Anemias & Case Study Practice
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Anemia
>10% decrease in
# of RBCs per unit volume
hematocrit
hemoglobin levels
Functional definition of Anemia
decreased oxygen carrying capacity
Response to Sudden blood loss
increased heart rate, respiratory rate, cardiac input → increases oxygenated blood flow
blood flow from skin to essential organs
Response to Slowly Developing Anemia
increase in 2,3-BP → decrease in hemoglobin’s affinity of oxygen → more oxygen release to tissues
increase in erythropoietin production by kidneys → release of more RBCs
Types of Iron deficiency anemias
Pernicious anemia (B12)
Aplastic anemia (bone marrow)
Neoplasia (leukemia)
Myelofibrosis (scarring in bone marrow)
Renal disease
Blood Loss and Hemolysis
hemorrhage
menstrual flow
gynecological disorders
pregnancy
parasitism
Decrease RBC Production
Iron deficiency anemia
Blood loss and hemolysis
Intrinsic Hemolytic Anemia
thalassemia
G6PD deficiency
Sickle Cell Anemia
Hereditary Spherocytosis
Extrinsic Hemolytic Anemia
infections (malaria, mycoplasma)
Lead poisoning
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Diagnosis of Anemia
physical exam
CBC count
Bone marrow biopsy
Fecal occult blood
Iron metabolism
Macrocytic anemia
High MCV (large RBCs)
hyper segmented neutrophil
some small spherocytes and teardrop cells
Microcytic anemia
Low MCV
Megaloblastic/Macrocytic Anemia
lack of folic acid or B12
Folate (folic acid) + B12 interact → Thymidine synthesis (dTTP)
Megaloblasts in bone marrow; macrocytes in peripheral blood
Affects all proliferating cells: Skin, gut, and blood
Causes of Macrocytic Anemia
lack of folate intake (alcoholics, teenagers, some infants)
increased need - pregnancy, lactation, etc.
Malabsorption
Impaired metabolism
Causes of Iron Deficiency
blood loss
Increased iron usage (pregnancy, infancy, etc.)
Malabsorption
Dietary inadequacy
Lab Tests for iron
Serum iron levels
Unsaturated Iron Binding Capacity (UIBC)
Total Iron Binding Capacity (TIBC)
Percent saturation
Plasma ferritin
serum transferrin receptor levels
free erythrocyte protoporphyrin
tissue iron
sideroblasts (erythroblasts) and siderocytes (macrophages)
Identification of Iron Deficiency
Low MCV
Low reticulocyte count
High RDW
Low Serum Ferritin
Transferrin (TIBC) increases
Blood Smear - microcytic, hypochromic (pale RBCs); aniso- & poikilocytosis
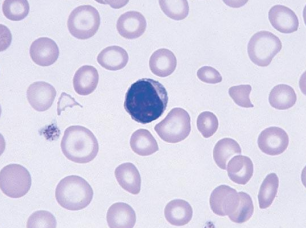
Sideroblastic Anemia
iron not incorporated into heme
ringed sideroblasts
iron in bone marrow
treated with vitamin b6
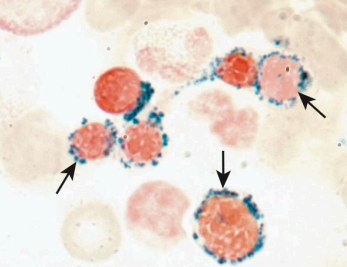
Lead poisoning (Acquired sideroblastic anemia)
inhibits ALA dehydratase and ferrochelatase
ALA and iron accumulate
High reticulocyte count and Free Erythrocyte Protoporphyrin (FEP) Test
increase of ALA in urine
Normocytic and normochromic; basophilic stippling (undegraded ribosomes)
Porphyria (Hereditary sideroblastic anemia)
deficiencies in enzymes in heme synthesis
Types of porphyrias
Cutaneous porphyria: affects skin; blisters; photosensitivity
Acute porphyria: affects nervous system (mental disorders, muscle numbness, paralysis, cramping)
RBCs may fluoresce
Hereditary Hemochromatosis
mutation in HFE (high iron) gene
HFE regulates hepcidin
overload of iron (increased iron absorption and transportation)
Effects of Hemochromatosis
RBCs most affected
skin, liver, pancreas and heart also affected (bronze diabetes)
Diagnosis of Thalassemia
CBC
Low: Hb, HCT, MCV, MCH, MCHC
High: Reticulocyte Count, ferritin + iron
Acquired Aplastic anemia
normo- to macrocytic
Low: reticulocyte count
High: serum iron
decrease in CD34+ (stem cells)
Iron Deficiency Lab Results
Low:
Iron
Ferritin
High:
TIBC
microcytosis
Anemia of Chronic Disease Lab Results
Low:
Iron
TIBC
High or normal
Ferritin
Hemochromatosis Lab Results
Low:
TIBC
High:
Iron
Ferritin