AQA Chemistry A Level - Amount of Substance
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Relative atomic mass (Ar)
The average mass of an atom of an element relative to 1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon-12
Calculate the relative atomic mass of chlorine. The abundance of chlorine-35 is 75%, and chlorine-37 is 25%
((35 x 75) + (37 x 25))/100
3550/100
=35.5
Relative formula mass (Mr)
The total number of relative atomic masses for all atoms in a compound relative to 1/12 the mass of a 12C atom
Avogadro constant (L)
6.02 x 1023
number of particles = moles x L
e.g. 1 Cu atom has a mass of 1.055 x 10-22g, so 6.02 x 1023 Cu atoms have a mass of 63.5g
Moles
mass = Mr x moles
The ideal gas equation
PV = nRT
P = pressure (Pa)
V = volume (m3)
n = number of moles (mol)
R = constant
T = temperature (K)
0 Kelvin to Celsius
0 K = -273 C
273 Kelvin to Celsius
273 K = 0 C
298 Kelvin to Celsius
298 K = 25 C
kPa to Pa
x1000
1 KPa = 1000 Pa
Volume conversions
1m3 = 1000dm3 = 1,000,000cm3
1L = 1dm3
4LiNo3(s) ---> 2Li2O(s) + 4NO2(g) + O2(g)
2.17g sodium nitrate heated until constant mass. Calculate the volume of gas produced at 298K and 110KPa. Gas constant = 8.31JK-1mol-1
V = (nRT)/P
moles = mass/Mr = 2.17/68.9 = 0.0315 mol
4 LiNO3 produces 5 mol of gas = 0.0394 mol
V = (0.0394 x 8.31 x 298)/110000 = 0.000887m3
= 0.887dm3
Empirical formula
The simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound - can be an odd number even if a diatomic molecule
Molecular formula
The actual number of atoms of each element in a compound, same as empirical if the empirical formula mass = molecular mass
Mass, moles and weight
Mass of substance(g) = molecular weight/number of moles
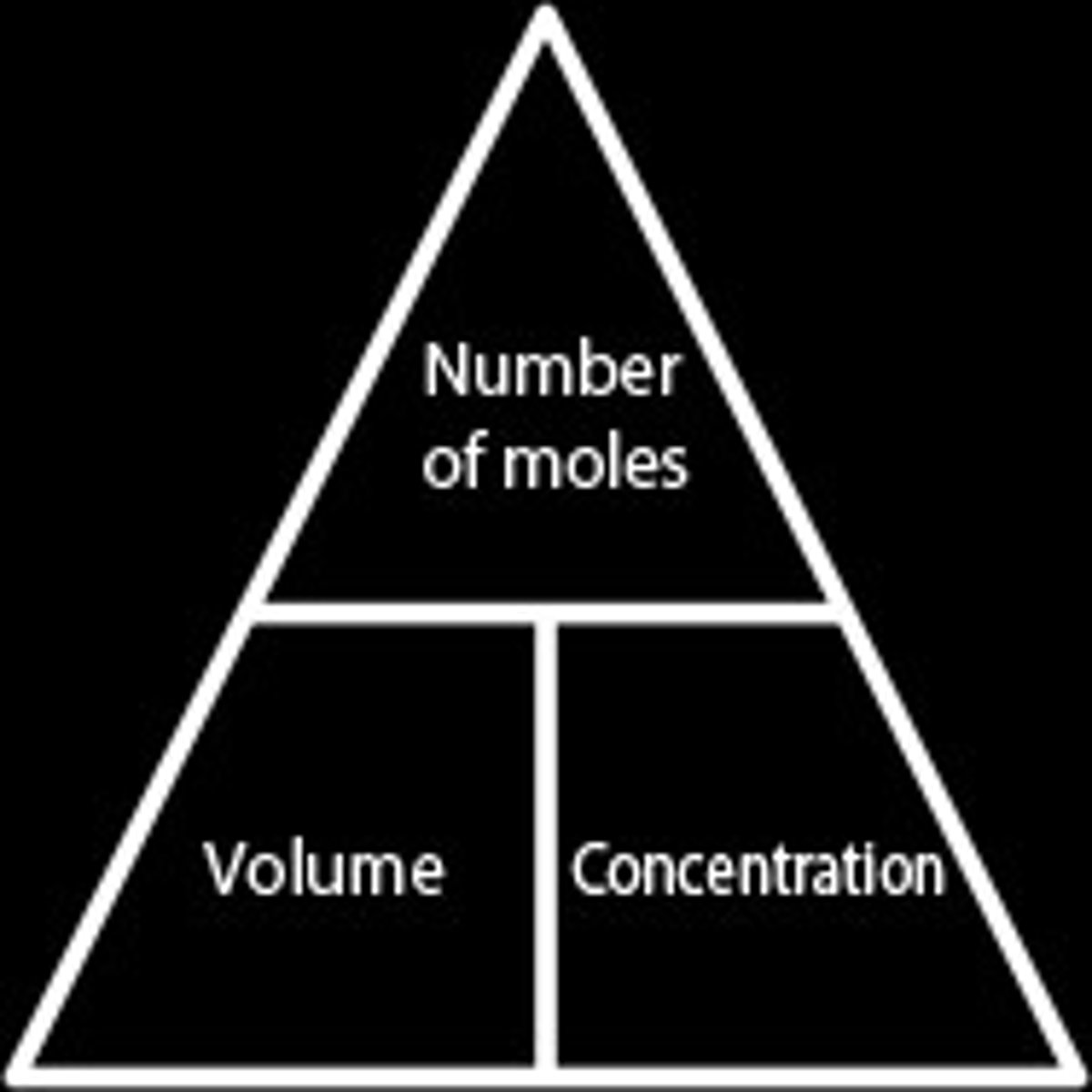
Moles, concentration, volume
Moles = concentration(mol/dm3) x volume(dm3)
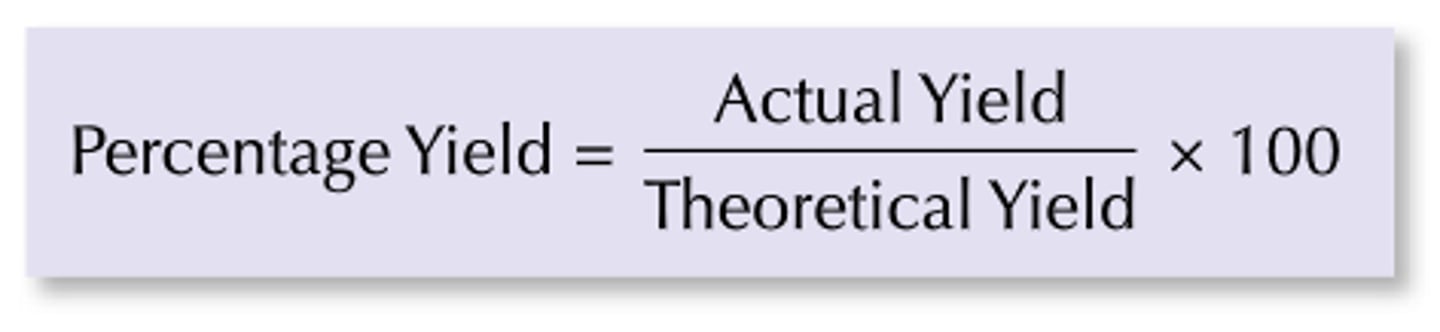
Percentage yield
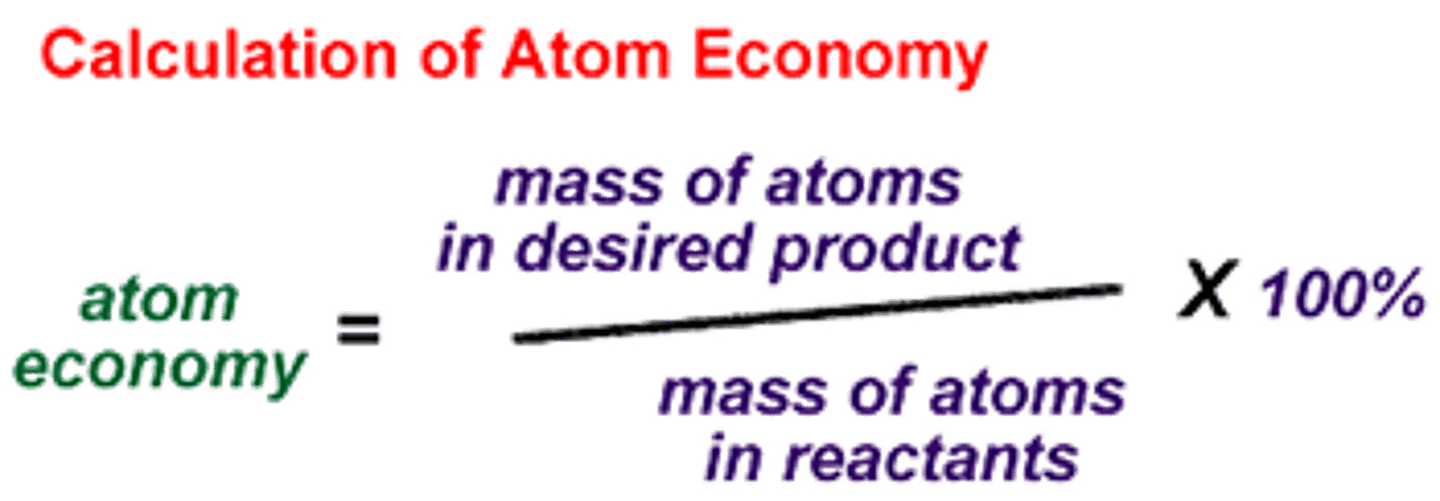
Atom economy
(include the moles e.g. if 4H2O its 4 x 18)
Why should small amounts of reactant not be used sometimes?
Percentage errors too high
Why should large amounts of reactant not be used sometimes?
Incomplete decomposition/combustion etc
Apart from cost, suggest one advantage of using magnesium hydroxide rather than magnesium carbonate to reduce acidity in the stomach
No gas/wind will be produced
Why would the mass of a solid obtained in an experiment have a slightly lower mass than expected
Solid may have been blown away with the gas, some of solid lost when weighing product
What is a mole
the Avogadro number of particles in a substance
Difference between pipette and burette
Pipette measures a certain volume whereas a burette measures a not set volume of a known concentration
Convert cm3 to dm3
Divide by 1000
Ethanol boiling point = 78C
Water boiling point = 100C
How is distillation used to separate a mixture of ethanol and water
Boil ethanol over 78C and under 100C so the water doesn't evaporate
Will be left just with the water
Condense the vapour
Platinum, palladium and rhodium are metals used inside catalytic converters. Explain why a thin layer of metal is used on a honeycomb ceramic support
- reduce the amount of metal used
- increase surface area
Refrigerator contains 1.41kg of CF3CH3. Calculate the number of molecules of CF3CH3 in the fridge (avo constant = 6.022 x 1023
Mr = 84
moles = 1410 / 84 = 16.79
16.79 x 6.022 x 1023 = 1.01 x 1025
Acid + base/alkali =
salt + water
Acid + metal
salt + hydrogen
Acid + carbonate
salt + water + carbon dioxide
How to find number of protons, neutrons, electrons
protons = atomic number
electrons = atomic number
neutrons = mass number - atomic number
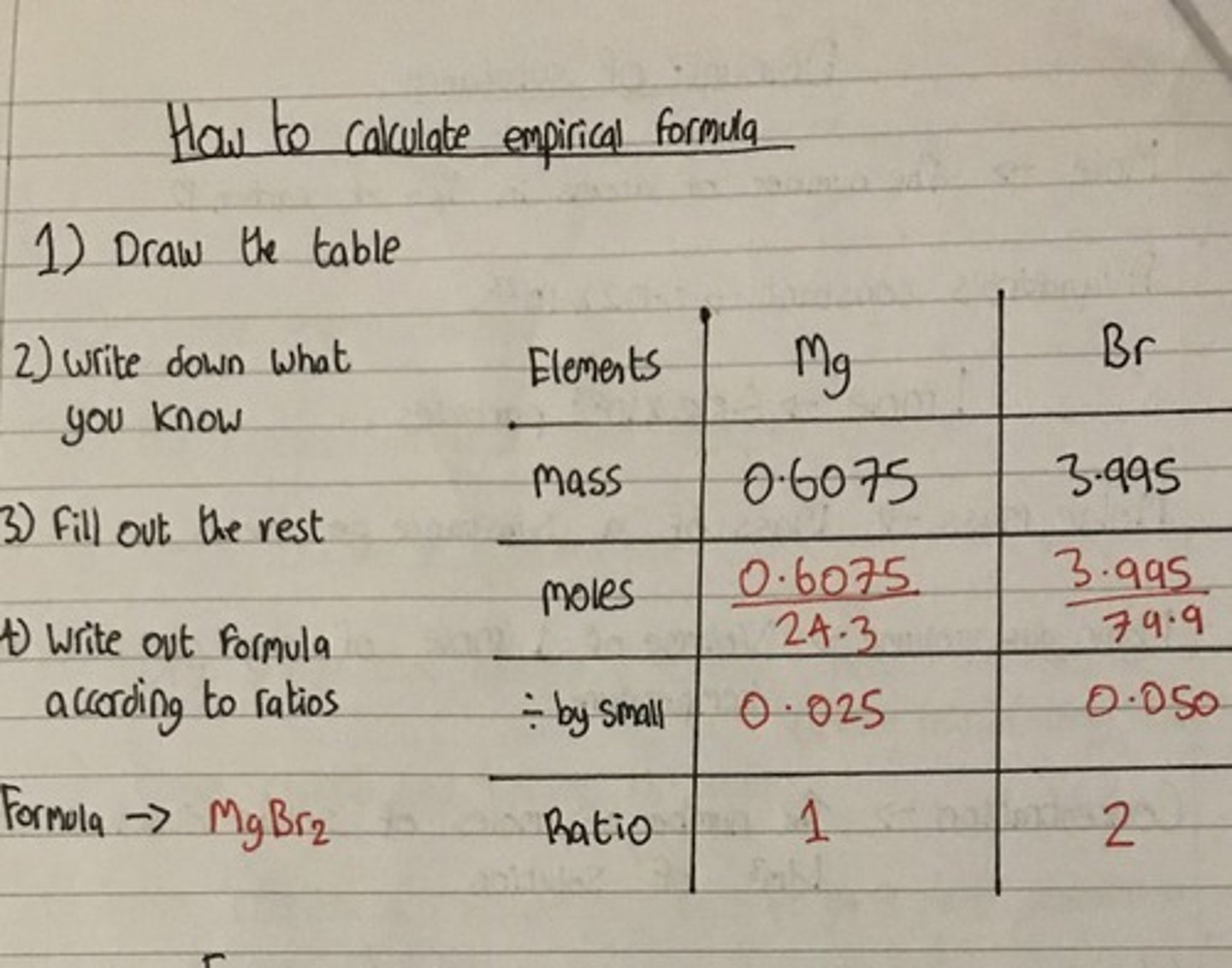
How to calculate empirical formula
divide the percentages given by the molecular mass of the element; then divide everything by the lowest number you get
How to calculate molecular formula
Add the Mr of empirical formula (e.g. if C3H7 it would be 43) and compare the number with the relative molecular mass of the compound we're finding the formula of (e.g. 86). See how many times the empirical formula Mr (43) fits into the number given (86) - (answer for this e.g. is 2 because 86/43). Times the empirical formula by this number so it would be C6H14
cm3 to dm3
divide by 1000
dm3 to cm3
x1000
mg to g
divide by 1000
1000mg = 1g
g to mg
x 1000
cm3 to m3
divide by 1,000,000
m3 to cm3
x 1,000,000
Percentage uncertainty
(Absolute uncertainty / measurement) x 100

Why does washing the conical flask with deionised water improve accuracy of titrations
Ensures there is no acid left over
What is a concordant titre
Within 0.1cm3 of each other
Ideal gas equation to find moles
PV/RT
Ideal gas equation to find pressure
nRT/V
Ideal gas equation to find volume
nRT/P
Ideal gas equation to find temperature
PV/nR
In view of low atom economy, suggest how a company can maximise its profits without changing the reaction conditions or production costs
Sell the product that isn't desired
If doing a table to find moles, Mr etc, don't use the moles to work out Mr e.g. if 2H2O the Mr is 18 not 36
-
What is the colour change when HCl is added to a sodium hydroxide solution containing phenolphthalein indicator
Pink to colourless
Titration
a measured amount of a solution of unknown concentration is added to a known volume of a second solution until the reaction between them is just complete
Describe the process of heating the sample of hydrated copper chloride to constant mass
Weight an empty container
Put hydrated copper in it
Weigh again with the copper in it
Heat, weigh, repeat
Until consecutive mass measurements are the same
Number of particles =
Number of moles x Avogadro's constant
The student noticed that some of the liquid injected into the gas syringe did not vaporise. Explain the effect this would have on the Mr calculation
Mr value would be greater than actual because lower volume would've been recorded so fewer moles calculated
Suggest one reason why it is difficult to obtain a pure sample of nitrogen dioxide from this reaction:
Pb(NO3)2(s) --> PbO(s) + 2NO2(g) + 0.5O2(g)
Hard to separate the two gases
An impure sample of zinc powder with a mass of 5.68g was reacted with hydrogen chloride gas until the reaction was complete. The zinc chloride produced has a mass of 10.7g. Calculate the percentage purity of the zinc metal
Zn + 2HCl --> ZnCl2 + H2
Moles ZnCl2 = 10.7/136.4 = 0.0784
Moles Zn = 0.0784
Mass Zn reacting = 0.0784 x 65.4 = 5.13g
(5.13/5.68) x 100 = 90.2%
Calculate the mass, in kg, of one atom of 49Ti
Avogadro = 6.022 x 1023
49g in one mole
= 0.049kg
0.049 / 6.022 x 1023
During the titration the student washed the inside of the conical flask with some distilled water, why doesn't this give an incorrect result
It doesn't react with the alkali so doesnt change moles or conc or vol
Explain why an air bubble increases the final burette reading of the rough titration
Air bubble takes up room that would be the solution so takes further for the solution to go
The equation below represents the complete combustion of butane C4H10(g) + 6.5 O2(g) --> 4 CO2(g) + 5 H2O(g)
20 cm3 of butane are completely burned in 0.20 dm3 of oxygen. Which statement is correct? All volumes are measured at the same temperature and pressure
A 40 cm3 of carbon dioxide are formed
B 0.065 dm3 of oxygen react
C 70 cm3 of oxygen remain
D 0.50 dm3 of steam are formed
1 : 6.5 ratio
So need 130cm3 O2 to burn 20cm3 butane
200cm3 of O2 is used
200-130 = 70cm3 leftover
C
When heated, a sample of KClO3 produced 67.2cm3 of oxygen, measured at 298K and 110kPa
2KClO3 --> 2KCl + 3O2
What is the amount, in moles, of KClO3 that has decomposed
Gas constant = 8.31
n = PV/RT
110,000 x 0.0000672/8.31 x 298
= 2.985 x 10-3 (moles of O2)
(2.985 x 10-3/3) x 2
= 1.99 x 10-3
In a titration 25cm3 of KOH is added to a conical flask using a pipette. 3 drops of indicator are added and nitric acid is added from a burette until the indicator changes colour. Which of the following would lead to a larger titre than it should be
- rinsing the conical flask with water before adding KOH
- rinsing the burette with water before adding HCl
- rinsing the pipette with water before adding KOH
- adding extra drops of indicator
B because will dilute the HCl, so more of it will be needed, so larger titre
A and C would dilute KOH so less HCl needed for neutralisation so smaller titre
Extra indicator has no effect
How many protons are in 6g of nitrogen gas?
Moles N2 = 6/28 = 0.214
Number of molecules = 0.214 x 6.022 x 1023 = 1.289 x 1023
N2 has 14 protons so 1.289 x 1023 x 14 = 1.8 x 1024
Some of the liquid injected did not evaporate because it dripped into the gas syringe nozzle outside the oven.
Explain how this would affect the value of the Mr of Y calculated from the experimental
results
Lower volume recorded
Mr would be greater
A student added 627 mg of hydrated sodium carbonate (Na2CO3.xH2O) to 200 cm3 of 0.250 mol dm-3 hydrochloric acid in a beaker and stirred the mixture. After the reaction was complete, the resulting solution was transferred to a volumetric flask, made up to 250 cm3 with deionised water and mixed thoroughly. Several 25.0 cm3 portions of the resulting solution were titrated with 0.150 mol dm-3 aqueous sodium hydroxide. The mean titre was 26.60 cm3 of aqueous sodium hydroxide. Calculate the value of x in Na2CO3.xH2O Show your working. Give your answer as an integer.
Na2CO3.xH2O + 2HCl --> H2O + 2NaCl + CO2
HCl + NaOH --> H2O + NaCl
M1 HCl added = 0.050 mol and NaOH used in titration = 3.99 x 10-3 mol 1
M2 So moles that would be needed to neutralise total excess HCl = 3.99 x 10-3 x 10 = 3.99 x 10-2 mol Alternative: divide moles HCl by 10 = 0.005 and 0.005 - 3.99 x 10-3 = 0.00101 1
M3 Therefore the moles of HCl reacted with the Na2CO3.xH2O = 0.050 - 3.99 x 10-2 = 0.0101 mol Alternative: 0.00101 x 10 to produce 0.0101 1
M4 So moles Na2CO3.xH2O reacted with the HCl = 0.0101 /2 = 5.05 x 10-3 mol 1
M5 Conversion of mg to g = 0.627 (g) or 627 x 10-3 (g) 1
M6 xH2O = 0.627/5.05 x 10-3 -106.0 = 18 (.16) Alternative: mass Na2CO3 that reacted with the HCl 5.05 x 10-3 x106.0 = 0.5353 g and mass H2O = 0.627- 0.5353 = 0.0917 g 1
M7 so x =1 Alternative: 0.0917 /18.0 = 5.094 x 10-3 so ratio Na2CO3 to H2O = 1:1.009 ie 1:1 so x = 1