DAY 4 EXAMS
1/237
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
238 Terms
Accuracy
How close the data is to the true value
Precision
How close all the data is to each other
Repeatability
consistency of results when repeated under the same conditions
Reproduceability
other researchers can obtain the same results using the original data and methods
True value
the actual, ideal value of a quantity that would be obtained if the measurement were performed perfectly without any errors
Validity
how well an experiment or investigation actually measures what it is supposed to measure
E.g of personal errors
misreading scales, miscalculations, or using the wrong procedure
E.g of systematic errors
a miscalibrated scale consistently registers weights as higher than they actually are
E.g of random errors
what is uncertainty
not being sure of the answer
what are outliers
observation that lies an abnormal distance from other values
what are stakeholders
a person with an interest or concern in something
what is something biotic
something in the environment thats living
what is something abiotic
something in the environment that’s not living
examples of biotic factors
plants, fungi, bacteria, animals, herbivores, carnivores, decomposers
examples of abiotic factors
temperature, terrain, soil, water, sunlight, oxygen
what is a biome
a large geographical area defined by its distinct climate, vegetation, and animal life
what is an ecosystem
a community of living organisms in a particular area
what is a habitat
natural home or environment of an animal, plant or other organism
what is a community
group of living things that live in the same place or have a particular characteristic in common and how they interact
what is a population
all the inhabitants of a particular place
what is an open system
a system that has influences from outside of its self
“a system that freely exchanges both matter and energy with its surroundings”
what is a closed system
A system that doesn’t get anything coming into it
what is a semipermeable system
Only some things can come into the system
e.g. semipermeable membrane
what is an organism
a living thing
what is an autotroph
Produces it’s own food
e.g plants, algae, phytoplankton
what is photosynthesis
Plants use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to create oxygen and energy in the form of glucose (sugar).
What is an heterotroph
Does not produce it’s own food
e.g animals, fungi, Detritivores
What is a food chain
illustrates the flow of energy in an ecosystem by showing who eats whom
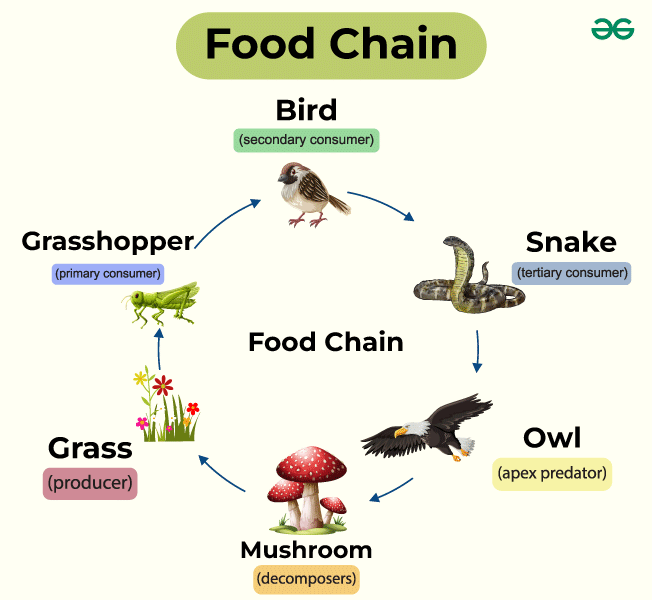
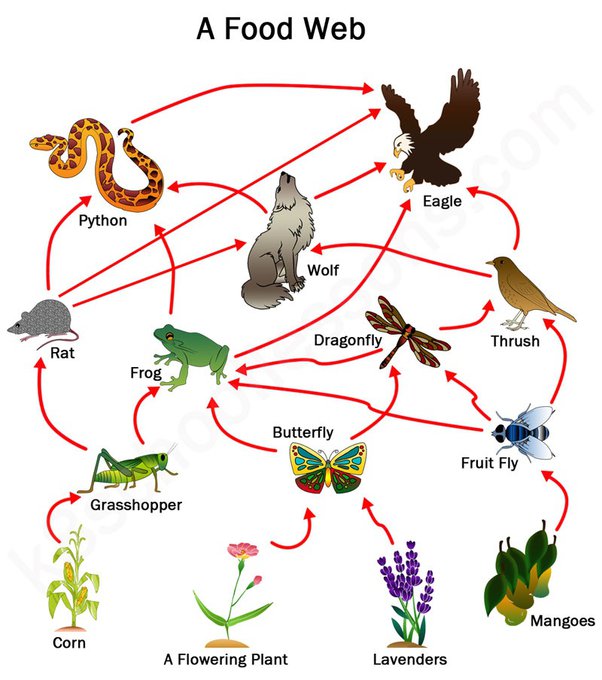
What is a food web
network of interconnected food chains, demonstrating the various paths that energy and nutrients can take through different species
What are the trophic levels
producers, primary consumers (herbivores)
secondary consumers (carnivores)
tertiary (third) consumers (carnivores)
What is a producer
organism that creates its own food
What is a consumer
something that doesn’t make it’s own food, eats producers
What is a primary consumer
an animal that eats producers, like plants or algae, and is the first level of consumer in a food chain
herbivores
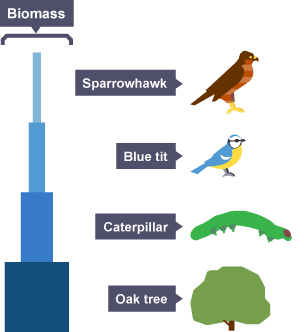
What is a biomass pyramid
illustrates the total mass of living organisms at each trophic level in a food chain or food web
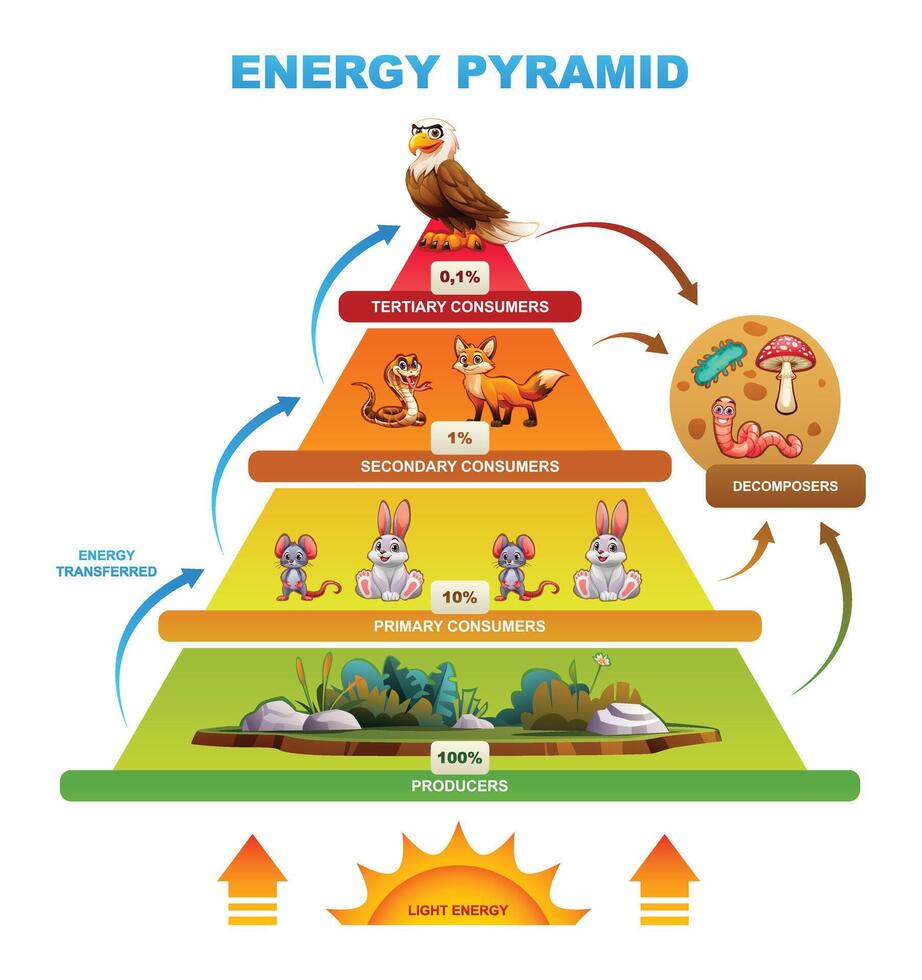
What is an energy pyramid
a diagram that represents the flow of energy from one trophic level to the next in an ecosystem
What is a numbers pyramid
represents the number of organisms at each trophic level within a food chain or ecosystem
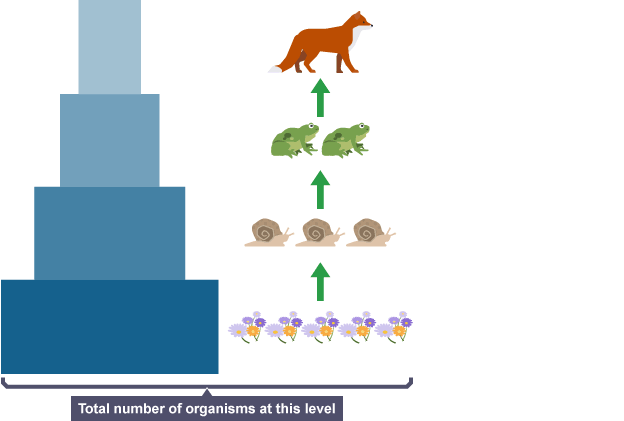
What is Anthropocentrism
viewpoint that places humans at the center of the universe
What is biocentrism
The value we give living things
What is ecocentrism
belief that gives inherit value to individual living things & ecosystems
What is technocentrism
world view that prioritizes technology & scientific advances
What’s the atmosphere
protective layer made of air, containing mainly nitrogen and oxygen, along with other gases like argon, carbon dioxide
What’s the hydrosphere
water on the surface of of earth
e.g oceans, rivers, lakes, rain
What’s the lithosphere
earths crust, landforms (rocks & soils)
continental crust
oceanic crust
soil structure
What’s the biosphere
living matter on earth, including all animal and plant life forms
What’s groundwater
all underground water
What’s the mantle
largest and thickest layer of the Earth, located between the crust and the outer core
What is continental crust
thicker, less dense crust that forms the landmasses of the Earth.
What’s oceanic crust
outermost layer beneath the oceans, thin, dense, and primarily composed of basalt and other mafic rocks.
What are the different soil textures
clay, silt, sand , loam
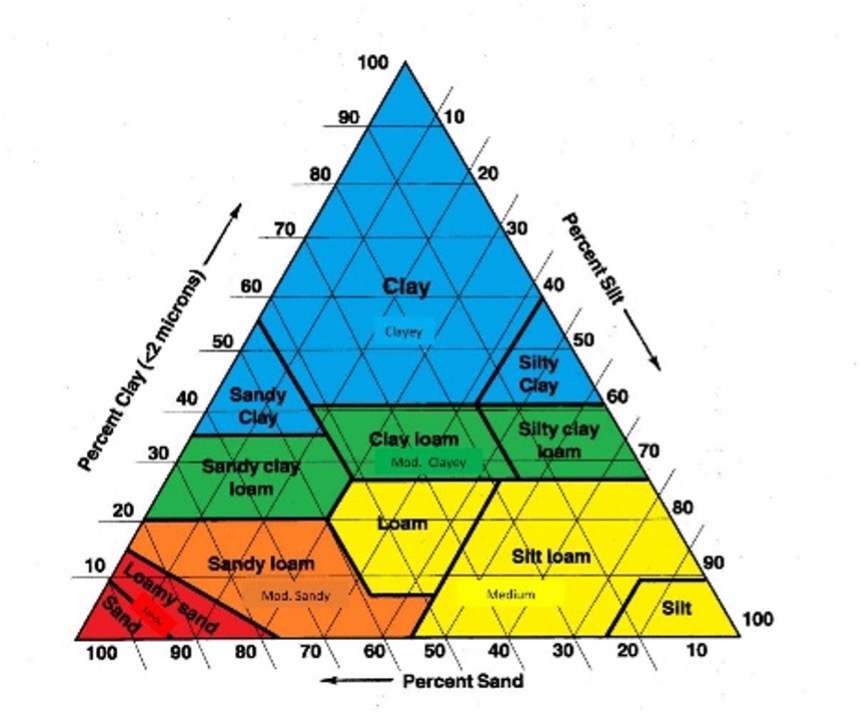
What does porosity mean
he quality of being porous, or full of tiny holes
What’s loam
Loam is a “perfect” mix of clay, loam and sand
What’s the O horizon
the topmost layer of soil, composed primarily of organic matter like decomposed leaves and plant material
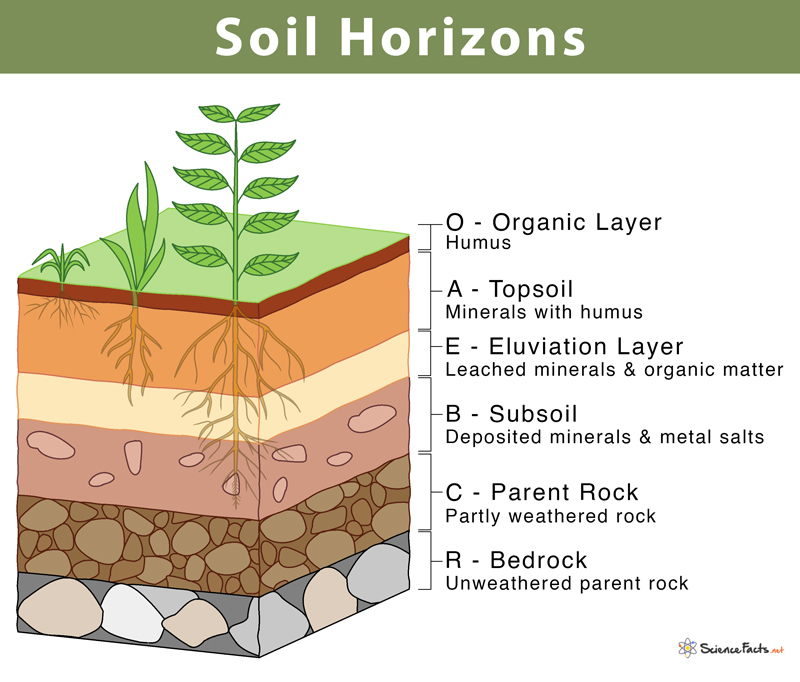
What’s the A horizon
topsoil, a mineral soil layer rich in organic matter and essential for plant growth
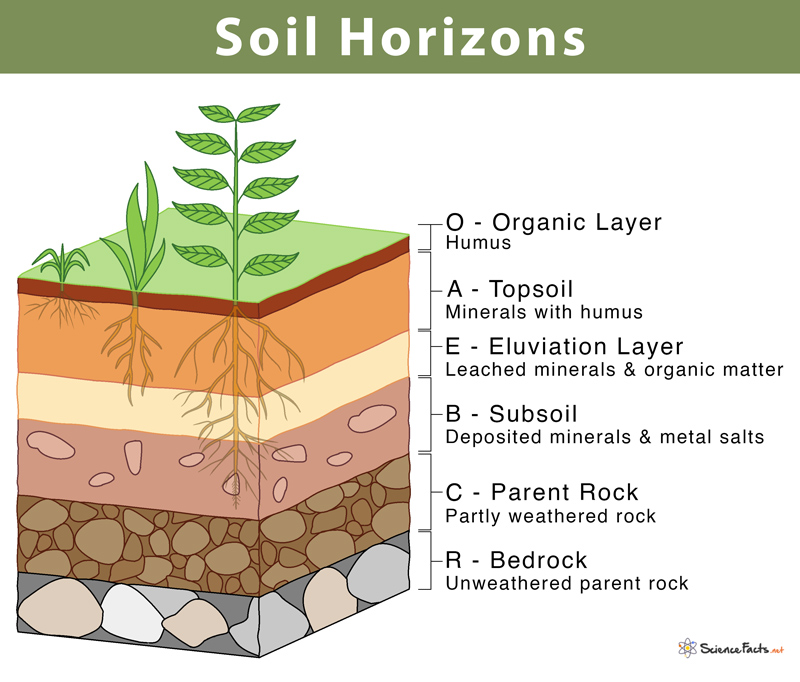
What the B horizon
accumulation of materials leached from the A horizon, particularly clay, iron, and aluminum oxides
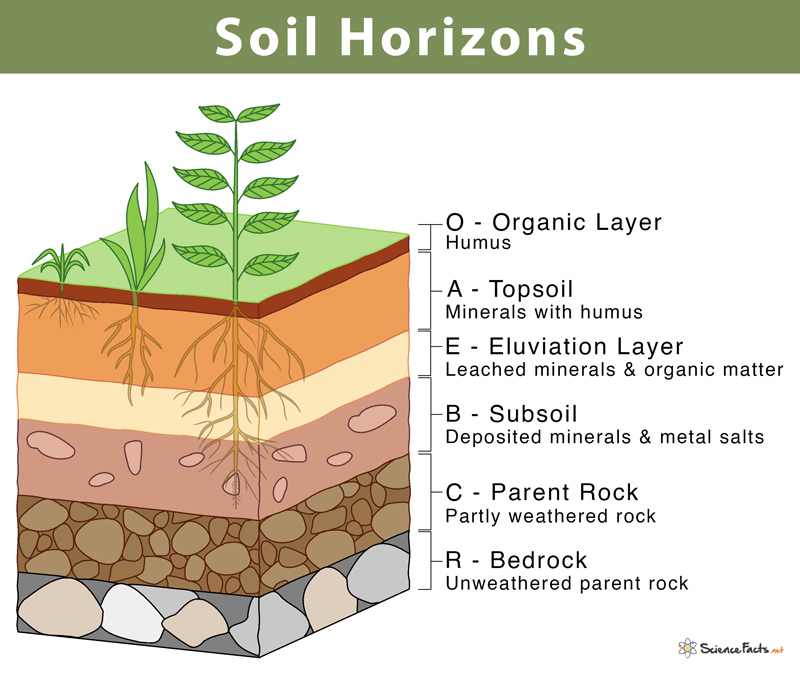
What’s the C horizon
primarily composed of unconsolidated parent material that has been little affected by soil-forming processes
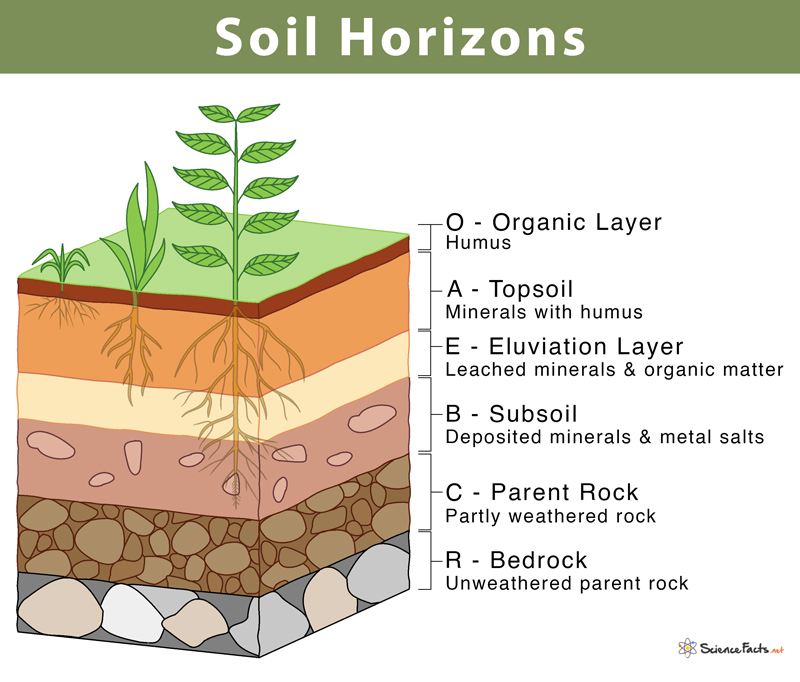
What’s parent rock
the original rock from which soil is formed
What’s the ozone layer
absorbs most of the Sun's harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation
the reason it’s thinning is because of the chlorofluorocarbons carbons
made up of O3 (three oxygen atoms)
What is weather
short term changes in the atmosphere
state of the atmosphere at a particular time
temperature changes
What is climate
long term changes in the atmosphere
What’s the Coriolis effect
circulating air is deflected toward the right in the Northern Hemisphere and toward the left in the Southern Hemisphere
What’s El Nino
the weather pattern where hot air is pushed towards south america through trade winds across the pacific ocean
What’s El Nina
Where hot winds are pushed from western south America towards the western pacific ocean
What is coal
combustible rock
primarily composed of carbon
formed from the remains of plants that died millions of years ago
What is oil and gas
naturally occurring
combustible hydrocarbons formed from the remains of prehistoric organisms
such as: giant ferns and trees
What is limestone
sedimentary rock primarily composed of calcium carbonate
formed by the accumulation and lithification of shell fragments, coral remains
What is nitrogen fixation
process of converting atmospheric nitrogen (N2) into reactive forms like ammonia (NH3) or ammonium (NH4+) that plants and other organisms can use
animals use nitrogen as sources of nitrogen for building organic molecules like proteins and nucleic acids
What is denitrification
naturally occurring process where bacteria convert nitrate in soil into nitrogen gases
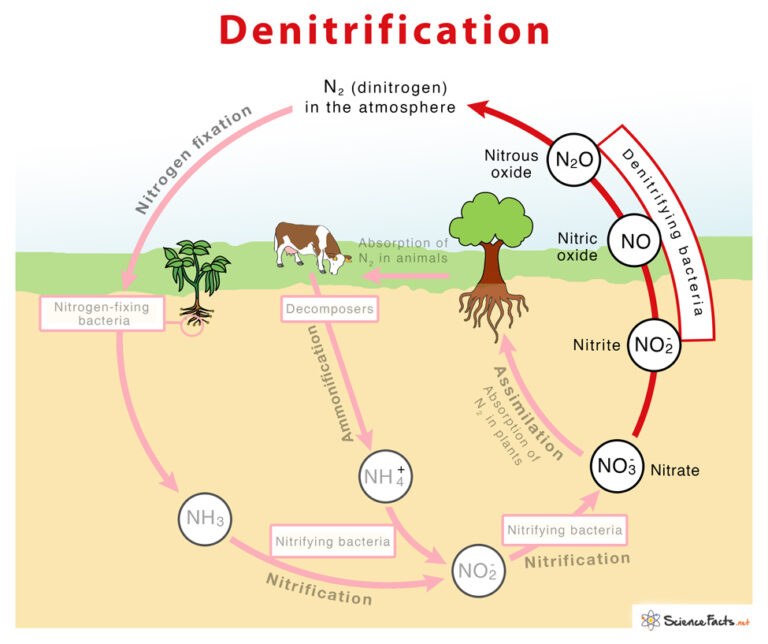
What is urea
Urea is the waste from the blood before it’s diluted with water in the kidneys
waste product formed by the body during protein breakdown
What are legumes
ecological importance due to their ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen into a form usable by plants
What is the carbon cycle
the movement of carbon atoms between different reservoirs on Earth, including the atmosphere, biosphere, ocean, and geosphere
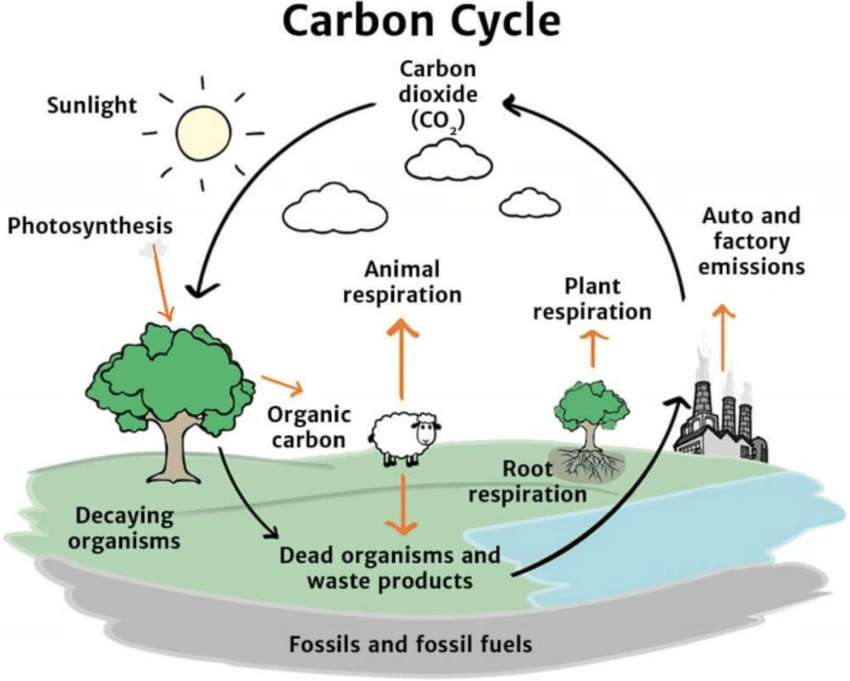
What is weathering
natural breakdown or dissolving of rocks, soil, and minerals at the Earth's surface due to exposure to the environment
What is desorption
the opposite of adsorption
process where a substance, previously adsorbed onto a surface, is released or detached from that surface
What is a limiting factor
any environmental factor that restricts the growth, distribution, or abundance of a population or an organism
What is eutrophication
excessive enrichment of a water body with nutrients, like nitrogen and phosphorus
Why is the sun so important
it's the primary source of energy for life on Earth
drives photosynthesis
What are the solar cycles
nearly periodic changes in the Sun's activity
characterized by variations in sunspot numbers, over an approximately 11-year period
represent the rise and fall of solar activity
transitioning from a minimum of sunspots (solar minimum) to a maximum (solar maximum) and back again.
What percentage of light reaches the earth?
38% visible light , 53% infrared light , 9% ultraviolet light
How did the atmosphere form
As Earth cooled, an atmosphere formed mainly from gases spewed from volcanoes
included hydrogen sulfide, methane, and ten to 200 times as much carbon dioxide as today's atmosphere.
What are short term changes?
Daily Changes – day/night cycles |
Monthly changes- The moon cycle
Seasonal changes – summer/winter, monsoon/dry season
What are long term changes?
Climate change, increased rainfall, droughts, glacial melting, land cover changes, desertification, ecological succession.
What’s the greenhouse effect
natural process that warms the Earth's surface
happens when gases in the atmosphere trap some of the Sun's outgoing heat preventing it from escaping back into space
This trapped heat contributes to the Earth's overall temperature
making it habitable for life.
What’s the enhanced greenhouse effect
increase in the Earth's surface temperature due to the trapping of more heat by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere
This occurs because human activities, like burning fossil fuels and deforestation
What are the effects of climate change
hotter temps
more intense natural disasters (drought and storms)
How do scientists use charcoal deposits in forest areas to determine past climates
to reconstruct past climates, specifically past fire regimes and vegetation changes
amount and type of charcoal found in sediments, soils, or lake beds can reveal information about the frequency and intensity of fires
types of trees that were present in the past.
What is geological sequestration
the process of storing carbon dioxide (CO2) in underground geological formations
What is biological sequestration
the natural process by which plants, soil, and oceans store carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, effectively removing it
What are ecosystem services
the numerous benefits that humans derive from healthy ecosystems, like clean air and water, food production, and flood control
services ecosystems do for free when we allow them to
What is intergenerational equity
emphasizes that decisions and actions of one generation should not unfairly burden or compromise the well-being and opportunities of future generations
What is intragenerational equity
fairness within the same generation
ensuring equitable distribution of resources and opportunities among individuals of the present time
What is a regulatory framework
regulatory framework is a structured set of rules, standards, and guidelines
established by a government or regulatory body to govern a specific industry or sector.
What is thermohaline circulation
movement of seawater in a pattern of flow dependent on variations in temperature
give rise to changes in salt content and hence in density.
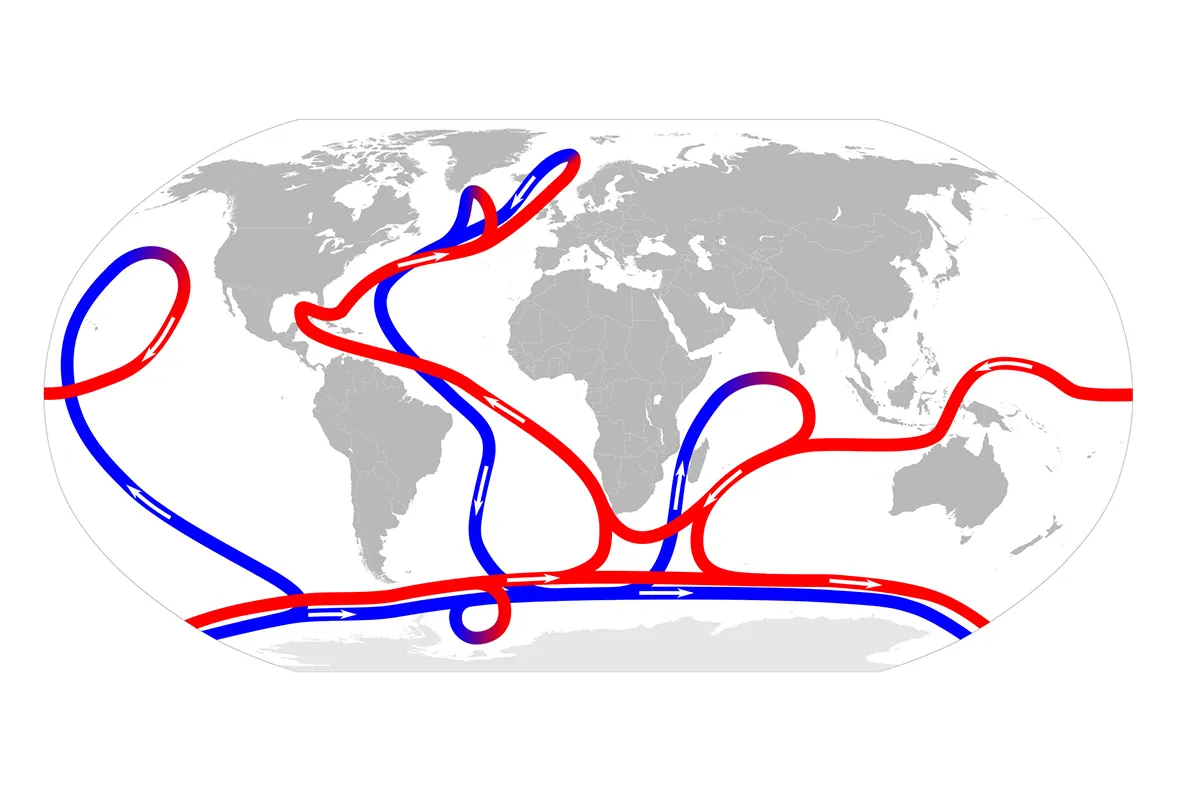
What is the southern oscillation (ENSO)
naturally occurring climate pattern across the tropical Pacific Ocean that swings between El Niño (warm phase) and La Niña (cool phase)
What is the water circulation
the movement and mixing of water within a body of water or a system
What are the trade winds
consistent, easterly prevailing winds that blow across the tropical and subtropical regions of Earth, primarily towards the equator
What is the Indian ocean dipole (IOD)
a climate pattern characterized by sustained changes in the difference between sea surface temperatures in the tropical western and eastern Indian Ocean
significant impact on Australia's climate and agriculture, particularly in southern and eastern regions.
What is the absolute location of Greenland?
71.7069° N, 42.6043° W
What is the relative location of Greenland?
In the north Atlantic ocean off the northeastern coast of Canada.
What continent is Greenland geologically apart of?
North America
What is the distribution of the population of Greenland?
Concentrated mainly on the southwest coast