Biology Exam 7
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Lamarck
Jean Baptiste Lamarck thought the more used traits became more dominant in offspring.
Like he would have thought that Giraffes had long necks because their ancestors stretched their necks to get the high fruits.
Hutton and Lyell
Lyell developed Hutton’s theories, together forming the concept of uniformitarianism, saying that the mechanisms of today are the same mechanisms from history.
Cuvier
Believed in catastrophism, that each boundary between strata of the Earth represented an ancient catastrophe.
Who advocates for catastrophism?
Uniformitarianism?
Catastrophism - Cuvier
Uniformitarianism - Lyell
Artificial Selection
Modification of species by selecting and breeding individuals with desired traits.
Natural Selection
Process by which individuals with certain inherited traits leave more offspring than individuals with other traits
What are the four evidence for evolution
Direct Observation
Fossil Record
Homology (similarities between species, ex: Similar forelimbs in vertebrates)
Biogeography (fossils line up on pangea)
Homologous Structures
Anatomical resemblances between species which come from a common ancestor
Analogous Structures
Anatomical resemblances in different species due to similar environmental pressures
Vestigial Structures
Structures which come from an ancestor but no longer serves a purpose
What are the three processes which change allele frequency (name don’t define)
Natural selection
Genetic drift
Gene flow
Genetic Drift
Definition
What is a possible outcome of genetic drift
Genetic drift describes how allele frequencies fluctuate unpredictably from generation to generation
Can result in a loss of variation as an allele might disappear from the population
Two types of genetic drift and what they mean
Bottleneck
Something causes a large reduction in the population
Founder Effect
A certain part of the population gets isolated from the larger population
Gene Flow
Definition
What is a possible outcome of genetic drift
Gene Flow describes the movement of alleles among populations (ex: pollen gets carried from one group of flowers to another)
This can result in less variation between populations as they end up becoming more homogenous with each other.
What are the five conditions for Hardy Weinberg equilibrium
Random mating
No natural selection
Extremely large population size
No gene flow
No mutations
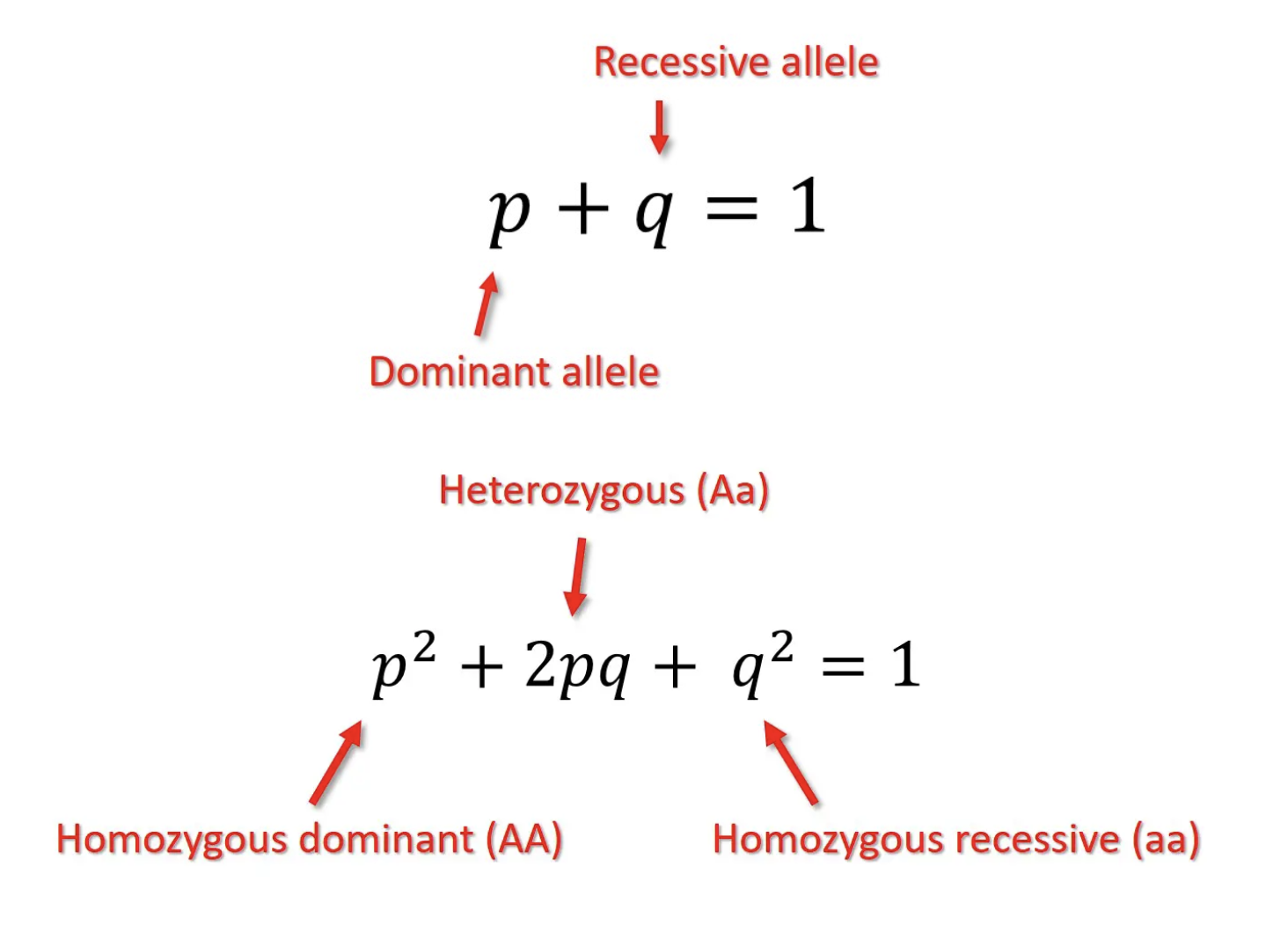
Hardy-Weinberg Formulas
Chi-Square Formula
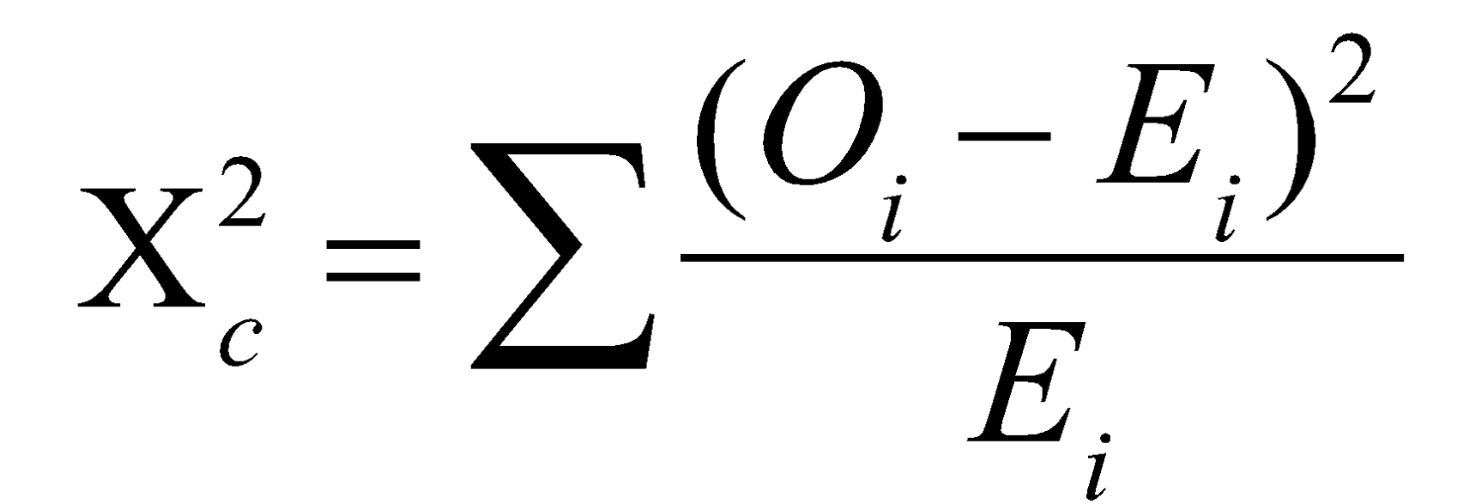
Standard Deviation Formula
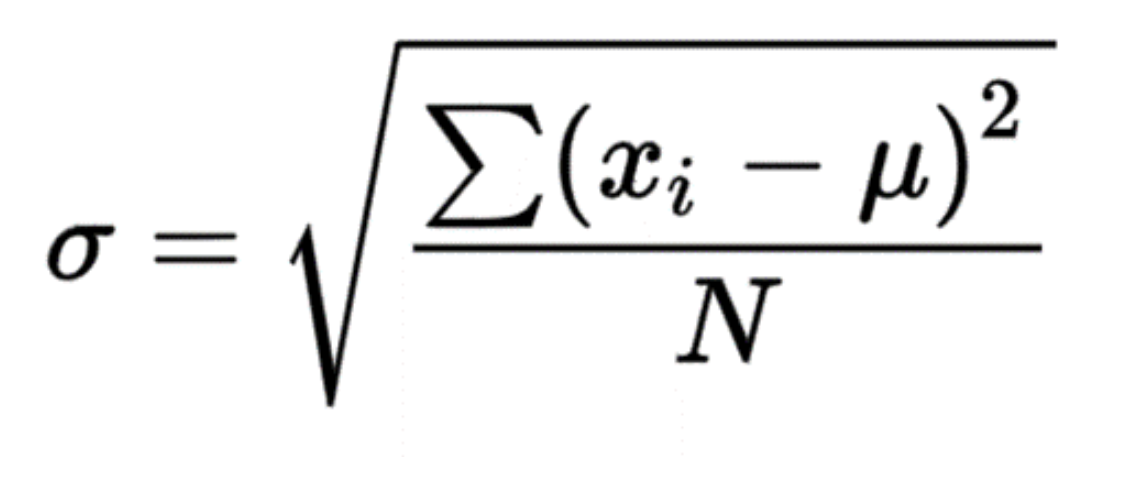
Standard Error Formula
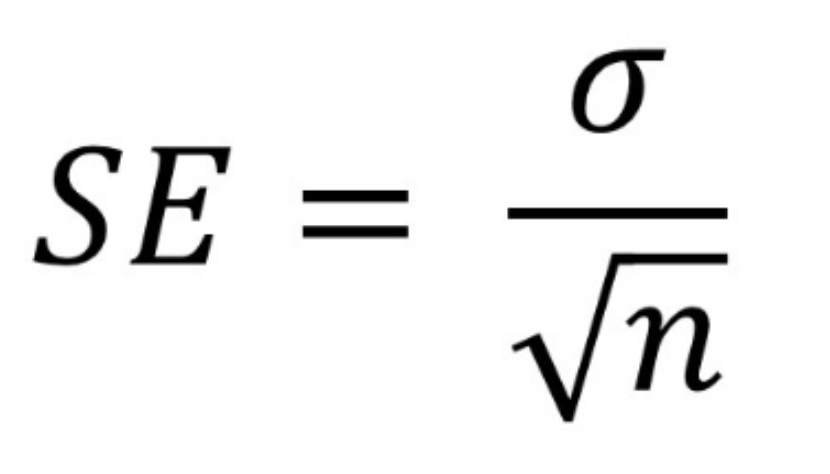
What are the sources of variation in a population?
Gene mutation
Crossing over
Independent Assortment
Fertilization
Change in chromosome number