Ultrasound physics Ch. 8
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
Transducers convert
one form of energy into another
transmission
electrical energy converted to sound
reception
reflected sound is converted to electricity
Transducer crystal property
voltage created when mechanically deformed or P (pressure) applied
Mechanical energy into electrical energy
reverse piezoelectric effect
apply voltage, crystal mechanically deforms. Electrical energy to mechanical energy
materials change shape when voltage applied
piezoelectric or ferroelectric materials
materials that convert sound into electricity (or the reverse)
piezoelectric effect may be found in
nature; quartz; tourmaline
synthetic lead zirconate titanate or PZT
manufactured PZT
-PZT properties are created
-material exposed to a strong electrical field while heated
-process of polarization
curie temp or curie point when
polarization occurs
properties destroyed if heating is
greater than curie temp
depolarization
loss of piezoelectric properties
transducer case
plastic or metal housing, protects internal components and protects patient from electrical shock
transducer electrical shield
thin metallic lining of inside case. Prevents outside electrical signals (static) from entering transducer. shields electrical noise from contaminating US signals
transducer acoustic insulator
-cork or rubber inner layer
-prevents vibrations within case that could induce electrical voltage to PZT
transducer wire
electrical connection between PZT and US system for transmission and reception
-each crystal has a wire hook-up
PZT also known as
-ceramic
-active element
-crystal
Transducer components: PZT
-coin shaped in a simple probe
-characteristics of sound beam related to crystal dimensions
transducer components: matching layer
-lies between crystal and skin
-increases efficiency of transmitting sound between crystal and skin
-protect the crystal
acoustic gel "Z" is between matching layer and skin to
optimize sound transmission
Impedances in decreasing order
(50Z)PZT > (40Z)matching layer > (30Z)gel > (20Z)skin
matching layer=
1/4 of wavelength
active element=
1/2 of wavelength
transducer components: backing material
-bonded to back side of crystal
-reduces ringing, restricts PZT deformation, shortens pulse
backing material also called
damping element
shorter pulses create
a better image
consequences of backing material
-decreased sensitivity
-wide bandwidth
-low quality factor
backing material decreased sensitivity
-transducers with backing material are less sensitive to low level sound reflections (during receptions_
damping material reduces crystal vibration during
transmission and also during reception
wide bandwidth
-Backing material prevents PZT from ringing freely.
-Abbreviated "ring" contains sound with many different frequencies.
bandwidth speaks to
range of frequencies or frequencies above and below resonant (main) f.
range of F is
bandwidth or broadband
imaging transducers have __________ bandwidth than therapeutic transducers
wider
damping material shortens pulse and increases
band width
quality factor
-Unitless
-describes transducer's ability to emit a clean pulse with a narrow bandwidth
quality factor and bandwidth relationship
inverse
quality factor equation
resonant F (MHz) / bandwidth (MHz)
imaging a _________ Q factor than therapeutic or non imaging transducers (CW)
lower
sterilization
destruction of all microorganisms by extreme heat (autoclave), chemical agents (Glutahaldaryde), or radiation. High heat can cause depolarization of crystal.
disinfection
chemical agent to reduce or eliminate infectious organisms on an object.
Transducers that penetrate skin or mucous membranes have highest potential for
transmitting infections and require sterilization. (TEE, transvag. transrectal)
what does not accurately describe an imaging transducer
High sensitivity
F of transducer depends on
whether transducer produces pulsed or CW sound
CW transducer F is determined by
electrical F applied to crystal
-electric=acoustic
in PW F determined only by
characteristic of PZT
-thickness of crystal
-Prop speed of sound in crystal
Crystal thickness and F relationship
inverse
PW crystal thickness =
1/2 wavelength
Prop speed and F relationship
direct
PW F (MHz) equation
PZT prop speed / 2 x thickness
T/F The purpose of using ultrasound gel is to avoid a big reflection.
true
If two crystals are made from the same material, the thicker transducer crystal will ________CW frequency?
have no affect
T/F Damping material of a transducer will improve image quality.
true
Describe the relationship between the damping material and the Q factor.
Damping material will decrease the Q factor.
T/F If PRF is increased, then f of US produced by the transducer is increased.
False: not related
A pulse has a primary f of 6 MHz, the lowest f is 4 MHz, the highest f is 7 MHz, what is the bandwidth and Q factor of this transducer?
3MHz, 2.0
Q-factor is ______________related to bandwidth:
inversely
T/F A pulse with a long spatial pulse length is likely to have a narrow bandwidth.
true
Imaging transducers have a __________ than therapeutic transducers:
greater bandwidth
What determines the frequency of a continuous wave transducer?
electrical F
If a transducer experiences heat above the Curie temperature, what happens?
depolarization
PZT has an impedance of 1,700,000 Rayls and the impedance of the skin is 1,200,000 Rayls. Matching layer Z should be:
1,500,000 Z
matching layer and gel increase
efficiency of sound transfer between transducer's PZT and skin
long duration events are ___________ bandwidth
narrow
short duration events are _________ bandwidth
wide (broadband)
characteristics of high F pulsed wave imaging transducers
-thinner PZT crystals
-PZT with higher speeds
characteristics of low F pulsed wave imaging transducers
-thicker PZT crystals
-PZT with lower speeds
US transducer converts (transmits)
electrical into sound (acoustic)
US transducer converts (receive)
sound (acoustic) to electrical
a shorter, dampened pulse has a _________ Q-factor
lower
A longer, undampened pulse has a ____________ Q factor.
higher
imaging transducers have pulses with short _________ and _________
duration, length
imaging transducers use __________ to limit ringing
backing material
imaging transducers have reduced or increased sensitivity
reduced
imaging transducers have a ____________ bandwidth/broadband
wide
imaging transducers have a _________ Q-factor
lower
what transducer has an improved axial resolution
imaging
non imaging transducers create
CW or pulses with long duration and length
T/F non imaging transducers use backing material
False
does non imaging transducers have reduced or increased sensitivity
increased
non imaging transducers have a _________ bandwidth
narrow
non imaging transducers have a __________ Q-factor
higher
T/F non imaging transducers cannot produce and image
true
transducer used in therapeutic US
non imaging transducer
acoustic insulation
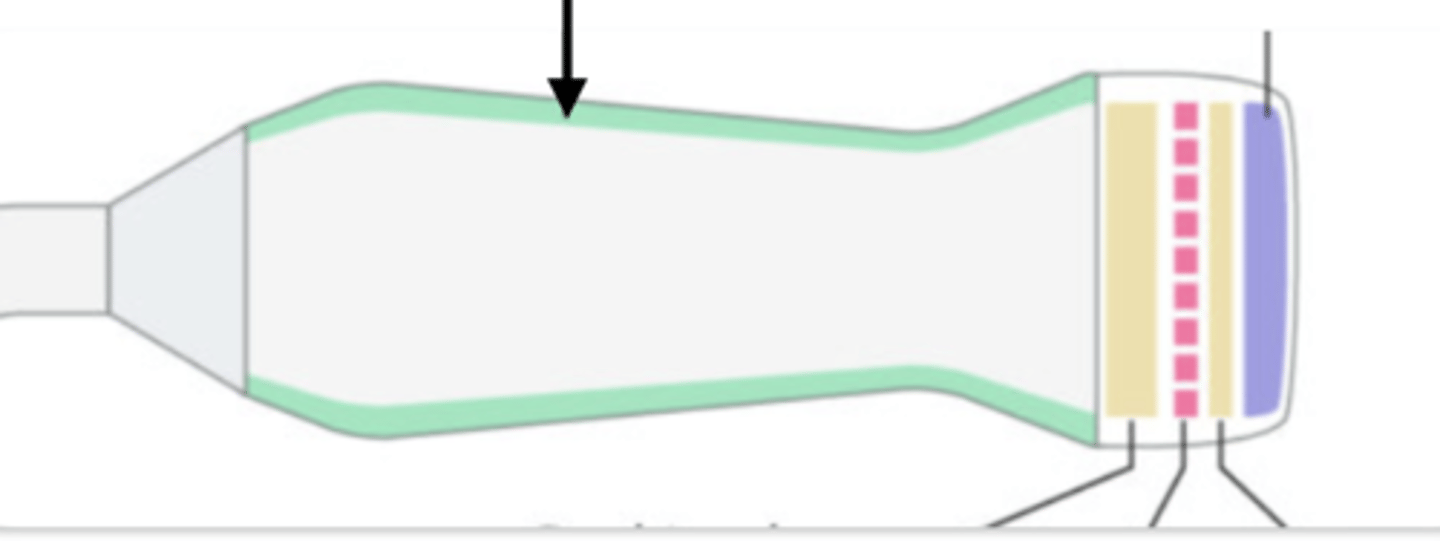
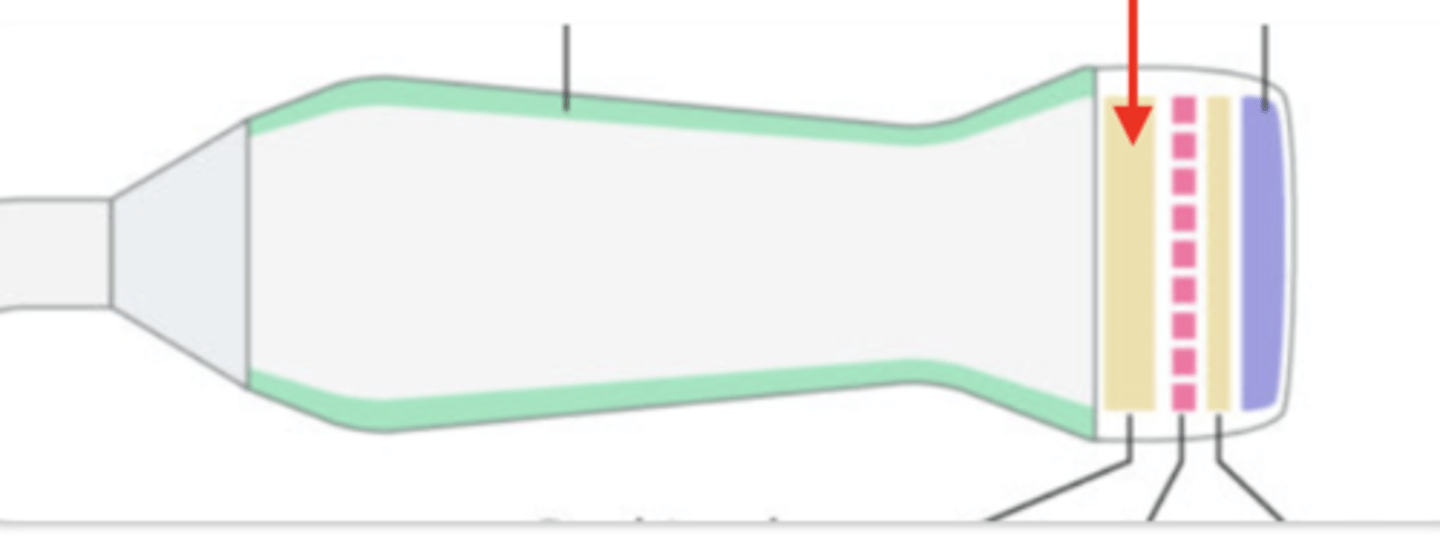
backing material
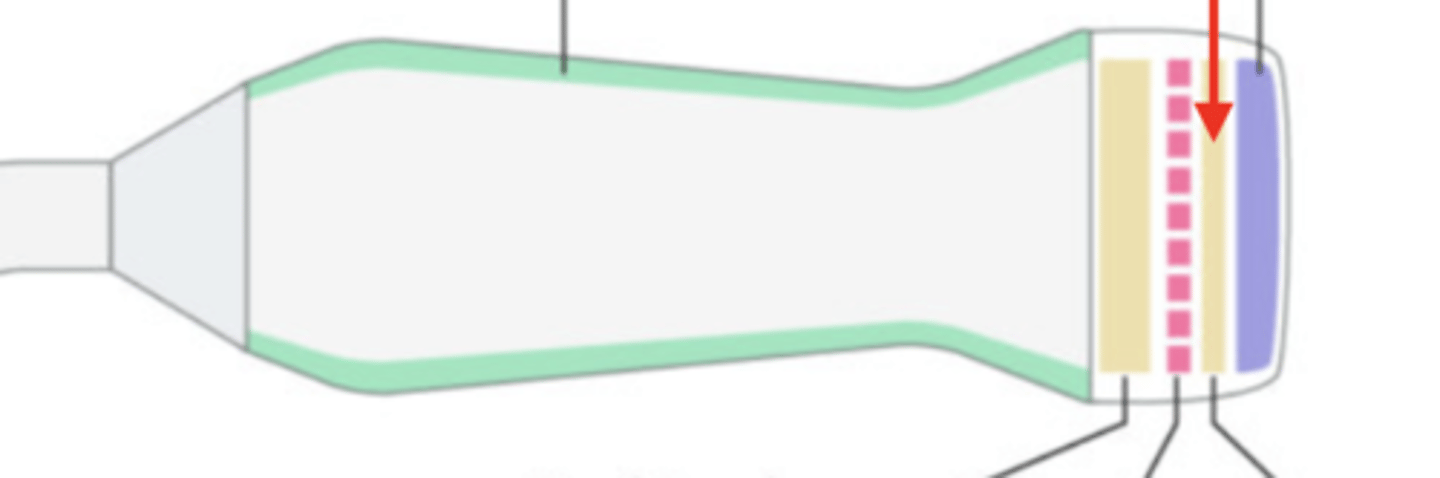
matching layer
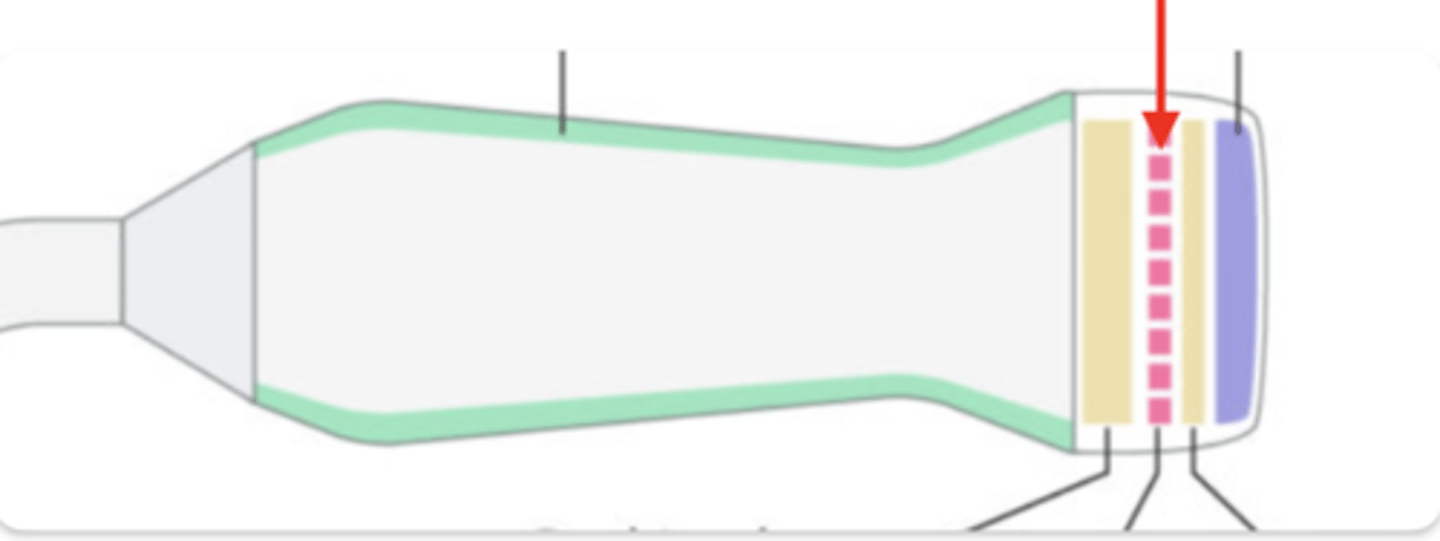
Crystals
electrical shield
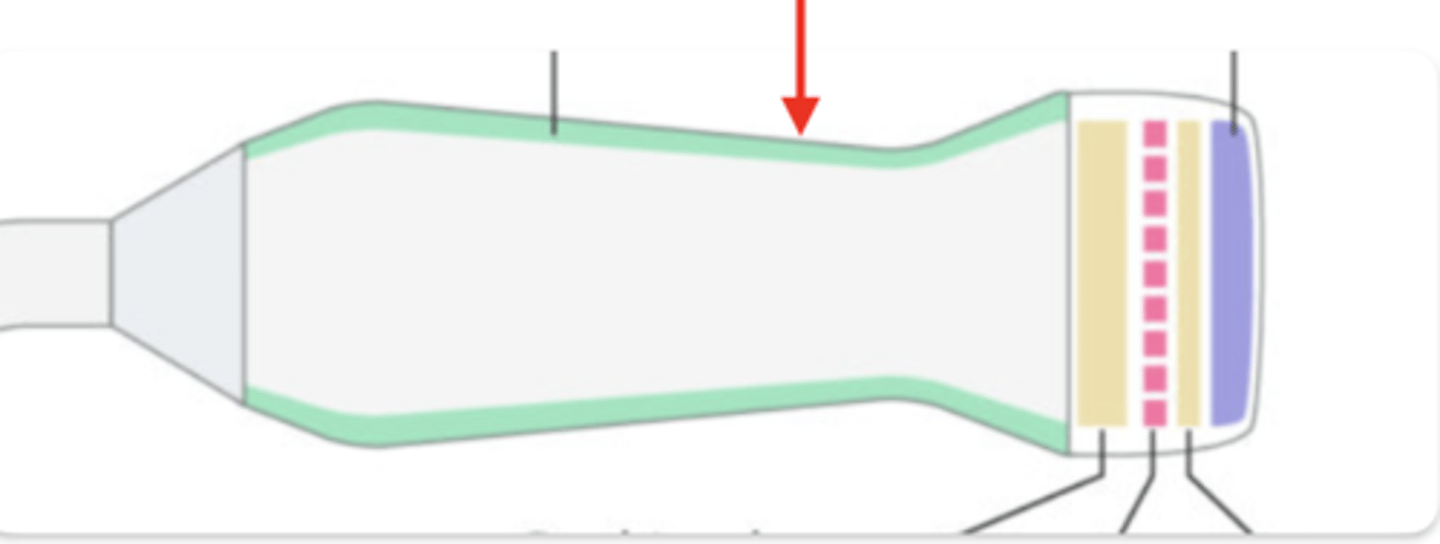
transducer case
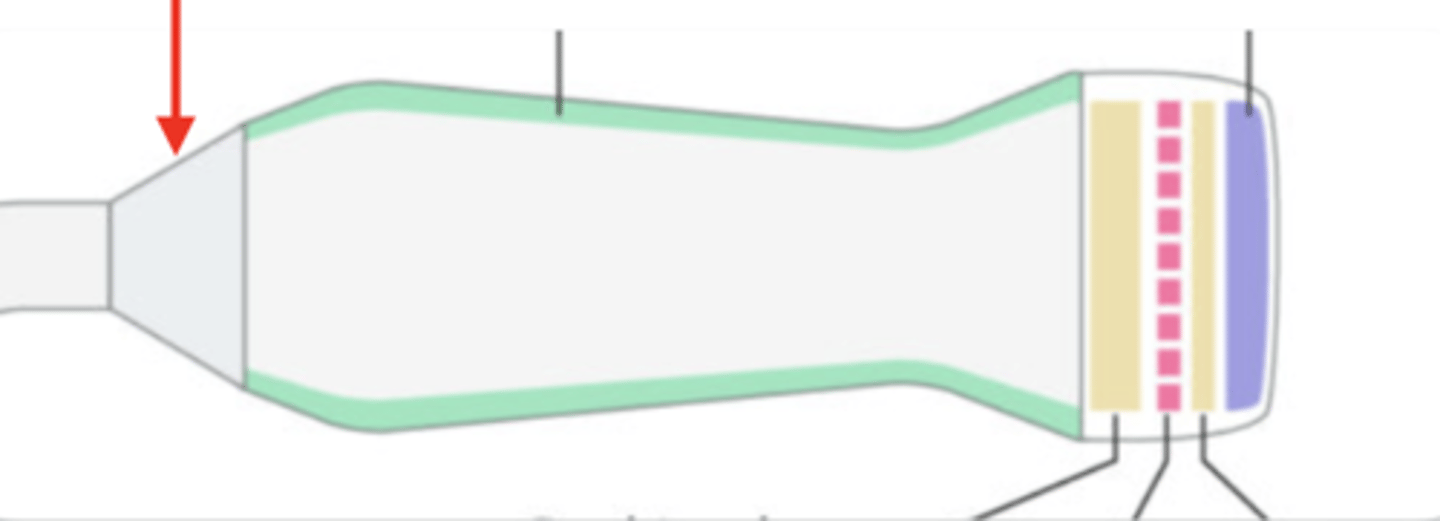
characteristics of damping material
-high degree of sound absorption
-acoustic impedance similar to PZT
the impedance of PZT is about _______ times greater than the impedance of skin
20
the F of sound emitted by a continuous wave probe is equal to
the F of the electrical signal
electrical=acoustic
the speed of sound in most piezoelectric material ranges from
4-6mm/us
PZT thickness and F relationship
inverse
thickness of PZT crystals in diagnostic imaging TRX range from
.2 to 1mm
piezoelectric/ferroelectric materials commonly used in clinical TRX
lead zirconate titanate or PZT
(synthetic/man-made)