Week 2 - BU111
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
KSF
drivers of any solution/strategy
factors to consider for long-term success
more about daily actions and considerations
Whats the difference between diamond-E and KSF
Diamond-E is about getting the right strategy for the organization and ensuring the organization can execute that strategy
Where do critical success factors come from?
They are related to all of the activities and resources that are crucial to business success in the short and the long-term.
What are the CSF
1) Employees - enable operation
2) Customers - provide revenue
3) Products/Services - revenue means
4) Innovation - environmental alignment; improvement
5) Uniqueness - market advantage
What are all the factors connected by?
they don’t perform independently
Financial performance which enables growth
The internal choices impact your potential financial performance both by how they directly affect financial performance and indirectly through their impact on other drivers.
What are employees doing?
creating value for customers as customers create revenue which motivates the company
the human resources that work for you (either paid or voluntarily)
execute the organization’s daily activities and determine and execute its strategies
What do customers pay for?
Products and services (this is what results in the revenue)
Innovation
Changing to improve and become more efficient or effective at what you do
changing to ensure the best position within the environment
Uniquness
allows you to attract resources and opportunities more easily
able to attract and retain customers due to differentiation/customers believing it serves better
Financial Reosources
allows to pay for resources needed for the organization
if there are extra resources, this can be used for growth
Traits of an employee
LOYAL: committed to the profession (not changing to other employments)
considers the organization’s success as theirs
goes above and beyond
psychologically and emotionally committed to the company and its success
Customer satisfaction
speak highly/promote products to others
satisfied services, where they avoid to go to competitors
Quality Products and Services
not every business needs to offer the same quality
businesses needs to offer the quality customers expect
ex. Walmart offers good quality @ low price, Holt Renfrew offers high quality & luxury
provide that level of quality, consistently and reliably
delivering value by deciding what features you will include (or not) and producing at a level of quality that customers view as appropriate for the price paid
“you get what you pay for”
willing to accept compromises in quality and/or features if
they are paying a lower price
Innovation and creativity
means developing and/or implementing new approaches to what you do (with strategies to hiring new employees)
includes what products and services you offer
Distinctive Competitive Advantage
being different from your competitors (strategically/financially valuable)
serving a particular group of customers better
more innovative
produce more cheaper
access to better quality inputs
Financial Performance
being profitable so that your operations can continue
doing as well as your competitors with respect to the return your company makes on money invested
achieved through good strategic decision and financial resources
Summary of KSF
1) Committed Employees - loyal, productive
2) Customer satisfaction - Loyal advocates/promote
3) Quality products/services - value, consistency, reliable
4) Innovative and Creativity - valuable
5) Distinctive Comparative Advantage - Valuably & sustainable differentiation from competitors
Financial Performance - Comparatively better & improving profit, ROI
Achieving KSF (employee)
offering higher salaries, more vacation, more flexible hours
depends on workplace qualities will attract and retain employees will depend on the environment from which they are drawn
Achieving KSF (customer)
meeting customer needs
first: select specific customers upon which to focus
then: to understand the target market
Achieving KSF (products/services)
what quality levels to pursue and how many features to add
Customers identify what they expect as “quality”
“Value” can describe quality & price, form, taste, convenience
To deliver the desired “quality” you need to think about the inputs you use = better outputs
To make a valuable product to sell, you need to combine good materials (inputs) using effective processes
processes allow consistency & with a quality control process ensuring that it has the same reliability
Achieving KSF (innovation)
how you structure and reward innovative activities is an internal decision, but the external environment determines what would be innovative versus just a change
need a workplace that encourages new ideas that challenge the status quo and encourage taking some risks
reward innovation - public recognition that ideas are being implemented and recognition of those that develop them encourage others to do the same
Achieving KSF (uniqueness)
achieved by understanding what your competitors are doing and what the market values
need to know what everyone else is doing before you can identify what would make you different
understand what the market values before you can say that the difference is going to be advantageous
develop capabilities that make you better
Resources that are rare and can’t be easily acquired by competitors can also give you a distinctive advantage
Achieving KSF (financial performance)
by the actions you choose to take such as what prices you charge, how much money you borrow and what interest expenses you pay
determined by economic conditions that drive customer spending, and interest rates that determine borrowing costs
Achieving KSF Summary
1) Employee - hire, train, motivate
2) Customer - Target, understand, anticipate, and satisfy
3) Product/Services - Define, inputs, processes
4) Innovation - Culture, structure, rewards
5)Uniqueness - Competitor & market insight; Unique resources or capabilities
Financial Performance - Sound strategic decisions; Efficient & effective execution
Whats KPI
Key Performance Indicator
provide management with performance feedback that link back to the key activities needed for success in each area
HELPS: identify and anticipate problems, causes of problems and identify explicit targets to work toward to improve performance
How committed employees linked to financial performance:
committed employees are more productive, which reduces the operation cost of the organization
reduces indirect and direct costs, as retaining employees reduces the indirect costs of lowered productivity
instead of hiring and training - helping maximum effectiveness
What do uncommitted employees tend to do?
leave the company
Committed employees & Quality Products/Services
ensure P&S are free of defects and best quality possible
Committed employees & Customers
ensure customers are treated the way they want to be treated with pride for customer satisfaction
Committed employees & Innovation
more likely to seek and share innovations that are likely to result in improvements or new, beneficial activities and actions
Risks/Mitgations with Employees
RISK: have the ability to control their efforts towards the organization and can leave the organization if they don’t find their work as satisfying
MITIGATION: the creation of a positive working environment where employees feel respected and valued, and they can meet their personal goals as they meet company goals
“good fit” determined as
their skills, knowledge and talents ensure that they can perform well in the tasks
you give them
“Fit” with respect to values, attitudes, and work style is important for the individual to feel like she belongs in the organization
“Fit” with respect to job requirements means the individual has the ability to execute the job well.
Once an employee is hired…
1) train
2) motivate - behaviours that you believe will contribute to organizational performance by identifying and rewarding those choices and by granting the rewards so the employee feels valued
3) the outcome is retaining
What would happen if committed employees leave and how to avoid?
face costs and lowered productivity to replace them
competitors benefit from the skills and knowledge these employees acquired while working for you
SOLUTION: rewarding their performance but also offering them opportunities to move up and around in the organization, learn and grow, and design the job so that they are happy doing it
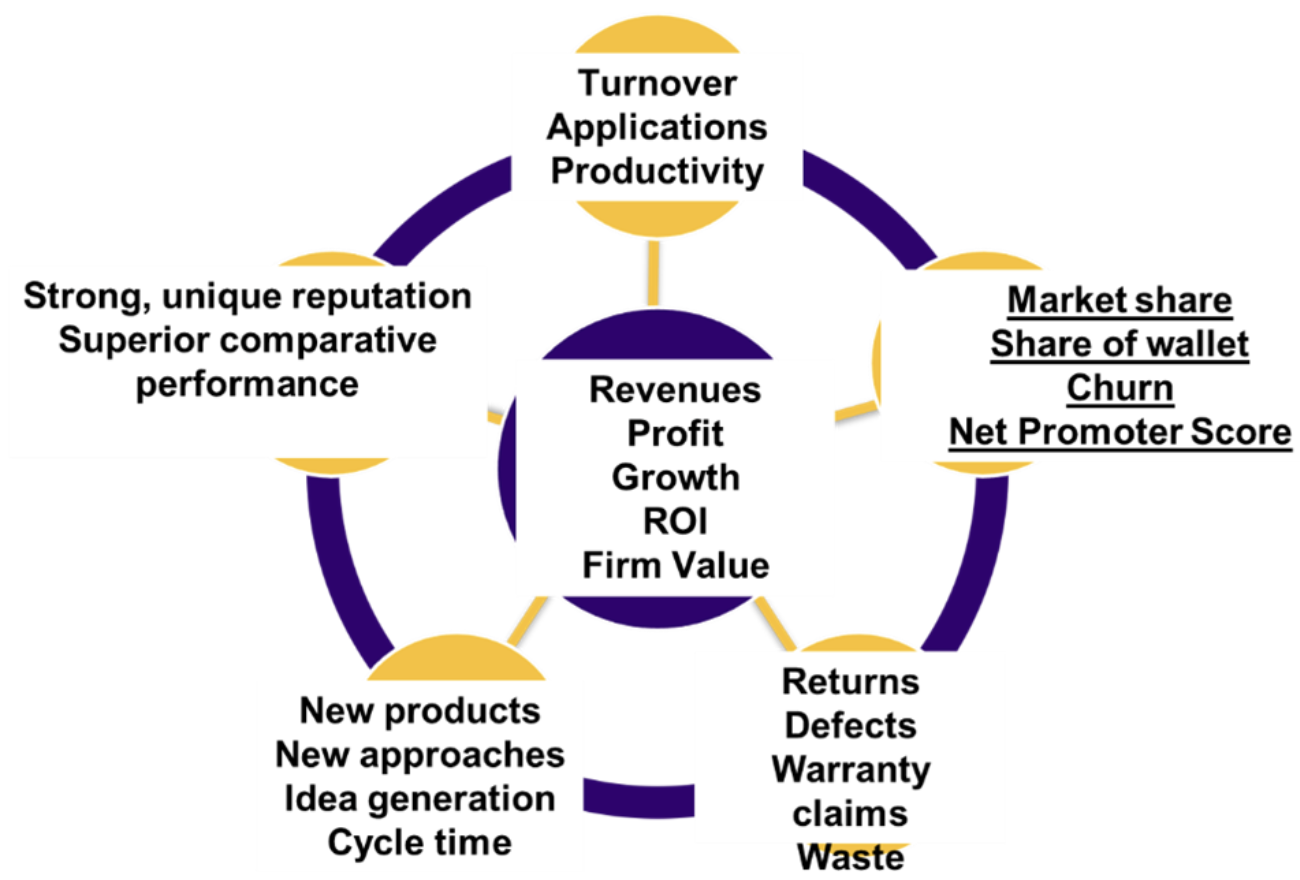
POSITIVE KPI Employee
TURNOVER/PRODUCTIVITY IS MOST IMPORTANT FOR EMPLOYEE COMMITMENT
low turnover rate: the costs you will incur to hire, train and wait for new people to become productive
(high means good) brand equity: the reputation of the employee, which is an indication of how attractive you are from the applications you receive
productivity: how efficiently the employee works in the industry
Low Absenteeism -consistently show up for work, ensuring smooth operations
whats is turnover
Turnover is the percentage of your employees that leave and must be replaced each year
1) Increased Cost - hiring new employees
2) Lower Productivity - till they reach full productivity
NEGATIVE KPI employee
high turnover rate
high absenteeism - “leading indicator”
low brand equity
Difference between profit and non-profit customers in an organization
PROFIT: customers provide the revenue that allows the company to cover its costs and ultimately generate a profit
NON-PROFIT: filling the needs of customers is the reason organizations are formed
Employees & Customers
if the products you create do not make
customers happy, it is more challenging for your employees to feel proud of the company
Products/Services & Customers
determine the ideal features and quality they want in a product or service
Innovation & Customers
their needs and wants inspire and drive product and service innovations
Uniquness & Customers
the target market will have different wants, needs and characteristics from other customer segments, where you need understand what to do differently to satisfy customers
How do you meet organizational success, while focusing on customer needs
having many customers (depending on your strategy), where they are satisfied, loyal and advocate for your organization
What are the steps to this success of focusing on customer needs
1) Target Market - give you the most value
2) to understand what that customer wants (decisions such as convenience, appearance, status, comfort, and safety)
3) Anticipating customer needs is away to continue to keep them loyal by anticipating future needs
4) making sure that the customer believes you are delivering what the customer wants or is expecting – satisfying the need or want.
KPI Customer
Market Share - (the portion of total market revenues that you earn) compared to other firms of similar size in your industry is an indication of how consumers view you (HIGH means your product appeals to many consumers and is comparatively more attractive than your competitors your product appeals to many consumers and is comparatively more attractive than your competitors’)
Share of Wallet - the percentage of a
customer’s total spending on your type of product is spent on your product
Churn Rate - how many customers leave you for your competitors every year YOU WANT LOW
Net Promoter Score (NPS) - likelihood that your customers would recommend you to someone else (high means customers are advocating for you)
KPI Product/Services
1) Performance reflected on returns - the percentage of products returned (did not deliver the “value” expected or perhaps does not do so consistently)
2) Defects and warranty - a product is not delivering the expected level of reliability
3) Waste - measures efficiency by comparing inputs to outputs. It reflects process consistency and input quality; better inputs often lead to less waste
KPI - Innovation
1) Idea Generation - starting point for innovation, measuring how many are put forward is valuable, and is an indicator of whether the culture, rewards and/or structure encourage ideation as well
2) Proportion of Ideas - Track the proportion of ideas that result in new products or approaches and Compare this proportion to competitors.
3) Cycle Time - how quickly an idea becomes an adopted approach or product (shorter the better)
KPI - Uniquness
1) Market Research - if the company is known for something specific and unique (strong reputation)
2) Financial statements - comparing to competitors and looking at: Better gross margins. Ability to charge higher prices while retaining customers. Lower production costs
3) To see if a company does better than competitors on key performance indicators
Employee & Financial Performance
More money means it can afford to pay its employees better, offer them nicer work environments and better benefits.
Customer - Financial Performance
More money means it can invest in market research to better understand its customers and thereby fill their needs, but also attract more customers through advertising
Product/Services - Financial Performance
create quality products and services by investing in technology that helps standardize the production process and test quality before the product reaches the customer
Innovation - Financial Performance
fuel innovation through investments in research and development
Unique - Financial Performance
create a unique reputation by promoting its activities and its unique features so that the market is aware of how it is different from competitors in a valuable way or acquire resources and capabilities that allow it be better than competitors
SUMMARY of KPI