L27 PCR How it Works and How it is used in Diagnoses
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards on PCR and its applications in genetics and diagnostics.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
A process used to copy specific regions of DNA using primers and DNA polymerase.
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme used by cells to replicate DNA, adding complementary nucleotides in the 5' to 3' direction to the 3' end of each primer.
Chain reaction
By using two short primers either side of DNA of interest, this region can be selectively copeid. Melting and cooling the reaction (cycles), DNA pol copies the copies, amplifying this region so we can see it using gel electrophoresis.
Primers
Short sequences either side of the DNA of interest, used to selectively copy a specific region of DNA in PCR.
PCR process
Make micron environment with DNA pol, a lot of specific primers, nucleotides, and salt and water to mimic natural environment.
Cycle process
At 95 degrees DNA goes from ds to ss. At 50 degrees, DNA primers can attach to template strands. At 72 degrees DNA pol can attach and build sequence. Repeat cycle again, until target sequence outnumbers template strands.
Gel Electrophoresis
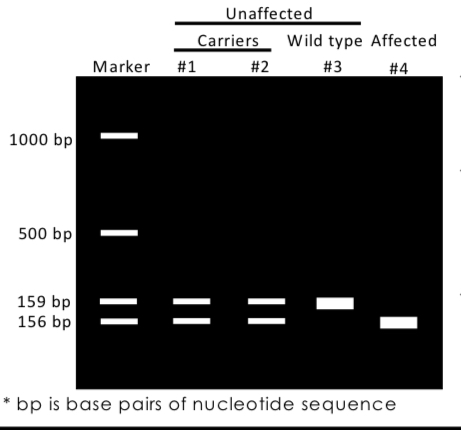
A laboratory method used to separate DNA fragments based on their size, where smaller fragments travel further through the gel. Individuals that are heterozygous for an allele are represented by two bands on gel, homozygous by 1.
Designing primers
Example cystic fibrosis. Causual variant is a 3 base pair deletion that code for (f) amino acid (deltaF508 allele 70% of cases). Using knowledge of exon 11 sequence and deltF508 allele, we can design PCR primers to selectively amplify region of interest.
Pre-implantation Genetic Diagnosis
Using PCR to diagnose IVF embryos for aneuploidies or specific monogenic diseases by removing one cell from the embryo for testing. At this stage, removing 1 cell does not affect embryo because cells have not specialised.
Aneuploidies
Condition where there are an abnormal number of chromosomes, detectable using PCR.
How biopsied cell is tested
Family has history of autosomal recesssive monogenic disorder. Parents are carriers for different pathogenic variants. PCR amplifies relevant region of DNA from each embryo cell biopsy and checked for each parents variant. Healthy embryos then selected for implantation.
Amniocentesis (testing for genetic disorders)
Amniotic fluid is taken from uterus and chorionic villus sampling where tissue is taken from placenta can be used. These are invasive and and have risk of miscarriage.
Discovery of foetal cfDNA
Fragments containing y chromosomes in mothers plasma (not possible because female) indicated it came from male foetus.
Cell-free DNA (cfDNA)
Fragmented DNA freely circulating in the bloodstream, used for non-invasive prenatal diagnosis; 10% cfDNA in maternal plasma comes from placental cells (foetal DNA). Foetal DNA is degraded by the time it reaches mothers circulation, DNA breaks between histones giving most common sizes 143 pair chunks (histone wrapped DNA), and 166 (the same but with linker DNA preserved)
PCR application to cfDNA
PCR could be used to selctively amplify foetal DNA, a more non-invasive prenatal testing. This has to be done without knowledge of sequence, so we must ligate “linkers” on ends of DNA fragments to be able to design primers to the known sequences. Once amplified, cfDNA can be sequenced, if number of sequences from a particular chromosome is wierdly high it could indicate foetal trisomy (3 copies of that chromosome)
cfDNA non-invasive prenatal diagnosis (NIPD)
Foetal DNA is more likely to be shorter. Knowing this we select fragments under 150 bp. As well as aneuploidies NIPD can be used to screen for single gene disorders using same methods as prenatal genetic diagnosis.
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)
DNA inherited from the mother that encodes proteins involved in oxidative phosphorylation, particularly the electron transport chain. Mitochondrial disease is sever and untreatble, all mothers offspring will inherit mutation.
Mitochondrial Replacement Therapy (three parent babies)
Results in a fetus with nuclear DNA from the parents and mtDNA from an egg donor to prevent mitochondrial disease. Some mtDNA (1%) will be tranfered with nucleus, when these remain blow 5% of total mitochondria chance of developing disease in negligable. PCR can be used to track mtDNA by amplifying and analysing. 1 in 5 babies from this therapy can still develope disease.