Nuclear Chemistry
1/28
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
define radioactivity
the spontaneous emission of radiation
define radiation
the emission of electromagnetic waves or subatomic particles (what is emitted during radioactive decay)define
define radioisotope
the nuclei of unstable isotopes
alpha particle
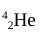
beta particle
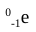
gamma ray
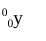
What does the stability of a nucleus depend on?
the nucleus has to be balanced (right amount of protons and neutrons)
How does an unstable nucleus release energy?
it emits radiation; radioactive decay occurs
penetrating power of an alpha particle
low; can be stopped by a sheet of paper
penetrating power of a beta particle
medium; can be stopped by a block of wood
penetrating power of a gamma ray
high; can be stopped by several meters of concrete

What part of the atom undergoes change during radioactive decay?
the nucleus undergoes change
define band of stability
the region that the stable nuclei are in
define positron
a particle with the mass of an electron but the charge of a proton
define half-life
time required for ½ of the nucleus of an isotope to decay
define transmutation
the process by which an element changes into another element
define transuranium elements
they are the elements on the periodic table above # 92 (uranium); all of them undergo transmutation
define electron capture
when an electron is absorbed into the nucleus
What is distinct about elements with an atomic number below 20?
the ratio of protons to neutrons is approximately 1 to 1
Above atomic number 20, stable nuclei must have more…
more neutrons than protons
What type of decay occurs if the nucleus contains too many neutrons?
Neutron decay
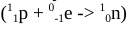
What is another name for “electron capture”?
inverse beta emission
Nuclei with atomic #s greater than what are radioactive?
greater than 92
How are half-lives used to calculate the age of a formerly living organism?
archaeologists can measure the amount of C-14 that an object contains (measuring the ratio of C-14 to other C isotopes w/half-lives)
half-life formula
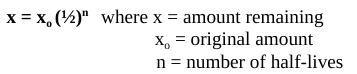
define nuclear fission
the splitting of a nucleus into smaller fragments
define nuclear fusion
when nuclei combine to form a nucleus of greater mass
medical uses of nuclear radiation
diagnostics, cancer treatment, food safety
How does a nuclear power plant work?
energy from nuclear fission leads to electricity being generated