Medical Terms Flashcards: Module 1 Exam Study Set
1/244
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
245 Terms
What is the name of the publication that exposed the serious morbidity caused to Americans by highway crashes? What was the effect of this publication?
Accidental Death and Disability: The Neglected Disease of Modern Society, prompted EMS as it is today with guidelines
What are the parts of the EMS System? (8 total)
1. bystanders
2. dispatch
3. first responder
4. EMS
5. ALS
6. transport
7. ED
8. Specialty Care (stroke center, burns center, cath lab, peds, poison control, trauma center, etc)
Emergency Medical Responder (EMR)
The first trained individual, such as a police officer, fire fighter, lifeguard, or other rescuer, to arrive at the scene of an emergency to provide initial medical assistance.
50-60 hrs of training
Emergency Medical Technician (EMT)
An individual who has training in basic life support, including automated external defibrillation, use of a definitive airway adjunct, and assisting patients with certain medications.
130-200 hrs of training
Advanced EMT (AEMT)
An individual who has training in specific aspects of advanced life support, such as intravenous therapy, and the administration of certain emergency medications.
150-250 hrs of training
Paramedics
Persons trained (sometimes coupled w/ associates or bachelors degree) and certified to provide advanced life support such as intubation, special medications, EKG, IV treatment, etc
abt 1600 hrs of training
What are the two levels of state-certified training for EMS in NJ?
EMT, Paramedic
What agency designs the EMS curricula?
US Federal Government - National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
What state office regulates and certifies EMS training?
New Jersey Department of Health - The Office of Emergency Medical Services (OEMS)
Medical Director
The physician who authorizes or delegates to the EMT the authority to provide medical care in the field.
EMS System (Emergency Medical Services System)
A network of trained professionals that provide emergency care and transport, governed by the state laws. Can be inside or outside the hospital, refers to anybody who tries to treat the patient
General requirements to be an EMT
- high school diploma
- immunization proof
- valid drivers license
- 16+ yrs old
- BLS/CPR course completion
- state approved EMT course
- written final exam
- state recognized practical exam
- mental and physical criteria met
- no felony
- compliance with other employer previsions
Where did EMS originate?
Napoleonic Wars, WWI, WWII, Korean War
- led to organization of EMS in civilian communities
What are the three levels of EMS training regulation?
Federal - National EMS Scope of Practice Model provides basic guidelines for EMS skills
State- state regulates EMS provider operations and implements federal rules, may only implement some
Local - Medical Director decides day-to-day limits of EMS personnel and decides what EMT can do (administer certain meds) or not (cannot expand beyond state/fed)
14 components of EMS system
1. Public Access
2. Clinical Care
3. Medical direction
4. Integration of Health Services
5. Information Systems
6. Prevention
7. EMS Research
8. Communication Systems
9. Human Resources, 10. Legislation and Regulation
11. Evaluation
12. System Finance
13. Public Education, 14. Education Systems
Public Safety Answering Point (PSAP)
Any location or facility at which 9-1-1 calls are answered, proper resources are called, and pre-arrival instructions given
Emergency Medical Dispatcher (EMD)
A member of the EMS system who provides pre arrival instructions to callers, thereby helping to initiate lifesaving care before EMS personnel arrive. Usually take EMD, telecommunications, and CPR courses first
Offline medical control
Indirect medical control through standing orders, protocol, training, and supervision authorized by the medical director. Times when do not need to directly contact medical director to get permission to do a procedure
Online medical control
Physician directions given over the phone or radio, usually during the call
primary prevention
Efforts to prevent an injury or illness from ever occurring such as immunizations
secondary prevention
Mitigating the effects of an illness after the problem starts such as taking aspirin for chest pain
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
Law that protects patient privacy so that EMS providers cannot disclose info w/o pt consent or discuss case w/ anybody not treating pt
Quality Control (QC)
The responsibility of the medical director to ensure that the appropriate medical care standards are met by EMTs on each call.
Continuous Quality Improvement (CQI)
A system of internal and external reviews and audits of all aspects of an EMS system to improve care
Licensing
The process whereby a competent authority, usually the state, allows people to perform a regulated act.
Credentialing
An established process to determine the qualifications necessary to be allowed to practice a particular profession, or to function as an organization
Certification
A process in which a person, an institution, or a program is evaluated and recognized as meeting certain predetermined standards to provide safe and ethical care.
Evidence-based treatment
Interventions/procedures are not adopted unless they are validated by a research study, duplicated, and shown to benefit enough to become standard of care
Control vs. Experimental Group
control: no intervention or receives an intervention that is unrelated to the independent variable being investigated
experimental: one or more treatment groups of participants that receive the intervention of the independent variable being investigated
treatment vs placebo study
Treatment group gets intervention being tested while placebo group gets fake version to see if effects due to psychology (placebo effect) or true validity
retrospective study
A study that monitors people who have been exposed to an environmental hazard at some time in the past.
Ethnocentrism
Belief in the superiority of one's nation or ethnic group.
cultural imposition
When one person imposes his or her beliefs, values, and practices on another because he or she believe his or her ideals are superior
Who is responsible for evaluating research and adopting new procedures in EMS?
Medical Director
open-ended questions
Questions that allow respondents to answer however they want
ex: "can you describe the pain for me?"
closed-ended questions
Questions that can be answered in short or single word responses
ex: ex: "do you have chest pain?"
American with Disabilities Act (ADA)
Comprehensive legislation that is designed to protect individuals with disabilities against discrimination by allowing for reasonable accommodations. Allows for guide dogs to be transported w/ pt to hospital (ex)
Shannon-Weaver Model of Communication
1) Sender
2) Encoder
3) Channel
4) Decoder
5) Receiver
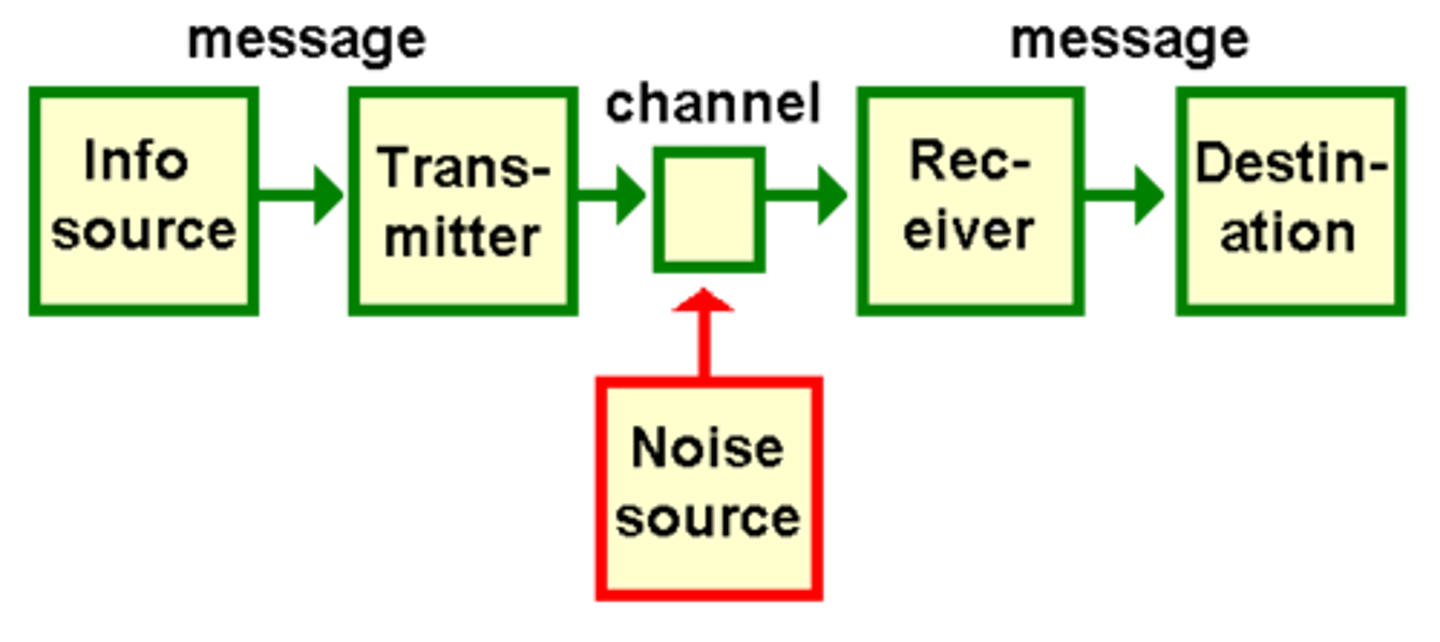
noise
anything that interferes with, distorts, or slows down the transmission of information
Proxemics
study of personal space and how distance btwn ppl affects communication
Simplex Radio
Radio using single frequency that enables transmission reception of voice or ECG signals but is incapable of simultaneous transmissions.
Duplex Radio
Can send and receive messages at the same time, can hear multiple frequencies at the same time
base station radio
A high-powered two-way radio located at a dispatch center or hospital
Mobile and portable radios
Radio that can be taken on scene or left in ambulance and communicates with hospital, dispatch, medical control, etc
mobile integrated healthcare (MIH)
A method of delivering health care which involves providing health care within the community rather than at a physician's office or hospital.
National EMS Scope of Practice Model
A document created by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) that outlines the skills performed by various EMS providers.
external public address system (PA)
Machine used to communicate with large groups of people, such as bystanders
Digital vs. Analog Signals
A signal representing values only at specific (discrete) moments in time. A signal that represents values continuously over time (analog)
computer-aided Dispatch (CAD)
Software that notifies ambulance of assignments and offers other supplemental data such as mapping
Steps of talking on the radio
1) identify yourself and party you want to reach
2) wait for response
3) acknowledge message
What federal agency regulates radio transmissions
Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
licenses call signs, allocates specific radio frequencies, establishes licensing standards + operating specifications, monitors radio operations, and establishes limitations for transmitter output
Repeater-based systems
A special base station radio that receives messages and signals on one frequency and then automatically retransmits them on a second frequency, better range and capibilities
Trunking system
A radio system that uses a shared bank of frequencies to make the most efficient use of radio resources.
mobile data terminal (MDT)
A small computer terminal inside the ambulance that directly receives data from the dispatch center such as a CAD
What determines the success of radio communications?
Efficiency of Equipment
Consent
Permission to render care, required for treatment and transport of a patient
Advance Directive
Written documentation that specifies medical treatment for a competent patient should the patient become unable to make decisions; also called a living will or health care directive.
Stages of Death
algor mortis - body cools to match temp of environment
rigor mortis - stiffening of the joints and muscles of a body
livor mortis - blood sinks w/ gravity (aka postmortem lividity)putrefaction - decay of body
Compensatory Damages
A monetary award equivalent to the actual value of injuries or damage sustained by the aggrieved party.
Punitive Damages
Monetary damages that may be awarded to a plaintiff to punish the defendant and deter similar conduct in the future.
Defamation
The communication of false information about a person that is damaging to that person's reputation or standing in the community
- libel = written
- slander = spoken
Do Not Resuscitate (DNR)
Written documentation by a physician giving permission to medical personnel to not attempt resuscitation in the event of cardiac arrest.
Requirements to properly maintain Refusal of Medical Attention (RMA)
1) adult (18+ yrs, emancipated)
2) A+O w/ decision making capacity
3) fully informed of what is happening, benefits, risks
Implied consent
Type of consent in which a patient who is unable to give consent is given treatment under the legal assumption that he or she would want treatment.
Involuntary Consent
Consent that is assumed when the patient is either mentally incompetent or legally not permitted to make his own medical decisions
4 definitive signs of death
1) decapitation
2) dependent livity
3) rigor mortis
4) putrification
Standard of care
Written, accepted levels of emergency care expected by reason of training and profession; written by legal or professional organizations so that patients are not exposed to unreasonable risk or harm.
Contributory Negligence
A legal defense that may be raised when the defendant feels that the conduct of the plaintiff somehow contributed to any injuries or damages that were sustained by the plaintiff.
Abandonment
Unilateral termination of care by the EMT without the patient's consent and/or without making provisions for transferring care to another medical professional with the skills and training necessary to meet the needs of the patient
scope of practice
Most commonly defined by state law; outlines the care you are able to provide for the patient.
Duty to Act
A medicolegal term relating to certain personnel who either by statute or by function have a responsibility to provide care.
Kidnapping/False Imprisonment
The seizing, confining, abducting, or carrying away of a person by force, including transporting a competent adult for medical treatment without his or her consent.
Good Samaritan Law
Provides limited protection to civilian who is trying to provide first aid without expectation of care as long as acting in good faith
Qualified Immunity
A defense which protects government officials from liability for civil damages insofar as their conduct does not violate clearly established statutory or constitutional rights of which a reasonable person would have known.
Forcible Restrainment
Physically preventing an individual from initiating any physical action because they are a harm to themselves and/or others. Usually done after contacting medical control and/or with law enforcement depending on state protocol
How would organ donation affect an ambulance call?
Would still treat patient as normal but may continue CPR even after death in order to preserve organs for hospital
Negligence
Failure to provide the same care that a person with similar training would provide in the same or similar situation such as a medication error or not administering oxygen when it should have been
Where can PHI be sent if requested?
Billing companies, other providers who are treating the patient, or if a subpoena is present
Who is allowed to make the official proclamation of death?
Physician
Assault
Unlawfully placing a patient in fear of bodily harm
Battery
Unlawfully touching a person such as providing care without consent
Objective statement vs subjective statement
Objective - factual such as patient complained of chest pain
Subjective - opinionated statement such as patient was drunk
What types of cases should be reported to an authority?
suspected abuse, childbirth, communicable diseases, attempted suicides, drug related injuries, restraints, death
Continuity of Care
Treatment transfers smoothly from one provider to another, so that the patient receives the most benefit and no interruption in care.
Who looks over PCR?
- hospital (RN, physician)
- legal system
prefix for slow
brady-
prefix for high/too much
hyper-
prefix for problem/dificulty
dys-
one sided
unilateral
prefix for fast
tachy-
prefix for low/too little
hypo-
prefix for absent
a-
both sided
bilateral
suffix for breathing
-pnea
suffix for related to lungs
-ary
suffix for study of
-logy
suffix for related to blood
-emia
suffix for inflammation of
-itis
suffix for procedure
-ectomy
suffix for related to pain
-algia