Biology Unit 4
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
Appendix I Species
species threatened with extinction, no trade
Appendix II species
species that may become threatened, limited trade
Appendix III Species
trade allowed by CITES
3 Definitions of Species
morphospecies, phylogenetic, biological
Morphospecies Concept
members of the same species usually look alike
Pros of Morphospecies Concept
easy to identify visually
Cons of Morphospecies Concept
mimicry
Phylogenetic Concept
identifies species based on evolutionary history, related to common ancestor
Pros of Phylogenetic Concept
applicable to any type of population, different species have different traits due to lack of gene flow
Cons of Phylogenetic Concept
phylogenies are available to subsets of populations, lead to recognition more species
Species
a unique group of organisms that share a common ancestor
Biological Concept
groups of actually or potentially interbreeding populations that are reproductively isolated from other such groups
Pros of Biological Concept
easy to identify
Cons of Biological Concept
asexual organisms, can’t be evaluated for extinct species, species like plants may produce hybrids
Microevolution
change in allele or genotype frequencies in a population, over time or a few generations
Macroevolution
origin of new species, over very long periods of time
Allopatric speciation via dispersal
population moves to a new habitat, colonizes it, finds new population
Allopatric speciation via vicariance
physical splitting of a habitat
How does dispersal and vicariance lead to allopatric speciation?
They create geographic isolation
Sympatric speciation
evolution of a new species from a single ancestral species within the same geographical area
How can disruptive selection result in sympatric speciation?
Among a species in a geographical area, the 2 extreme phenotypes are favored compared to the middle, which causes the population to split and evolve in a single habitat
Biological community
consists of all the populations of interacting species living within a define area
Commensalism
one organism benefits and other is unaffected (+/0); too much can cause competition between the 2 species
Ex: epiphytes on trees gaining benefits, but too many will cause competition for sunlight
Competition
competiting uses resources that can’t be used for foraging, mating , or other activities to increase fitness (-/-)
Ex: pack of wolves hunting for deer or other food resources so they don’t compete with each other
Intraspecific competition
occurs between members of the same species (population)
Interspecific competition
occurs between members of different species
Consumption
organism acquires or uses a resource (+/-)
Ex: wolves eat a deer
Mutualism
both species benefit from interaction (+/+)
Ex: bees get nectar and pollinate flowers
Ecological Niche
range of resources that a species can use and the range of conditions it can tolerate
Ex: what types of seeds a bird can eat based on their beak’s size
3 Outcomes of Competition
realized niche, competitive exclusion, coexistence/niche differentiation
Realized niche
minimized ecological niche, which is the parts of the niche that are not as competitive
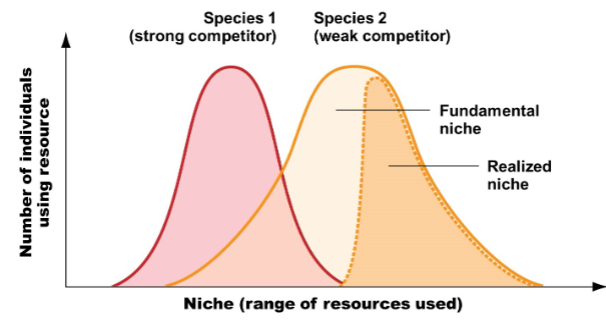
Competitive Exclusion
a weak competitor has narrower niche and there are fewer individuals in the population
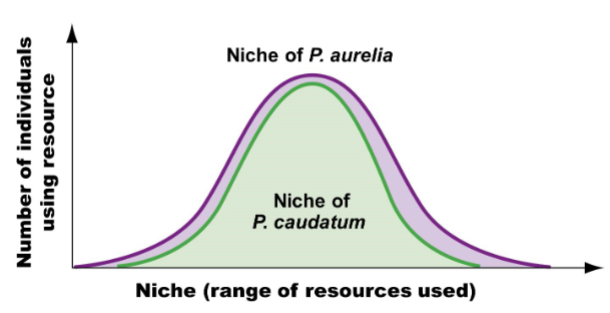
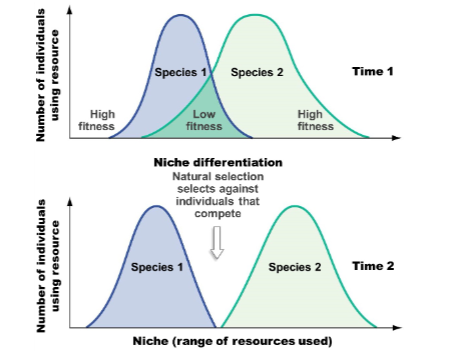
Coexistence/niche differentiation
individuals are cut out by natural selection
Herbivory
consumption of plant or algal tissues by herbivores
Predation
killing and consumption of most or all of another individual (prey) by an individual
Parasitism
consumption of tissues from another organism, or host, by a parasite
Sister group
single ancestral lineage gives rise to 2 daughter lineages
Outgroup
sister group that shares a recent common ancestor with a taxa being studied
Clade
group of organisms that includes a single ancestor and all of its descendants
Ancestral trait
characteristic that existed in an ancestor
Derived trait (synapomorphy)
modified form of the ancestral trait, found in a descendant (new trait evolution)
Shared character
shared within a lineage
How is parsimony used to find most likely evolutionary sequence of a group of organisms in a phylogeny (evolutionary history of a group of organisms)?
Tree with the least evolutionary change is most likely the one that most accurately reflects what occurred during evolution
Homology
similarity in organisms due to common ancestry
Homoplasy
similarity in organisms due to resources other than common ancestry
Monophyletic group
evolutionary unit that includes an ancestral population and all of its descendants (clade group)
Polyphyletic group
unnatural group that doesn’t include the most recent common ancestor
Paraphyletic group
group that includes an ancestral population and some of its descendants
Convergent evolution
development of similar traits due to similar environmental pressures, occurs in homoplasy
What are the 2 main outcomes of interactions among species?
influences distribution and abundance of interacting species, species are agents of natural selection which influences the fitness of the population
Adaptive radiation
a single species or common ancestor rapidly produces a variety of adaptive forms
What causes adaptive radiation?
ecological opportunity and adaptations (morphological, behavioral, or physiological innovation)
Cambrian Explosion
enormous proliferation of biological diversity occured
What are the 4 hypotheses of the Cambrian explosion?
higher oxygen levels, evolution of predation, niche differentiation drove evolution, new genes led to new body plans
Higher oxygen levels hypothesis
Cyanobacteria in plants that could photosynthesize made aerobic respiration more efficient, made oxygen to support large, complex bodies
Evolution of predation hypothesis
Increased selective pressures for defensive mechanisms, drove morphological divergence among prey
Niche differentiation drove evolution hypothesis
Species interactions led to niche differentiation and speciation
New genes led to new body plans hypothesis
early animals had few body genes, which eventually duplicated and mutated to increase the complexity of potential body plan designs
Background extinction
Occurs from normal environmental change
Ex: emerging disease, predation pressure, competition with other species
Mass extinction
Sudden change in environment
Ex: volcanic eruption or asteroid attack
What is the cause of the onset of the 6th mass extinction?
Climate change