chapter 8 appendicular: LOWER LIMBS
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
pelvis
sacrum, coccyx, right ossa coxae, left ossa coxae
supports viscera in inferior part of ventral body cavity
pelvis
pelvic girdle
ONLY L & R ossa coxae - ilium, pubis, ischium
distribute weight / supp soft organs
the pelvic girdle is angled ________ when standing upright
anteriorly
3 multiple choice options
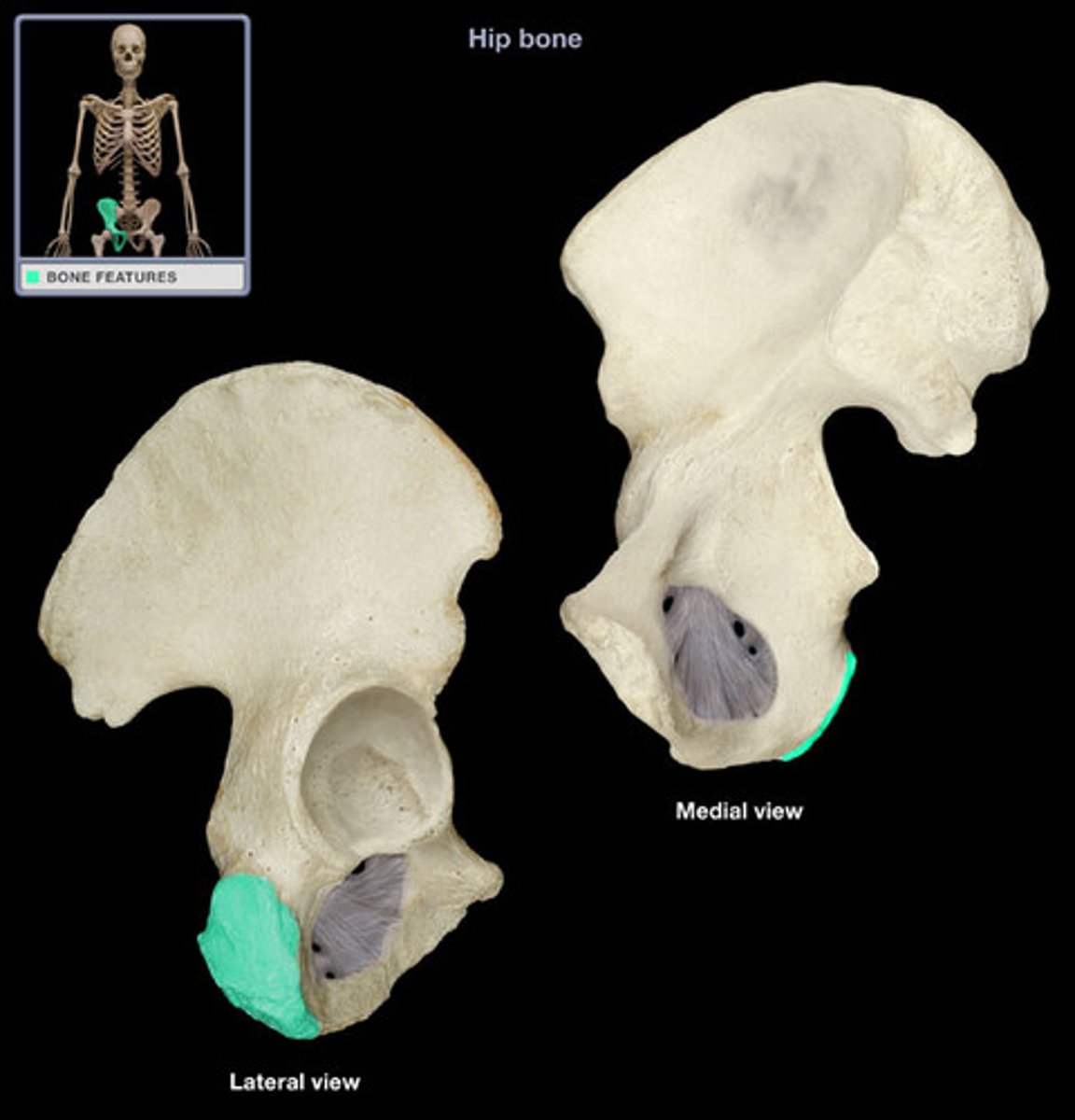
ossa coxae / coxal bones
hip bones
compare mobility and stability of SHOULDER JOINT and PELVIC GIRDLE. pelvic girdle is....
less mobility, more stability
3 multiple choice options
the 3 coxal bones r fused
through puberty
acetabulum
LATERAL!!
hip socket, articulate w femur; region where the 3 bones have FUSED
lunate surface
Smooth articulating surface on the periphery of the acetabulum - w femoral head
articulation btwn os coxae and sacrum
sacroiliac joint
acetabular rim
outside edge of acetabulum, fibrocartilage
the lunate surface is made of
cartilage
obturator foramen
opening in hip bone formed by the pubic and ischial rami - passage for nerves, blood vessels
ala
wing of ilium
pubic symphysis
cartilaginous joint at which two pubic bones fuse together
anterior superior iliac spine
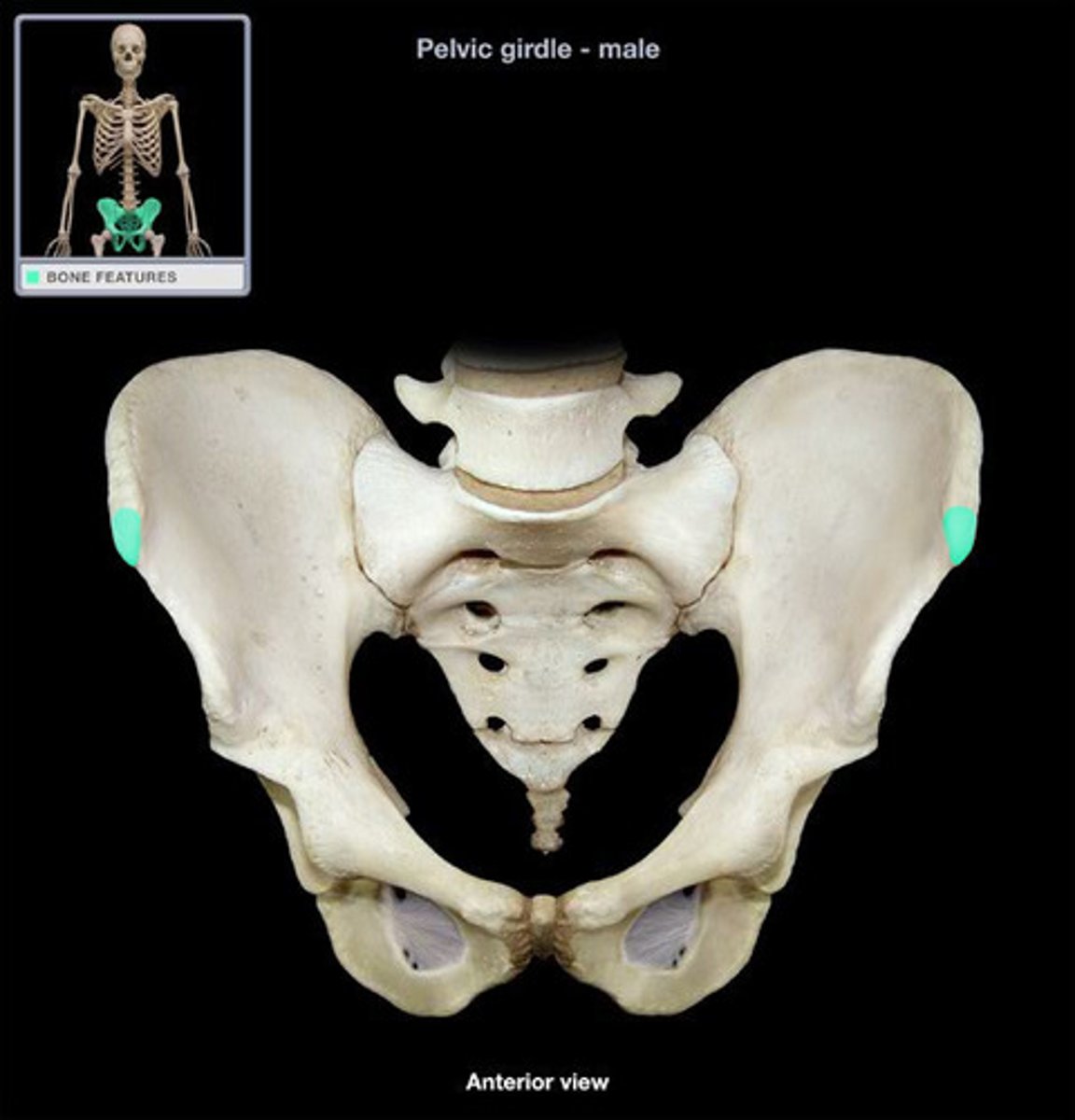
anterior inferior iliac spine
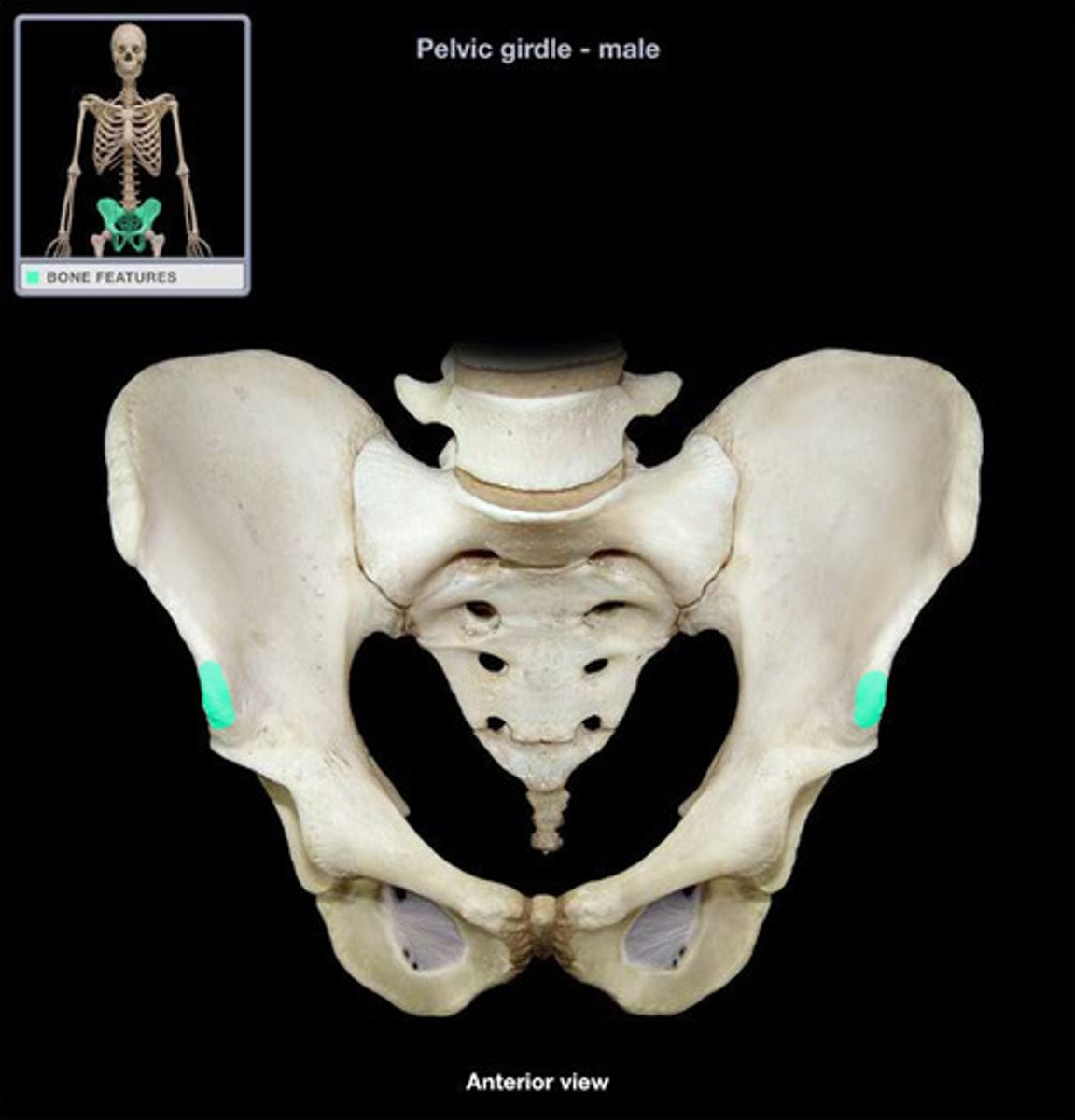
iliac crest
upper margin of iliac bones
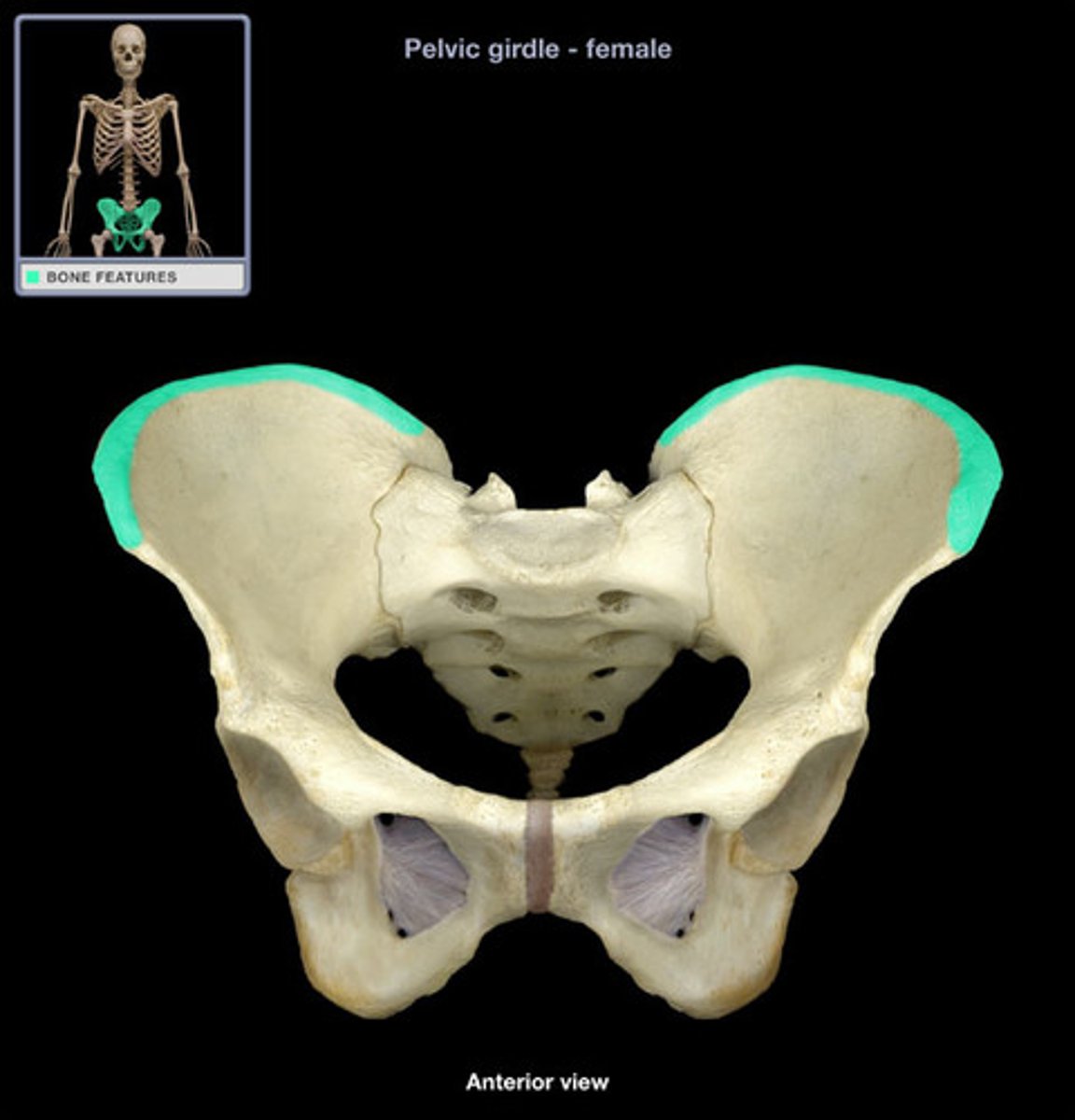
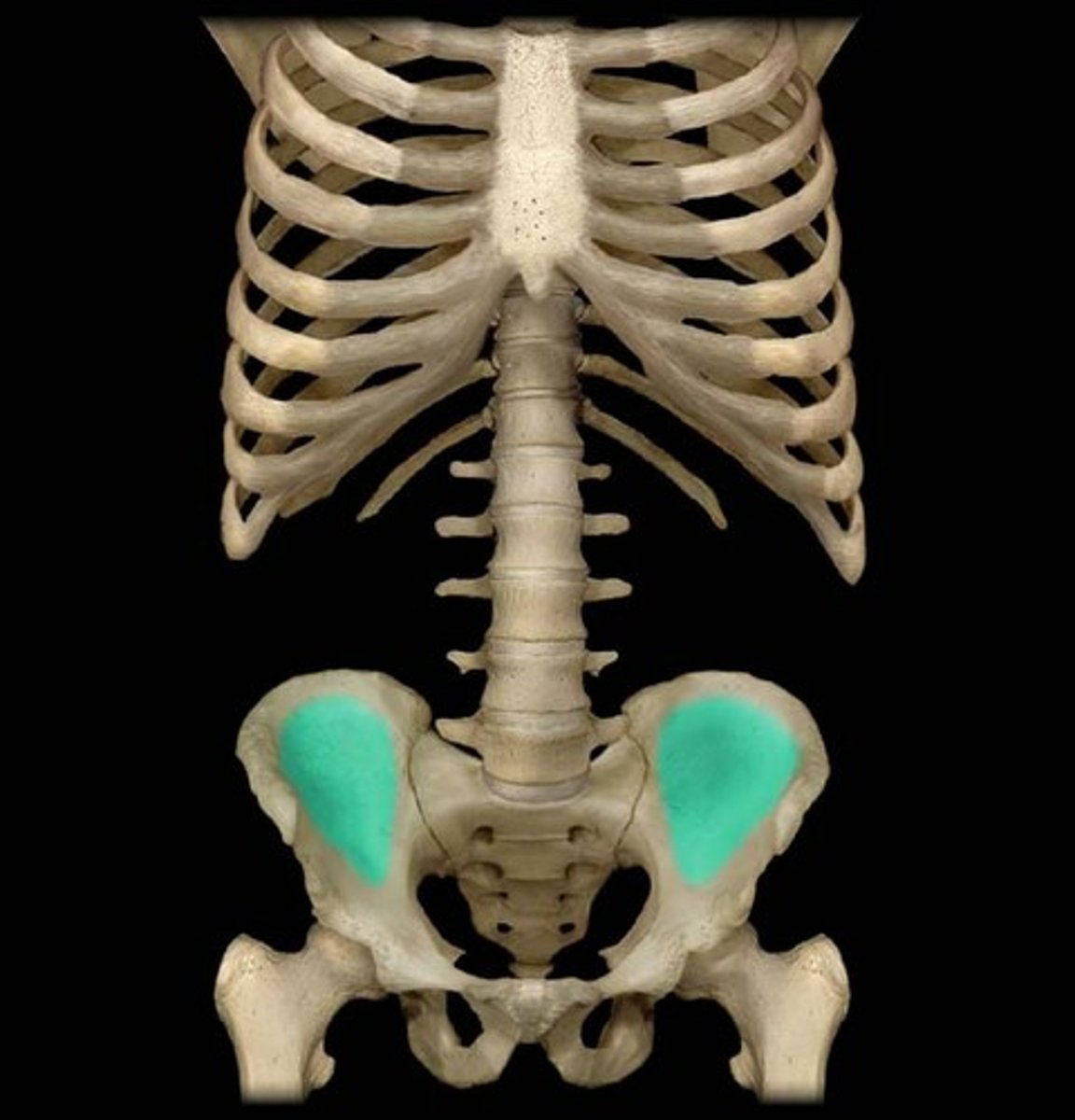
iliac fossa
The broad, slightly concave inner surface of the ilium.
superior and inferior pubic ramus
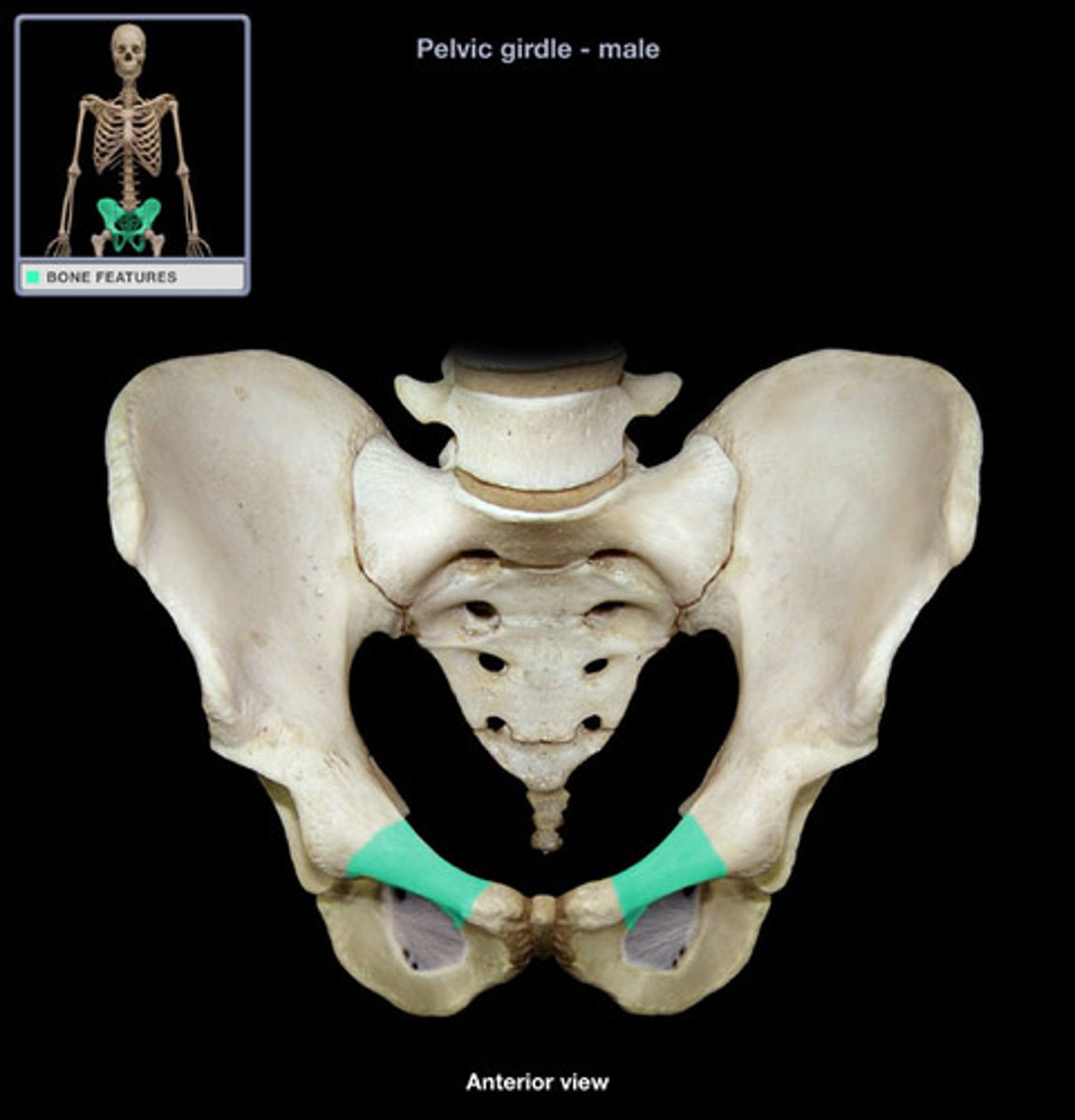
sciatic notch
angled: on the POSTERIOR side. separated by ischial spine !!
ischial tuberosity
receives the weight of the body when sitting
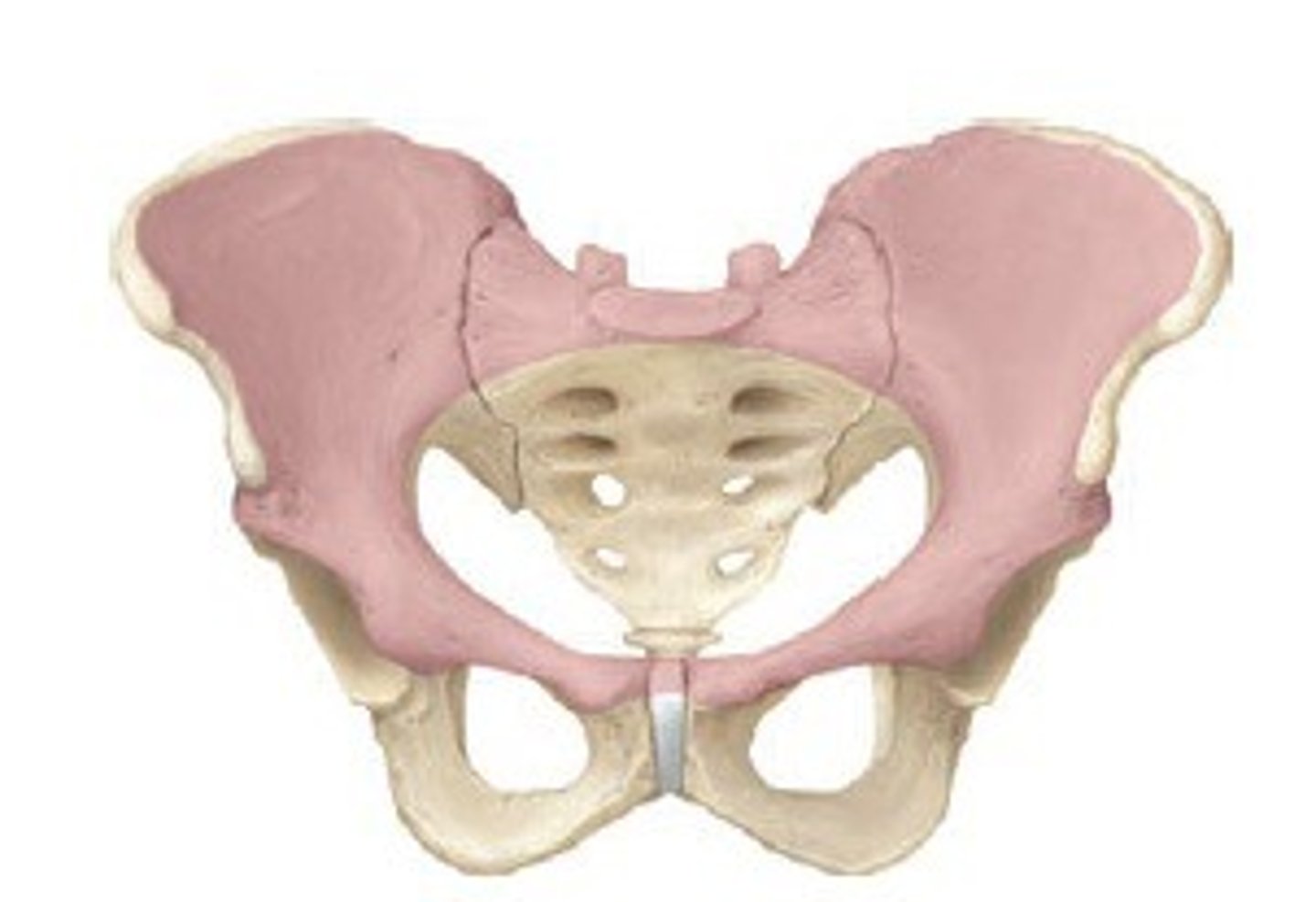
greater/false pelvis
Above the pelvic brim
Borders:
Lumbar vertebrae
Upper portions of hipbone
Abdominal wall
Contains urinary bladder (full) and uterus (pregnancy)
lesser/true pelvis
Below pelvic brim -- Surrounds pelvic cavity
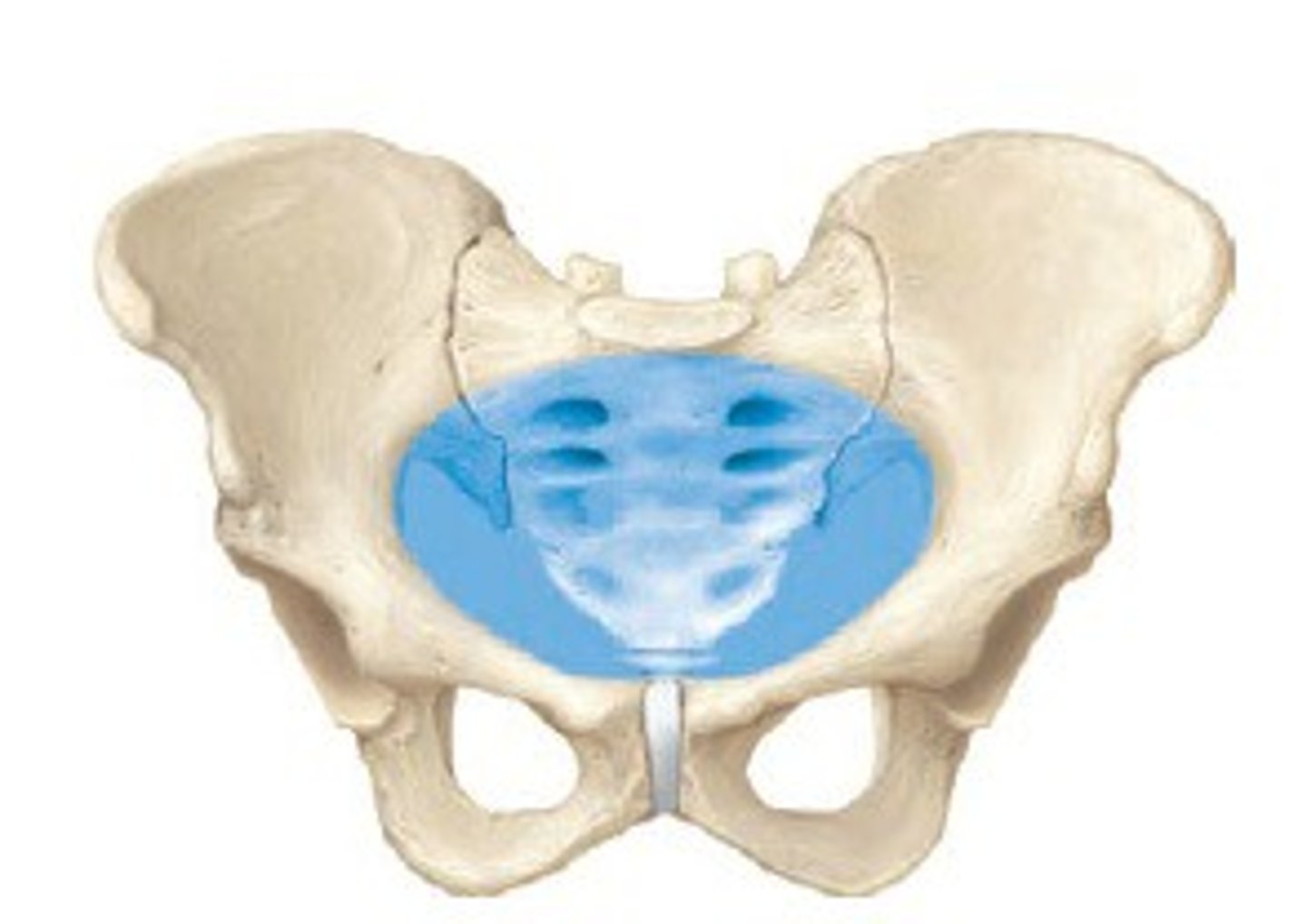
baby passes through
lesser/true pelvis
female vs male pelvis
Female pelvis is lighter, thinner, and wider than male pelvis, flares out anteriorly and has a wider sacrum, wider ilium
Make titled less far forward - support heavier organs
* sex differences happen during puberty
broad, shallow pelvis
female
narrow, deep pelvis
male
largest and strongest bone in body?
femur
preauricular sulcus
depression btwn greater sciatic notch & sacroiliac articulation; only in females
subpubic angle
degree of angle formed under the pubis symphysis; wider and more convex in F!!
components of the lower limb
thigh + leg + foot
how many bones in lower limb
30: femur, patella, tibia / fibula, 7 tarsals, 5 metatarsals, 14 phalanges
how many tarsals
7
femur: proximal vs distal articulations
proximally: fovea / fovea capitis in head articulates with the acetabulum
distally:
- patellar surface articulates with articular surface of patella
- medial & lateral condyles articulate with medial & later condyles of tibia
femur is abt ___ of height
1/4
femur: anterior, top to bottom
TOP
lateral to medial: greater trochanter, intertrochanteric line, neck, head w fovea capitis, lesser trochanter (a bit under, from behind)
MIDDLE nothing
BOTTOM
lateral to medial: lateral epicondyle, lateral condyle, patellar surface (v bottom), medial condyle, adductor tubercle, medial epicondyle
femur: posterior, top to bottom
TOP
intertrochanteric CREST!,
medial: pectineal, lateral: gluteal tuberosity
merge into LINEA ASPERA which is kinda MIDDLE
BOTTOM - up 2 down
medial & lateral supracondylar lines
popliteal surface (middle ish)
intercondylar fossa
condyle vs epicondyle
condyle: covered w cartilage - make joint / articulaysh
epicondyle: point 4 attachment for ligaments
trochanter
attach 4 muscle
what results in the medial angling of the femur
the elongated neck which joins the shaft @ an angle
Both trochanters are
insertion sites for gluteal and thigh muscles
patella
- kneecap, sesamoid - housed within tendon
- superior base
- inferior apex
POSTERIOR: articular surface covered by cartilage, articulates w femur; medial and lateral facet
UNDER: patellar ligament -> tibia
what is the only weight-bearing bone in the crural region?
tibia
crural region
leg
fibula is
lateral
between the tibia and fibula
interosseous membrane, extends between interosseous borders
what provides a pivot of minimal rotation for bones
interosseous membrane
tibia, anterior top to bottom
TOP:
medial & lateral condyles, separated by intercondylar eminence
tibial tuberosity -middle ish
MIDDLE
anterior border - "shin"; ridge
BOTTOM
medial malleolus
bottom bottom: inferior articular surface
tibia, posterior top to bottom
TOP
laterally: fibular articular facet
BOTTOM
laterally: fibular notch
what can be palpated on the medial side of the ankle
medial malleolus of tibia
inferior tibiofibular joint
fibular notch + fibula
superior tibiofibular joint
fibular articular surface/facet + fibula
hammer reflex
patellar ligament
attachment for patellar ligament
tibial tuberosity
fibula, top to bottom
TOP
articular facet (more anterior); head & neck
BOTTOM
lateral malleolus
what can u palpate on lateral side of ankle
lateral malleolus
tarsals
proximal: talus, calcaneus, navicular
distal: cuneiforms and cuboid
largest bone of foot
calcaneus
talus
articulates w tibia, superior, 2nd largest
cuneiform category
medial intermediate, cuneiform
cuboid
lateral
great toe
hallux
3 phalanges
proximal, middle, distal
foot arches
- support weight of body
- ensure blood vessels on sole of foot not pinched
- ligaments & tendons PLUS bones create arch
3 arches: medial & lateral longitudinal; transverse
the highest of the three arches
medial longitudinal arch
3 multiple choice options
Formed from calcaneus, talus, navicular, cuneiform bones, metatarsals I-III
medial longitudinal arch
Formed from calcaneus, cuboid bones, metatarsals IV-V
lateral longitudinal arch
transverse arch
perpendicular to other arches; along distal row of tarsals
Formed from distal row of tarsals and bases of all metatarsals
pes cavus
long arch too high
pes planus
long arch too flat
The ossa coxae collectively make up the
pelvic girdle
Which portion of the os coxae is most anterior and inferior?
pubis
The sacrum, the coccyx, and hip bones make up the
pelvis
When a person is standing upright, the pelvis is tipped
anteriorly
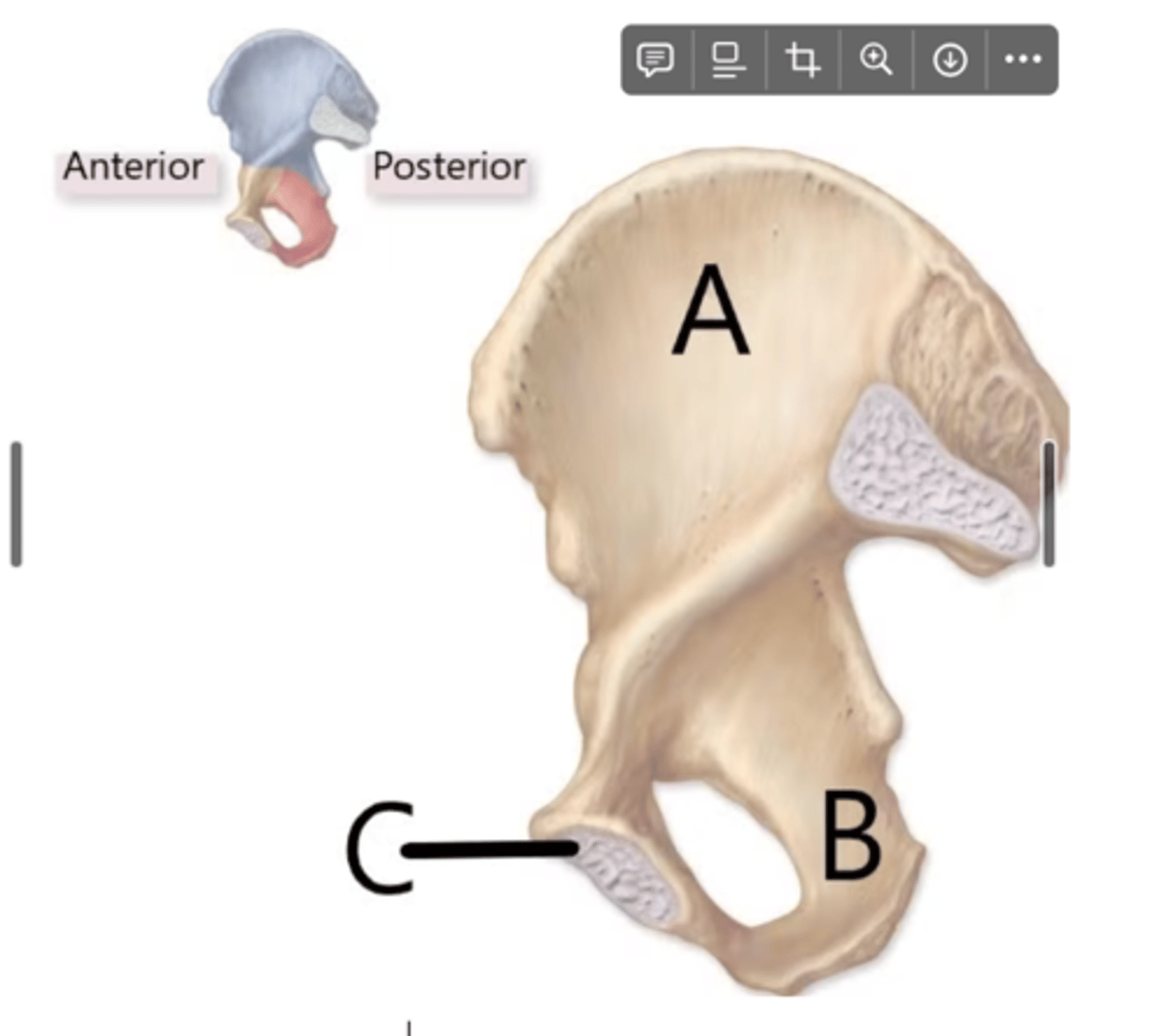
name the parts of the coxal bones
A, B, C
ilium, ischium, pubis
The rough anterior surface of the tibia that can be palpated just inferior to the patella is the
tibial tubersoity