IB CHEMISTRY HL
1/150
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
Boyle's Law
P1V1=P2V2 (inversely proportional)
Charle's Law
V1/T1=V2/T2
Gay-Lussac's Law
P1/T1=P2/T2
Combined Gas Law
P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2
Ideal Gas Law
PV=nRT
conditions of PV=nRT
Pascals
ideal gas
low molar mass and weak to no IMF
effective nuclear charge formula
of protons - # of protons of previous noble gas
effective nuclear charge
extent to which the nucleus is attracting the valence electrons (more difference
effective nuclear charge increase across periods
linear
atomic radius
half the difference between the nuclei of an element (depende on what it is bonded with)
atomic radius trend
increases down a group because more shells
more effective nuclear charge means
smaller atomic radius
ionic radius
half the distance between the nucleus of the cation and the anion (Average)
parent ion has _______ ionic radius than cation
higher (because loses electron and less shells)
ionic radius trend
decreases across a period and increases down a group
ionization energy
minimum amount of energy required to remove one mol of electrons from a neutral gaseous atom in its ground state
ionization energy trend
decreases from top to bottom in a group
electron \ trend
increases from left to right in a period
electron affinity
energy released when 1 mol of electrons is attached to 1 mol of neutral gaseous atoms or molecules
melting point trend
decreases down group 1
increase down 17
increase across a period and reach a maximum at group 14
alkali metal properties (group 1)
-very reactive -form ionic compounds with non-metals -react with H2O to produce hydroxide and gas -intensity increases down group (valence further away)
Halogen properties (group 7)
-some gas/liquid/solid -colored -very reactive -diatomic -Fluorine
sulfuric acid reaction
SO3 + H2O = H2SO4
sulfurous acid reaction
SO2 + H2O = H2SO4
ionic bond electronegativity difference
more than 1.8
coordination number
how many anions around cation in a lattice
lattice energy
how much energy needed to break ionic bond
ionic compound physical properties
brittle
volatility
ability of a liquid/solid to become a gas at room temperature
pure covalent electronegativity difference
0
polar covalent electronegativity difference
between 0 and 1.8
pure covalent properties
symmetric electron distribution
polar covalent properties
asymmetric electron distribution
dative bond
pair of electrons donated from one atom to another
dipole-dipole
attraction between polar molecules
hydrogen bonds
strong dipole-dipole
London dispersion
temporary dipole
what is responsible for partial bonds and resonance structures
delocalized pi electrons
formal charge formula
valence electrons-available electrons
formal charge characteristics
-closer to 0 more stable -used to see which suitable Lewis Structure more appropriate -most electronegative atoms will be further from ideal formal charges
linear BA
180
bent/v-shape/angular BA
118
trigonal planar bA
120
tetrahedral BA
109
bent with 2 lone pairs BA
105
trigonal pyramidal BA
107
trigonal bipyramidal BA
120 and 90
square pyramidal BA
180 and 90
square planar BA
180
ammonium
NH4+
Hydroxide
OH-
Nitrate
NO3-
Hydrocarbonate
HCO3-
carbonate
CO3 2-
Sulfate
SO4 2-
phosphate
PO4 3-
metallic bonding definition
lattice of metal cations in a sea of delocalized electrons
malleability
ability to be shaped
ductility
ability to form threads
alloys
homogeneous mixture of two metals or metal with another substance. metals combine to improve the individual qualities of the metals
hybridization
overlap of atomic orbitals to create hybrid orbitals that can form covalent bonds
radical
substance or species with one or two unpaired electrons
conditions when measuring heat change
298K
specific heat capacity
amount of energy needed to increase temperature of a substance by 1C or 1K
enthalpy change
amount of energy released or absorbed PER MOLE of substance
Hess' Law
enthalpy of any reaction is independent of the route you take
standard enthalpy change of formation
enthalpy change when one mole of a substance is formed from its elements in standard states
bond enthalpy
energy required to break one mole of bonds in gaseous molecules under standard conditions
wavelength formula
(planck's x speed of light) / (enthalpy/avogadro)
Lattice Enthalpy
enthalpy change when one mole of a solid ionic compound is separated into its respective gaseuous ions (BORN HABER CYCLE)
factors affecting lattice enthalpy
-ionic radius (assume spherical shape) -ionic charge (Coulomb's Law) -STP
Enthalpy change of solution
enthalpy change when 1 mole of an ionic substance dissolves in water to give a solution of infinite dilution (100% of sample diluted)
steps in forming liquid solution (particles)
-separate solute -separate solvent -allow solute and solvent to interact
enthalpy change of hydration
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of aqueous ions is formed from gaseous ions
entropy
the tendency of a system to become disorganized
negative ΔS
less disorder
positive ΔS
more disorder
absolute entropy
ΔS reaction= ΔSproducts-ΔSreactants ΔS surrounding = -ΔS system/ T absolute
gibbs formula
G = H - TS
at low temps (exo)
ΔG is < 0
at low temps (endo)
ΔG is > 0
at high temps (endo)
ΔG is < 0
at high temps (exo)
ΔG is > 0
chemical equilibrium characteristics
rate of forward/reverse reactions equal amount of reactants/products constant
Q meanings
if Q > Kc, left
if Q = Kc, equilibrium
if Q > Kc, right
Kc formula
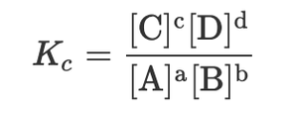
Le Chatelier's principle
if a system is at equilibrium and a change is made that disturbs the equilibrium, then the system responds in such a way as to counteract the change and eventually a new equilibrium is established
concentration effect on Kc
adding more reactants will favour the products side
pressure effect on Kc
added pressure, shift to side with less moles
temp effect on Kc
if temp increases, shift in endo direction
how to get overall Kc
multiply individual ones
Gibbs free energy
the energy of a system that is available to do work at a constant temperature and pressure
rate of reaction can be measured through
water displacement and gas formation
collision theory
not every collision forms a reaction. successful collisions are chemical reactions and need activation energy and certain orientation
factors affecting rate of reaction
-catalyst -concentration -surface area -temperature -pressure (gases)
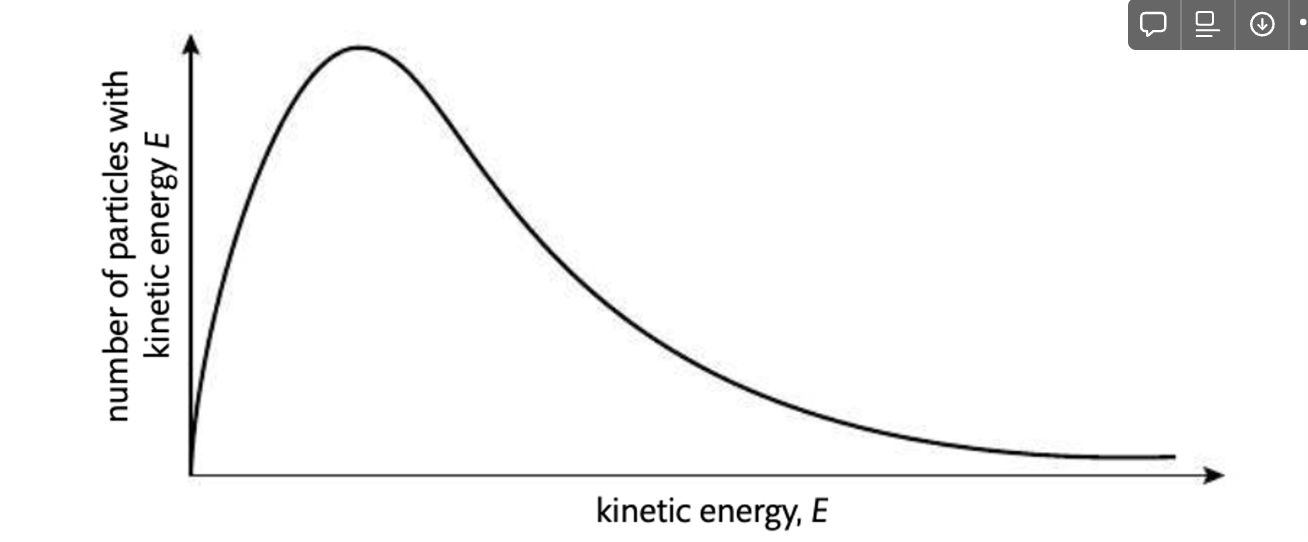
Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution curve
factors that change K in kinetics
catalyst and temp
winkler method
used to measure Biological Oxygen Demand (a measure of the dissolved oxygen required to decompose organic matter in water over a set time period)
lewis acids
accept pairs of electrons