Med-tech Cardiac Test
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Gap Junctions
Specialized connections between cells allowing direct electrical and chemical communication; found in cardiac and smooth muscle.
Desmosomes
Anchoring junctions that hold cells together, providing structural integrity; prevalent in cardiac muscle and skin.
SA Node (Sinoatrial Node)
Located in the right atrium; the heart's natural pacemaker, initiating electrical impulses.
AV Node (Atrioventricular Node)
Located near the septal wall of the right atrium; delays and relays impulses from the atria to the ventricles.
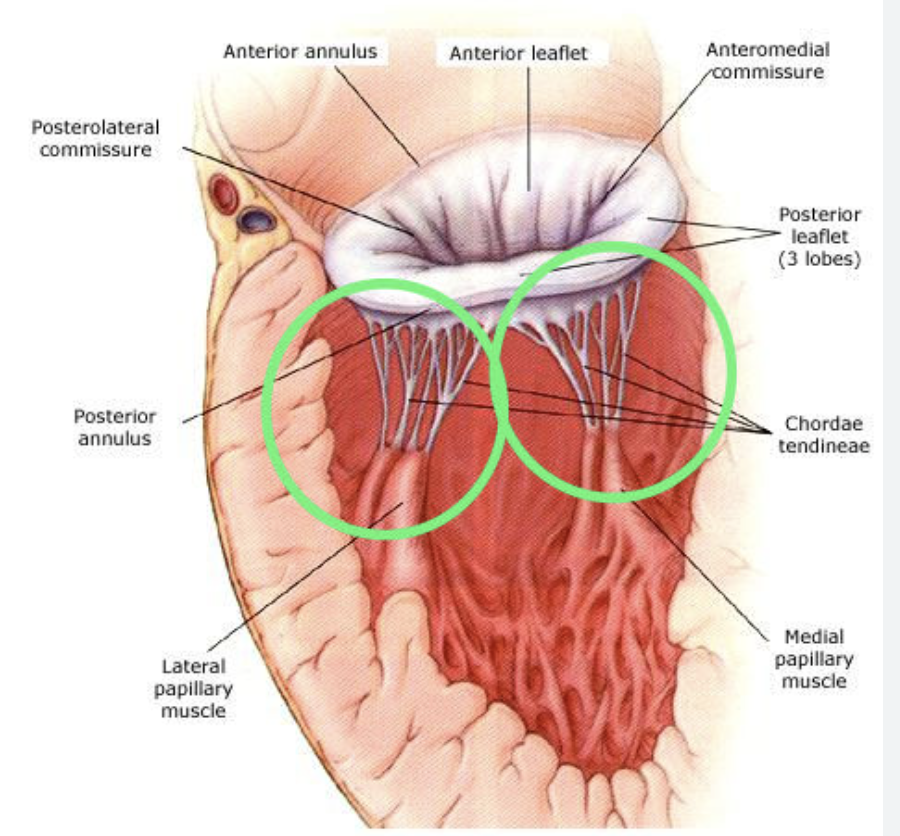
Papillary Muscles
Located in the ventricles; contract to prevent prolapse of atrioventricular valves during systole.
Chordae Tendineae
String-like structures connecting papillary muscles to valve leaflets; prevent valve backflow
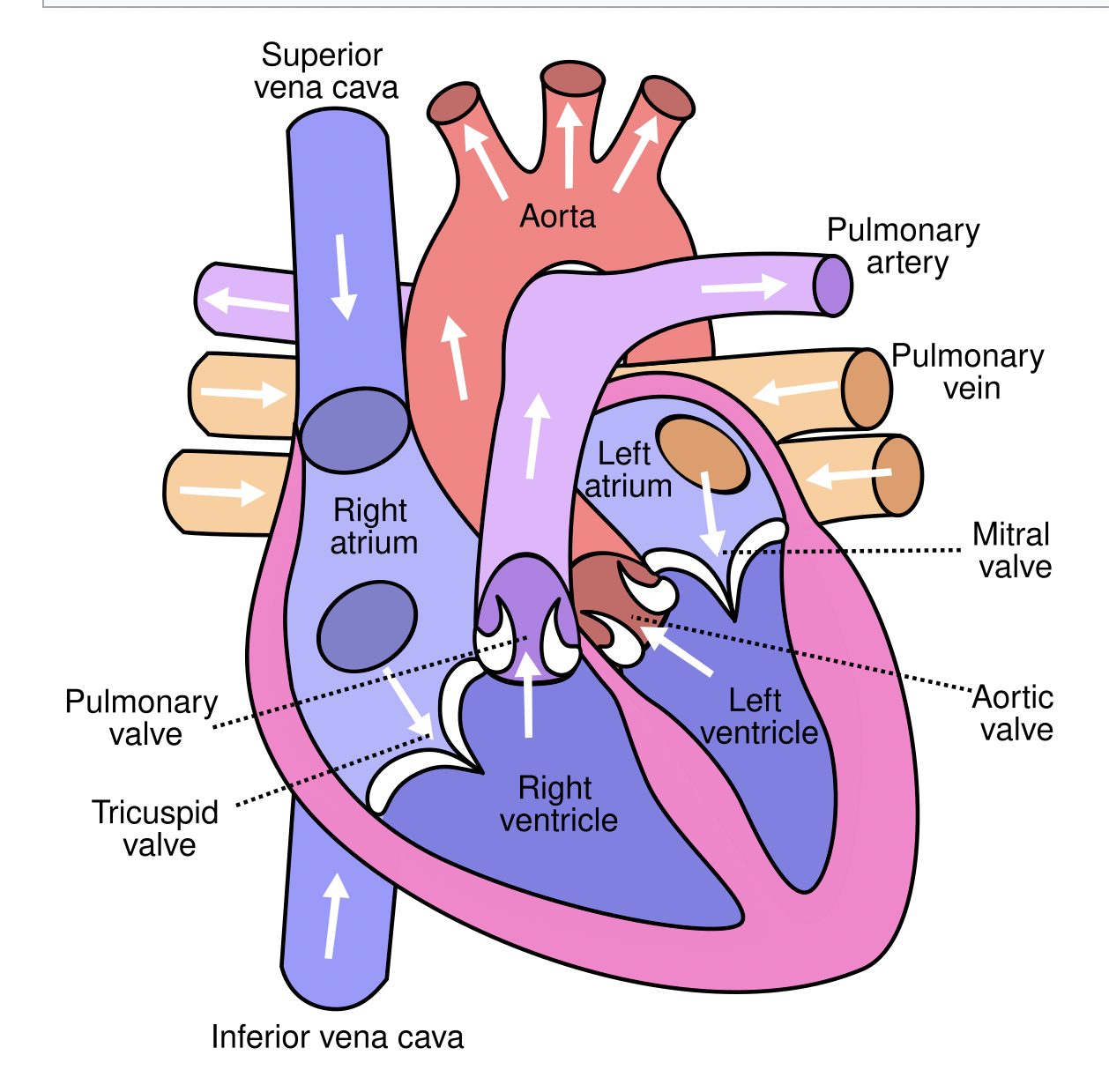
Pulmonic Valve
Located between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery; prevents backflow of blood into the right ventricle
Aortic Valve
Located between the left ventricle and the aorta; prevents backflow into the left ventricle.
Mitral Valve
Between the left atrium and left ventricle; prevents backflow into the atrium.
Cardiac Auscultation Locations:
1) Aortic Area:
2) Pulmonic Area:
3) Erb’s Point:
4) Tricuspid Area:
5) Mitral Area (Apical):
1) 2nd intercostal space, right sternal border
2) 2nd intercostal space, left sternal border
3) 3rd intercostal space, left sternal border)
4) 4th-5th intercostal space, left sternal border
5) 5th intercostal space, midclavicular line
Syncytium
A multinucleated cell-like structure enabling synchronized contraction; key in cardiac muscle
Bruit
An abnormal sound caused by turbulent blood flow, often indicative of vascular abnormalities
Innocent Murmur
A harmless heart murmur without underlying pathology, common in children
Aneurysm
A localized dilation or bulge in a blood vessel wall due to weakness
Arrhythmia
An abnormal heart rhythm caused by electrical disturbances.
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
Irregular atrial rhythm; increases stroke risk
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)
Rapid ventricular rhythm; potentially life-threatening
Bradycardia
Abnormally slow heart rate; may require pacemaker
Superior Vena Cava location and function
Location: drains the upper body into the right atrium
Function: Return deoxygenated blood to the heart.
Inferior Vena Cava location and function
Location: drains the lower body.
Function: Return deoxygenated blood to the heart.
Myocardial Infarction Causes:
Blockage of coronary arteries due to plaque rupture, thrombus, or vasospasm.
Atrial Fibrillation Side Effects:
Palpitations, fatigue, and increased risk of embolic stroke
Arterial Layers:
1. Intima:
2. Media:
3. Adventitia:
1. Innermost endothelial layer
2. Middle muscular and elastic layer
3. Outer connective tissue layer
Cardiomyopathy Causes and Effects:
Causes: Genetic factors, hypertension, alcohol, infections.
Effects: Impaired cardiac function, heart failure.
Types of Cardiomyopathy:
1. Dilated:
2. Hypertrophic:
3. Restrictive:
1. Enlarged ventricles with weakened contraction
2. Thickened ventricular walls obstructing blood flow
3. Stiffened ventricles reducing filling
Congestive Heart Failure Signs and Symptoms:
Shortness of breath, edema, fatigue, weight gain, and jugular vein distension.
Pressures in the Heart:
Highest in the left ventricle during systole due to systemic circulation demand.
First Heart Sound (S1):
Created by closure of mitral and tricuspid valves during systole
Second Heart Sound (S2):
Created by closure of aortic and pulmonic valves during diastole.
Blood Flow Through the Heart:
1. Vena cava → Right atrium → Tricuspid valve → Right ventricle → Pulmonic valve→ Pulmonary artery → Lungs.
2. Pulmonary veins → Left atrium → Mitral valve → Left ventricle → Aortic valve →Aorta → Body.
Purpose of an EKG:
Records the heart’s electrical activity to diagnose arrhythmias, ischemia, or conduction abnormalities.
P Wave:
Represents atrial depolarization (electrical) and atrial contraction (mechanical).
QRS Complex:
Represents ventricular depolarization (electrical) and ventricular contraction (mechanical).
T Wave:
Represents ventricular repolarization (electrical) and ventricular relaxation (mechanical)