Biology 115 Exam 2
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Review (from 2021-2022 Fall Semester)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Identify chromosome number. In the following image, cell A has _______ chromosomes and cell B has ________ chromosomes
a. 6, 6
b. 6, 3
c. 12, 6
d. 3, 6
a. 6, 6
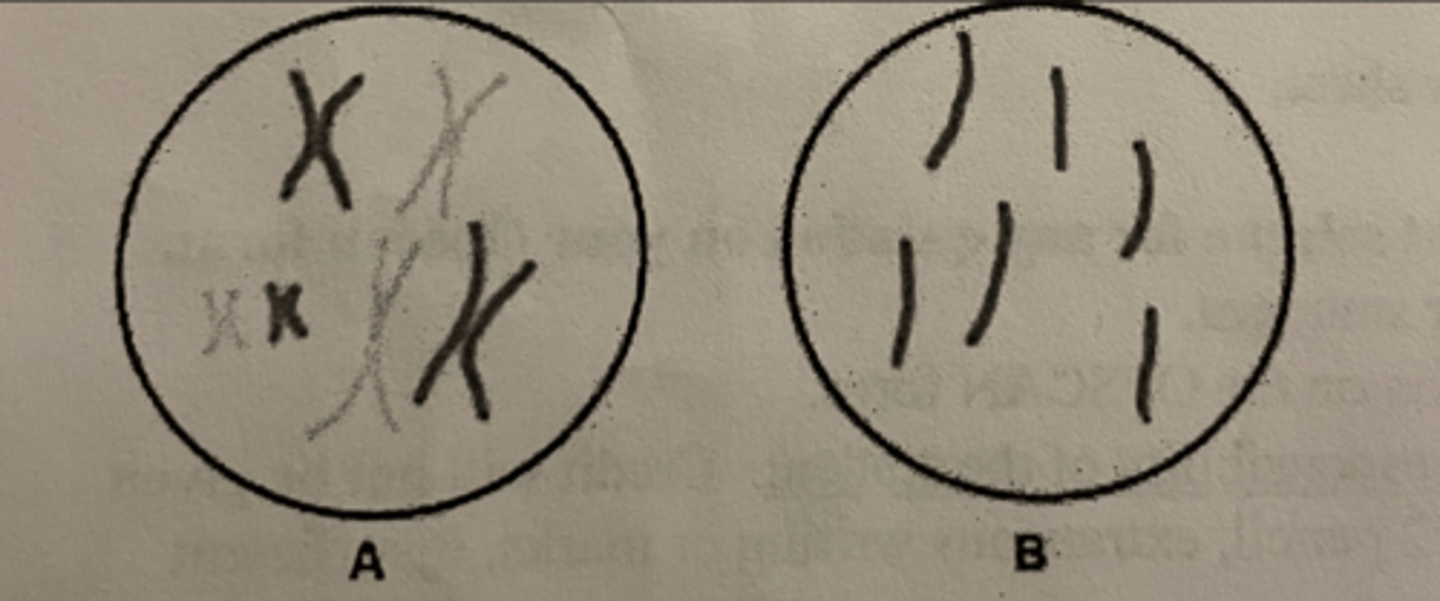
White-tailed deer have 70 chromosomes in each of their kidney cells. During the cell cycle of a deer kidney cell, there are _______ chromosomes in the cell during interphase and ______ chromosomes in the cell during the mitotic phase.
a. 35; 70
b. 70; 35
c. 35; 35
d. 70; 70
d. 70; 70
A cell that is in the M phase of the cell cycle is exposed to a toxin that prevents the separation of identical DNA molecules. Hypothesize which of the following will be the most immediate outcome.
a. The sister chromatids will not move to opposite poles
b. The microtubules will not depolymerize.
c. The nuclear envelope will not break down.
d. The chromosomes will not line up.
a. The sister chromatids will not move to opposite poles
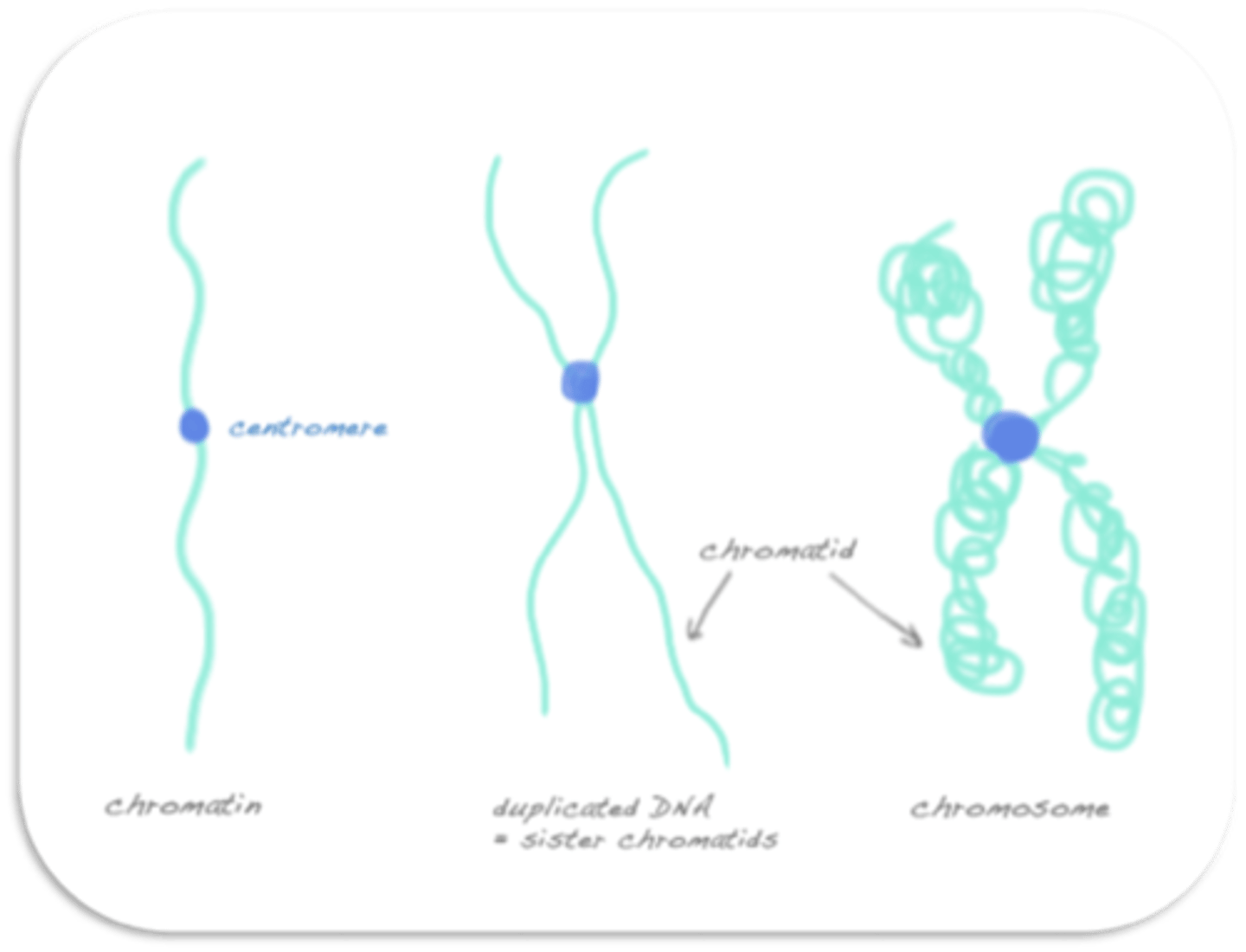
(Image of chromosomes Q#4)
In the following image, Y is a _____ and Z is a _____.
(Y is the image on the far most right, Z is the entire image in the middle)
a. sister chromatid, centromere
b. kinetochore handles, chromosomes
c. chromosome, centromere
d. chromosomes, sister chromatid
d. chromosomes, sister chromatid
A cell in G1 is diploid and has 34 chromosomes. What is the ploidy of the daughter cells after this cell goes through mitosis?
a. 2n=34
b. n=34
c. 2n=17
d. 2n=68
a. 2n=34
Correctly SEQ the following events in the cell cycle starting with the start of S phase.
I. DNA is replicated
II. Nuclear envelope reforms
III.Chromosomes condense
IV. Mitotic spindle fibers attach to the kinetochores
V. Sister chromatids move to opposite sides of the cell
I, III, IV, V, II
SEQ mitosis and meiosis. During which stage[s] of mitosis and meiosis do sister chromatids separate?
I. Anaphase
II. Anaphase I
III. Anaphase II
I and III
A scientist is studying the cell cycle. She lyses several cells and runs an assay for cell components. Her sample shows high levels of helicase and SSBP (single-stranded binding proteins.) In which stage of the cell cycle are her sample cells currently?
a. Metaphase
b. Anaphase
c. Interphase
d. Prophase
c. Interphase
Compare and contrast life cycles. Which of the following occur in the lifecycle of BOTH a fungus and an animal?
I. fertilization
II. mitosis
III. meiosis
IV. 2n cells
V. haploid cells
I, II, III, IV, and V
SEQ meiosis. During which phase of meiosis is ploidy reduced?
a. Second meiotic division
b. First meiotic division
c. S phase of interphase
d. Interkinesis
b. First meiotic division
Aedes aegypti (mosquitos) have 6 chromosomes in their somatic cells. In males, specialized cells undergo meiosis to produce sperm. Those cells that are undergoing meiosis contain ______ chromosomes during prophase I and ______ chromosomes during prophase II.
a. 6; 6
b. 3; 12
c. 6; 3
d. 3; 6
c. 6; 3
SEQ the process of meiosis. You have found a plant cell that has a ploidy of 20n and 2000 chromosomes. A cell from this plant in metaphase II has a ploidy of __________ and the number of chromosomes is ______________.
a. 20n, 1000
b. 10n, 500
c. 10n, 1000
d. 20n, 2000
c. 10n, 1000
Identify the stage of meiosis where the cell(s) is/are haploid.
a. S phase of interphase
b. Prophase I
c. Interkinesis
d. Metaphase I
c. Interkinesis
Identify which of the following is a benefit of asexual reproduction
a. Need to find a mate
b. Genetic variation
c. Mutations take a toll
d. Only a single parent
d. Only a single parent
(Image with 4 different stages, Q#15)
Compare and contrast stages of meiosis. Which of the following images depicts a cell in Metaphase II?
a.IV
b. I
c. II
d. III
d. III
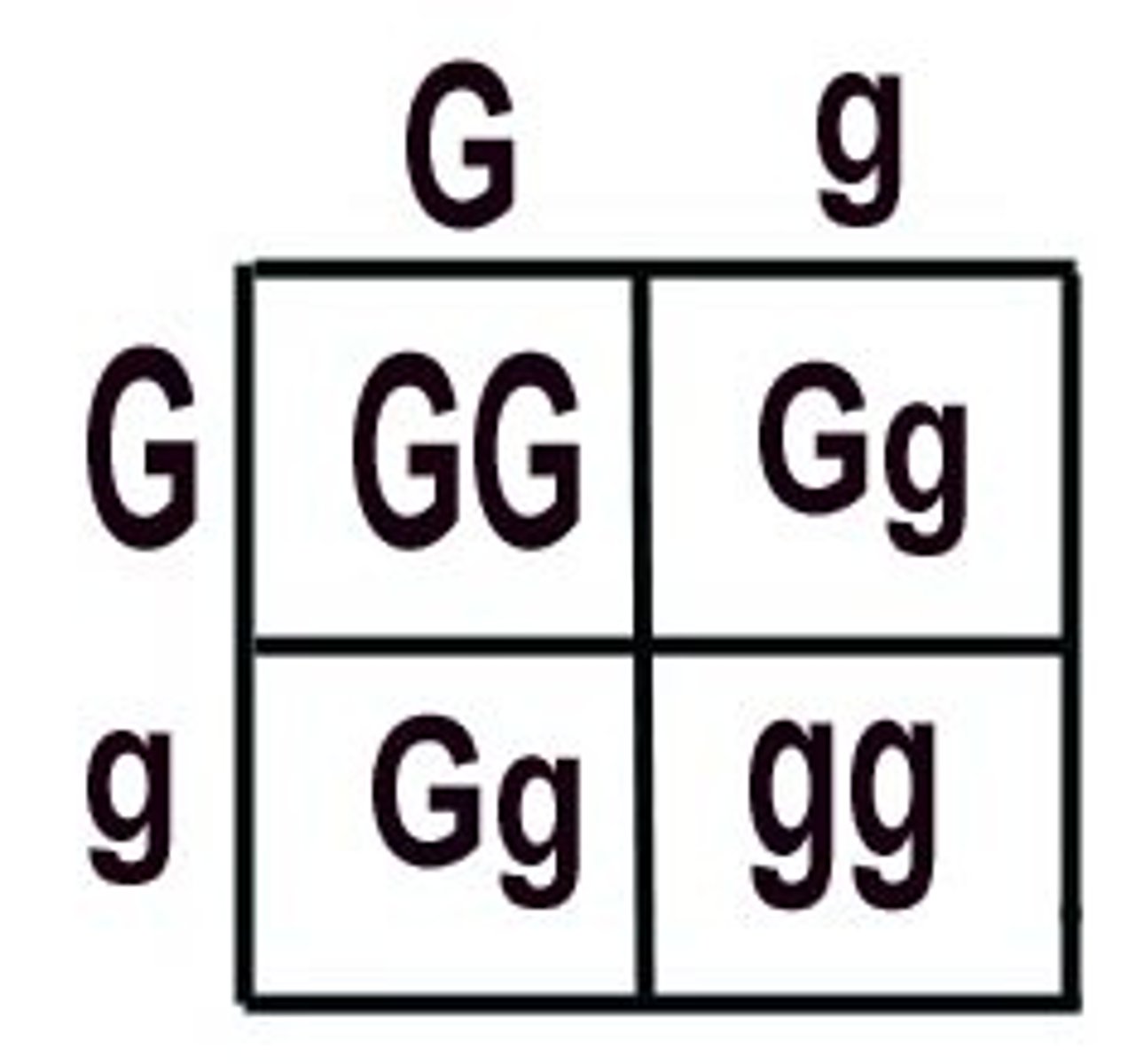
Based on this Punnet Square, which of the following statements are TRUE?
I. This is a monohybrid cross
II. This is a test cross
III. Both parents are heterozygous
IV. The parents are homozygous individuals
V. All of the offspring express the dominant trait
I and III
Which of the following statements are TRUE regarding alleles? They are:
I. sequences of DNA
II. segregated into different gametes
III. only found in diploid organisms
IV. versions of a gene
I, II, and IV
Identify which of the following terms describes an individual who has 2 different alleles for a gene.
a. Homozygous
b. Heterozygous
c. Homozygous dominant
d. Hemizygous
b. Heterozygous
Which of the following observations made by Mendel invalidated the hypothesis of blending inheritance?
I. F1 and F2 individuals were identical to parental generation
II. F1 was comprised entirely of a single parental phenotype
III. F2 contained parental phenotypes that were absent in F1
IV. One parental phenotype was permanently lost
II and III
Golden retriever dogs can carry a recessive trait for deafness (h). A dog breeder wants to test if their dogs are carrying deafness, so they conduct a test cross. Which of the following genotypes represents a test cross with a dog that is a carrier for deafness?
a. Hh x Hh
b. hh x hh
c. HH x hh
d. Hh x hh
d. Hh x hh
Identify which of the following is true of dominant and recessive alleles?
a. Dominant alleles will mask the presence of recessive alleles
b. Dominant and recessive alleles are never found in the same individual
c. When both are present, the resulting phenotype is a combination of the two.
d. Only dominant alleles can determine phenotype
a. Dominant alleles will mask the presence of recessive alleles
The combined probability of two independent events is:
a. described as 'the probability of one event OR the probability of the other event'.
b. the probability of two events that are mutually exclusive
c. also described as the probability of independent events
d. determined by multiplying their separate probabilities
d. determined by multiplying their separate probabilities
Apply probability rules. Identify in which of the following situations is it appropriate to use the addition rule.
I. Determining the combined probability of mutually exclusive events
II. Determining the combined probability of independent events
III. Determining the combined probability of events that cannot occur simultaneously
I and III
Identify which of the following is NOT a reason that fruit flies made a good test organism.
a. easy to control breeding
b. many chromosomes
c. many distinct characteristics
d. short generation time
b. many chromosomes
You are studying gene expression in humans. The trait that you are interested in has the following pattern: Neither parent expresses the trait. One-quarter of the daughters and one-quarter of the sons express the trait
Hypothesize what type of inheritance this pattern COULD be.
I. Mendelian
II. Sex-linked on the X chromosome
III. Sex-linked on the Y chromosome
I only
A female carrying a recessive X-linked trait, mates with a male who does not have the trait. Calculate the probability that the first offspring is a male who does not have the trait.
a. 0.5
b. 0.25
c. 1
d. 0.75
b. 0.25
An animal with the sex chromosomes XY is hemizygous for certain characters. What does this mean?
a. Every allele in the nucleus is expressed
b. All of the recessive alleles on the somatic chromosomes are expressed
c. On the X chromosome, recessive alleles mask dominant alleles
d. Every allele on the X chromosome is expressed
d. Every allele on the X chromosome is expressed
Male cockatiels have the sex chromosome pair ZZ while female cockatiels have the sex chromosome pair ZW. Identify which of the following statements are TRUE.
I. Z-linked diseases are more commonly expressed in female cockatiels
II. One Z chromosome in male cockatiels is condensed into a Barr body
III. Male cockatiels can be heterozygous for sex-linked traits
IV. Female cockatiels are heterogametic
I, II, III, and IV
Identify which of the following is the central finding of Thomas Morgan that was different from what Mendel concluded?
a. Homozygous recessive individuals exhibit recessive phenotypes
b. Alleles segregate during gamete formation
c. Genes move on chromosomes, not as individual units
d. Dominant alleles mask recessive alleles
c. Genes move on chromosomes, not as individual units
Diagnose sex linkage. A man inherits a X-linked disorder. Hypothesize which of the following ancestors could be the source of his disorder.
I. Paternal grandmother (his father's mother)
II. Maternal grandmother (his mother's mother)
III. Paternal grandfather (his father's father)
IV. Maternal grandfather (his mother's father)
II or IV
Barr bodies:
a. Occur when one X is randomly deactivated
b. Involve the Y chromosome
c. Occur in autosomal chromosomes in females
d. can only occur in females
a. Occur when one X is randomly deactivated
(Image on Q#32)
Referring to the following image, which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE?
I. 5' end of the molecule (top right)
II. 5' end of the molecule (top left)
III. Elongation only occurs here (bottom right)
I only
Correctly SEQ the following proteins in the order in which they participate in DNA replication, starting with the breaking of hydrogen bonds.
I. DNA polymerase
II. Primase
III. Helicase
IV. Single-strand binding proteins
III, IV, II, I
A SEQ of one DNA strand is:
3' A A T G G C T A C 5'
a. 5' A A T G G C T A C 3'
b. 5' T T A C C G A T G 3'
c. 3' C A T C G G T A A 5'
d. 5' U U A C C G A U G 3'
b. 5' T T A C C G A T G 3'
Identify which of the following are components of a cytosine nucleotide.
I. a purine
II. a pyrimidine
III. a five-carbon sugar
IV. a phosphate group
II, III, and IV
Identify which of the following correctly describes the operation of DNA polymerase
I. Adds new nucleotides to the 5' side of the new DNA strand
II. Catalyzes the formation of phosphodiester bonds
III. Synthesizes a complementary daughter to the parent strand
II and III
Hypothesize the result of a mutation that prevented RNA primase from functioning. How would DNA replication be affected?
a. Replication would not be bidirectional from the origin of replication
b. DNA replication would be unaffected
c. Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand would not be joined
d. DNA polymerase would be unable to place the first DNA nucleotide
d. DNA polymerase would be unable to place the first DNA nucleotide
Hypothesize where a reaction which breaks hydrogen bonds would affect a DNA molecule. Between a pyrimidine and:
a. a phosphate group
b. a purine
c. the 3' hydroxyl group
d. the 5' carbon of deoxyribose
b. a purine
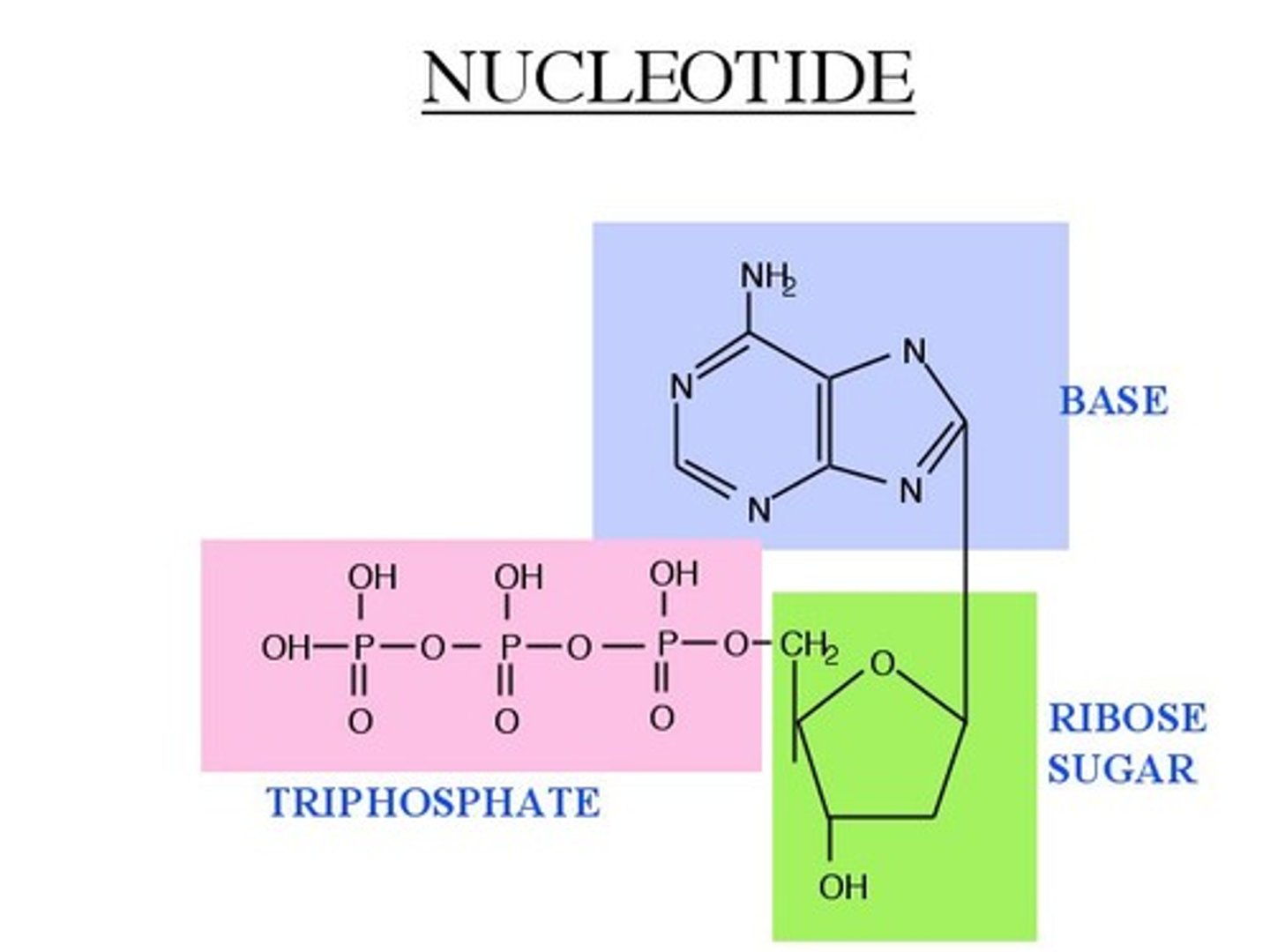
This structure represents a nucleotide. Based on this information, which statements are TRUE?
I. This will pair with a pyrimidine
II. It is either adenine or guanine
III. The hydroxyl group is attached to the 5' carbon
IV. It is found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
V. It is found in chromosomes, but not in chromatids
I, II, and IV
Correctly sequence the following events in eukaryotic gene expression.
I. RNA polymerase attaches to promotor
II. mRNA molecule receives poly A tail
III. mRNA leaves the nucleus
IV. Start codon triggers translation initiation
V. Transcript is elongated
I, V, II, III, IV
Compare and contrast DNA and RNA. Which statement(s) describe(s) BOTH DNA and RNA?
I. It is a polymer of nucleotides
II. It has a sugar linked to a phosphate group
III. It can be found in the nucleus
IV. It is normally double-stranded in cells
I, II, and III
Identify which of the following statements best describes transcription.
a. Polypeptide used to generate specific mRNA
b. DNA used as template to generate specific mRNA
c. mRNA converted into polypeptide
d. mRNA used to generate specific polypeptide
b. DNA used as template to generate specific mRNA
Identify which of the following occurs ONLY in eukaryotes.
a. placement of a 5' cap on pre-mRNA
b. translation
c. mRNA binding to ribosomes
d. formation of peptide bonds
a. placement of a 5' cap on pre-mRNA
Compare and contrast DNA replication, transcription, and translation. Which of the following processes are dependent on complementary base pairing?
I. Transcription
II. Translation
III. DNA replication
I, II, III
Identify the function of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase
a. Terminate translation
b. Catalyze peptide bond formation between amino acids
c. Translocate the ribosome by binding to a tRNA
d. Covalently link an amino acid to a tRNA
d. Covalently link an amino acid to a tRNA
Cycloheximide is a chemical that interferes with translocation and thereby inhibits protein synthesis in eukaryotes. Hypothesize the effects when a cell is treated with cycloheximide
I. Translation elongation will not occur normally
II. The translation initiation complex will not form
III. No mRNA will be produced
IV. RNA polymerase will not function normally
V. Peptide bond formation by will be inhibited
I and V
On a prokaryotic operon, where does the repressor protein bind?
a. Start codon
b. Promoter
c. Inducer
d. Operator
d. Operator
Hypothesize the effect on operon expression if a mutation prevents the inducer from binding to the repressor.
a. Operon would never be expressed
b. Operon always expressed at high levels.
c. Only low levels of expression possible
d. Operon always expressed at low levels
a. Operon would never be expressed
Correctly sequence translation.
I. Large ribosomal subunit joins the initiation complex
II. Small ribosomal subunit binds with mRNA
III. Peptide bond formation
IV. Release factors bind to codon in A site
V. Initiator tRNA base-pairs with start codon
II, V, I, III, IV
Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA and gene regulation. Which of the following processes occur in BOTH?
I. Translation
II. Replication
III. Regulation by operons
IV. Histone modification
V. Transcription
I, II, and V
A mutation occurs in your pet rabbit that prevents DNA methylation in a specific gene. Hypothesize the effect of this mutation on that gene.
a. more frequent transcription
b. translation cannot occur
c. transcription is inhibited
d. this mutation does not have any effects
a. more frequent transcription
A rise in active catabolic activator protein (CAP) in an E. coli cell indicates that:
a. allolactose will bind efficiently to the operator
b. the cell has equal amounts of glucose and lactose available for metabolism
c. very little glucose is available and cAMP levels are rising
d. the lac operon promoter's affinity for RNA polymerase will decrease
c. very little glucose is available and cAMP levels are rising
Sequence gene regulation in eukaryotes.
I. Adding a 5' cap to pre-mRNA
II. DNA packaging
III. Regulation of translation
IV. Protein processing and folding
II, I, III, IV
Hypothesize which of the following would be TRUE for an E. coli cell living in a medium of high glucose and high lactose?
I. High levels of activated CAP (catabolic Activator Protein)
II. Low cAMP levels
III. High levels of LAC transcription
IV. Operator on LAC operon is blocked by a repressor
V. Low level of LAC transcription
II and V
Which of the following is an example of positive regulation of an operon?
a. CAP helps RNA polymerase attach to the promoter
b. several genes are transcribed simultaneously
c. the operator of an operon is blocked by a repressor
d. levels of translation are adjusted based on cellular changes
a. CAP helps RNA polymerase attach to the promoter
Correctly sequence the steps of DNA dideoxy sequencing.
I. DNA fragment is denatured into single strands
II. Load single strands onto gel
III. Detector senses fluorescent tag
IV. Begin incubation with primer, polymerase, dNTPs, and ddNTPs
V. Strand elongation
I, IV, V, II, III
(Image on Q#57)
Identify which of the following nucleotides would allow the elongation of a new strand of DNA?
II and III
During the annealing step in PCR, the:
a. hydrogen bonds between bases break
b. DNA molecules are synthesized
c. primer binds to the target
d. backbone of the DNA denatures
c. primer binds to the target
Which of the following are REQUIRED for DNA replication, transcription, PCR, AND dideoxy chain termination sequencing?
I. Complementary base pairing
II. DNA primers
III. DNA polymerase
IV. RNA nucleotides
I only
Dr. Patel is running a thermocycler in her lab to PCR a small sample of DNA. She places the sample in the machine and leaves for the night. Later that night, the machine breaks, and the temperature remains at a high 75 degrees C for the entire process. What is the result of this malfunction.
a. Taq polymerase cannot extend from primer
b. RNA polymerase does not bind to the promoter
c. DNA strands do not separate
d. Excess DNA is sequenced
c. DNA strands do not separate
Compare and contrast DNA replication, transcription and PCR. Which of the following are TRUE?
I. All involve a leading and lagging strand
II. All involve DNA polymerase
III. All require a template strand
IV. Only DNA replication requires RNA primers
III and IV
Compare and contrast DNA replication and PCR. Which of the following occurs in DNA replication in a eukaryotic cell, but NOT during PCR?
a. Hydrogen bonding between complementary nucleotides
b. Unwinding of the DNA helix by helicase
c. Synthesis of DNA in the 3' to 5' direction
d. Binding of a DNA primer to the template
b. Unwinding of the DNA helix by helicase
Identify which of the following is TRUE regarding gel electrophoresis.
a. DNA migration is due to its negative charge
b. It involves several cycles of DNA synthesis
c. Large DNA molecules migrate faster than small DNA molecules
d. Heat is used to move DNA molecules
a. DNA migration is due to its negative charge
(Pedigree image Q#64 )
This chart represents the expression of an autosomal recessive disease. Affected individuals are represented by filled in shapes. Males are represented as squares and females are represented by circles.
If the individual II-2 is cross-bred with individual IV-4. What percent of their children will be carriers for the disease?
a. 100%
b. 25%
c. 75%
d. 50%
d. 50%
Identify which of the following indicates a trisomy in humans.
a. a somatic cell with 46 chromosomes +Y
b. a 3n somatic cell
c. a gamete with 22 autosomes +Y
d. a somatic cell with 44 autosomes +XX
a. a somatic cell with 46 chromosomes +Y
Which of the following is a mechanism that could preserve harmful recessive traits in a population?
a. Heterozygote advantage
b. Aneuploidy
c. Natural selection
d. Dominant lethality
a. Heterozygote advantage
Cystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive genetic disease where a person must inherit two recessive alleles to express the disease. Which of the following represent possible parents of a child with cystic fibrosis?
a. X^f X^f x X^f y
b. Ff x Ff
c. Ff x FF
d. X^F X^f x X^F y
b. Ff x Ff
For an individual to express an autosomal recessive trait, what must be true?
a. They must have two recessive alleles
b. They must have a parent who expresses the recessive trait
c. Both parents must express the recessive trait
d. They must receive a recessive allele from just one parent
a. They must have two recessive alleles
For an individual to express an X-linked recessive trait, what must be true?
a. They must have two X chromosomes
b. They must have at least one dominant allele
c. At lease one parent must express the recessive trait
d. XY individuals can express the trait with just one recessive allele
d. XY individuals can express the trait with just one recessive allele
Identify the types of human genetic disorders that can be caused by nondisjunction
I. Monosomy
II. Aneuploidy
III. Autosomal recessive
IV. X-linked recessive
I and II