A2 Forces and Momentum
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Forces and Momentum
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
A2.1 Force, resultant, momentum basic
Force = push or pull causing acceleration of a body (change v/deform.(newtons: kg m s -2)
Adding vectors of force → resultant force
Momentum p=mv =mass x velocity,conserved
A2.2 Components of vectors
imagine you have θ and the magnitude: Fsinθ = Fx, Fcosθ = Fy
A2.3 (translational) Equilibrium
Resultant/Net force = 0, balanced → no acceleration
A2.4 Free body diagrams
Draw forces on centre of body. Body can be a block, even if it isnt. Force always attatched to something, usually considers one body at a time. Can define own x,y axes. Label forces

A2.5 Newtons first law of motion (Inertia)
A body is at rest/moving with constant velocity unless acted on by a resultant force.
A2.6. Contact vs non-contact forces
Contact require phys contact: friction, tension (spring and string) , drag, normal
Non contact: no contact: grav/electr/magnet
A2.7. Tension
taut = under tension.
the force that arises in any body when it is stretched - (pulled on from opposite sides)
Opposite to applied force. through string, rope, cable etc.
C2.8 Normal Force
Reaction force exerted by surface perp. to object resting on it: FN = mg cosθ (θ angle of inclination). Counteracts vertical forces, needed in equilibrium/friction calculations. Always equal to “other” force.
C2.9 Weight (grav)
Fg :force due to gravity acting on objects mass: weight = W = mg (g=9.81 ms-2).
Acts downwards to center of earth from middle of body. - non contact F
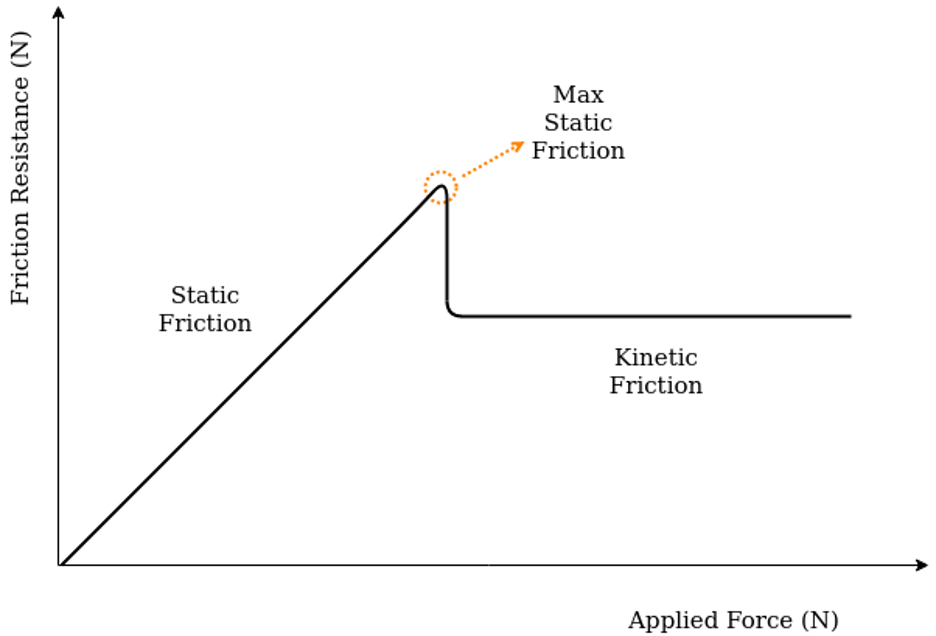
C2.10 Friction
Ff(s) Static: resists motion between stat. surfaces, matches applied force until motion starts. Fs < μsFN
Ff(d) Dynamic: resists motion between moving surfaces, constant: Fd = μdFN
μs>μd so Fs>Fd
A2.11 Electrostatic
Force between charged particles, can be attracting/repulsive, see later but know its NON—CONTACT
A2.12 Magnetic
exerted by magnetic field on moving charge/wire - non contact
A2.13 Buoyancy (Upthrust)
Fb = Upward force exerted by fluid on object in it; due to displacement of fluid; causes floating.
Archimedes: Fb = ρgV
(ρ=fluid density, V=displaced volume)
A2.14 Viscous Drag
Resistive force opposing motion through fluid. Increase with speed; leads to terminal velocity when Fnet = 0.
Stokes law: Fd = 6πηvr
(η. =viscosity of fluid, r = radius of moving body, v = velocity of body)
When Fd = Fg ; terminal velocity.
A2.15 Elastic (restoring) force
Elastic material being stretched or compressed. FH is opposing the applied force
FH = kx
(k=spring constant, x=displacement from equilibrium)
A2.16 Newtons Third Law of Motion
If Body X exerts a force on body Y, body Y will exert an equal and opposite force on body X. Fab = -Fba.
A2.17 Newtons 2nd law of motion
F = ma = change in momentum/t
kg m s-2.
A2.18 Momentum and Impulse
Momentum =m x v (Ns)
Change in momentum = impulse = J
J = Ft, F = J/t
A2.19 Conserving momentum
No external force = momentum always conserved.
A2.20 Collisions (→←)
Elastic: ← → (no change in Ek)
Inelastic: → —> (heaviest one directs)
Perfectly in.: → (both)
A2.21 UCM
Uniform circular motion. Always accelerating, velocity changes; speed is constant but directino is not. (centripetal) Force pointing inwards to centre of circle; cause centripetal acceleration. No work is done
A2.22 Quantities of UCM
Time period (one circle): T
Angular displacement (angle swept): θ rad
Angular velocity: ω = θ/t rad s-1 = 2π/T = 2πf
Frequency: rev/time: f = 1/T
Speed: v = ωr
Arc length: s = θr
Centripetal acceleration: a = vω = v2/r - pointing to centre.
Centripetal force: F. =mv2/r = mω2r