Transcription regulation
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Transcription initiation is regulated by
proteins (trans factors) that bind to specific sites (cis elements) on the DNA
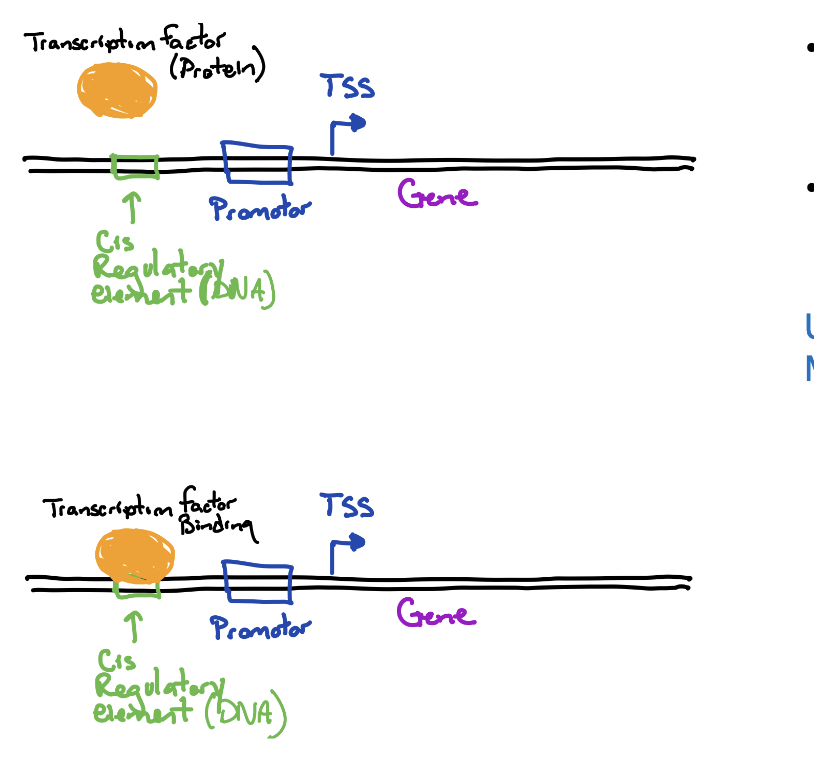
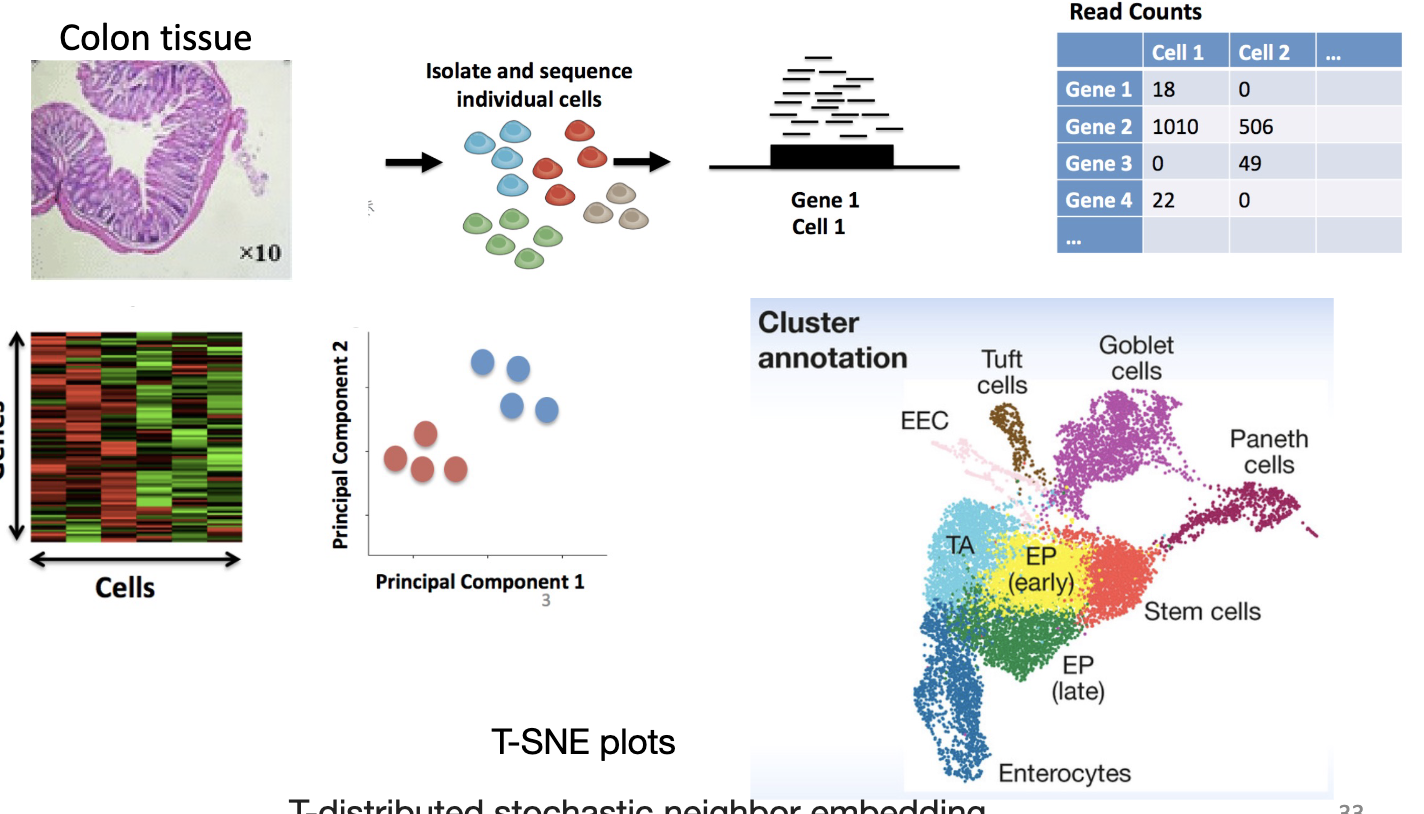
Transcriptional regulators can be both
positive and negative
activators are trans acting factors upstream of promoter
repressors are trans acting and bind to DNA to block promotor
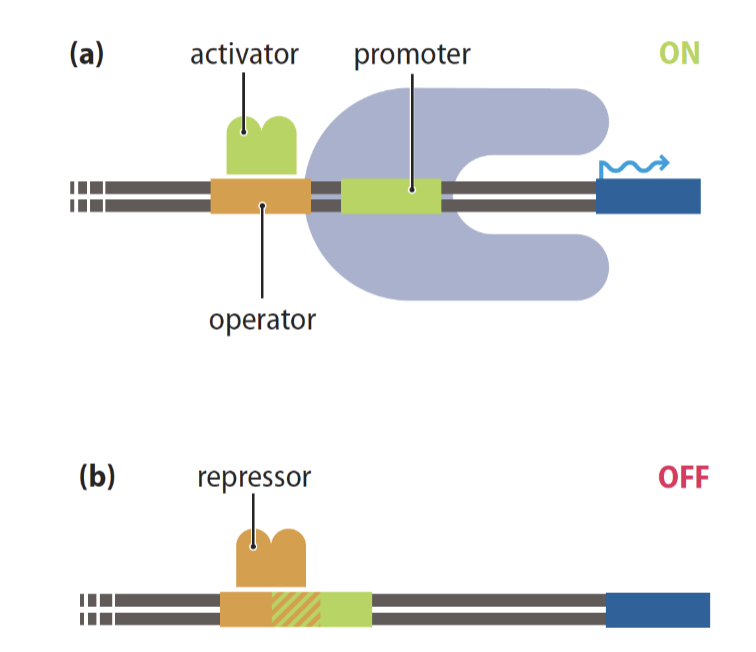
polycistronic
in bacteria groups of related genes are grouped together under shared promoter = operon
makes one polycistronic mRNA
genes are co-regulated
anti-sigma factor
binds to alternate sigma factor and blocks binding to promotor
how small molecules can regulate transcription
bind to transcription factors
ex: tryptophan binds to repressor so no more tryptophan can be made
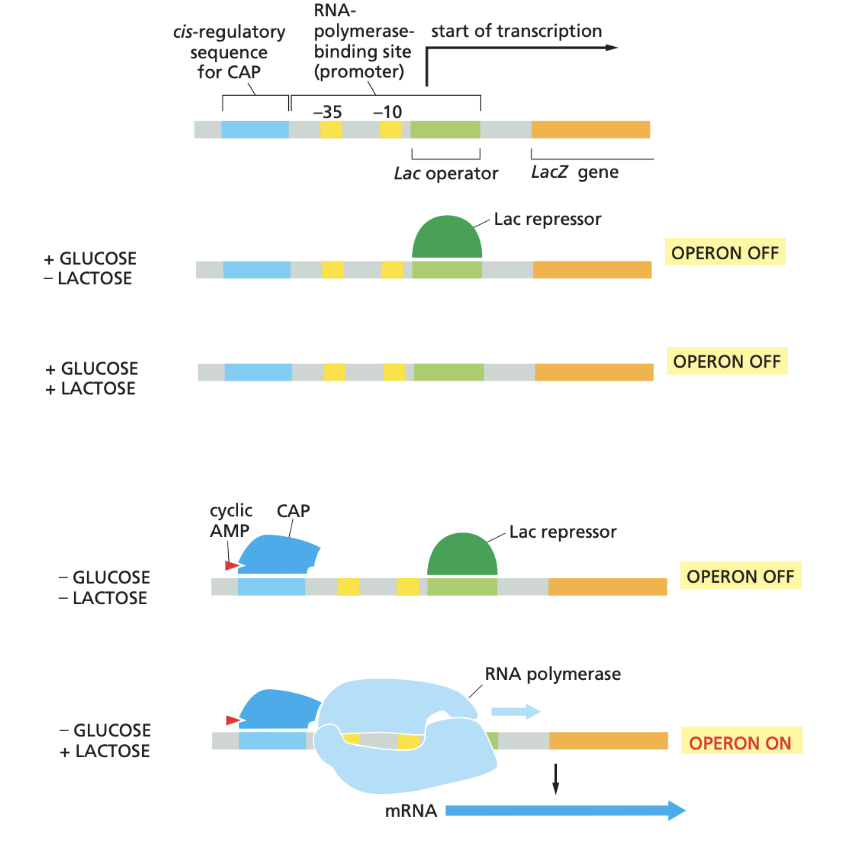
Lac operon regulation
When lactose is absent Lac repressor binds to Lac operator
When glucose is absent CAP activator can bind to promoter
transcription only occurs when glucose is absent and lactose is present
cyclic AMP also needed for CAP to work
Attenuation
Regulation of transcription termination in bacteria
low levels of tryptophan, ribosome pauses at Trp codons in leader peptide upstream fo Trp operon
stem loop 2:3 is formed blocking pairing of sequence 3 and 4 to form intrinsic terminator
high levels of tryptophan ribosome doesnt pause and covers region 2 so 3:4 stem loop can form intrinsic terminator → polymerase dissociates and does not make more trp
how can we compare RNA levels in cells treated under different conditions?
RNA-seq
to compare between samples need to normalize read count for a gene to the total reads in the experiement
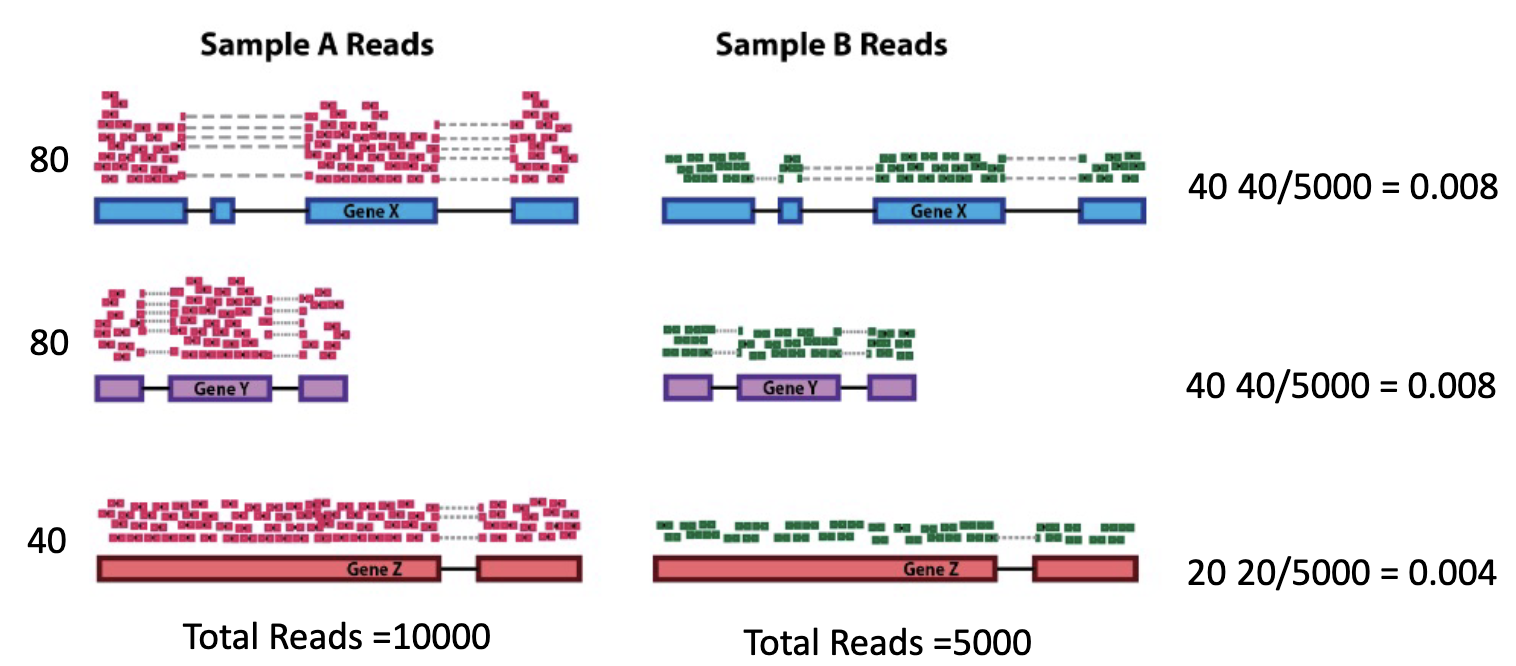
RPKM and FPKM
reads per kilobase per million
fragments per kilobase per million
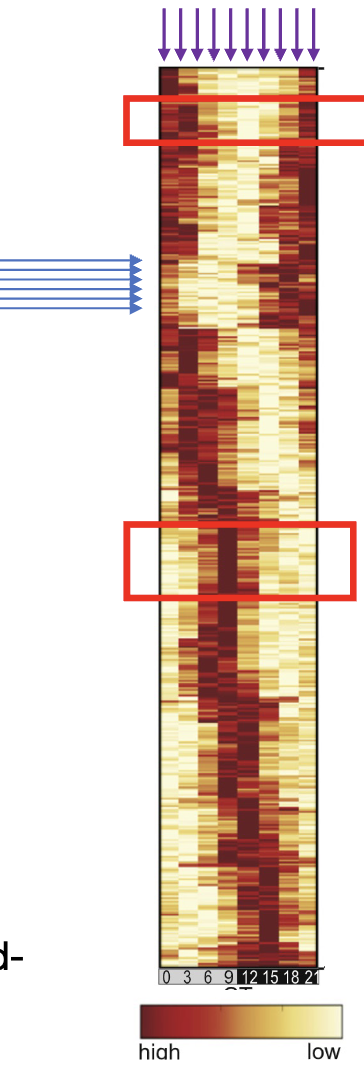
what does this show?
RNA seq heat map
each line is a specific gene
each column is a condition
compares changes in gene expression across many genes
if similar pattern in genes then may be coregulated
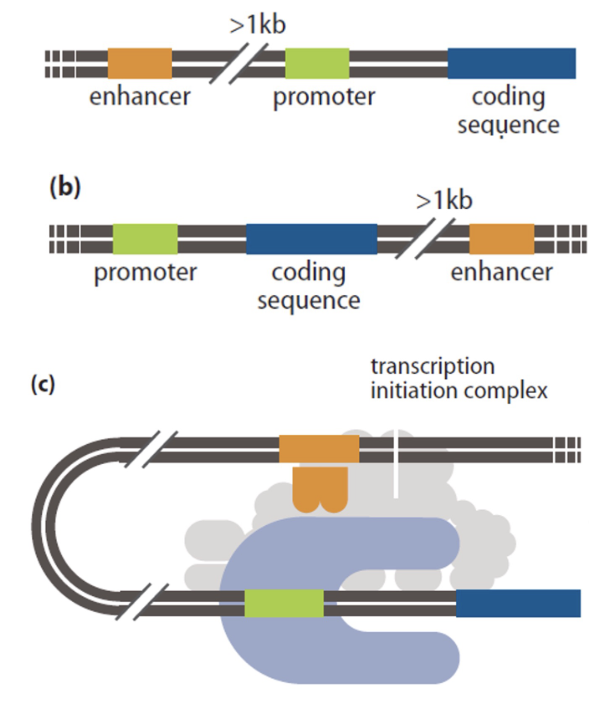
enhancers
eukaryotic regulatory regions that can bind far away from gene being regulated
upstream or downstream
loop DNA so regulatory elements contact Mediator
can have multiple enhancers for one gene
Co-activators and Co-repressors
bind to DNA binding proteins
do not bind directly to DNA
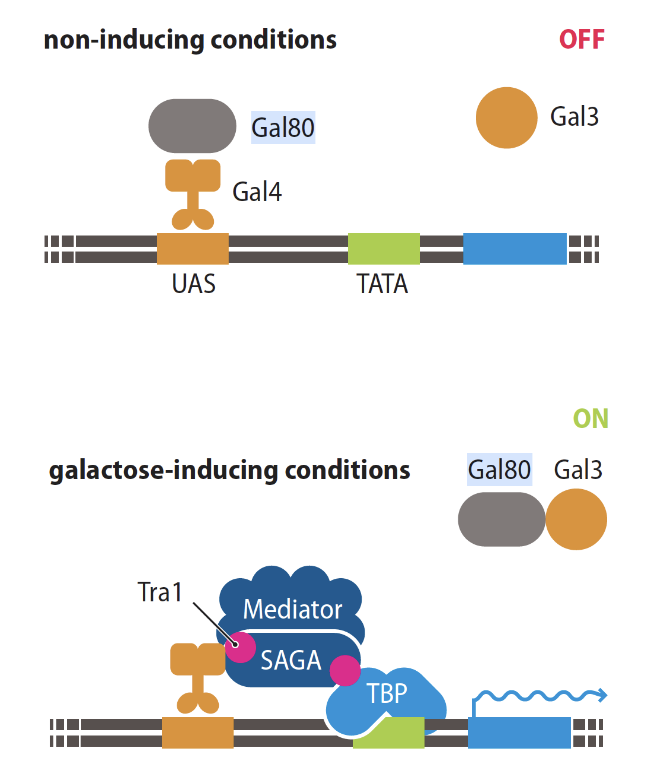
How does Gal4 recruit RNA polymerase?
through a co-activator complex
in presence of galactose Gal3 binds to Gal80 and exports it from the nucleus so it can’t inhibit Gal4
then Gal4 recruits SAGA co-activator complex which promotes assembly of mediator complex
histone modifications and transcription
H3K9me3 and H3K9Ac = gene expression
H3K9me3 = gene silencing and heterochromatic formation
H3K27me3 = gene silencing
specific modifications found at certain locations relative to gene body
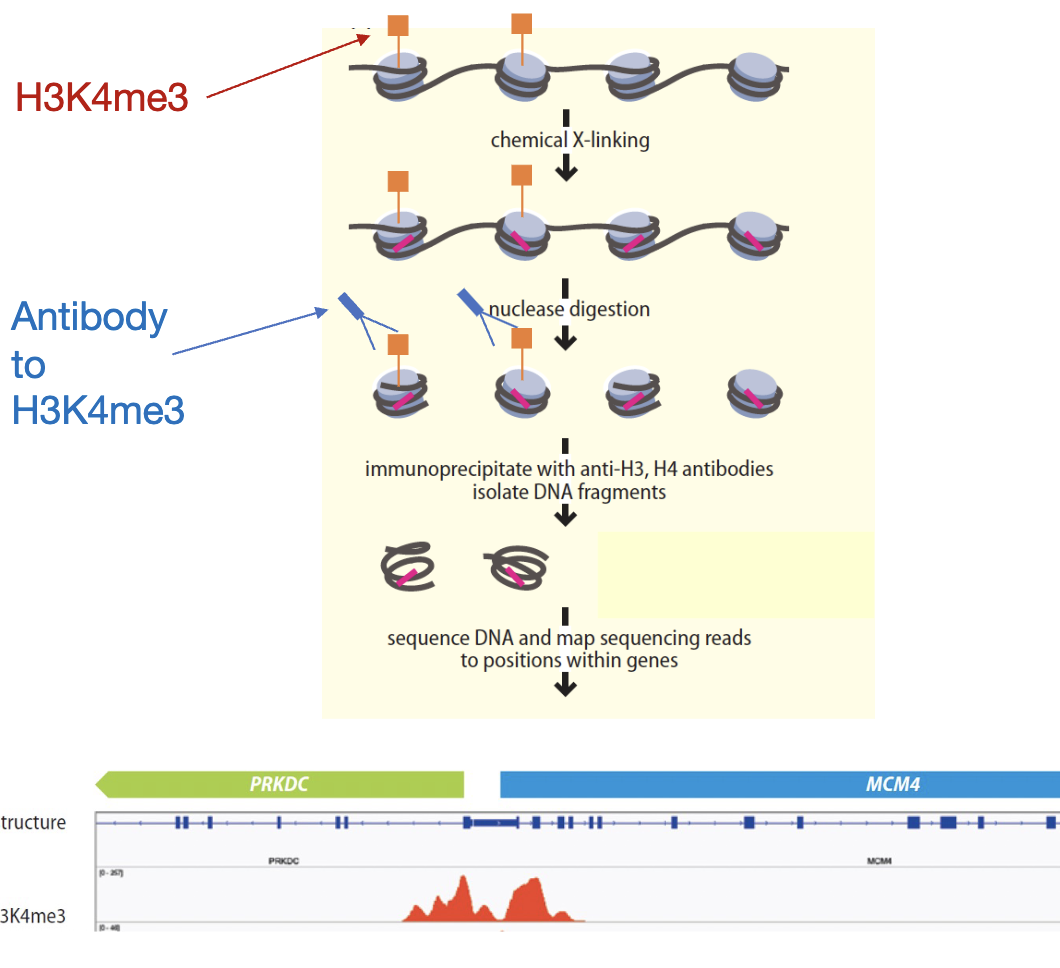
How to map histone modifications
ChIP-seq
histone deacetylase
represses transciption
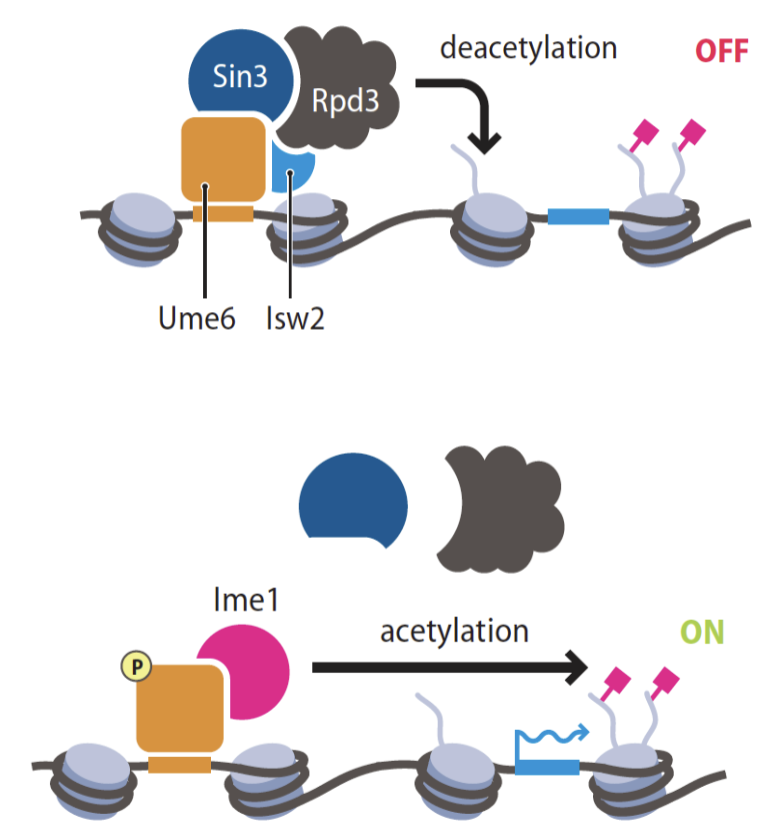
spreading of histone modification by sequential action of modification enzymes
ORC, Rap1 and ABF1 recruits Sir1 to Rap1 then Sir 2, 3, 4 bind and Sir2 deacetylates H3 then sir 3 and 4 do the same which brings in sir2 again
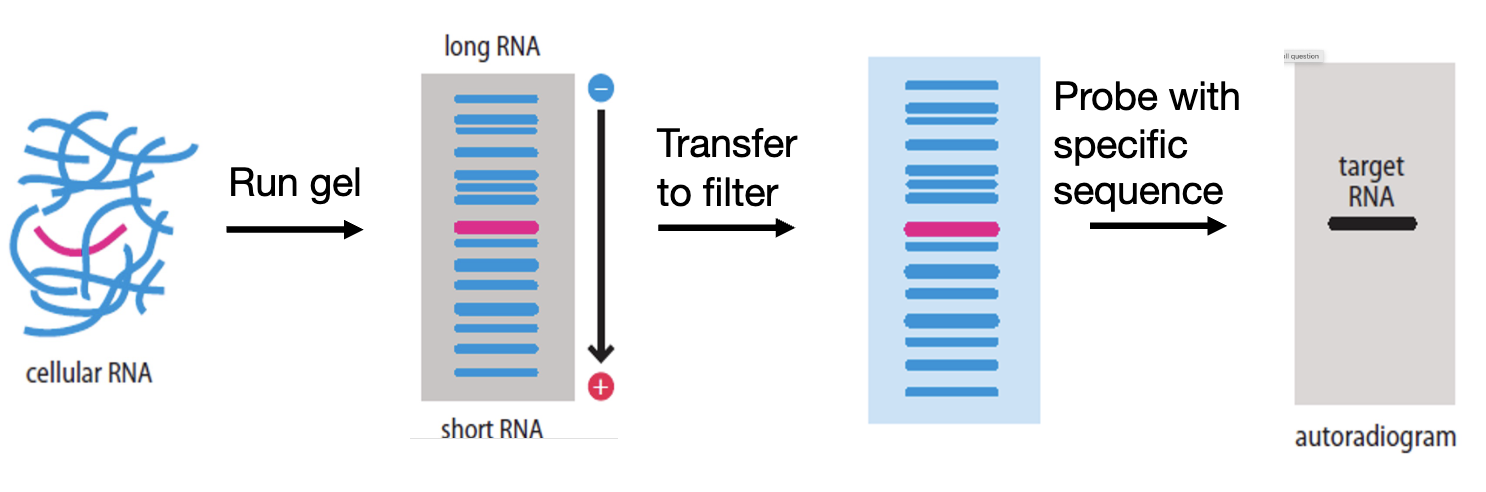
Northern blots
examine levels of a single specific RNA similar to southern blot
to amplify mRNA need to convert to cDNA and add adaptors for PCR primers to bind
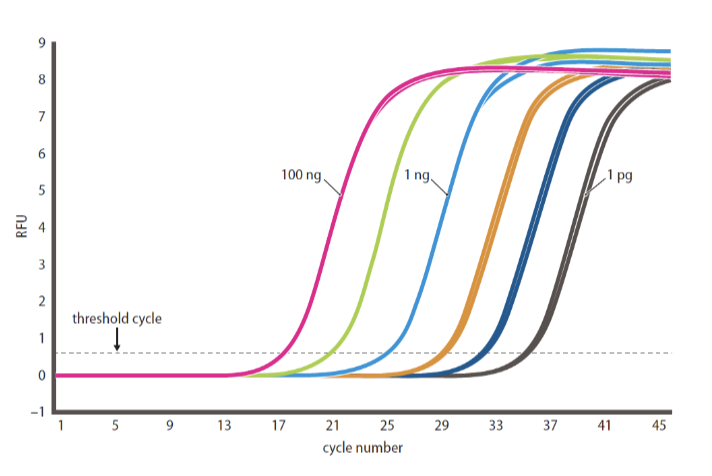
Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR)
determines relative amount of an RNA in diff samples
number of cycles it takes to cross threshold is proportional to amount of input DNA
Single cell RNA-Seq (scRNA-seq)
used to identify cells that express similar set of genes