Trade-offs in Homeostasis and Metabolism of Organisms
1/120
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
121 Terms
Trade-offs
Competing investments affecting organism performance.
Fecundity
Number of offspring and investment level.
Growth
Size and strength versus defense capabilities.
Longevity
Duration of individual survival.
Metabolizable Energy Intake (MEI)
Energy absorbed by organisms at varying temperatures.
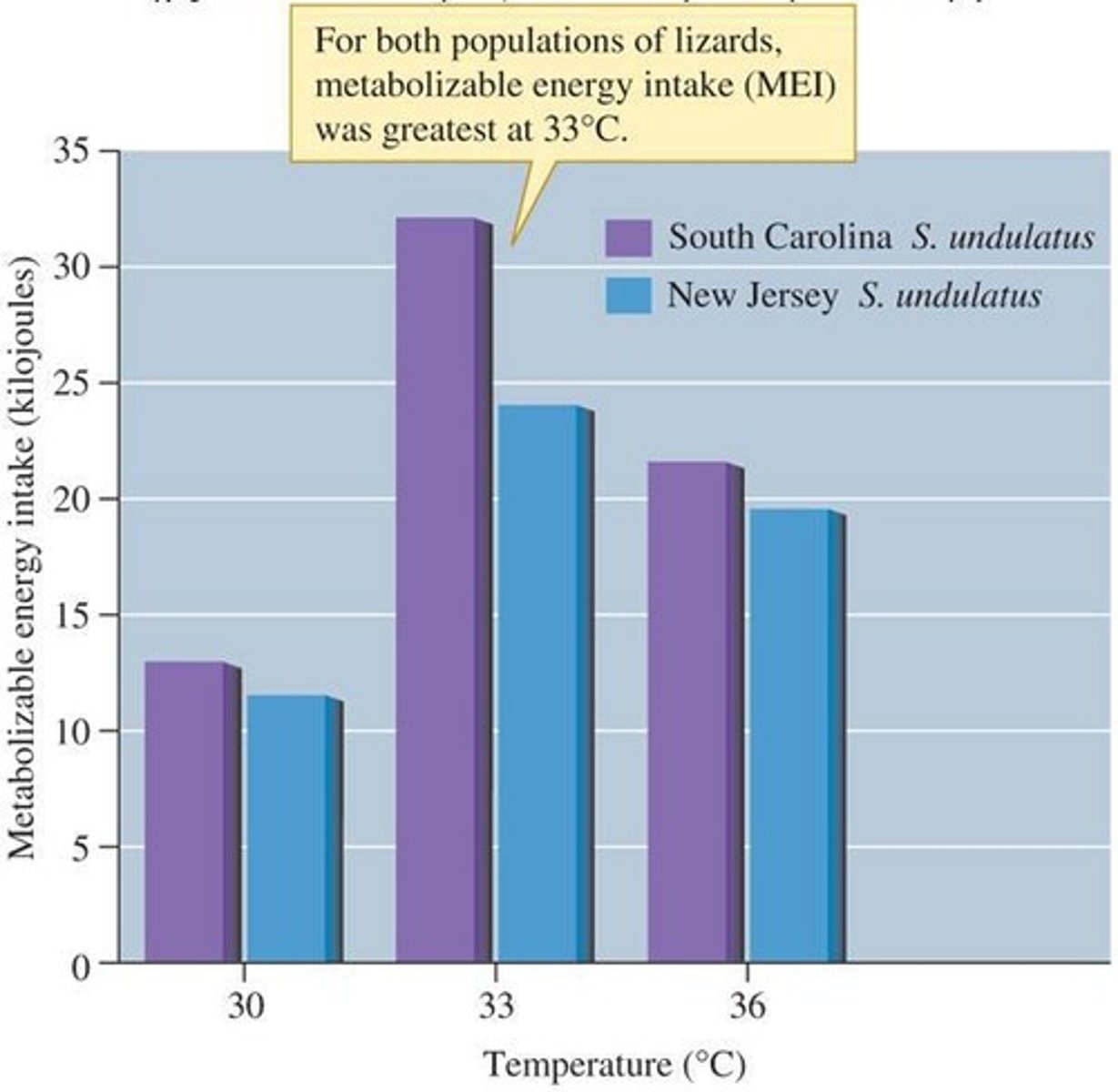
Eastern Fence Lizards
Species studied for temperature and energy intake.

Optimum Temperature
Ideal temperature range for maximum performance.
Acclimation
Short-term physiological changes to environmental shifts.
Adaptation
Long-term physiological changes in response to environment.
Evolution
Change in allelic frequencies over time.
Photosynthesis
Conversion of light to energy in plants.
Photosynthetic Rate
Rate at which plants convert light energy.
Homeostasis
Regulation of internal conditions for optimal performance.
Ectotherm
Organism relying on external heat sources.
Endotherm
Organism generating internal heat for temperature control.
Poikilotherm
Organism with variable body temperature matching environment.
Homeotherm
Organism maintaining constant body temperature despite changes.
Stenotherm
Organism surviving only within narrow temperature ranges.
Regulation
Mechanisms maintaining internal temperature and chemistry.
Temperature Variability
Fluctuations in temperature affecting organism performance.
Optimal Performance Zone
Range where organisms perform best.
Environmental Conditions
Factors influencing organism performance and survival.
HS
Total heat stored in an organism.
Hm
Heat gained via metabolic processes.
Hcd
Heat gained/lost through conduction.
Hcv
Heat gained/lost through convection.
Hr
Heat gained/lost via electromagnetic radiation.
He
Heat lost through evaporation.
Convection
Heat diffusion through gas.
Conduction
Heat diffusion through liquid or solid.
Radiation
Electromagnetic movement of heat.
Poikilotherm
Organism with variable body temperature.
Endotherm
Organism generating heat metabolically.
Stenotherm
Organism with narrow temperature tolerance.
Insulation
Anatomical features reducing heat loss.
Counter Current Heat Exchange
Mechanism for conserving heat in organisms.
Rete mirabile
Network of blood vessels for heat exchange.
Surface to volume ratio
Influences heat retention in organisms.
Thermal inertia
Ability to resist temperature changes.
Bradycardia
Reduced heart rate during dives.
Vasoconstriction
Blood shunted to maintain core temperature.
Sweating
Physiological response to cool the body.
Behavioral adaptation
Actions taken to maintain temperature homeostasis.
Thermal Neutral Zone
Temperature range with stable metabolic rate.
Aquatic endotherms
Endotherms facing unique challenges in water.
Hs
Heat storage equation: Hs = Hcd ± Hcv ± Hr
Hcd
Heat gained through conduction from surroundings
Hcv
Heat lost or gained through convection
Hr
Heat gained or lost through radiation
Desert plant adaptations
Decrease conduction, increase convection, reduce radiation
Arctic plant adaptations
Increase radiation, decrease convection for warmth
Araceae lilies
Use stored starch for heat in spring
Water regulation in animals
Maintain water concentration through loss and gain
Water balance equation
Wd + Wf + Wa - We - Ws
Wd
Water gained through ingestion
Wf
Water gained through metabolism of food
Wa
Water absorbed from the environment
We
Water lost through evaporation
Ws
Water lost through secretion
Transpiration
Water evaporation from plant surfaces
Potential Evapotranspiration (PET)
Water loss potential for plants in environment
Metabolism
Transforming environmental energy into usable energy
Photosynthesis equation
CO2 + H2O → CH2O + O2 using light
Respiration equation
CH2O + O2 → CO2 + H2O releasing energy
Photosynthetic autotrophs
Organisms using light and CO2 for energy
Chemosynthetic autotrophs
Organisms using inorganic molecules for energy
Heterotrophs
Organisms obtaining energy from organic molecules
Metabolic diversity
Variety of energy acquisition methods in organisms
Prokaryotic diversity
Includes autotrophy and heterotrophy for carbon
Nitrosomas
Bacteria involved in nitrogen oxidation.
Beggiatoa
Bacteria that oxidize hydrogen sulfide.
Eukaryotes
Organisms with membrane-bound nucleus and organelles.
Autotrophy
Organisms that fix CO2 for carbon.
Heterotrophy
Organisms that consume organic molecules for carbon.
Photo-autotrophy
Using light to convert CO2 into organic compounds.
Chemo-autotrophy
Using inorganic compounds for energy and carbon.
Cyanobacteria
Photosynthetic bacteria that produce oxygen.
Sulfur bacteria
Bacteria that use hydrogen sulfide for energy.
Photosynthetically Active Radiation (PAR)
Light useful for photosynthesis, ~400 to 700 nm.
C3 Photosynthesis
Carbon fixation using RuBisCO, producing 3-carbon sugar.
C4 Photosynthesis
Uses 4-carbon acid, separates fixation and synthesis.
CAM Photosynthesis
Separates fixation and synthesis by time of day.
RuBisCO
Enzyme that catalyzes CO2 fixation in plants.
Photorespiration
Wasteful reaction using RuBisCO, reduces efficiency.
Light Reaction
Initial phase of photosynthesis, converts light to energy.
Calvin Cycle
Second phase of photosynthesis, fixes carbon.
Stomata
Pores on leaf surfaces for gas exchange.
Bundle Sheath Cells
Cells in C4 plants where Calvin cycle occurs.
Mesophyll Cells
Cells in C4 plants where light reaction occurs.
Vacuole
Storage organelle in plant cells for acids.
Prokaryotes
Unicellular organisms without a nucleus.
Heterotrophs
Organisms relying on organic matter for energy.
Chemosynthetic Autotrophs
Bacteria and Archaea using inorganic compounds for energy.
Inorganics
Non-organic compounds like ammonium and nitrate.
Sulfur oxidizers
Use CO2 and sulfur compounds for energy.
Nitrosomas
Bacteria involved in nitrogen cycling.
E. coli
Common bacterium found in intestines.
Cyanobacteria
Photosynthetic bacteria producing oxygen.
Halophiles
Archaea thriving in extremely salty environments.
Thermophiles
Archaea living in high-temperature environments.