Surveillance of Vector Borne Diseases
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
VBD facts and stats
Vector-borne diseases account for more than 17% of all infectious diseases, causing more than 1 million deaths annually.
More than 2.5 billion people in over 100 countries are at risk of contracting dengue alone.
Malaria causes more than 400 000 deaths every year globally, most of them children under 5 years of age.
Other diseases such as Chagas disease, leishmaniasis and schistosomiasis affect hundreds of millions of people worldwide.
Many vector Borne Diseases are ________.
preventable through informed protective measures.
Risk factors of mosquito-borne disease in the U.S.
Migrating birds.
Lack of mosquito control at ports of entry.
High quantities of vectors in area of concern.
Lack of public education.
Lack of funding for surveillance and equipment.
Lack of funding for insecticide resistance testing.
Vector competence of mosquitoes, host susceptibility, lack of surveillance-based targeted control, time spent outdoors (mosquito-human contact).
Increased global travel
Climate change and natural disasters (e.g., hurricanes)
Invasive mosquitoes
Introduction, establishment, and spread of invasive mosquito species (globalization of trade/travel) is concerning.
they compete with native species, transmit disease pathogens, biting nuisance, etc. (e.g. Aedes albopictus)
Lack of mosquito control infrastructure at ports of entry.
Framework for surveillance and vector Borne diseases (emerging and re-emerging)
Prevent introduction of invasive species
Prevent spread of invasive species into new areas
Prevent vector borne disease outbreaks
Improve entomological surveillance of mosquitoes
Improve human disease management, reduce morbidity/mortality
Improve public education about mosquito-borne disease (PSAs, school curriculum, etc.)
Preventing introduction of invasive species
Restrictions on importation of high risk goods and/or use of pesticides
Changes in packaging, ex: pack bamboo in hydrogel rather than standing water
quarantine step for packages
Ex: Imported goods from countries with Japanese beetles need to have palettes irradiated.
Ex: importation via used tires, Lucky bamboo
Preventing spread of invasive species in new areas
Entomological surveillance in early phases of colonization
Pesticides targeting immature and adult mosquitoes
Integrated surveillance should be ______.
analyzed and used to decide on control measures
ex: vector control when vector populations above a certain level
Entomological surveillance
trapping mosquitoes and identifying
larval surveys
Epidemiological surveillance
case-reports
Risk factor surveillance
indices (House index, Container index, breteau index)
standing water
Preventing outbreaks
National preparedness plans in place to respond to early signs of outbreaks when local transmission has been observed.
Rapid communication between local and regional health authorities essential.
Sustained federal/state funding for mosquito control programs is needed (currently not the case).
Improving human disease management
Early and efficient diagnosis crucial to management.
Misdiagnosis a problem as symptoms of vector borne disease may be complex and vary at different phases of infection.
Laboratory confirmation is important to exclude other diseases and to ensure proper treatment.
Molecular and serological techniques.
Political support
Advocacy should be based on surveillance data, risk analysis, and data on effectiveness of control methods.
Disease prevention should not be political.
Communication strategies
Physicians should be alerted to clinical signs and symptoms of vector borne diseases that could be mistaken for other viral or parasitic diseases.
Health agencies should alert the public where local cases have been reported.
Programs need to communicate with each other.
Components of Vector Borne Disease Surveillance
Disease in humans or domestic animals
Vector surveillance for pathogen
Wild vertebrate host surveillance
Weather patterns related to pathogen transmission
Affects vectors and vertebrate hosts
ArboNET
National surveillance system for arboviral disease in US.
CDC - DVBD.
Set up in 2000 after WNV entered the US (1999).
In 2003, several non-WNV arboviruses added.
Cases mapped by CDC and USGS
The arboNET monitors the ______.
epidemiology, incidence, and spread of WNV and other arboviruses.
State health departments send data to CDC weekly
Inform public health officials, government leaders, researchers, clinicians, and the public.
Support control efforts, encourage arboviral disease research.
Detect spatial patterns of emerging/re-emerging pathogens
Types of pathogen surveillance
cell cultures
molecular biology
seroepidemiology
Seroepidemiology
examination of sera for antibodies
Determine virus spread, geographical distribution, and virus prevalence
sentinel chickens
Sentinel chickens
chickens in a vector control programs that serve as an early warning system for mosquito-borne viruses or avian flu
Regular blood tests to detect antibodies from mosquito Borne disease or avian flu
Cell culture
presence/absence of live virus
quantification of virus titer (concentration of viruses in a sample)
Molecular biology
Identify and differentiate virus isolates from individuals and geographic areas
A virus with similar genotype can _______.
show different phenotypes
ex: Small West Nile virus plaque variant in mammalian cells showed minor nucleotide differences in virus membrane protein and one non-structural protein.
ex: Mutation caused phenotypic differences in vector competence in Culex pipiens pipiens (i.e. lower dissemination and transmission rates)
Electron cryomicroscopy
Rapid freezing (liquid nitrogen)
Permits visualization of particle.
Reconstruct 3-D images from frozen virus particle.
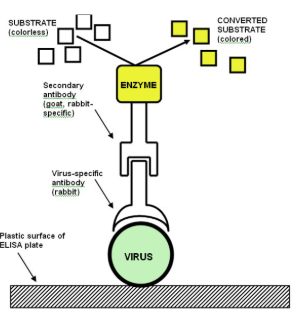
Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay is a ______.
serologic method to detect antibodies or antigen
Quantative polymerase chain reaction detects ______.
virus nucleic acid
reverse transcription in real-time
How to screen collected mosquitoes for viruses in Vero Cells
Mosquitoes collected in the field are sorted according to species.
Mosquitoes are then homogenized using a mixer mill.
The resulting mosquito homogenate is inoculated into separate Vero cell cultures.
Mosquito homogenates are placed on a shaker for 5 minutes.
The inoculated cell cultures are incubated at 37°C to allow for virus replication.
Ultimately, the cultures are examined visually for evidence of viral induced cytopathic effects.
Viable virus
Is the virus alive and multiplying?
methods: plaque assay (cells) and cytopathic effects in cell culture
explanation: virus infects/kills cells in dish
Testing methods for viable virus
plaque assay
cytopathic effects in cell culture
Testing methods for Virus antigen
Immunoflorescent assay (IF A)
Enzyme Linked Immunoassay (ELISA)
Hemagglutination Inhibition (HI)
Testing methods for Nucleic acid detection
PCR
Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR)
Testing methods for serology
general antibody detection
plaque reduction neutralization test
Immunofluorescent assay
Enzyme linked Immunoassay
hemagglutination assay
Virus antigen
looking for virus pieces, like proteins
methods: Immunofluorescent assay (IF A), Enzyme Linked Immunoassay (ELISA), and Hemagglutination Inhibition (HI)
detects viral proteins with glowing tags, color change, or blood cells clumping
Nucleic acid detection
looking for the virus’s genetic code
methods: PCR, Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction, and quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
copies DNA/RNA so virus can be seen or measured
Serology
looking for body’s antibodies
methods: general antibody detection, plaque reduction neutralization test, Immunofluorescent assay, Enzyme linked Immunoassay, and hemagglutination assay
checks if body made antibodies or if the antibodies block the virus
The BG sentinel trap was _____.
designed in response to the Zika outbreak