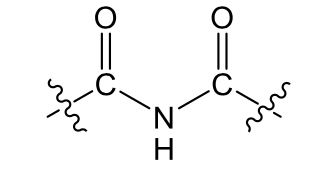
name, polarity
Imide (weakly polar)
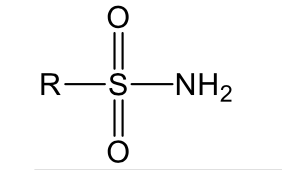
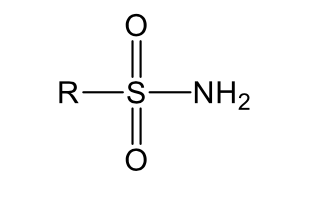
Sulfonamide weakly polar, increase solubility of 2-3 carbons
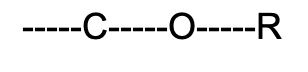
Ether (weakly polar)
Alkyl groups: very lipophilic (more carbons = more lipophilicity= better absorption)

Methyl
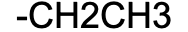
Ethyl
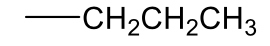
n-propyl
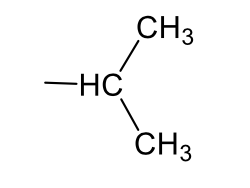
iso-propyl
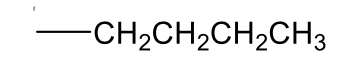
n-butyl
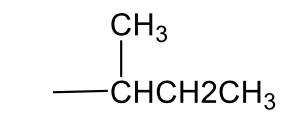
iso-butyl, 1° butyl
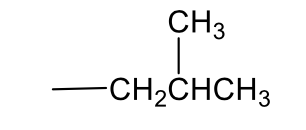
2°-butyl
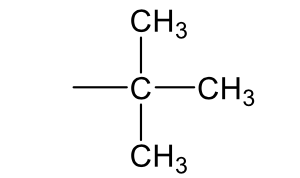
3°-butyl, t-butyl
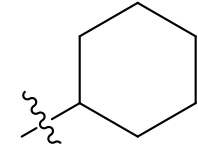
Cyclohexyl & other cyclic alkyls: very lipophilic, highly absorbed
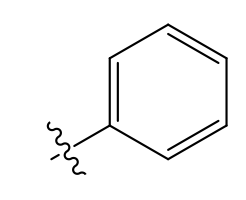
Phenyl (very lipophilic)
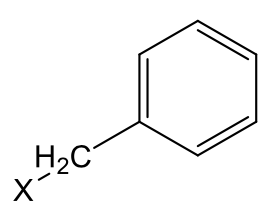
Benzyl (very lipophilic) (x=ONS)
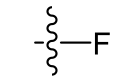
Fluoro (very lipophilic)
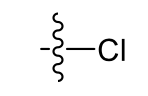
Chloro (very lipophlic)
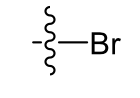
Bromo (lipophilic)
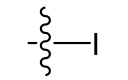
Iodo (lipophilic)
Acidic Functional groups: are capable to ionize in the body fluids
Carboxylic, Imides, Sulfonamides, Phenolic
Basic Functional Group
Aliphatic Amines (pkb 3-5), Pyridine type nitrogen (pkb 7-9), Anilino type nitrogen (pkb 7-9)
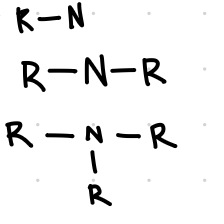
name (acidic, basic, neutral)
Aliphatic Amines (basic)
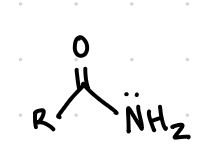
name, a b n
Amides (basic)
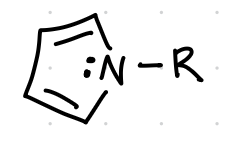
name, acid basic neutral
Pyrrole (basic)
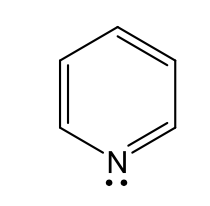
name, acid basic neutral
Pyridine type nitrogen (basic)
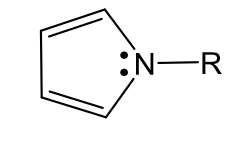
Neutral Nitrogen atoms
cyano, amides, Pyrrole-like nitrogen, Quaternary Ammonium nitrogen
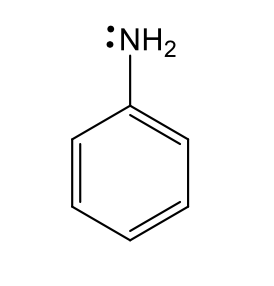
anilino type nitrogen (weakly basic)
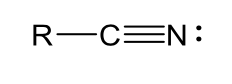
cyano (neutral)
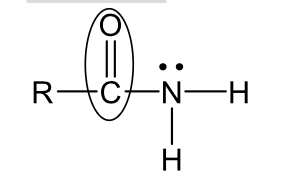
amides (neutral)
Recall Huckle’s equation to determine aromaticity: 4n+2=π
pyrrole like nitrogen (neutral)
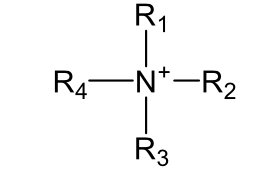
Quaternary Ammonium nitrogen (neutral)
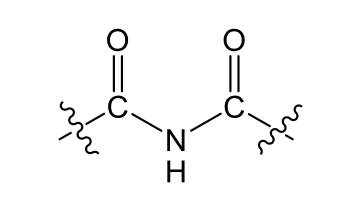
D. Nitrogen atoms capable of losing protons (acidic functional groups with nitrogen atoms):
_____: two carbonyl groups around the nitrogen strongly
withdraw electrons from the nitrogen and the nitrogen in turn
withdraw electron from the hydrogen leading to acidic property.
Imides
D. Nitrogen atoms capable of losing protons (acidic functional
groups with nitrogen atoms):
______: the sulfone group next to the nitrogen strongly
withdraw electrons from the nitrogen and the nitrogen in turn withdraw electron from the hydrogen leading to acidic property.
Sulfonamides
The term _____ refers to the replacement of an atom or functional group with certain number of electrons in the outer most shell with another atom or group with the same number of electrons in the outermost shell.
bioisosteres
The major site in our system that conducts metabolism is the ___, however some metabolic reactions occur also in different organs and tissues such as plasma, nerve endings, and lungs.
liver
metabolism
Phase I: makes drug polar by creating a single polar group
Phase II: conjugates drugs to enhance water solubility.
A. Phase-I microsomal reactions: Three types:
_____: CYP450 inserts an “O” between aliphatic or aromatic C-H bonds. If the compound is aromatic, the para position is preferred for oxidation. If it is an aliphatic compound, the last (ω) or second to last carbon (ω-1) is preferred.
Hydroxylation
A. Phase-I microsomal reactions: Three types:
______: removal of an alkyl group form a heteroatom on the drug molecule. If the heteroatom is oxygen, we call O-de-alkylation, Nitrogen; we call it N-de-alkylation, Sulfur, we call it S-de-alkylation. The alkyl groups that are fast to remove are the small groups such as methyl or ethyl. Once the alkyl group becomes bigger than 4 carbons, it unlikely to be removed by de-alkylation. The name of the alkyl group may be added to the de-alkylation reactions so we say O-demethylation, of N-de-ethylation, etc.
De-alkylation metabolic reactions
A. Phase-I microsomal reactions: Three types:
____
Oxidative deamination (remove NH2 group from secondary carbon → ketone and ammonia)
B. Phase I Non-microsomal reactions
1. _____ removes a primary amino group connected to primary carbon.
Monoamine oxidase (MAO) (primary amines → aldehyde and ammonia)
B. Phase I Non-microsomal reactions
2. _____ . are the most abundant enzymes in our system and exist in multiple areas throughout the body fluids in all organs including the GIT, Plasma, liver, lungs, CNS.
• This is the fastest metabolic reaction that occurs in the
biological system, it occurs everywhere in the body including
GIT,Liver, Plasma.
Esterases (hydrolyze esters) (ester → carboxylic acid and alcohol or phenol)
B. Phase I Non-microsomal reactions
are localized mainly in the enzyme is localized mainly in the he liver and very little, if any, in the GIT or plasma.
• This reaction is slower than ester hydrolysis and occurs mostly in the liver and to less extent in plasma.
Amidases (hydrolyze amides) (amide → carboxylic acid and primary or secondary amine)
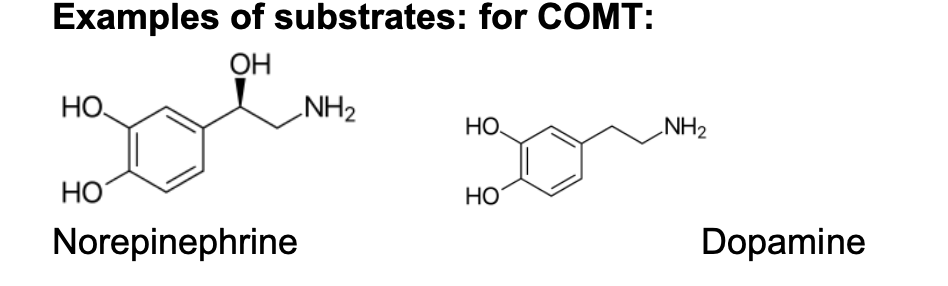
3. :
The enzyme is localized mostly at the adrenergic nerve endings, and to much less extend in the liver cells cytosol.
COMT (catechol-O-methyl transferase) (converts catechol into 3-methoxy derivative as a deactivation mechanism of catechol-amines)
The water soluble molecules include:
Glucuronic acid (primarily), Sulfates, Glycine, Glutathione
The most commonly water soluble molecule involved in phase II metabolism is _____ (oxidized glucose molecule at C-6 into carboxylic group).
Glucouronic acid
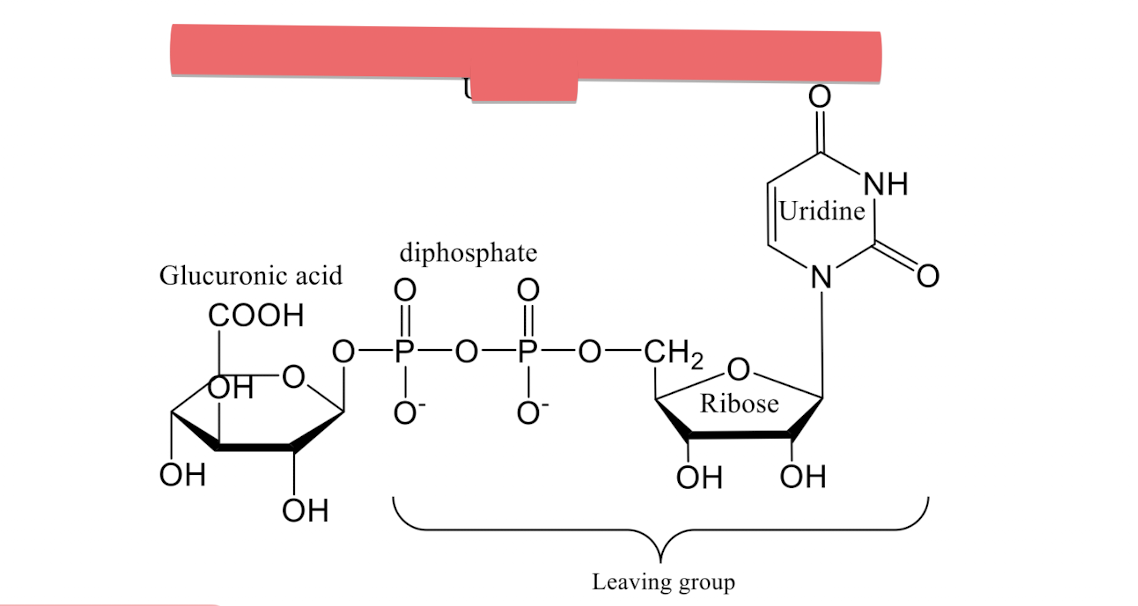
Uridine diphosphate glucuronic acid (UDPGA)
Drug-Drug interactions related to ADME
C. Enzyme inhibitors and activator drugs
Another potential source of drug-drug-interactions is through the
activation/deactivation of ____
cyp450.
Enzyme inducers activate/speed up an enzyme, results in faster metabolism of drugs that are metabolized by CYP450.
As a result, a drug may be metabolized more rapidly to metabolites that are more potent, more toxic, or less active than the parent drug.
Phenobarbital, carbamazepine (Tegretol)
Enzyme inhibitors deactivate/slow an enzyme, resulting in slower metabolism of drugs that metabolized by CYP450.
This will cause the drug to stay in the system longer than their normal duration of action.
Tagamet (cimetidine), Valproic acid, Erythromycin, Grape fruits