Introduction to Evolution and Natural Selection
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Evolution
Change in traits of a population over time.
Microevolution
Small-scale evolution within a single species.
Macroevolution
Large-scale evolution leading to new species.
Allele Frequency
Proportion of a specific allele in a population.
Natural Selection
Process where organisms better adapted survive.
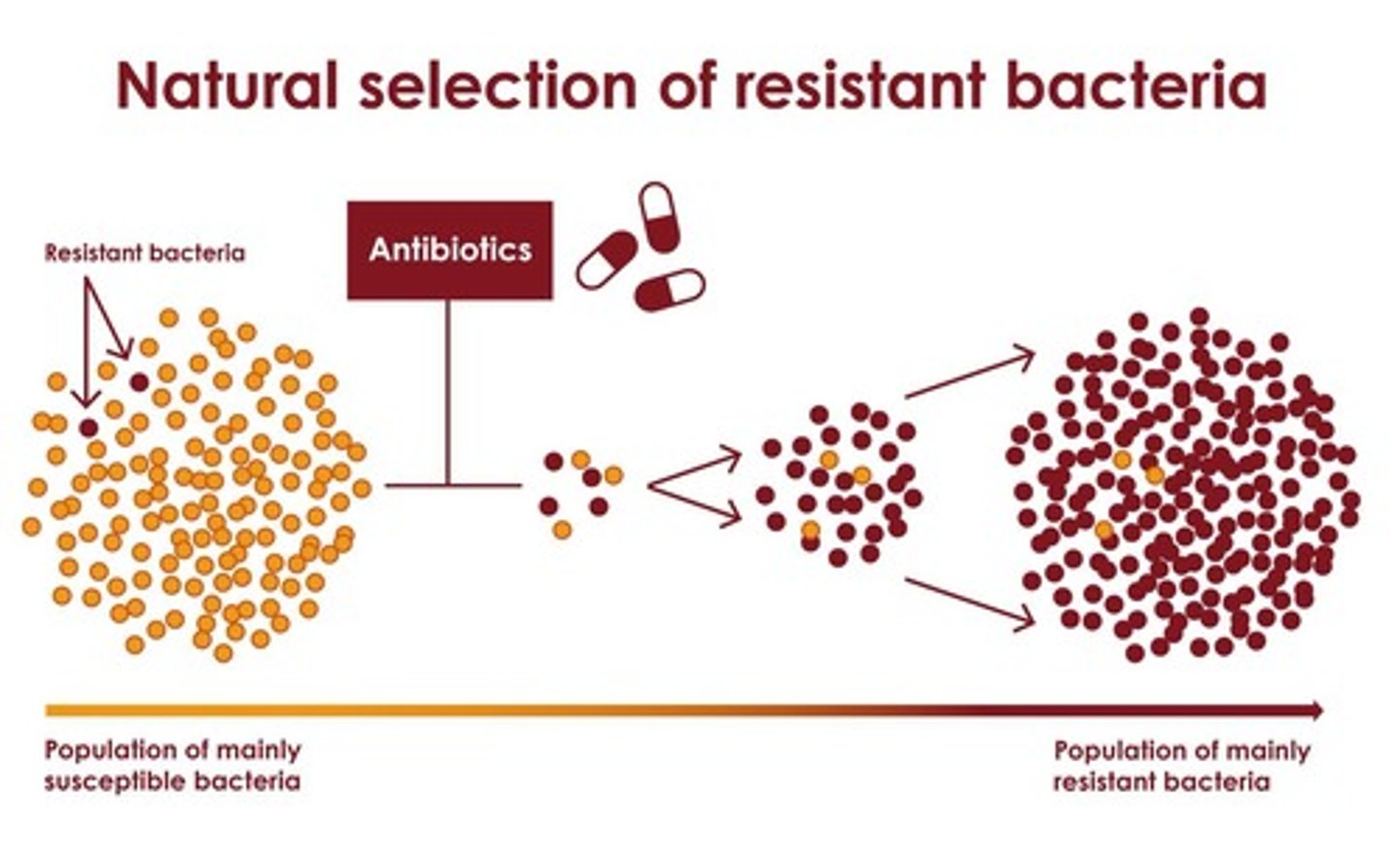
Antibiotic Resistance
Bacteria's ability to survive antibiotic treatment.
Random Mutations
Spontaneous changes in DNA creating variation.
Phenotype
Observable traits resulting from genotype expression.
Genotype
Genetic makeup determining an organism's traits.
Common Ancestry
Theory that modern organisms share ancestors.
Darwin's Theory
Evolution through descent from common ancestors.
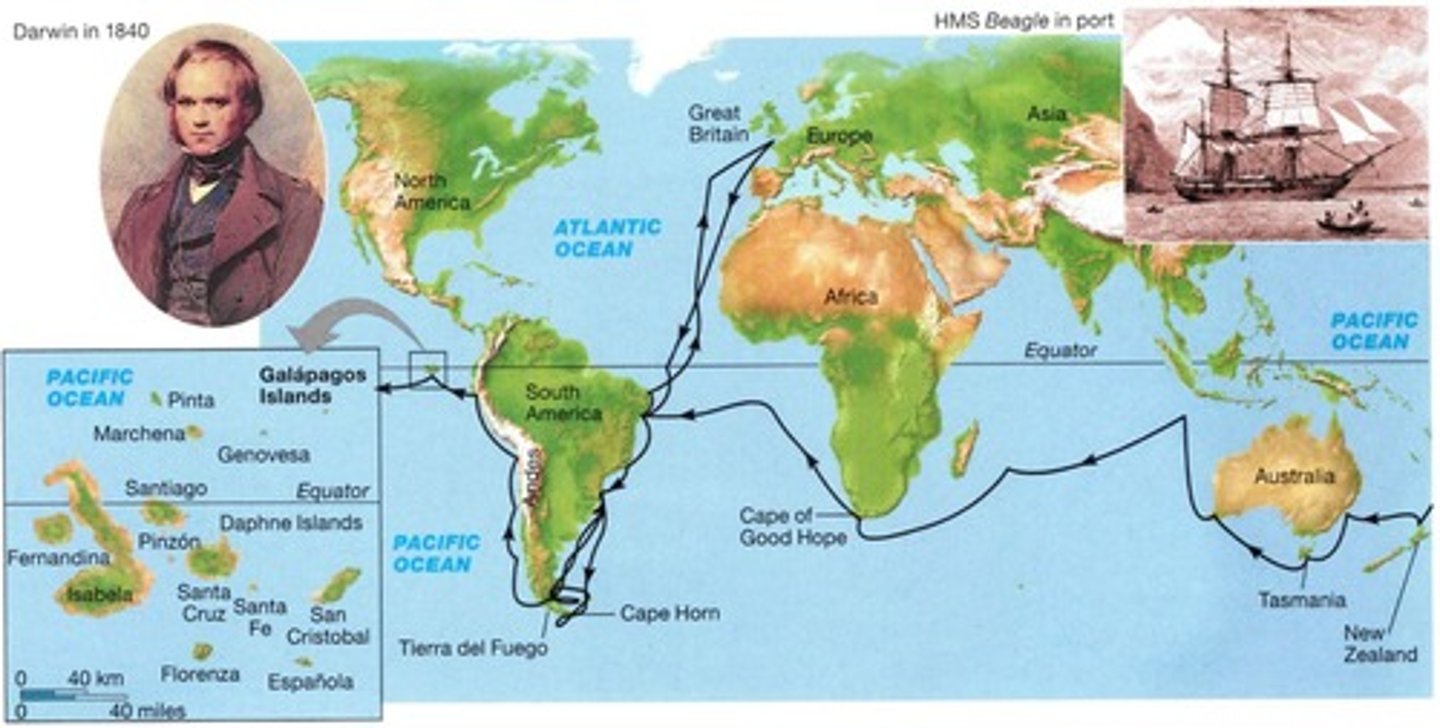
Galápagos Islands
Location where Darwin observed diverse species.
Struggle for Existence
Competition among organisms for limited resources.
Uniformitarianism
Geological processes shaping Earth occur gradually.
Cuvier's Catastrophism
Extinction occurs due to sudden catastrophic events.
Lamarckism
Theory that acquired traits can be inherited.
Artificial Selection
Humans breed organisms for desired traits.
The Origin of Species
Darwin's 1859 publication on evolution by natural selection.
H.M.S. Beagle
Ship used by Darwin for his research voyage.
Adaptation
Trait that enhances survival and reproduction.
Inheritance of Acquired Characteristics
Discredited idea that traits gained in life are inherited.
Geological Time
Concept that Earth is ancient and has changed.
Extinct Species
Species that no longer exist.
Alfred Russel Wallace
Developed natural selection theory independently of Darwin.
Survival of the fittest
Darwin's concept of natural selection favoring best adaptations.
HMS Beagle
Darwin's ship for extensive evidence collection.
Artificial Selection
Humans breed individuals for desirable phenotypes.
Selective Breeding
Choosing specific traits in breeding for desired outcomes.
Phenotypic Variation
Diversity in physical traits due to selective breeding.
Overproduction
More offspring produced than can survive to maturity.
Inheritance
Genetic traits passed from parents to offspring.
Natural Selection
Process favoring organisms best suited to their environment.
Competition
Offspring compete for limited resources like food.
Adaptation
Heritable traits enhancing survival and reproduction.
Favorable Combinations
Genetic traits that increase reproductive success.
Differential Reproductive Success
Variation in offspring production among individuals.
Biogeography
Study of species distribution across geographical areas.
Comparative Anatomy
Comparison of body structures across different species.
Molecular Biology
Study of biological processes at the molecular level.
Paleontology
Study of fossils to understand past life forms.
Fossil Formation
Best when organisms buried quickly, slowing decay.
Sedimentary Rock
Common rock type where fossils are found.
Wallace Line
Biogeographical boundary separating distinct species.
Descent with Modification
Ancestral forms adapt over time to new environments.
Evolutionary Theory Evidence
Supported by observations from various scientific fields.
Endemic Species
Species unique to a specific geographic area.
Trilobites
Extinct marine arthropods preserved in rock.
Ammonite
Fossil with a shell covering stone interior.
Fossil Record
Ordered array of fossils in sedimentary strata.
Strata
Layers of sedimentary rock containing fossils.
Relative Age
Age determined by comparing fossil strata.
Biogeographical Evidence
Species distribution suggests evolutionary relationships.
Transitional Fossils
Fossils showing features of both ancestors and descendants.
Archaeopteryx
Transitional fossil between birds and dinosaurs.
Homologous Structures
Similar structures indicating common ancestry.
Adaptive Radiation
Species evolve to occupy different niches.
Divergent Evolution
Lineage splits, evolving independently into new species.
Convergent Evolution
Unrelated species evolve similar traits in similar environments.
Analogous Structures
Similar functions in different species, different origins.
Developmental Biology
Study of organism growth and development processes.
Embryonic Stages
Similar developmental stages indicate shared ancestry.
Selection Pressures
Environmental factors influencing species evolution.
Fish and Dolphin
Example of convergent evolution in aquatic environments.
Galápagos Islands
Location with species similar to mainland but distinct.
Tar Pit Fossils
Preserved remains of organisms trapped in tar.
Fossil Fish
Ancient fish preserved in sedimentary layers.
Vertebrate Embryos
Share developmental stages, supporting common ancestry.
Vestigial Organs
Degenerate structures with reduced function in species.
Whale Ancestors
Large, four-legged mammals evolved into modern whales.
Cladogram
Diagram showing evolutionary relationships among species.
Genetic Code
Universal instructions for building proteins in organisms.
DNA Analysis
Technique to determine evolutionary relationships among species.
Hemoglobin
Oxygen-transporting protein found in vertebrates' blood.
Phylogeny
Study of evolutionary relationships among biological entities.
Molecular Homology
Similarities in DNA/proteins indicating common ancestry.
Evolutionary Fitness
Ability of an organism to survive and reproduce.
Fossil Record
Historical evidence of organisms preserved in rocks.
Drought Impact
Environmental change affecting survival of species.
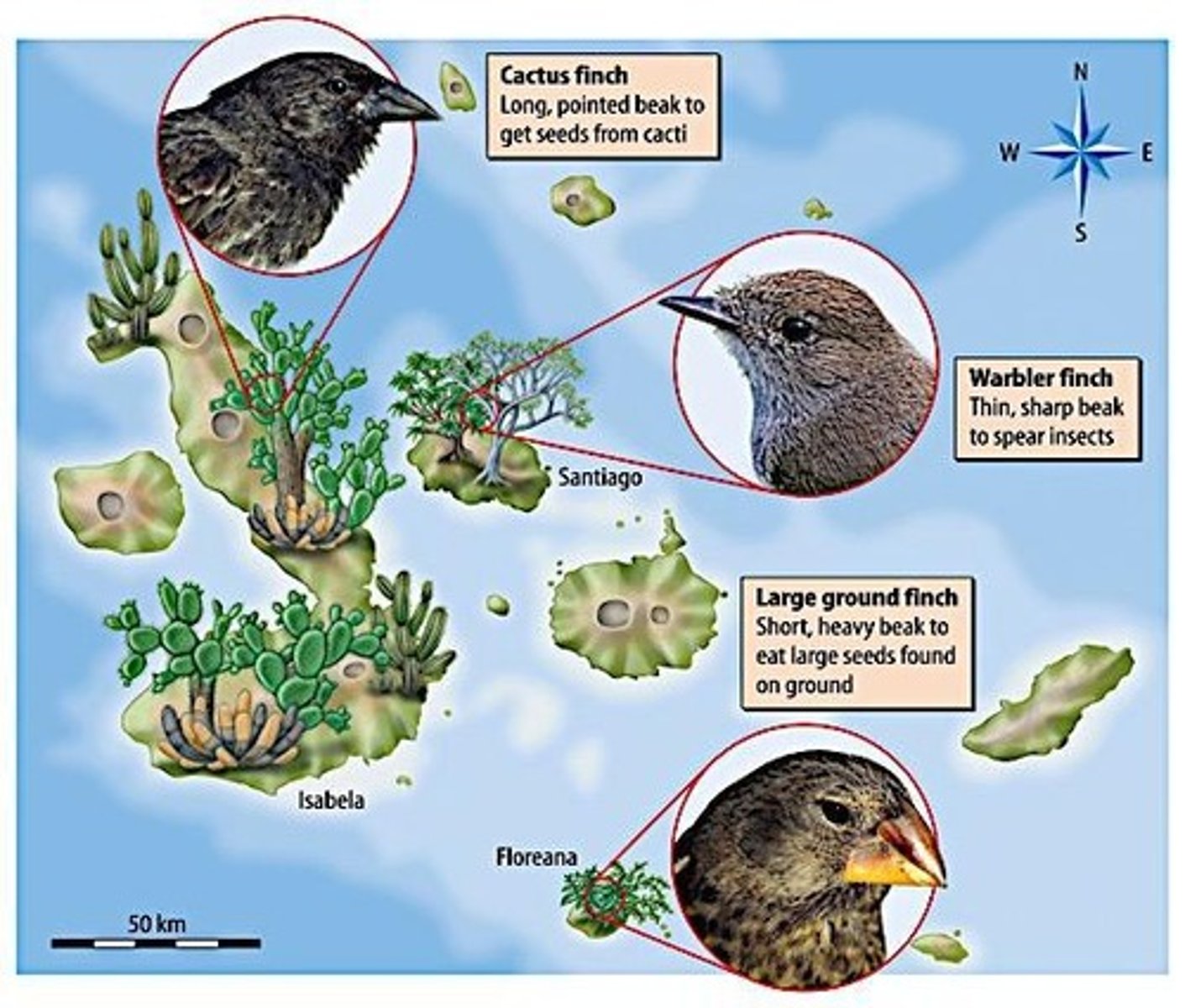
Finches
Birds studied for natural selection in Galapagos.
Pelvis in Whales
Reduced structure indicating evolutionary adaptation to aquatic life.
Species Diversity
Variety of different species within an ecosystem.
Common Ancestor
Theoretical original organism from which others evolved.
Genetic Similarity
Degree of shared genes among different species.
Morphology
Study of the form and structure of organisms.
ATP
Universal energy-carrying molecule in all living cells.
Burrowing Animals
Species with vestigial eyes, no longer used for vision.
Kiwi Wings
Tiny vestigial wings, non-functional for flight.
Self-replicating DNA
Molecules that replicate themselves in living systems.