Mating systems: current AB Final 1
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
Mating System
The number of sexual partners an individual acquires during a breeding season.
The strategy used to acquire those partners.
selection of a mating system is directed toward gaining_________________
fitness within the constraints of the environmental conditions.
males usually have
Polygynous” tendencies
females usually have
Monogamous” tendencies
conditions that favor monogamy in males?
why would a male be monogomous?
Availability / distribution of females
Mobility of individuals
Forced monogamy
mate assistance
distribution of mates
availability of mates
male assistance hypothesis
provides parental assistance which increases offspring survival
example of male assistance hypothesis
Male seahorse incubates eggs.
Female seahorse provides a new clutch once the first one is hatched and leaves the male.
Female cannot produce more than the male can handle, so no need for her to find other males.
Male gets a constant supply of eggs, so no need for him to find other females.
mobility of male causes this
Mate Guarding Hypothesis
Male guards his mate who would otherwise use the sperm of other males to fertilize all or some of her eggs.
example of mate guarding hypothesis
Male clown shrimp will spend weeks with one female
This strategy makes sense if the female is still receptive after breeding and the operational sex ratio favors males (more sexually receptive males than females).
why does mate guarding work
this strategy makes sense if the female is still receptive after breeding and the operational sex ratio favors males (more sexually receptive males than females).
• if females are scattered and hard to find, it makes sense to guard a single female.
ecological factors that dictate how females are distributed spatially have major effects on the evolution of male mating strategies
female enforced monogamy
Female blocks the male from mating with multiple females, thus gaining his parental assistance.
Similar to mate guarding by the male
indirect female enforced monogamy
Female chats attack intruder females
direct female enforced monogamy ex
Female burying beetle actively keeps the male from secreting pheromones and thus attracting other females
why does the female beetle care about recruiting another female?
the first pair lay their eggs on a dead mouse, which will provide food for larvae
Recruitment of another female could reduce fitness of the first female via offspring competition, because that second female will want to lay her eggs on the same dead mouse.
is male monogamy common?
no its rare in mammals, but there are exceptions
can predict that if a male exhibits paternal behavior, he leans toward monogamy
wants to protect offspring
ex of male monogamy in mammals
Djungarian hamsters who help with delivery, a behavior that likely increases pup survival.
advantages of male monogamy
helping keep pups warm, protecting them from infanticide
increases pup survival
what happens if males are monogamous but females are scattered?
If a male ventures off looking for another female, other males may come into his territory (he is not there to guard it)
ex. is rock haunting possum
male monogamy in mammals is related to
male paternal behavior
an overall evaluation of mammalian sp shows that
male paternal behavior occurs in monogamous species and polygynous species
polygynous
males can have multiple mates, while females may only have one
pair bonded birds are monogamous?
female engage in extra pair copulations so male could be caring for someone else’s offspring
male at the same time could be mating with other female
bonded pair but with potential polygynous behavior in the system
advantage of above system with pair bonded birds
female choice
female choice
the female is driving the system, taking precautions to limit risk against loss of the male or other factors
extra pair copulations
mating behaviors where a paired individual in a socially monogamous relationship mates with another individual outside of their social bond
so basically with male birds….
•Males may care for some of the neighbor's offspring, but the neighbor may be doing the same.
monogamous voles?

Polyandry: what is it and why?
female has lots of males
Lots of males for protection of offspring and resources.
costs of polyandry
time & energy
losing primary partner
sexually transmitted disease
benefits of polyandry
ensures all eggs are fertilized
social partner has lower genetic quality than other sperm donors
increases genetic variety of sperm available to the female, increasing chances that DNA of male will be very compatible with female
more paternal care/resources
more mates=confusion abt whos baby that is=less infanticide
ex of material benefits hypothesis
Some female bees mate with other males to gain access to nectar in that male’s territory.
why would a female copulate more frequently with the males that normally spend less time with her?
encourages male to stick around and ultimately helps with rearing the young and probably protecting local resources

an example of polyandry
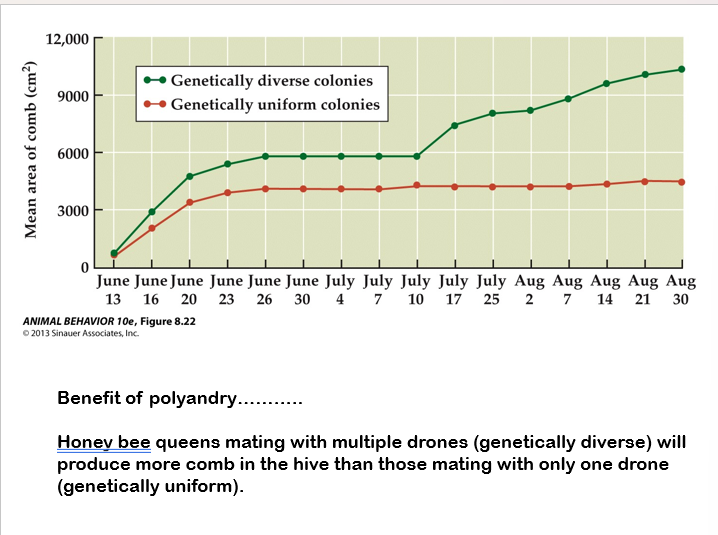
another example of polyandry

male tactics to achieve polygyny?
Males of different species may “defend” different things in an attempt to monopolize the females.
Males may defend the female herself or some resource attractive to the female
males may opt for no defensive strategy at all, and rather simply try to outrace other males to receptive females
female defense polygyny
fighting with other males to monopolize female
predictable based on females being distributed in defensible clusters.
male may seek out a cluster of females, and defend them against rival males.
a male may create his own cluster of females
Resource Defense polygyny
defending a resource that females need (food, nesting sites, etc.).
So females may not live in clusters, so males cannot control the cluster of females.
So a male may seek out a resource needed by the females, and defend it against rival males
Or…..a male may create or enhance the resource.
Scramble competition polygyny
males skip competition and outrace one another to females
females and resources are widely dispersed, then they are hard to defend so the strategy becomes one of persistent searching by the male
required good spatial memory!
useful when breeding is highly compressed
ex of scramble competition polygyny
frogs

lek polygyny
males defend a small piece of ground at a location where females will congregate. The males display at this location.
hotspot hypothesis
males congregate there because it is a good spot to find females
Hotshot hypothesis
subordinate males congregate around a dominant male and thus increase their chances of breeding
Female preference hypothesis
females prefer clusters of males so they can make quick and safe decisions about mates
So more males ≠ more mating opportunities unlessss
Unless….mating chances ≠ among males.