Urinary Analysis
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
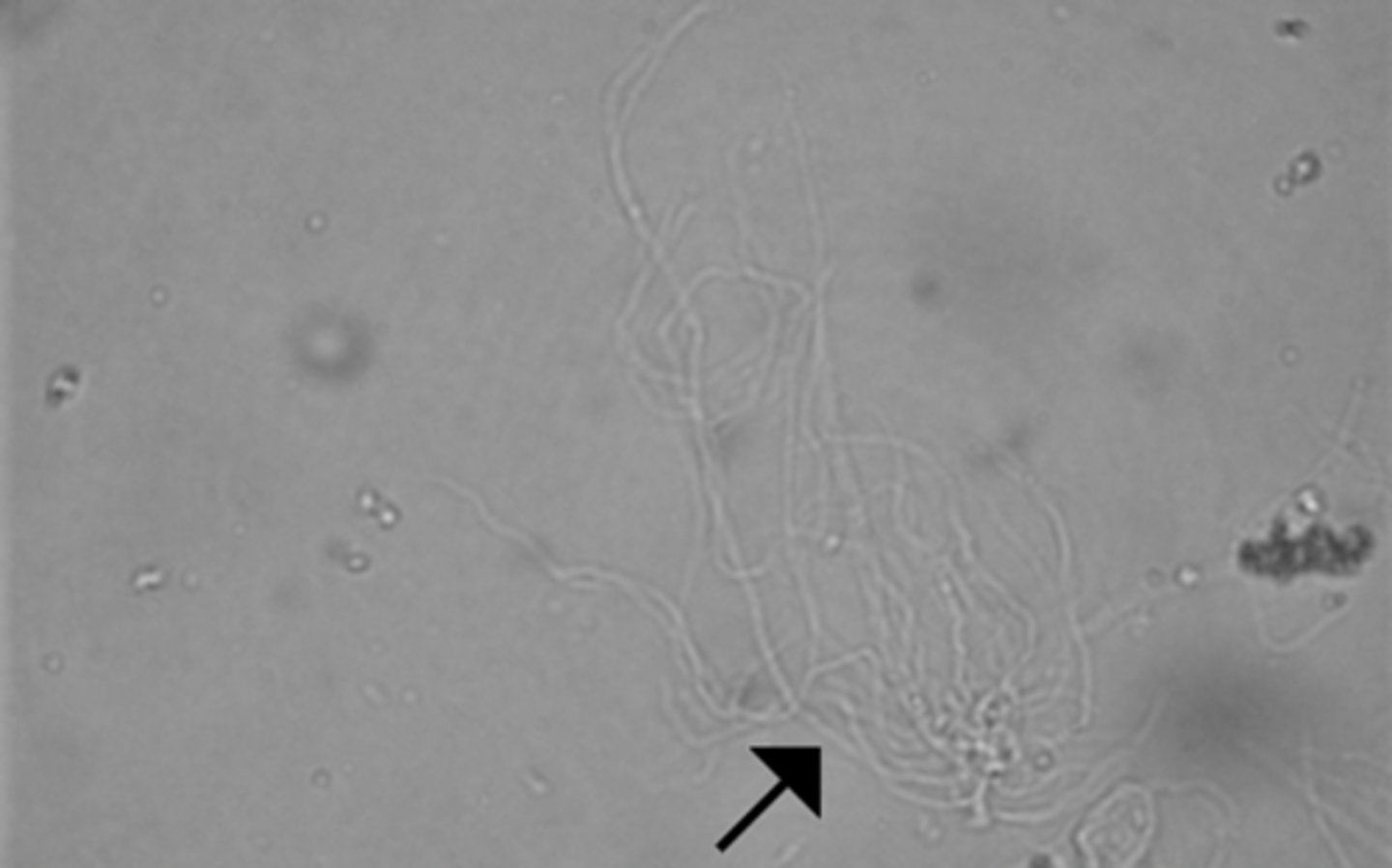
Hyaline casts
consist of only the uromodulin protein matrix (0-2/low power field) are normal. They may be visible in the urine sediment if the individual has been exercising heavily, has a fever, or is undergoing diuretic therapy.
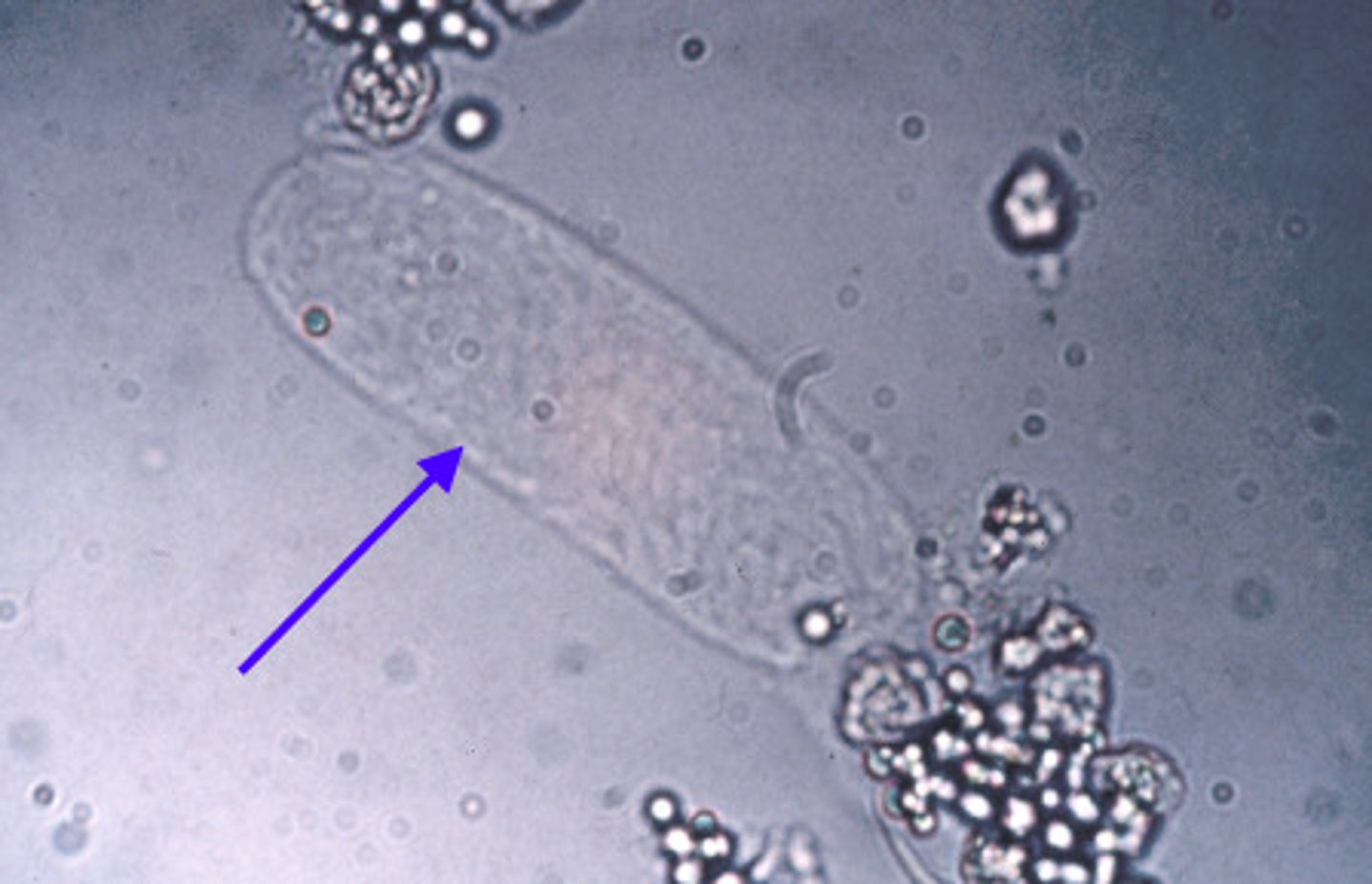
Cellular Casts
consist of a uromodulin mucoprotein matrix containing RBCs, WBCs, renal tubular epithelial cells, or a mixture of these cell types. Originate from the distal tubules. The presence of ______casts is always abnormal.
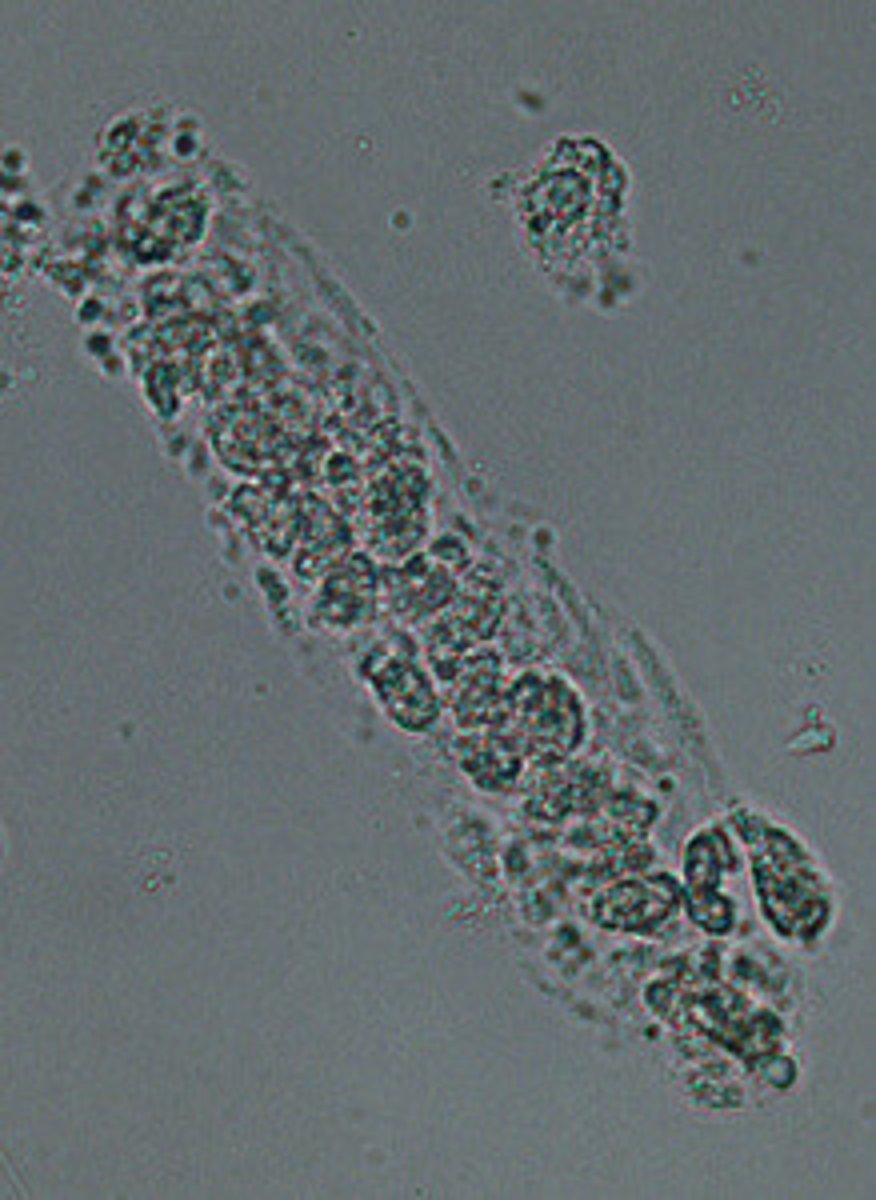
(WBC)White Blood Cell Casts
appear as clear cylinders containing leukocytes. They are associated with infection or inflammation of the nephron. can be seen in cases of pyelonephritis and interstitial nephritis.
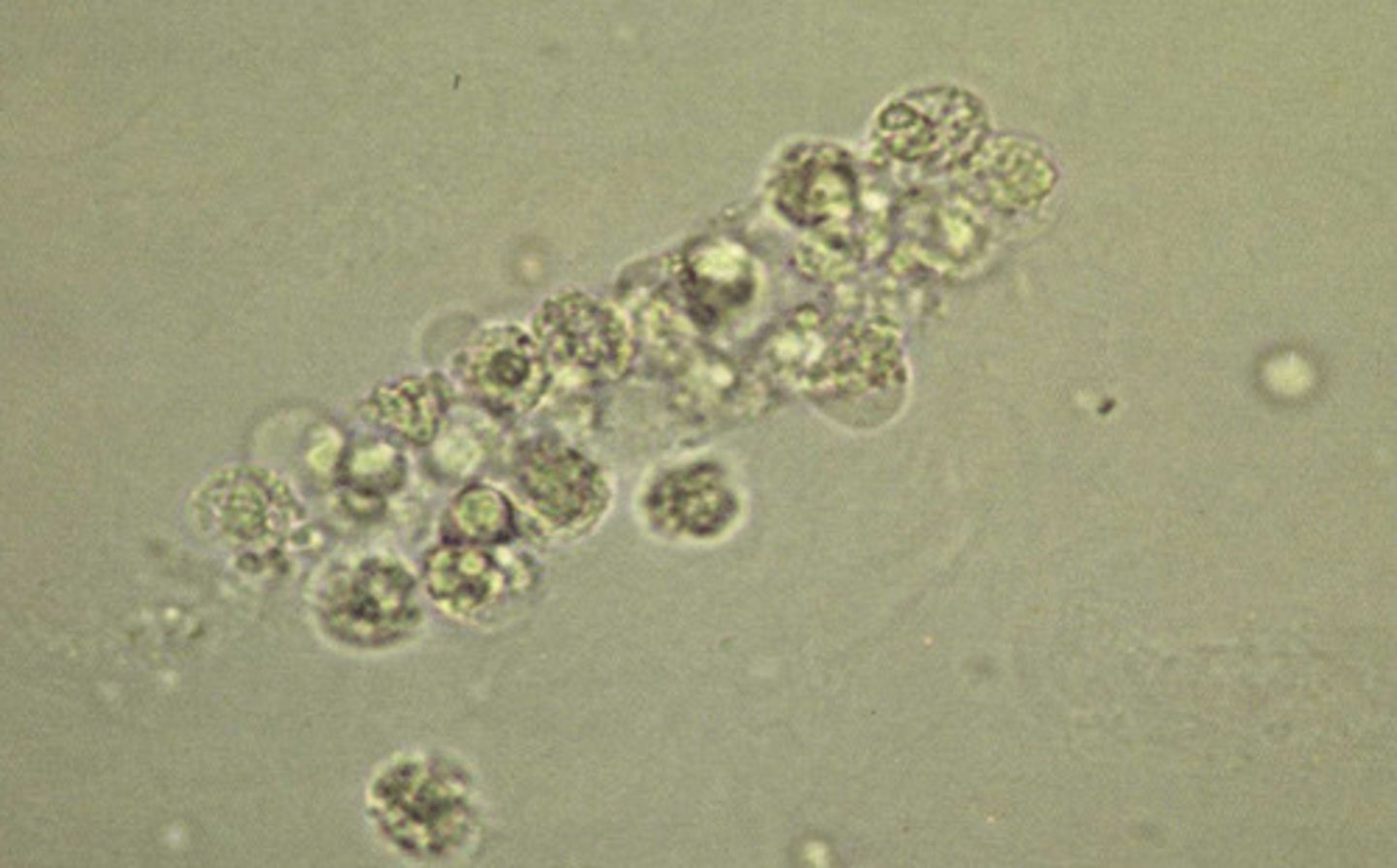
(RBC) Red Blood Cell Casts
contain intact and disintegrated or crenated red blood cells. When many cells are enclosed within the matrix of the cast, a red blood cell cast appears yellow or reddish-brown. The presence of ______ casts in the urine indicates bleeding into the nephron.
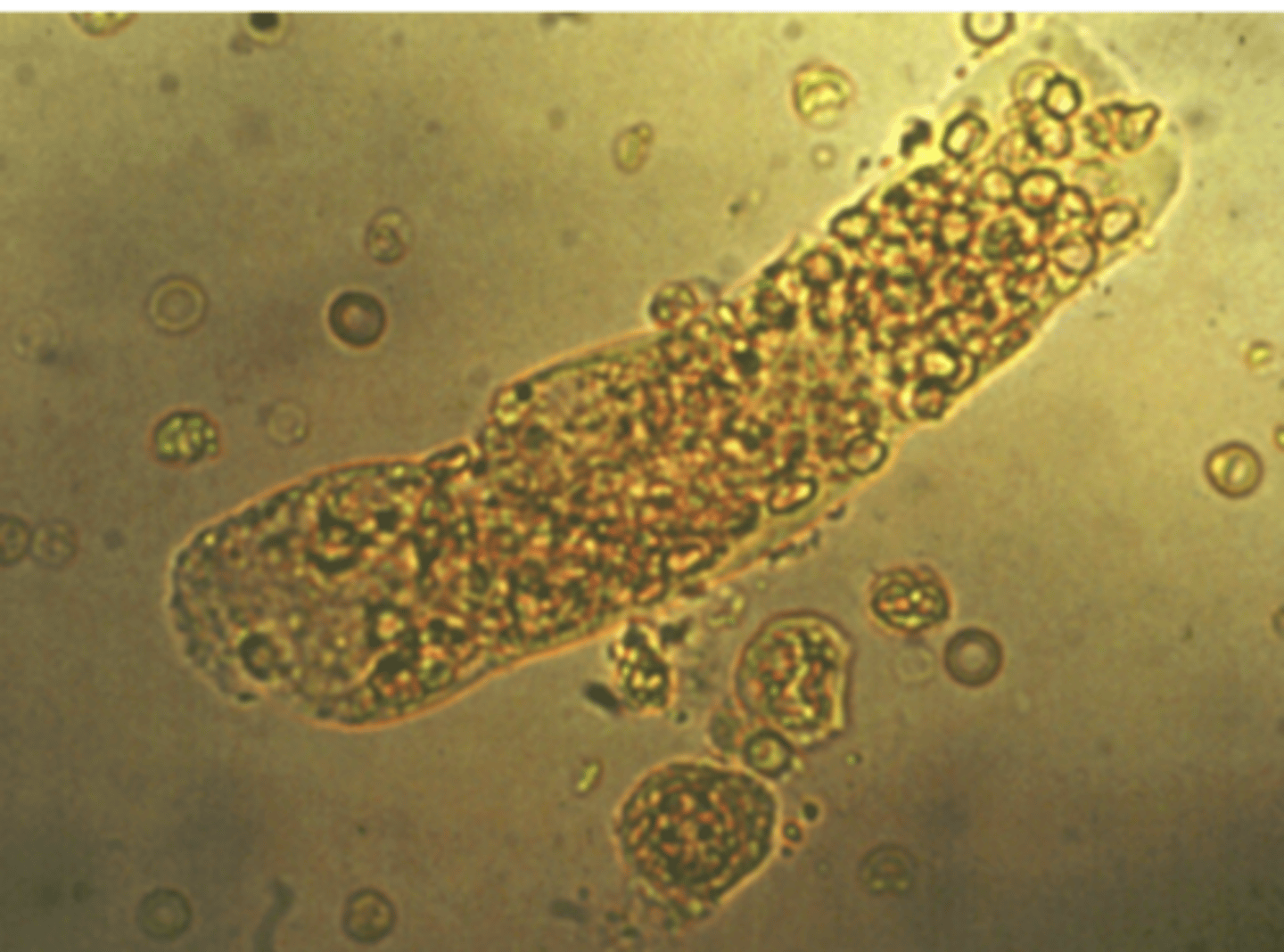
Renal tubular epithelial (RTE) cell casts
These casts indicate tubular damage. In some ____cell casts, the ____ cells may appear in rows, indicating that the epithelium of an entire tubule has sloughed off. May look similar to WBC casts
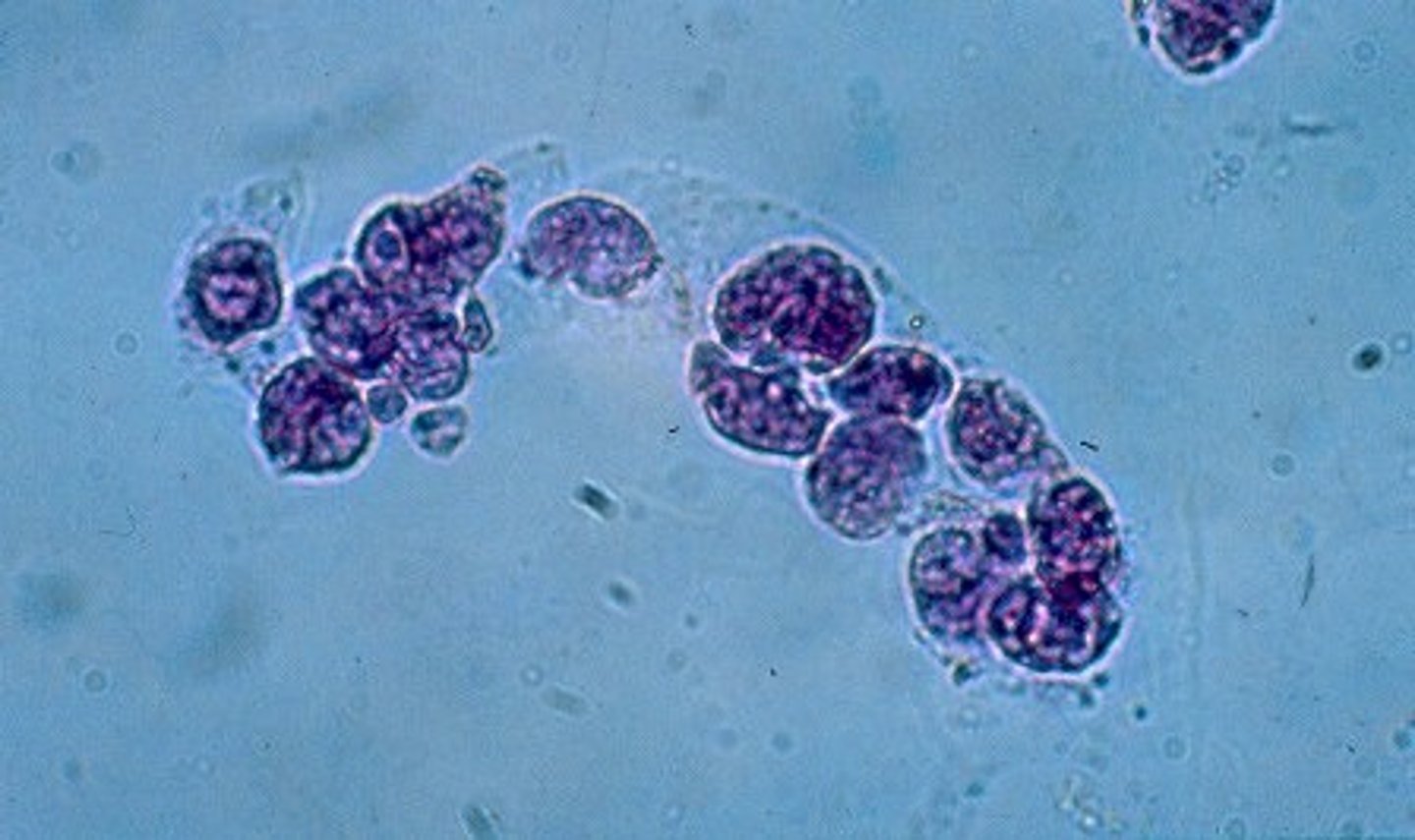
Granular Casts
composed of cellular remnants and by-products of protein degradation. appear as irregularly shaped cylinders of coarse or fine, highly refractive particles.
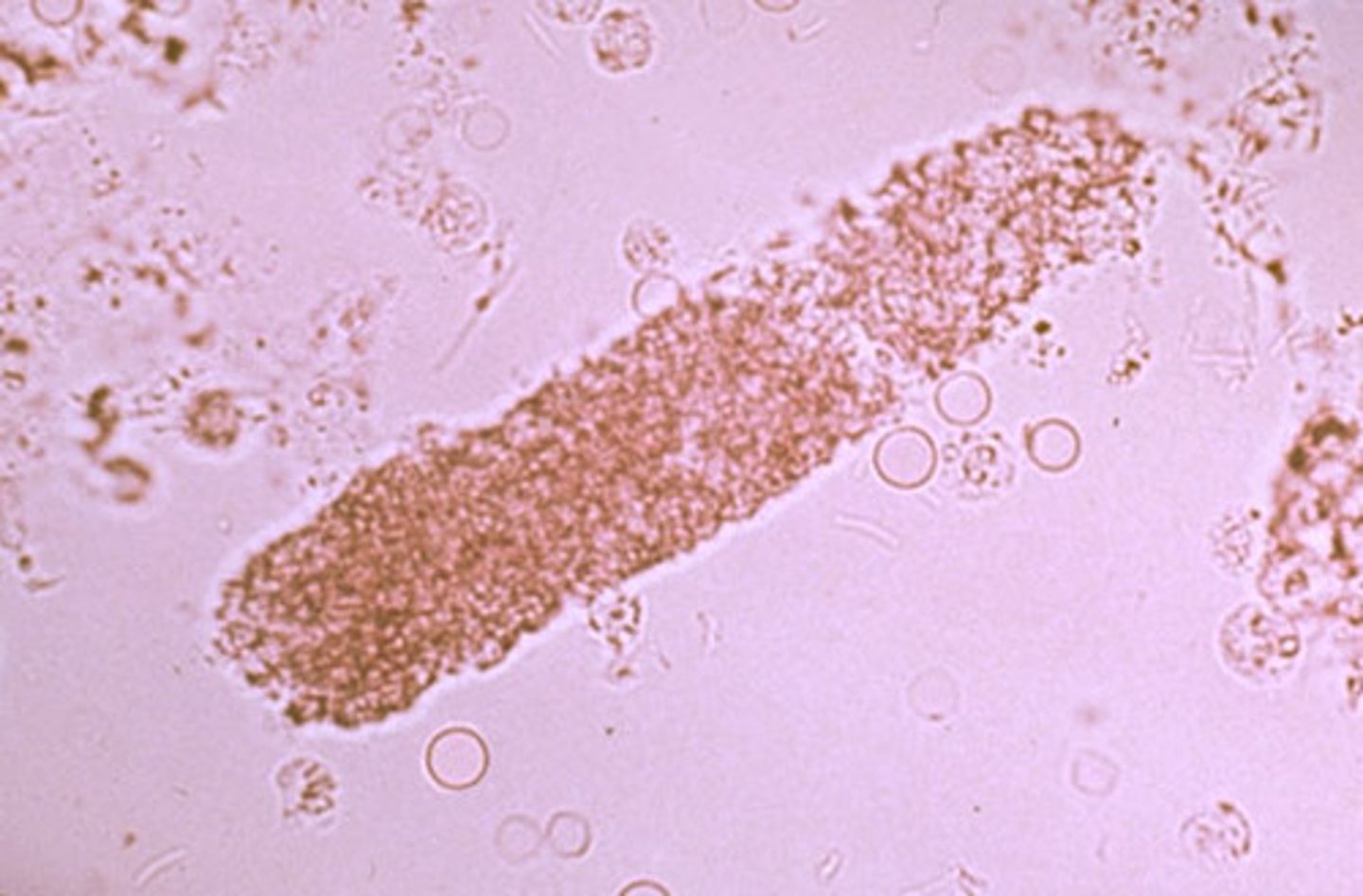
Waxy Casts
appear as cylinders of smooth, highly refractile material. They are homogeneous with sharp, defined edges and usually squared-off ends. Cracks may occur within the cast, giving it a segmented appearance. Some believe ___ casts are the final stage of degeneration of the fine granules of granular casts. _____casts are seen in chronic renal failure and acute and chronic renal allograft rejection.
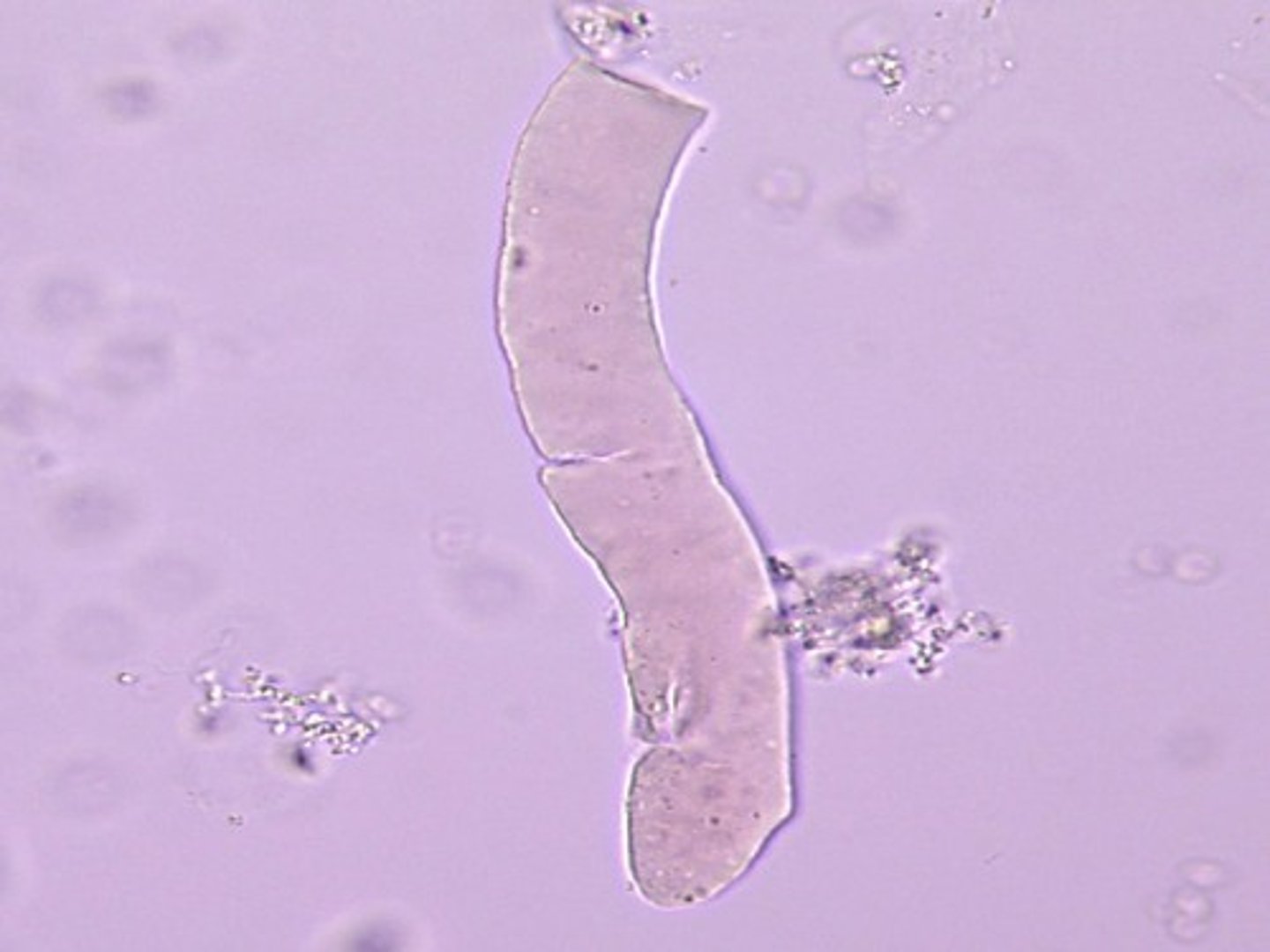
Fatty Casts
highly refractile with the appearance of oil droplets on the cast matrix, as shown in the top image on the right. containing cholesterol will produce classic Maltese cross formations under polarized light. Are characteristic of degenerative tubular disease and are frequently associated with heavy proteinuria.
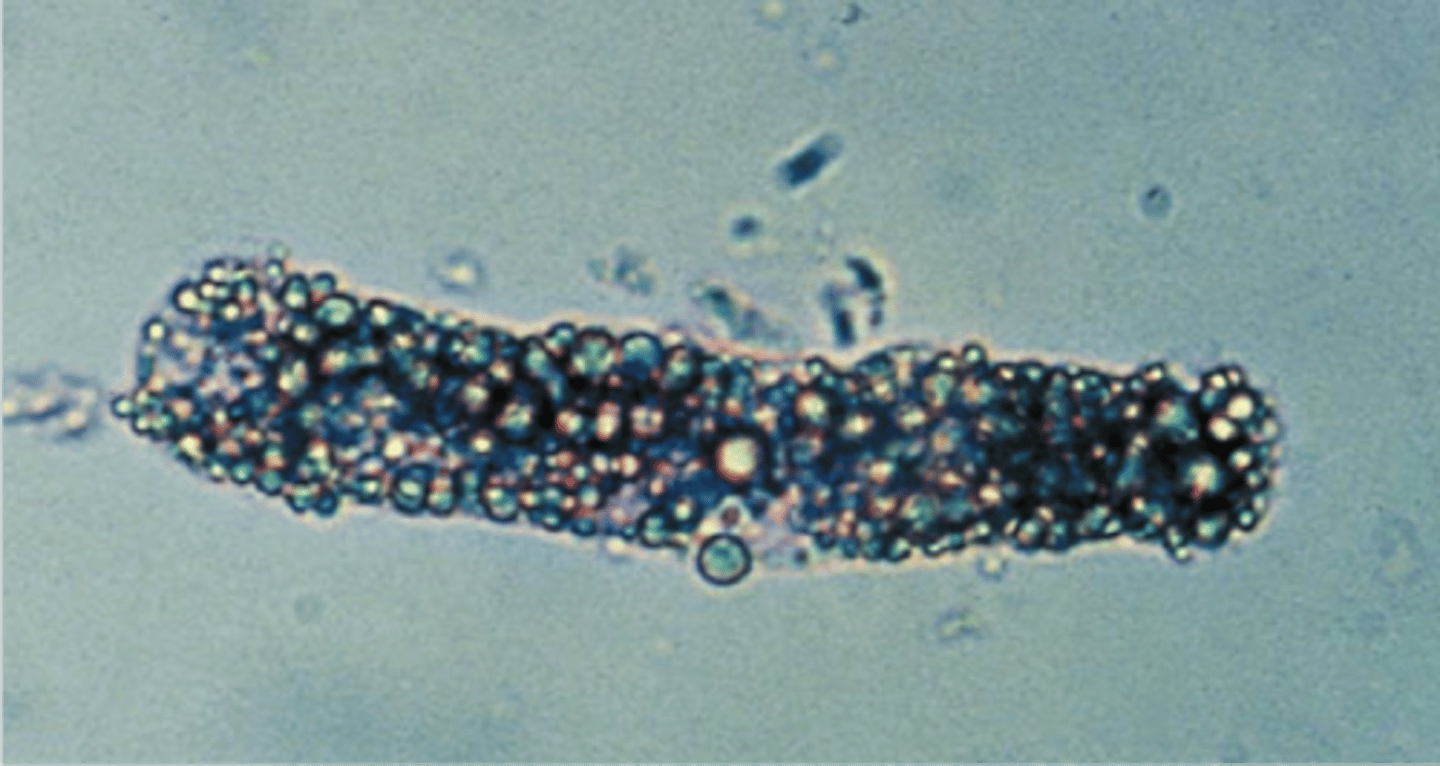
Broad Casts
"renal failure" casts are associated with end-stage renal disease. They are formed in the collecting ducts due to urinary stasis and are two to six times the size of other types of casts.
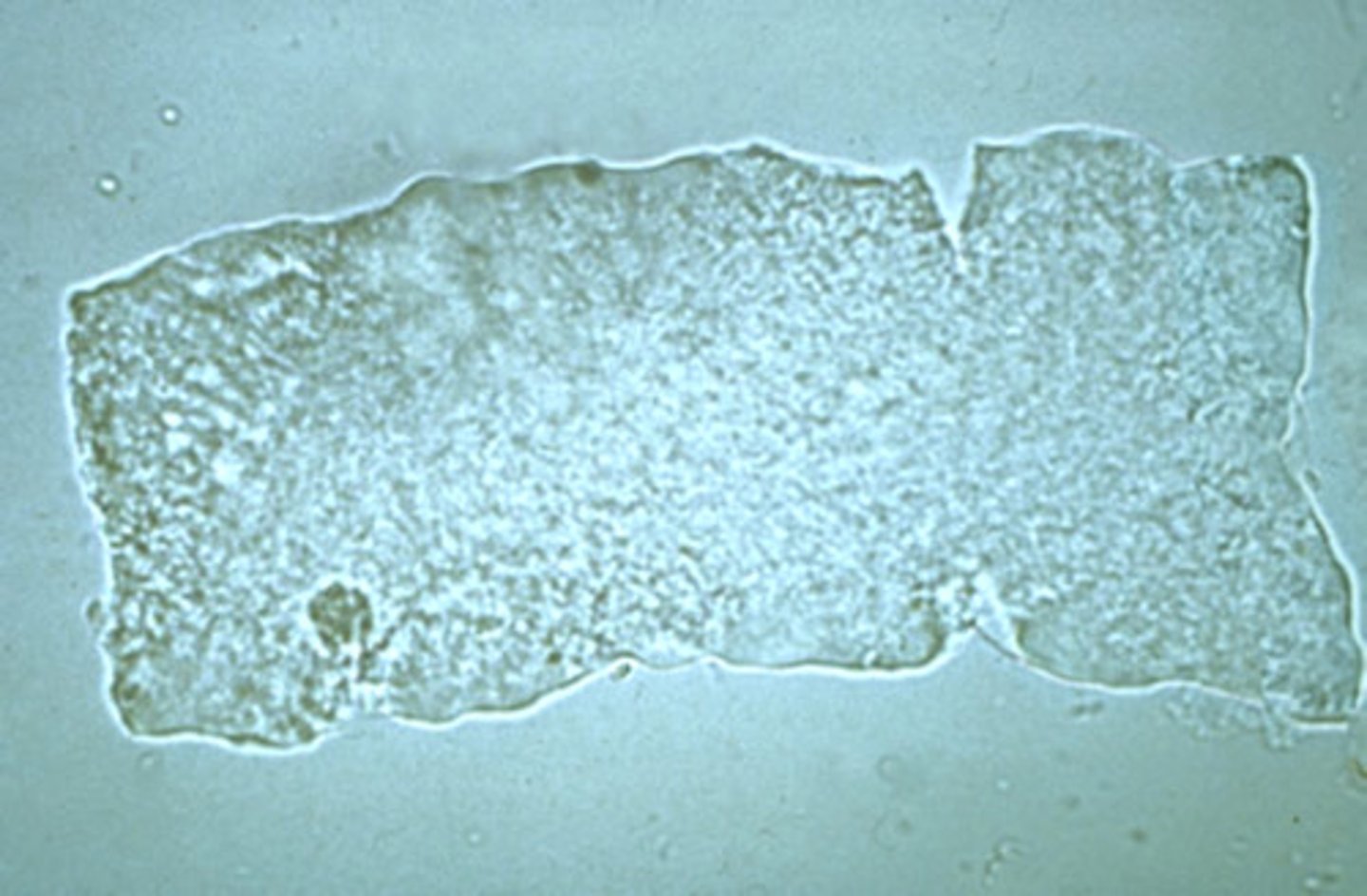
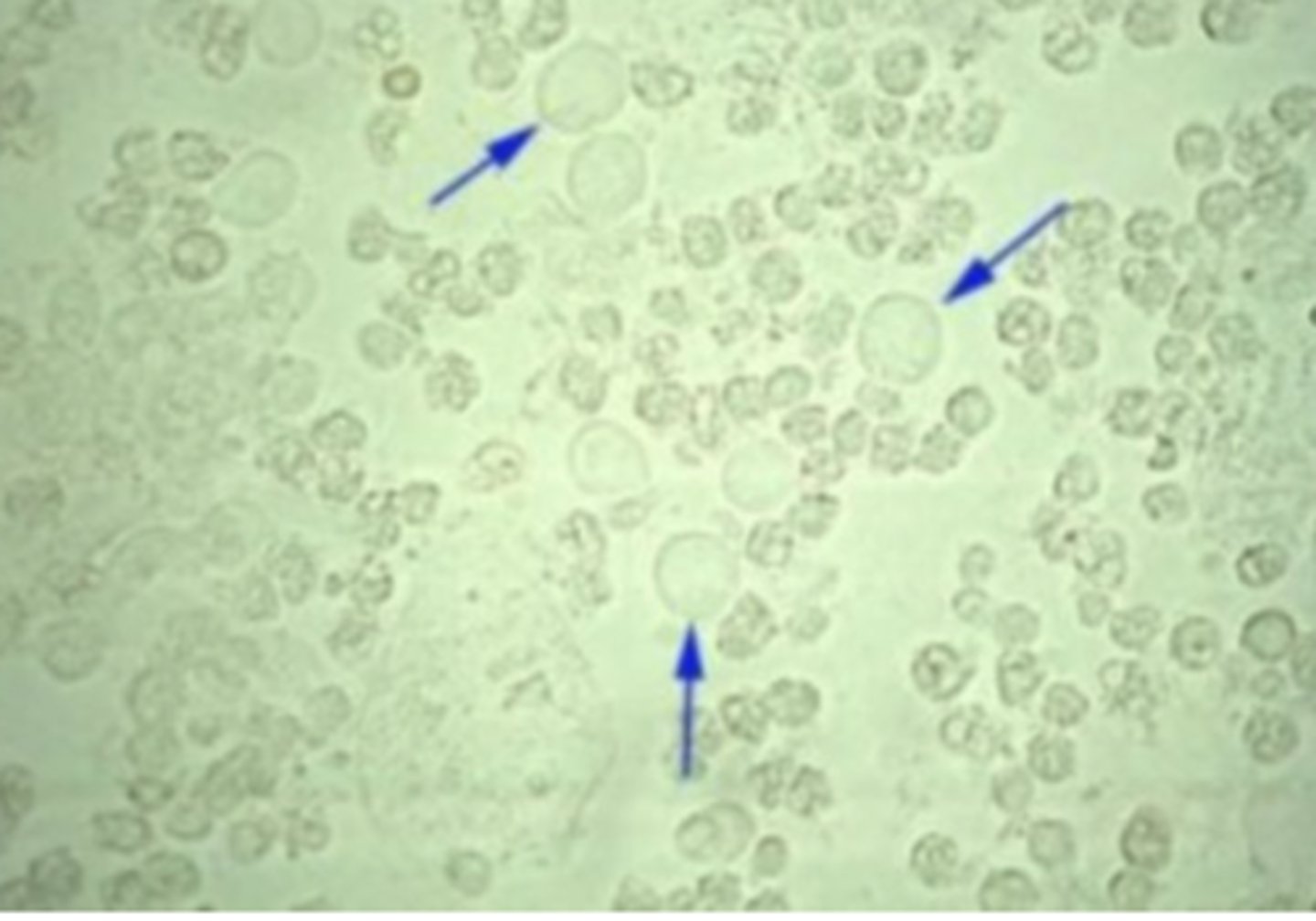
Squamous Epithelial Cells
is the most common type of cell seen in urine sediment. It is a large, flattened cell with abundant cytoplasm and a small, round central nucleus. Although they have little clinical significance. Commonly seen in females due to natural flora
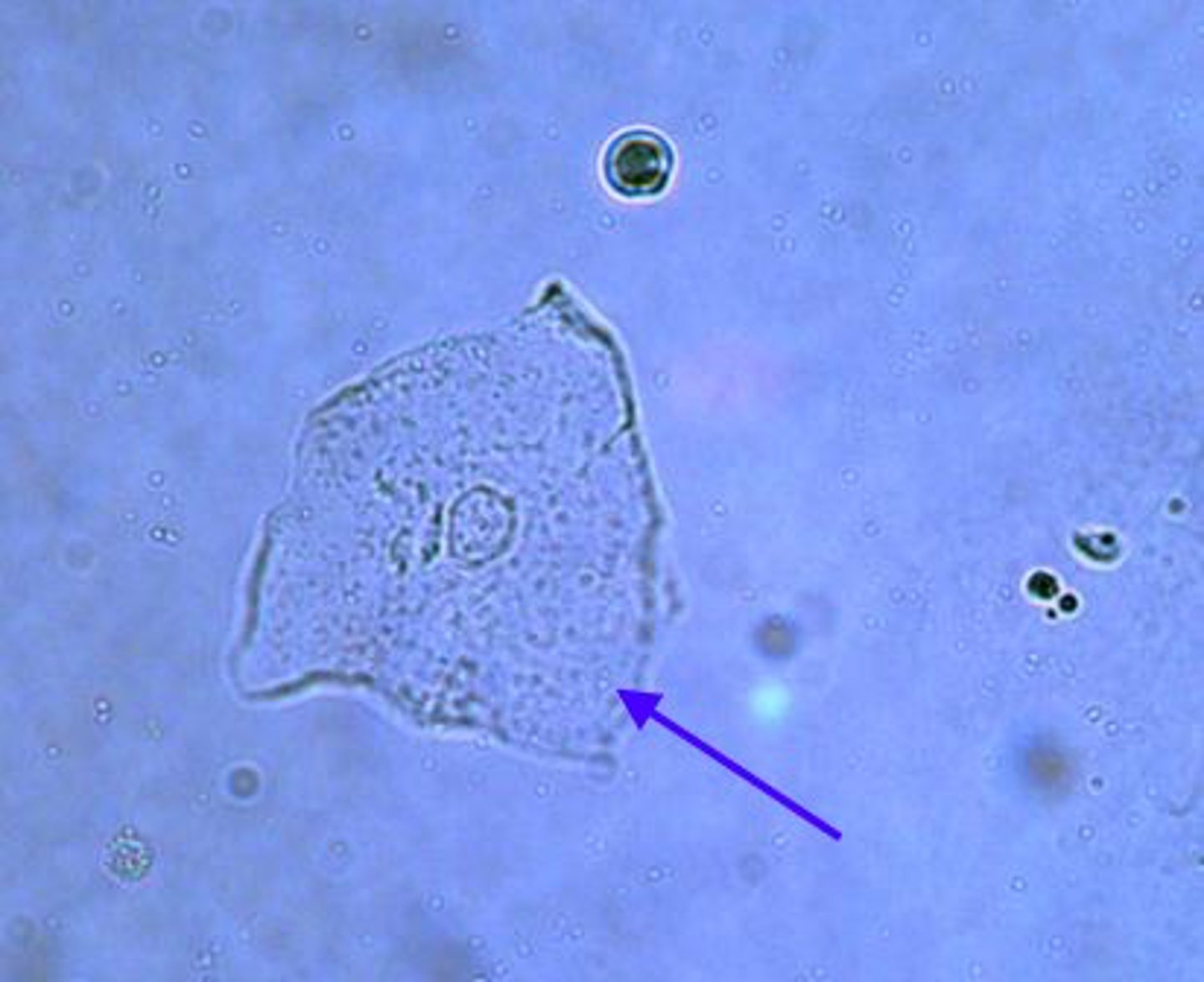
Transitional Epithelial Cells
Another type of epithelial cell, also known as a urothelial cell. It is smaller than a squamous epithelial cell and has a centrally located nucleus.
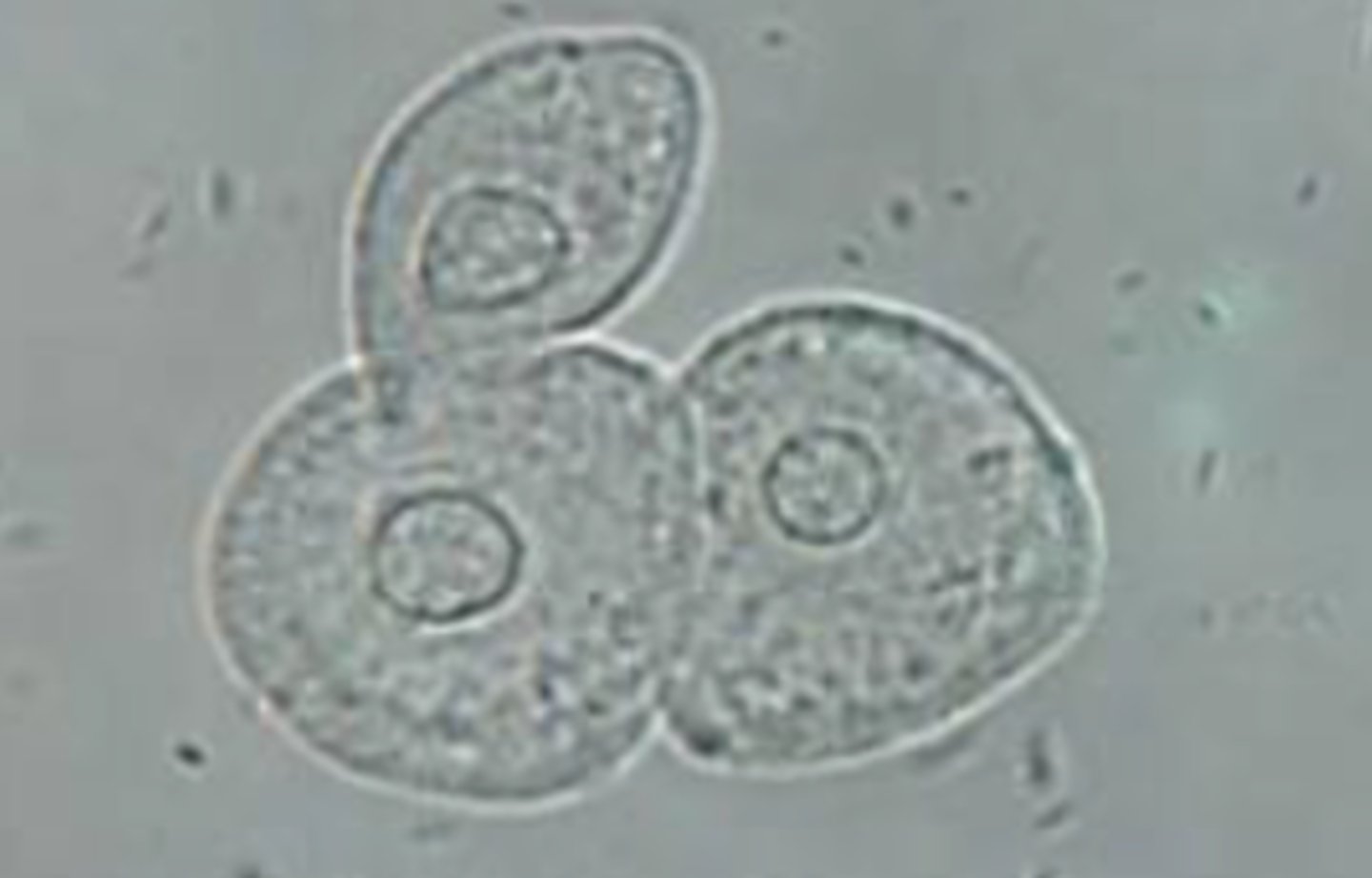
Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells
distinguished by its eccentrically placed nucleus. The cells can be round, oval, columnar, or cuboidal. Papanicolaou stain helps distinguish from other mononuclear cells in urine.
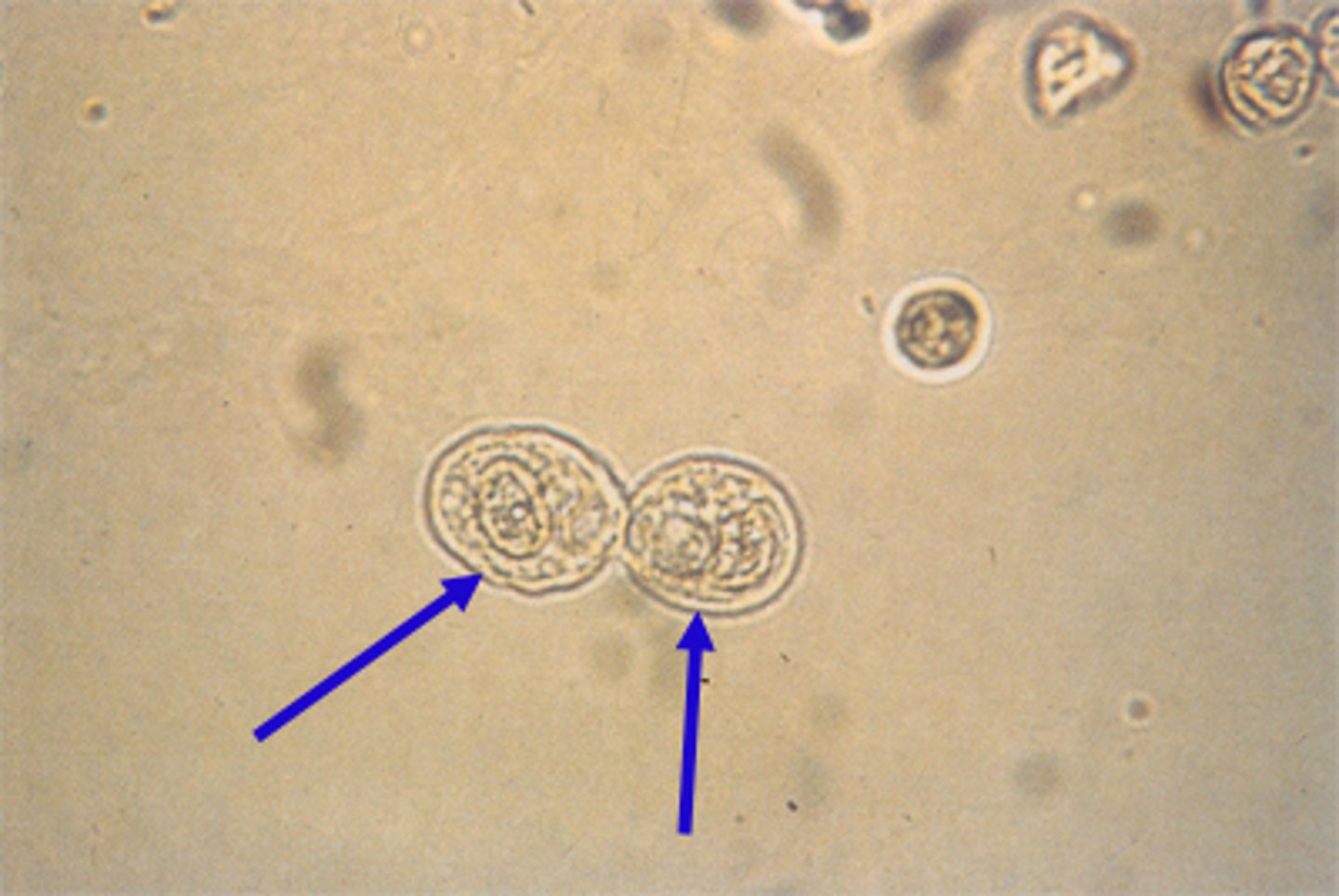
White Blood Cells
swell in dilute alkaline urine, and the cytoplasmic granules exhibit Brownian movement, resulting in "glitter cells." These cells lyse rapidly. "Glitter cells" are most easily seen when viewed under phase-contrast microscopy.
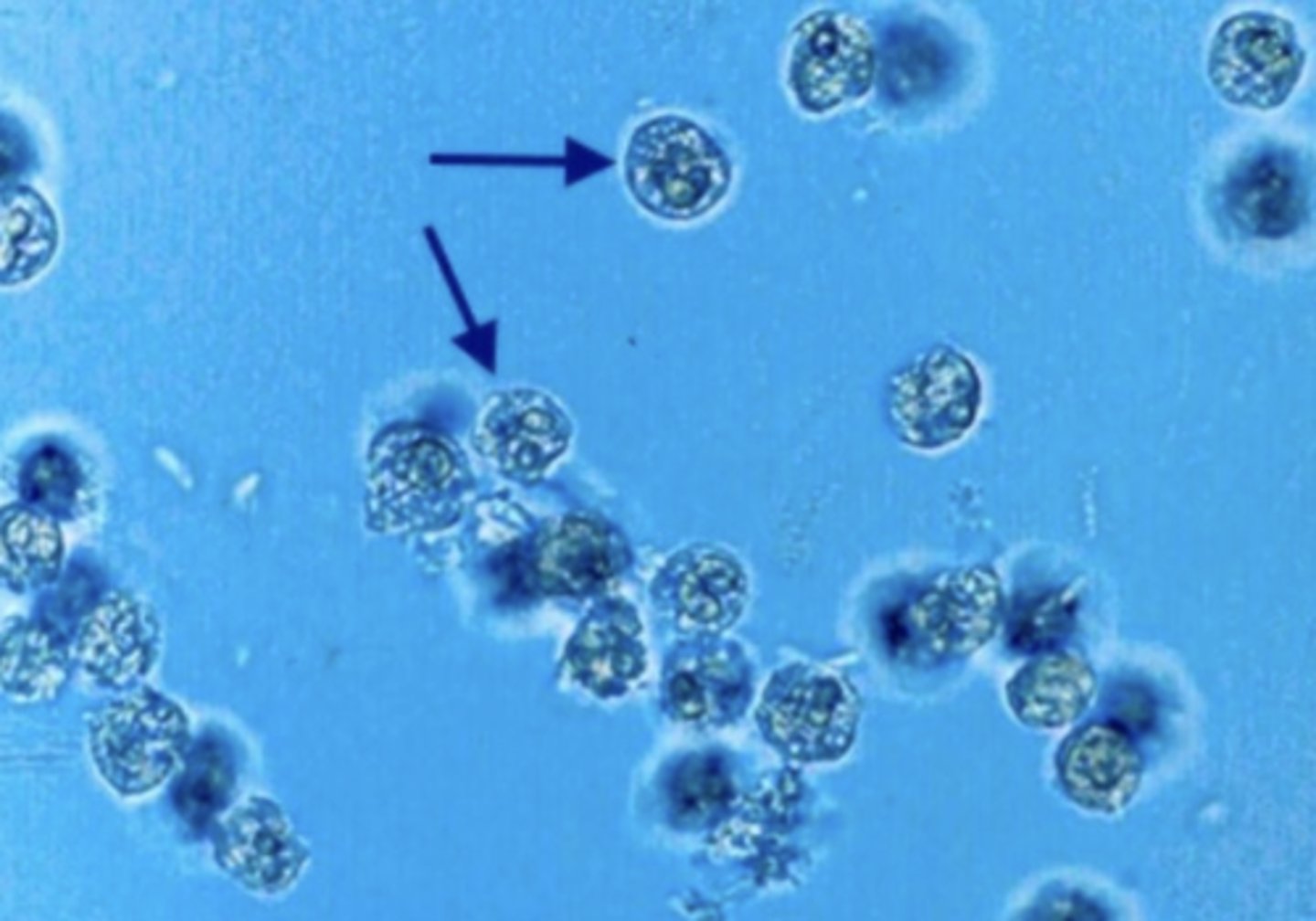
WBC Clumps
typically observed when there is inflammation or bacterial infections of the renal and urinary tract. The clumping is due to increased mucus in the urine.
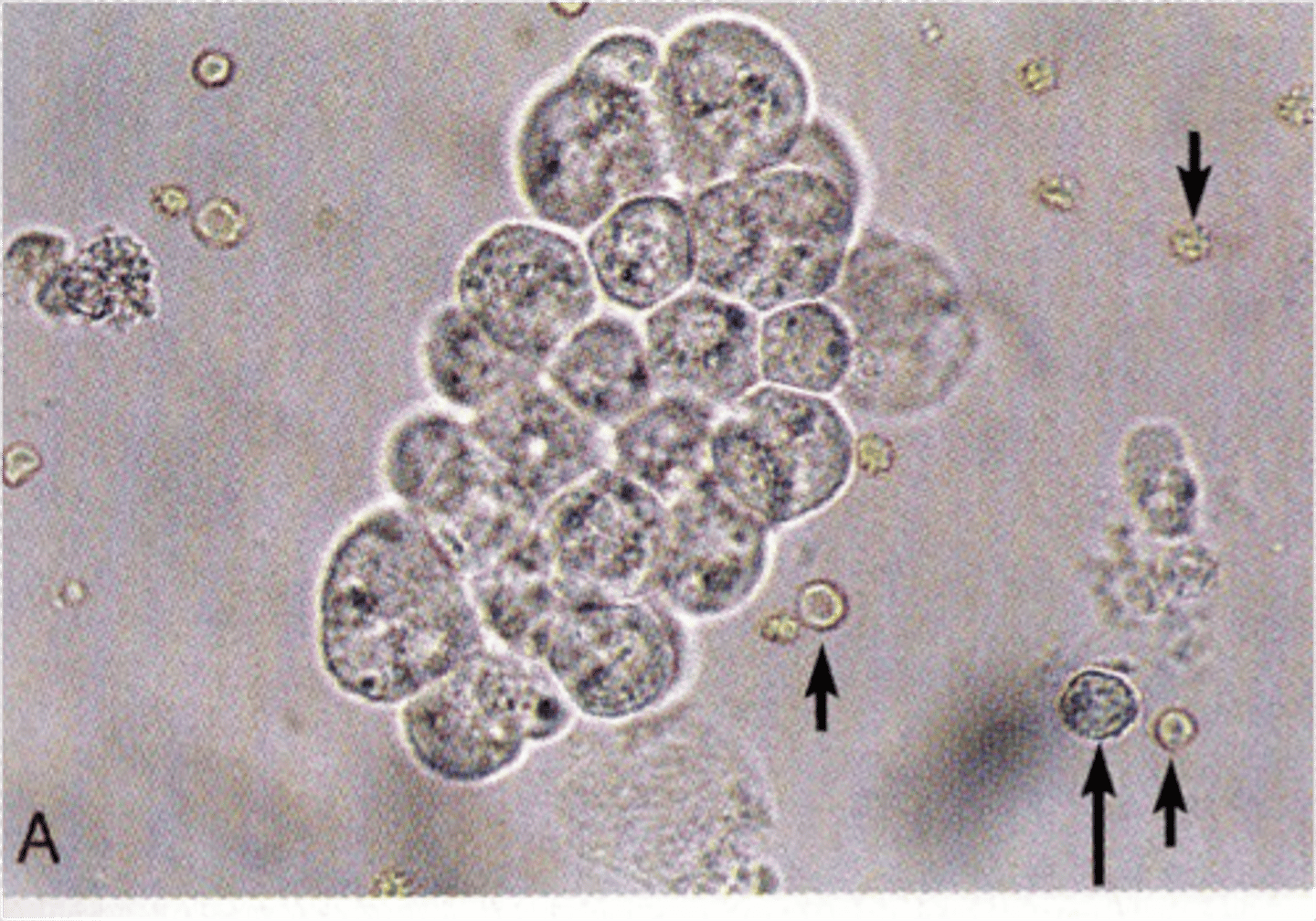
Red Blood Cells
smaller than WBCs but do not have a nucleus. They may be disc- or spherical-shaped or have spiked or crenated appearance. The top image illustrates the disc shape and crenated appearance. associated with damage to the glomerular membrane or vascular injury within the genitourinary tract.
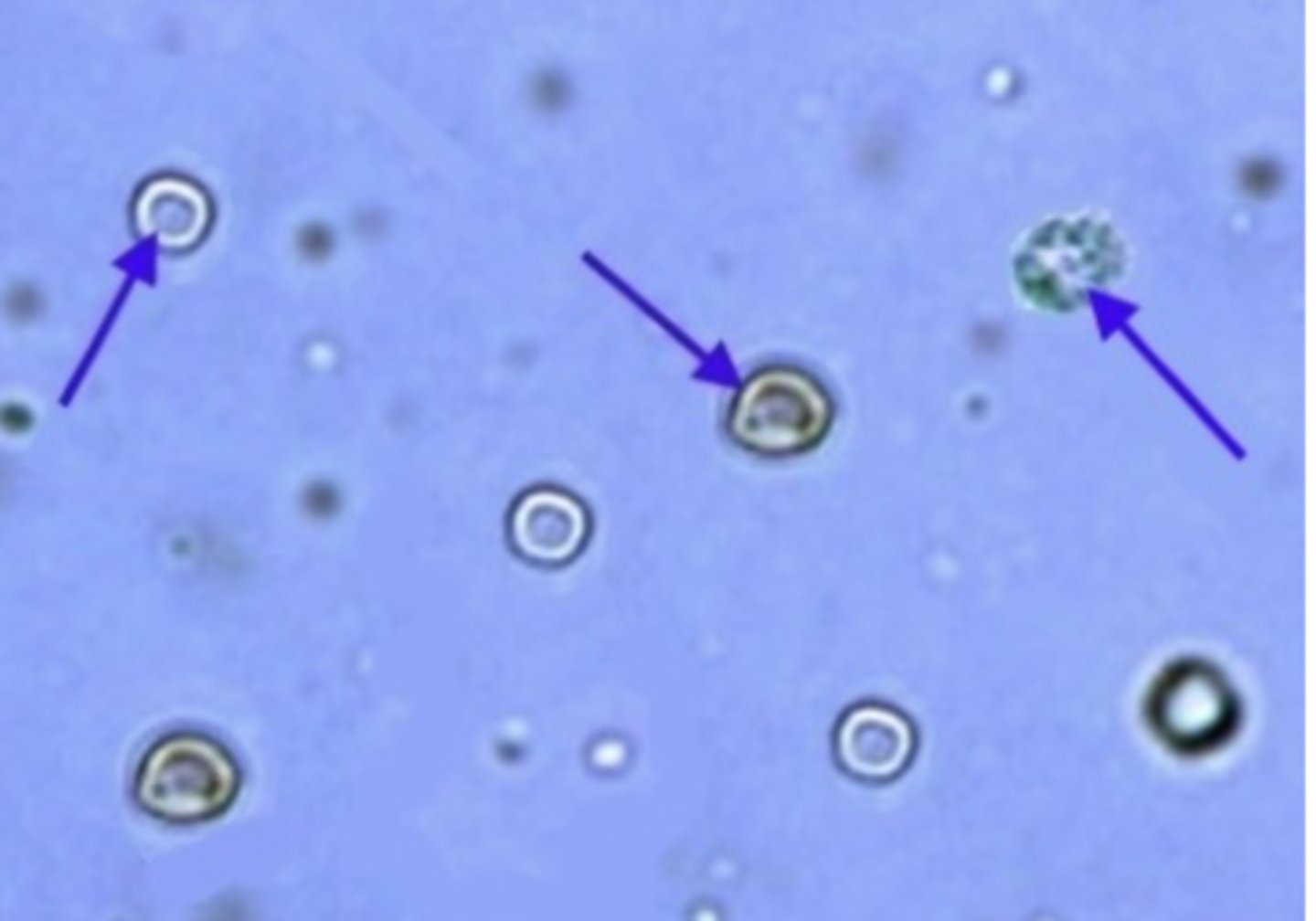
Crenated Red Cells
appears when urine is too concentrated
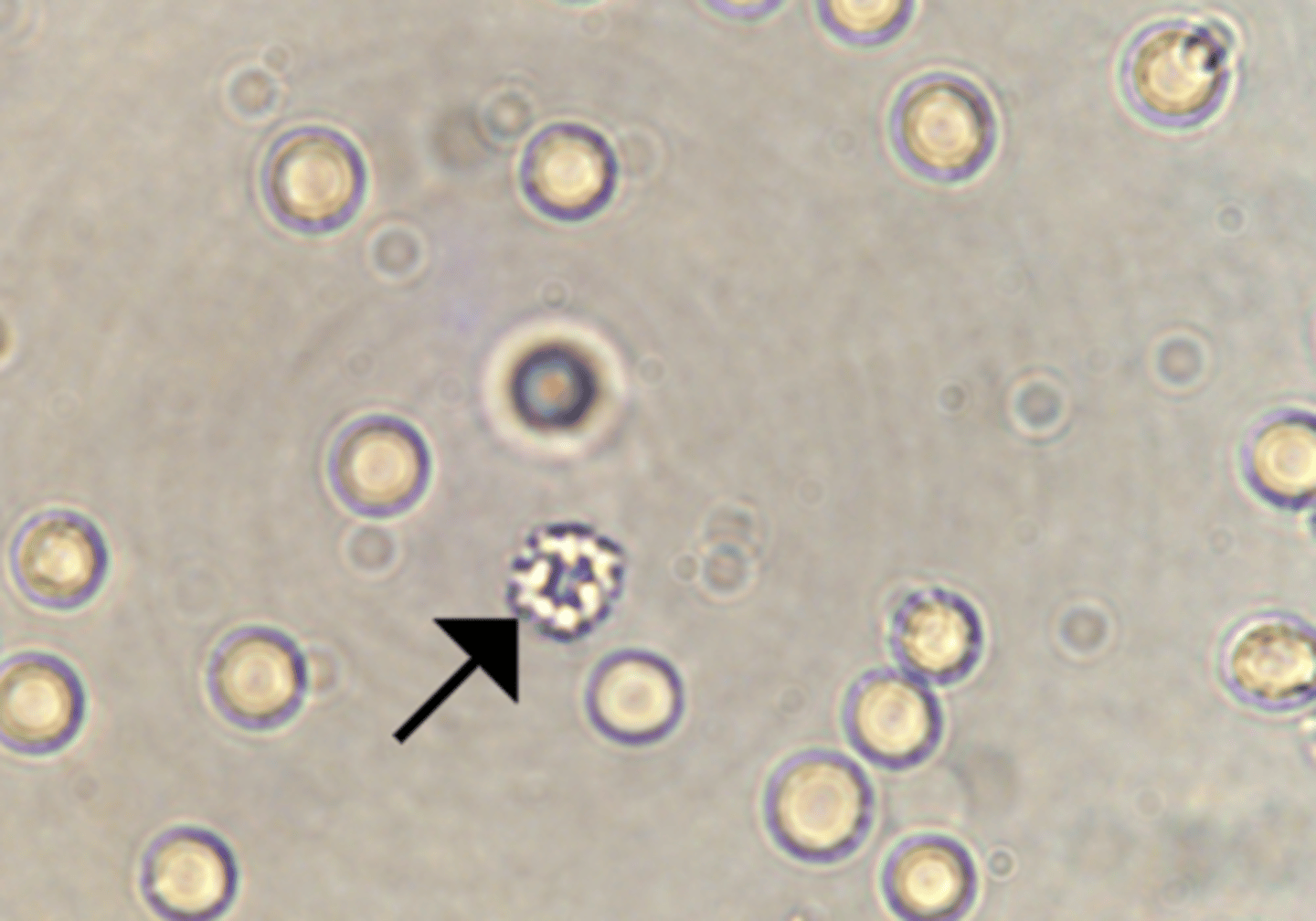
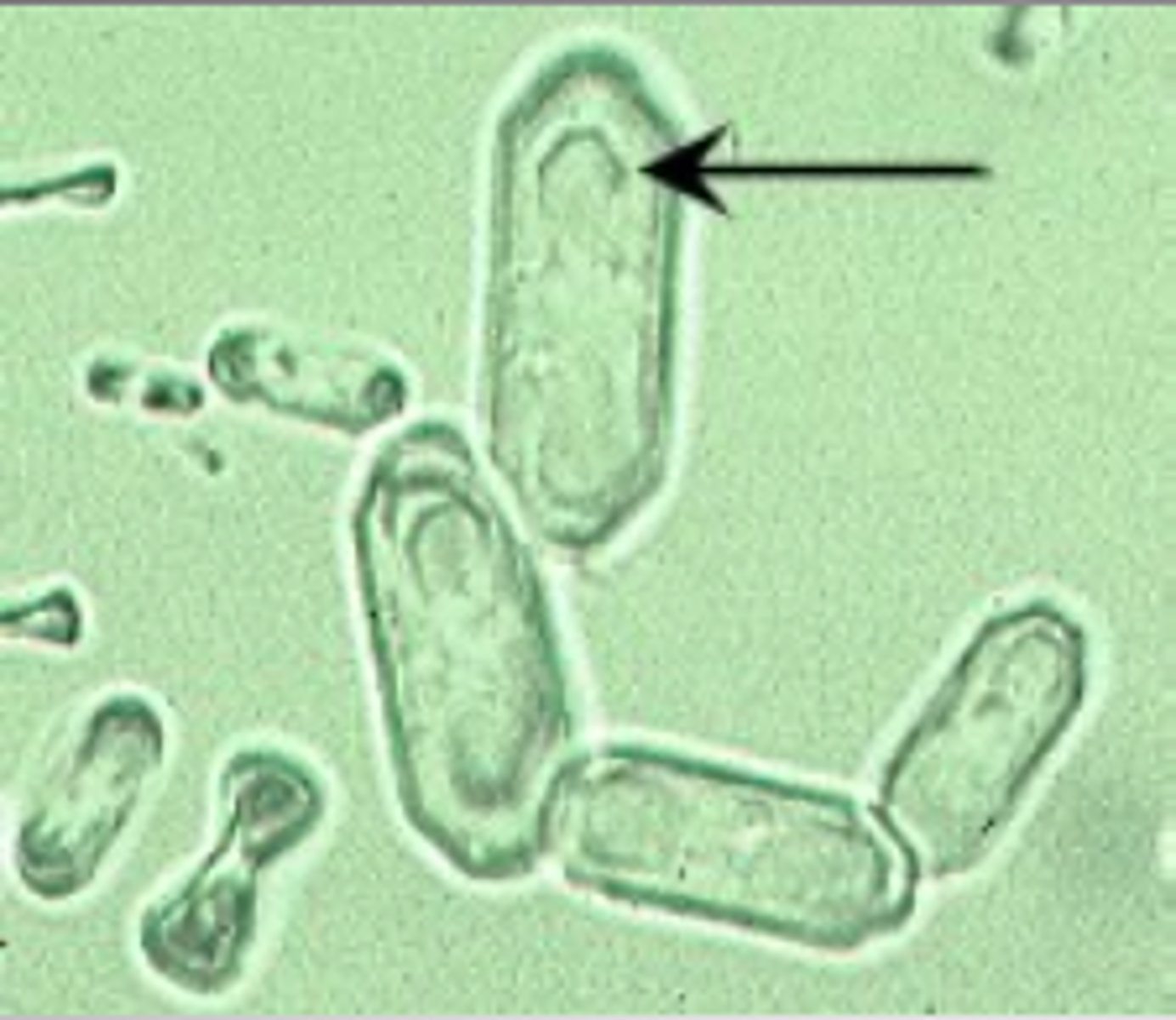
Yeast
appear as single cells or in budding form, as indicated by the arrow in the top image. The most common _____ found in urine is Candida albicans, which typically demonstrates budding forms. The presence of budding forms helps to distinguish _____ from RBCs when urine sediment is viewed microscopically.
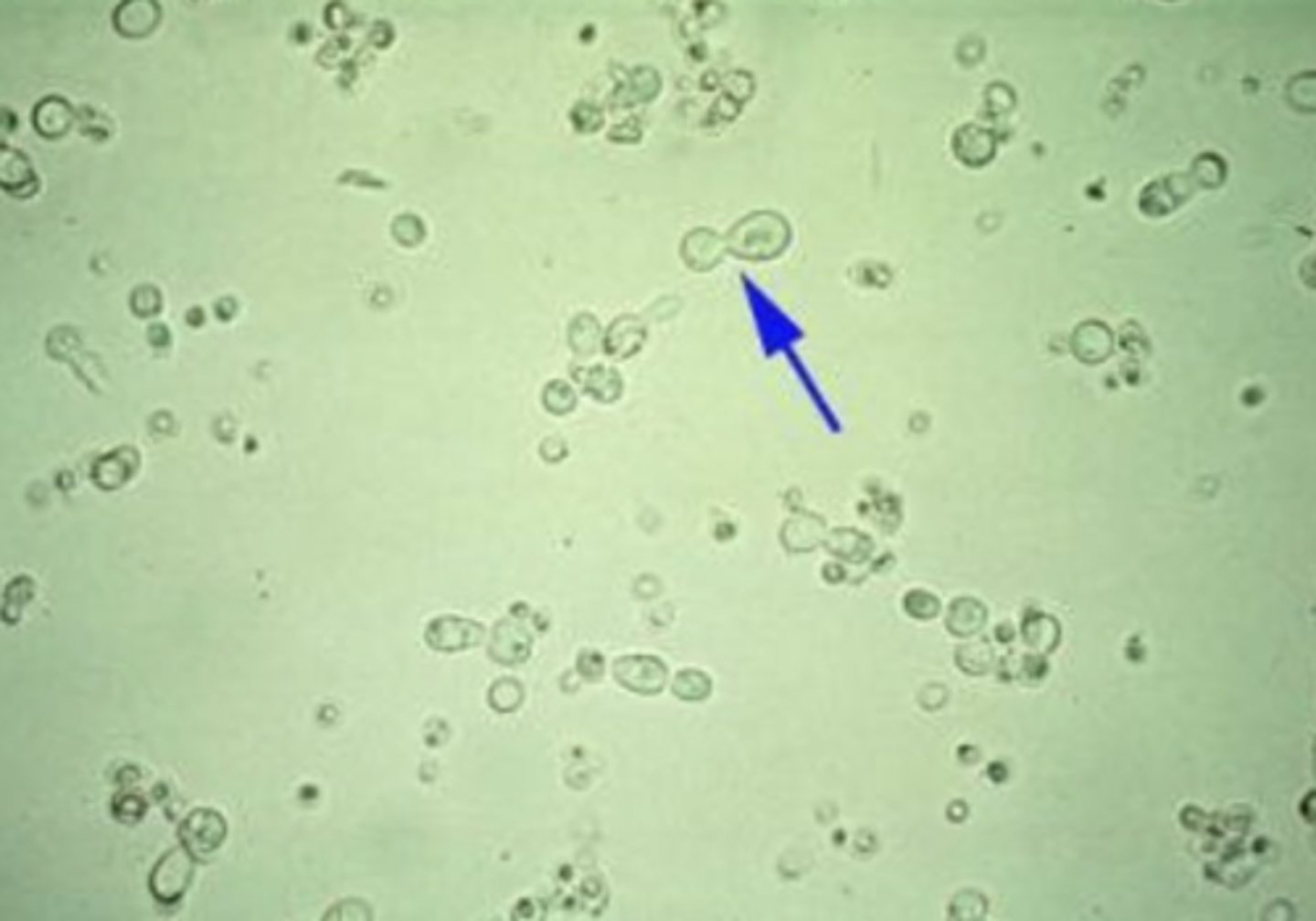
Bacteria
may indicate a urinary tract infection. Still, it may also be contaminated if the specimen has been held at room temperature for a prolonged period and/or not collected using a clean-catch protocol. It is essential to perform a urinalysis on a freshly collected midstream specimen to determine the significance of the _____ that may be seen.
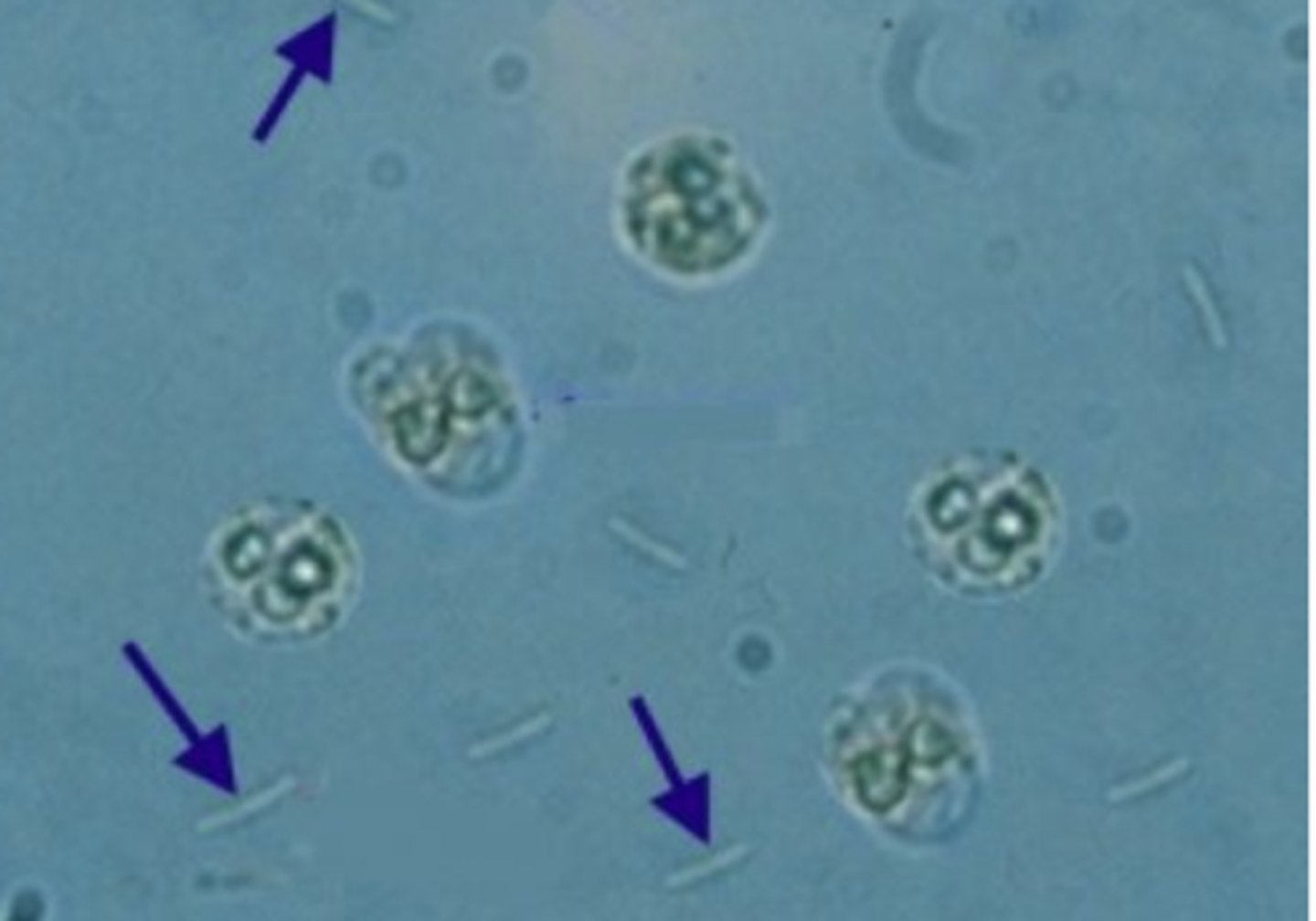
Parasites
Trichomonas vaginalis, Enterobius vermicularis, and Schistosoma haematobium. Parasites and parasitic ova are usually present in urine sediment due to vaginal or fecal contamination.
Amorphous urate
Dark or yellow-red granules, Urine pH: Acidic
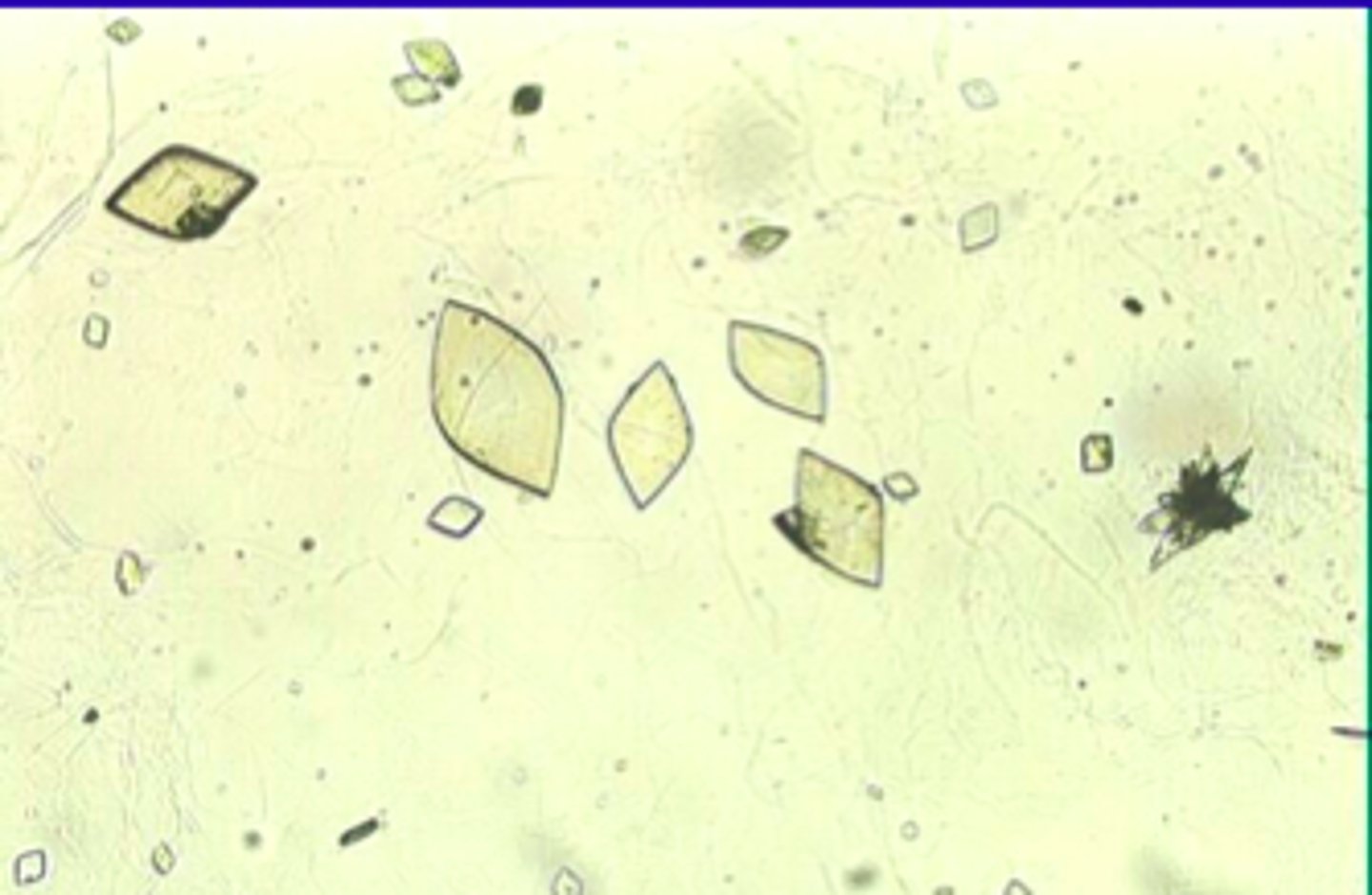
Calcium oxalate dihydrate(Envelope)
can be found in both normal and abnormal urine and in a range of pH levels from acidic to neutral.
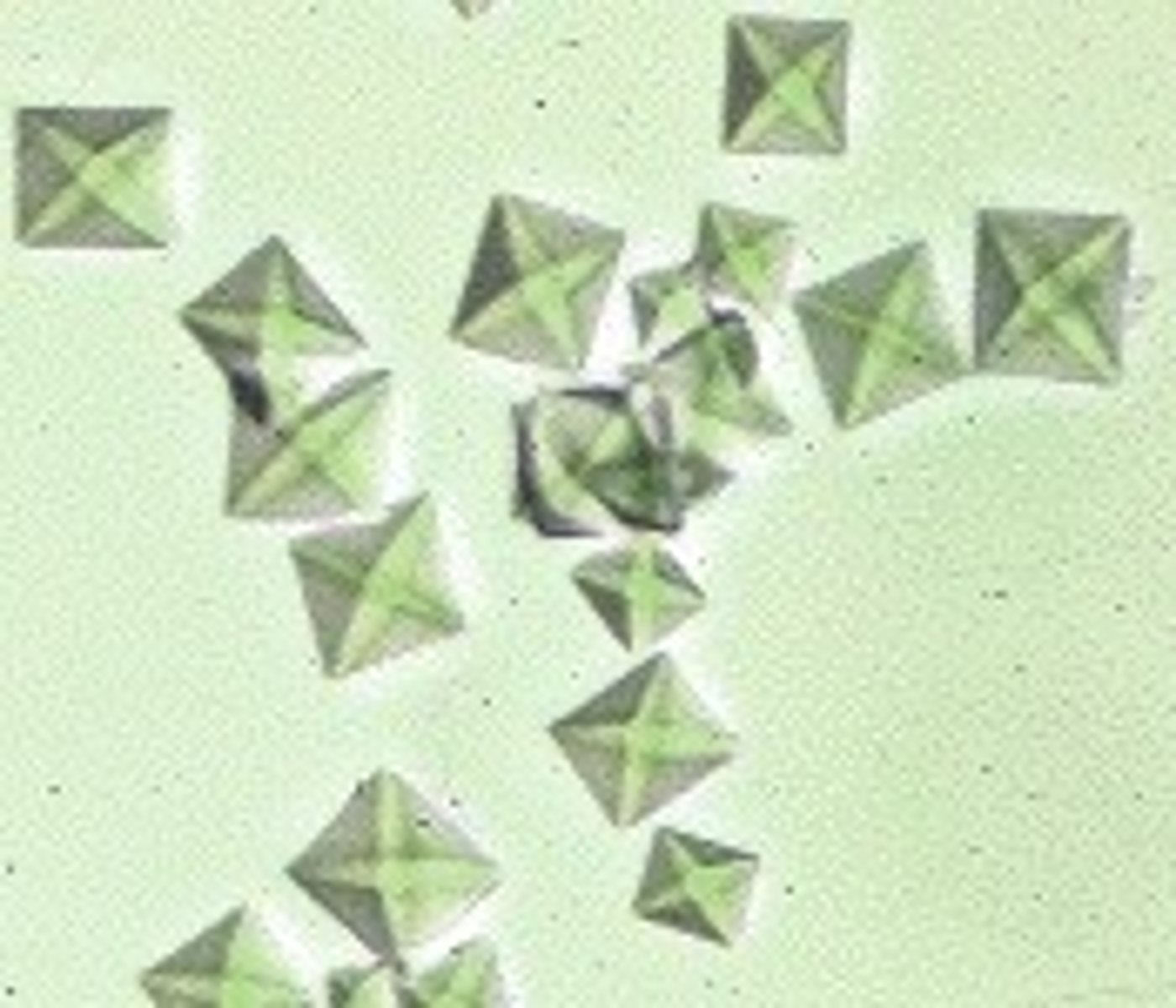

Calcium oxalate monohydrate
Oval, dumbbell, can be found in both normal and abnormal urine and in a range of pH levels from acidic to neutral.
Uric acid
Various shapes - rhombus, hexagonal plates, rosettes, rectangles, irregular shapes Colorless to yellow or brown. Urine pH: Acidic
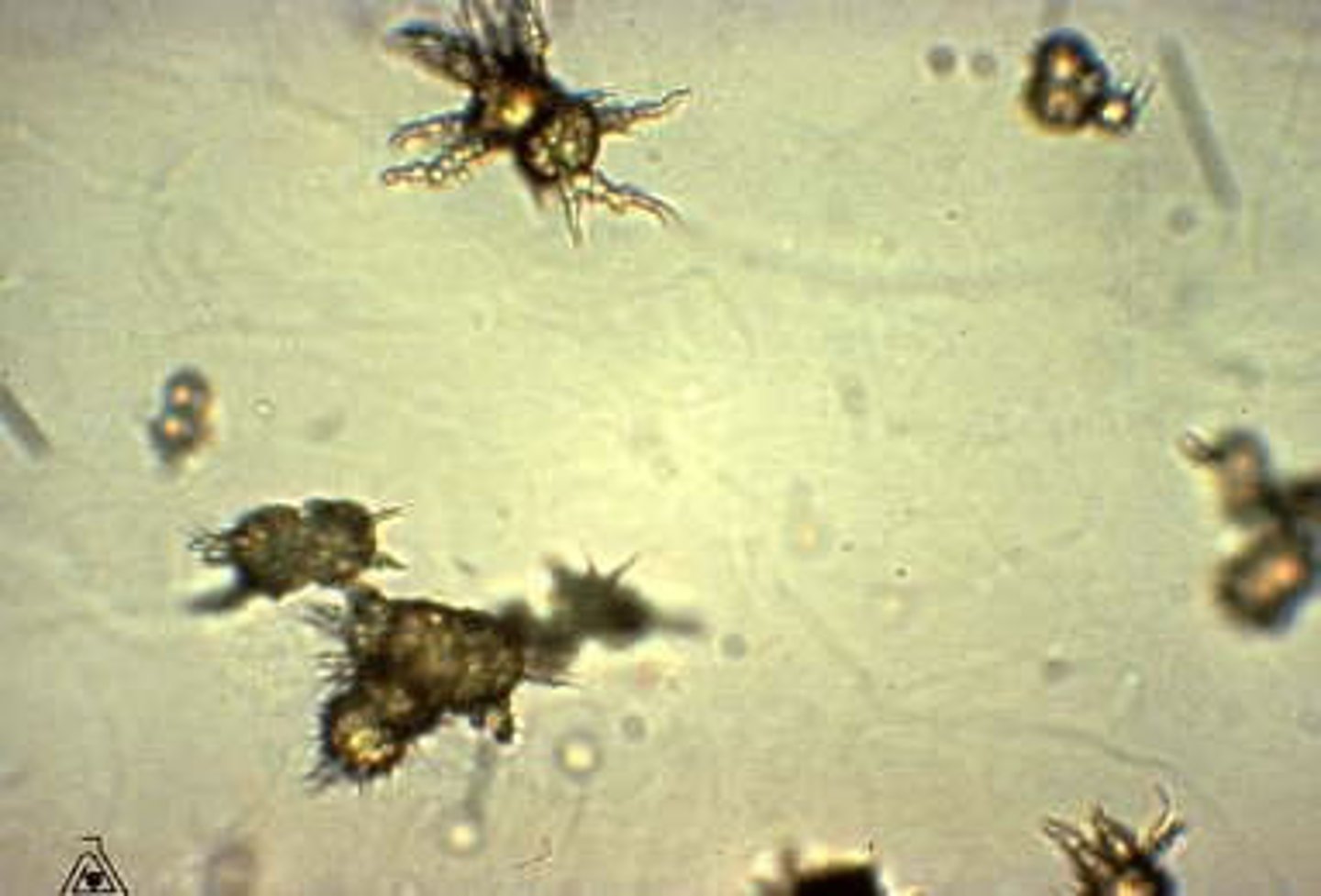
Ammonium biurate
Round with thorny projections Dark yellow to brown. Urine pH: Alkaline
Amorphous phosphate
Amorphous granules. Urine pH: Alkaline
Calcium phosphate
Flat rectangles, prisms, rosettes. Urine pH: Alkaline
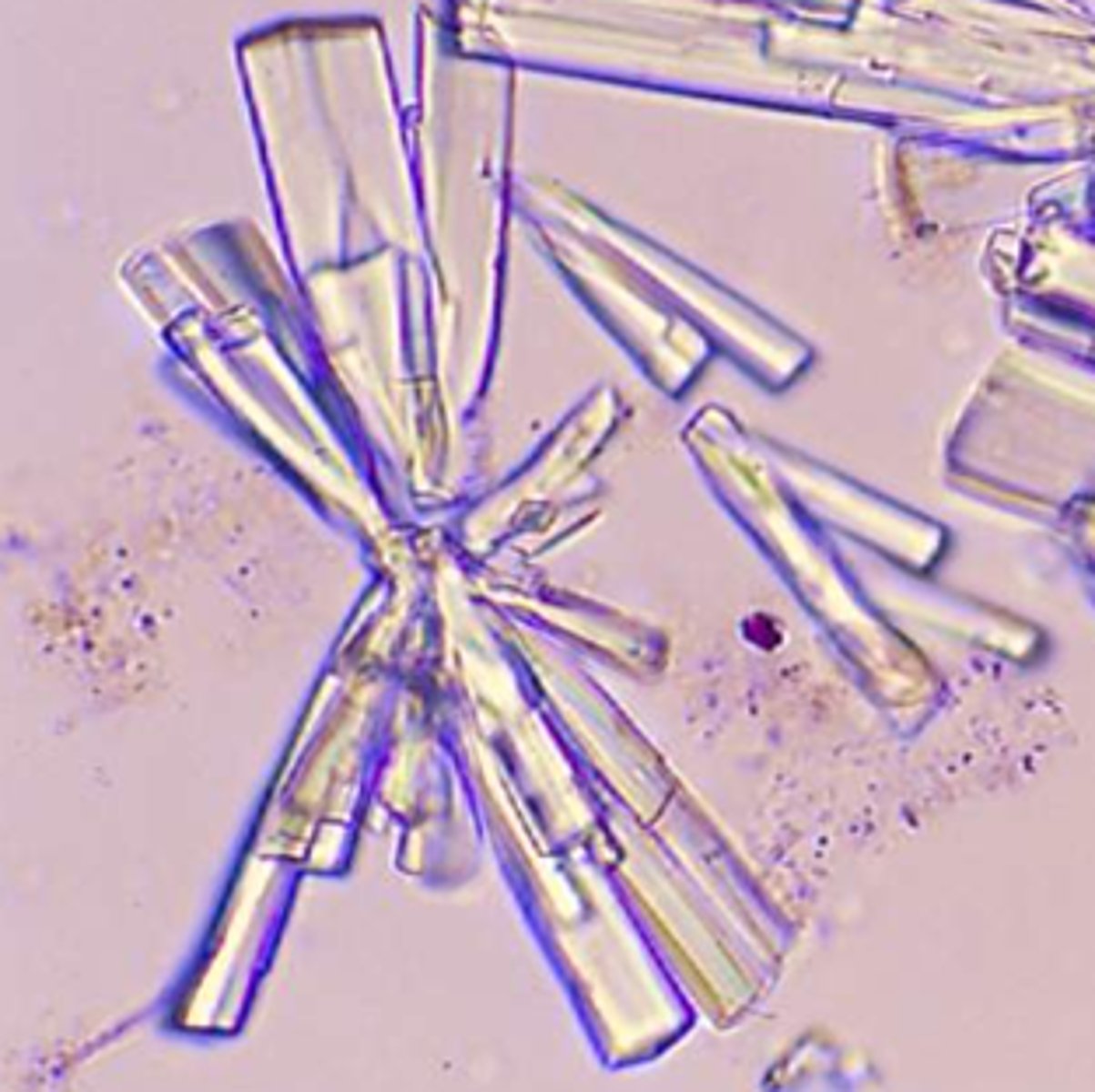

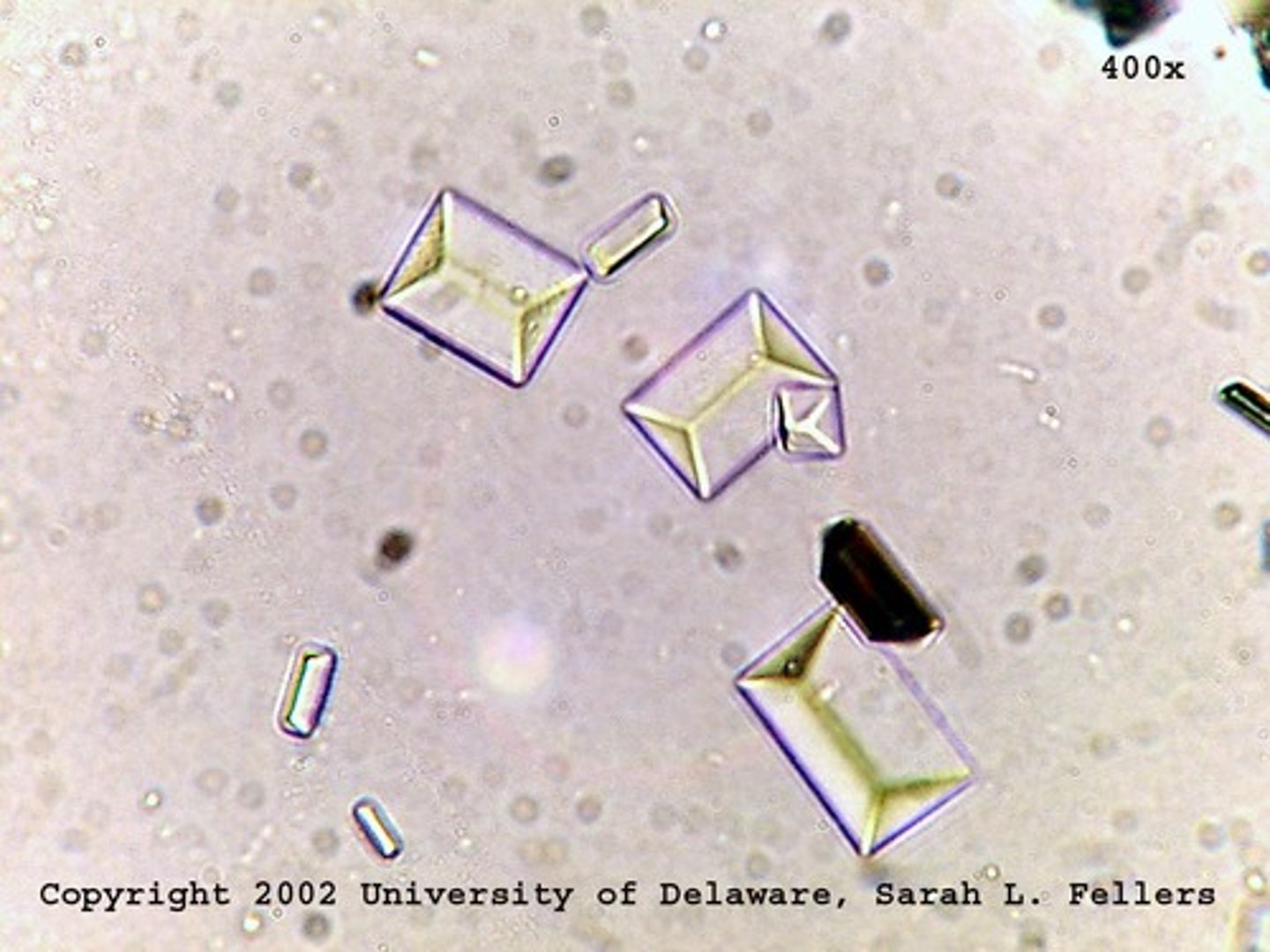
Triple phosphate
Four to six-sided prisms resembling coffin lids. Urine pH: Alkaline
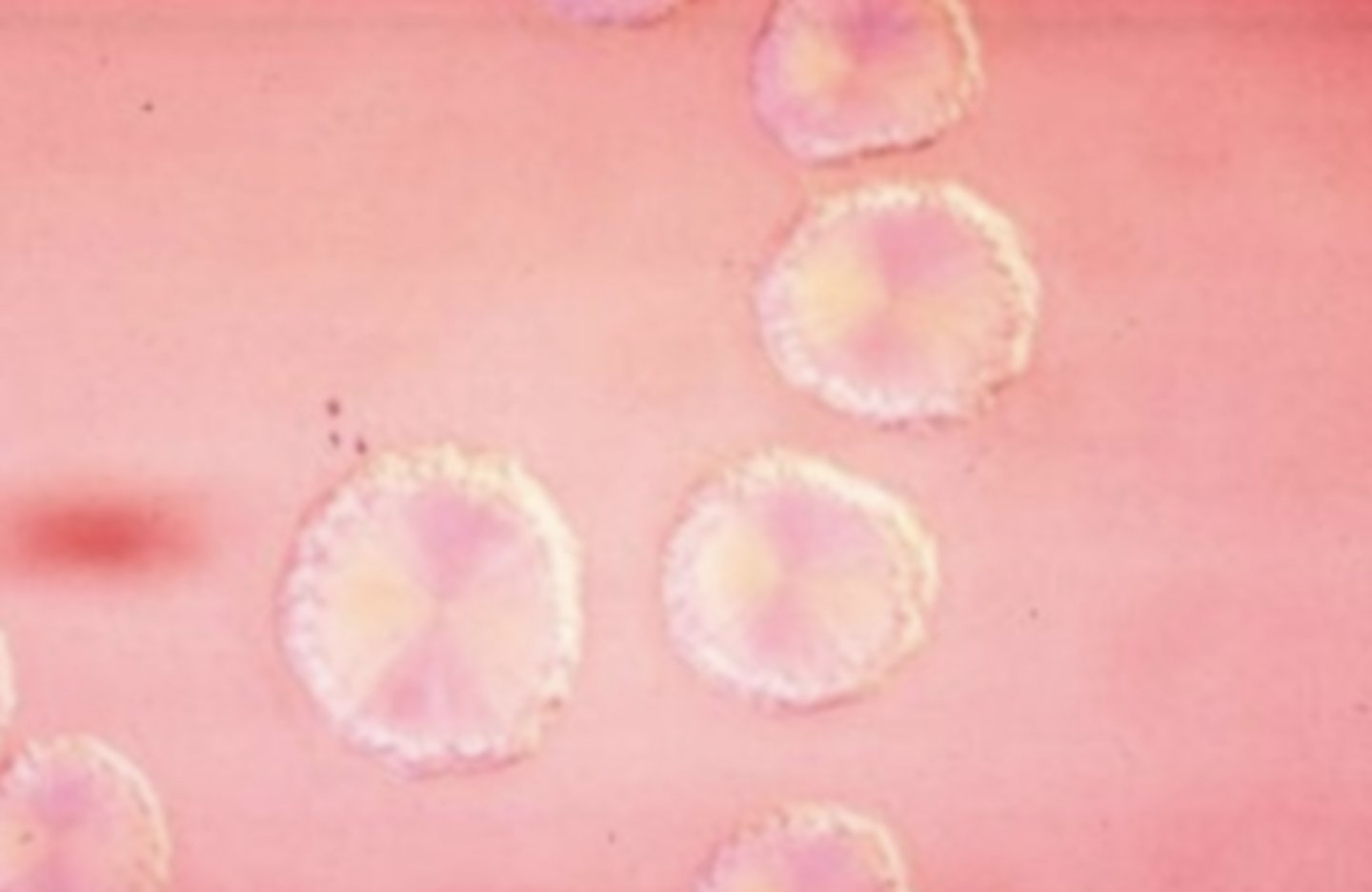
Leucine Crystals
indicate a problem with the metabolism of the amino acid leucine. They are round to oval with radiating bands going from a center point out to the periphery, often called a "wagon wheel."
Tyrosine Crystals
appear as fine silky needles arranged in sheaves or bundles in acidic urine. They are rarely present and may appear together with leucine crystals in liver disease.
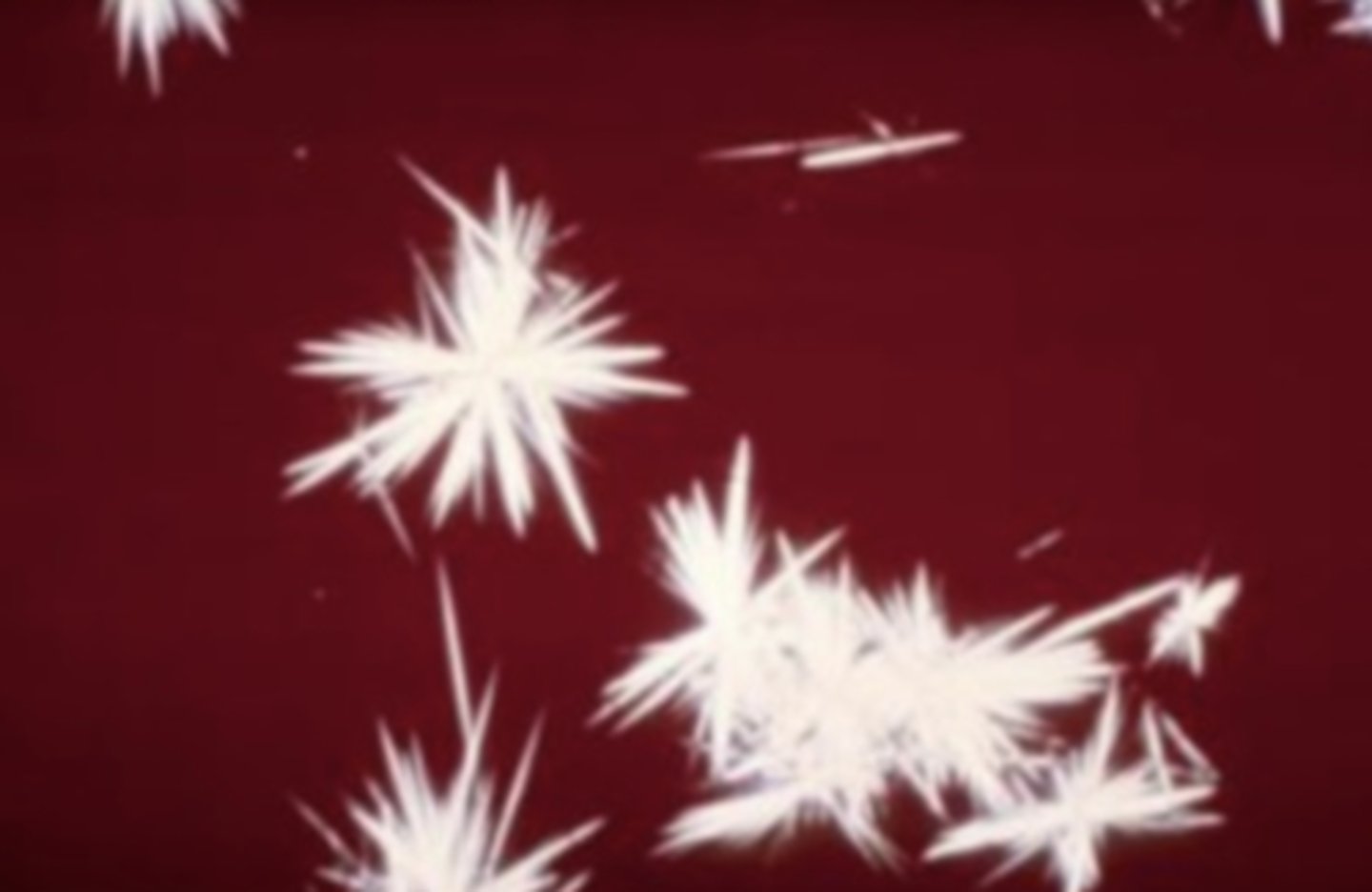

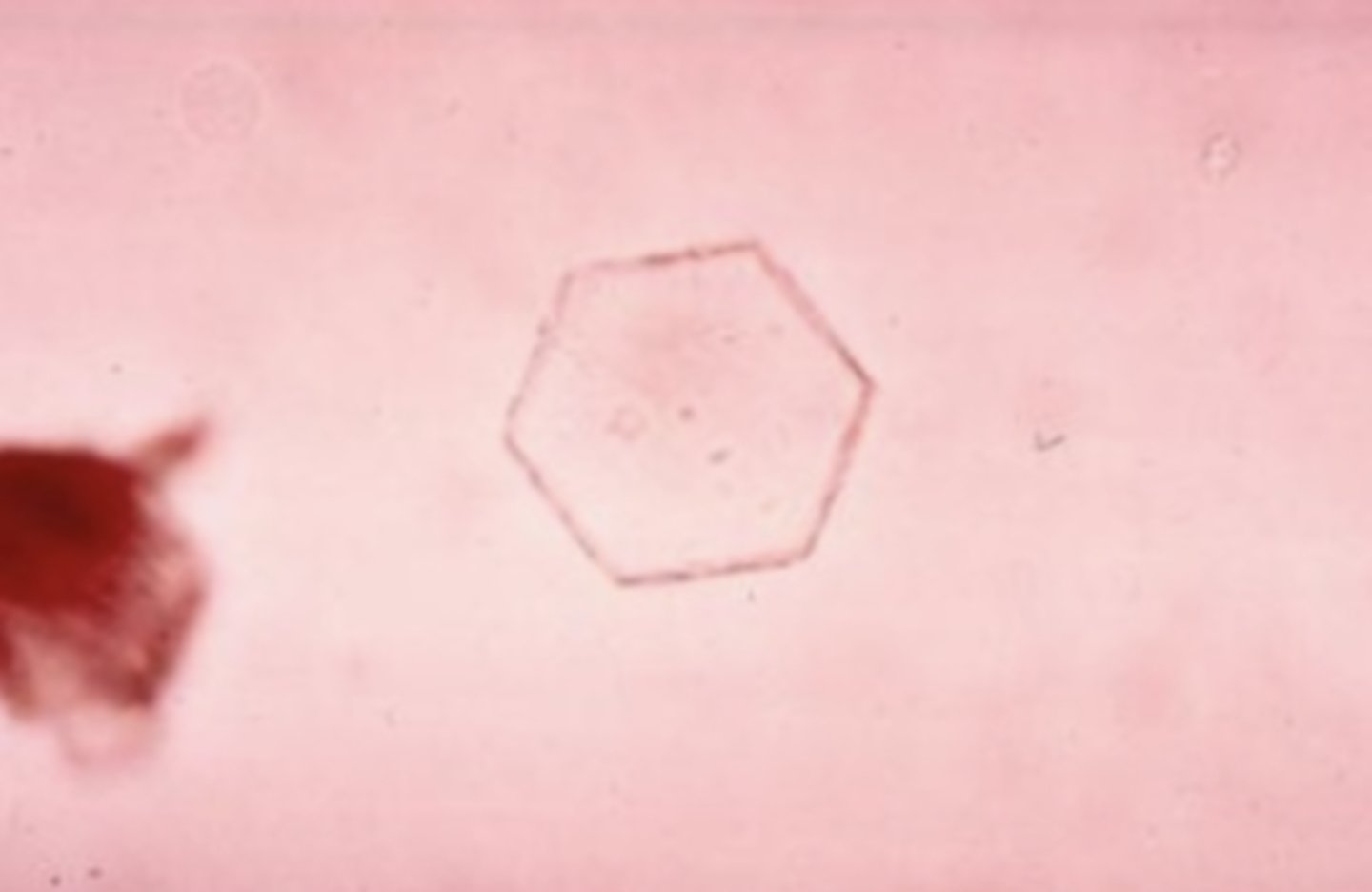
Cystine Crystals
an abnormality in the metabolism of the amino acid cysteine. These crystals appear as colorless, refractile, hexagonal plates with even sides.
Cholesterol Crystals
These crystals look like plates of glass, sometimes with a notch out of one corner. Under polarized light, they exhibit a stained glass effect. These crystals are rarely seen unless the specimen has been refrigerated because the lipids remain in droplet form. Large amounts of protein, lipid droplets, fatty casts, or oval fat bodies should be found along with ______ crystals. found in acid or neutral urine.
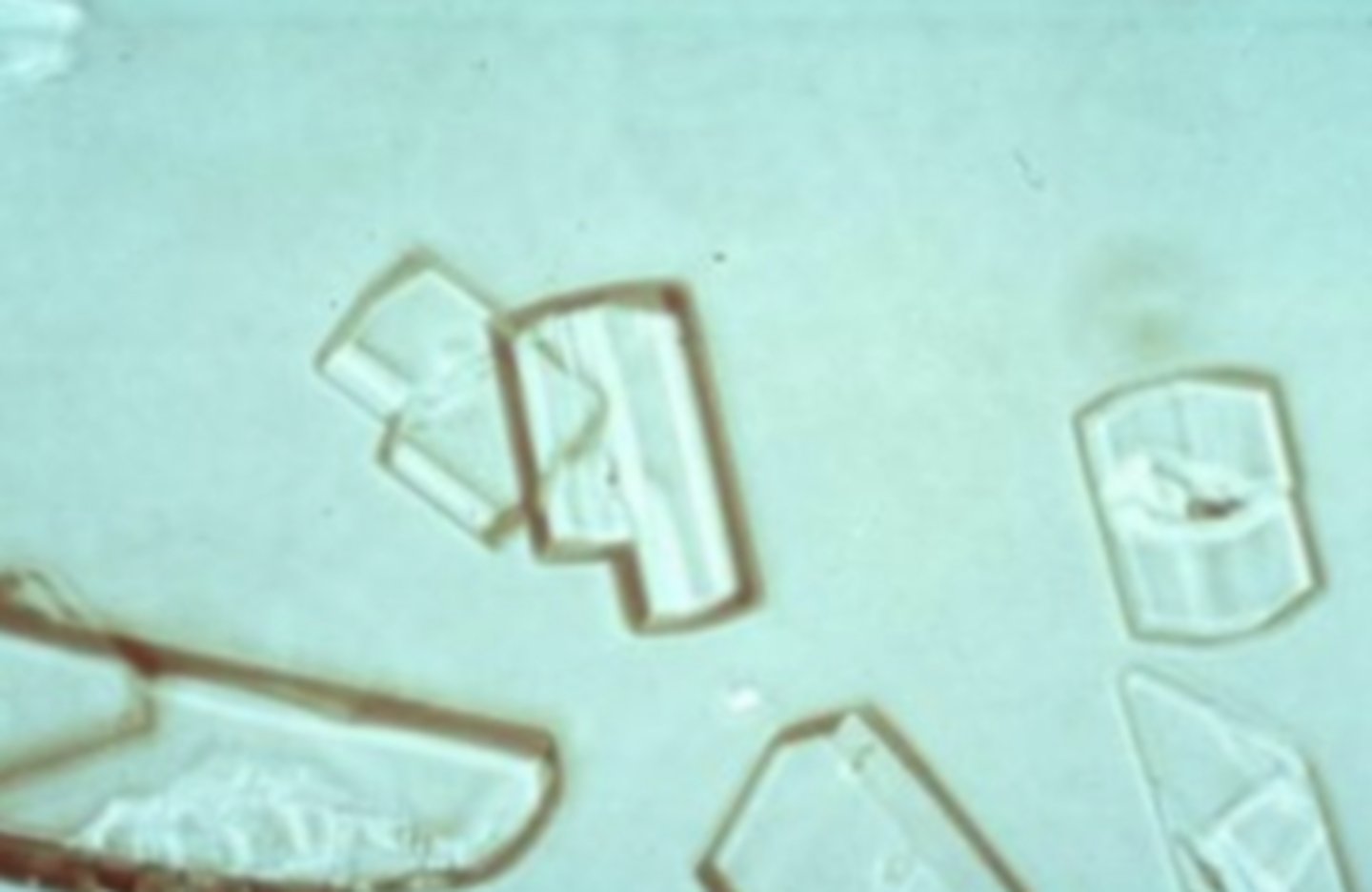
Bilirubin Crystals
seen in the urine when the serum bilirubin level increases. The macroscopic appearance of urine with bilirubin crystals is orange to almost black. The crystals themselves appear as gold-orange needle-like forms that are sometimes clumped together.
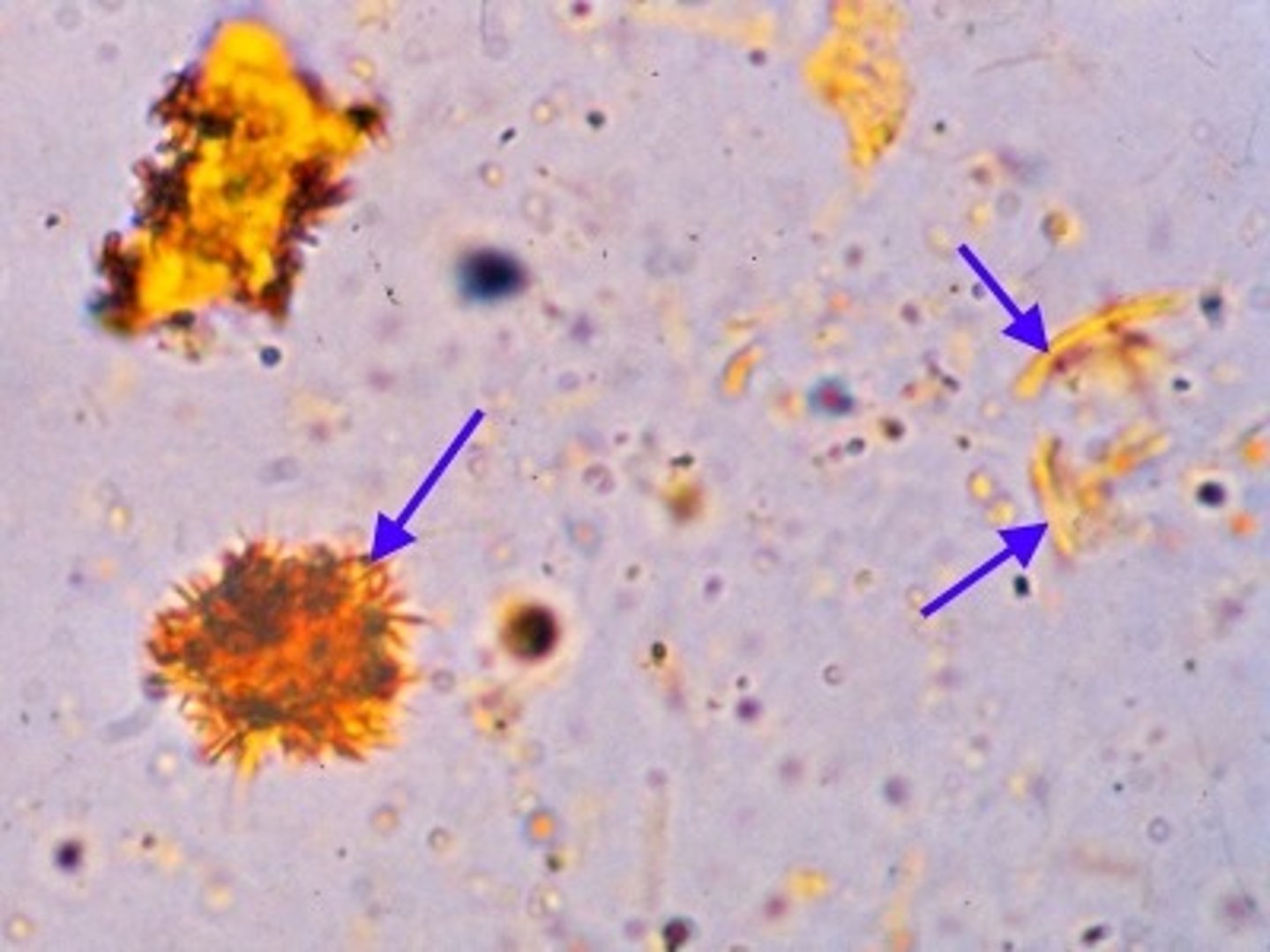
Oil or Fat Droplets
artifacts
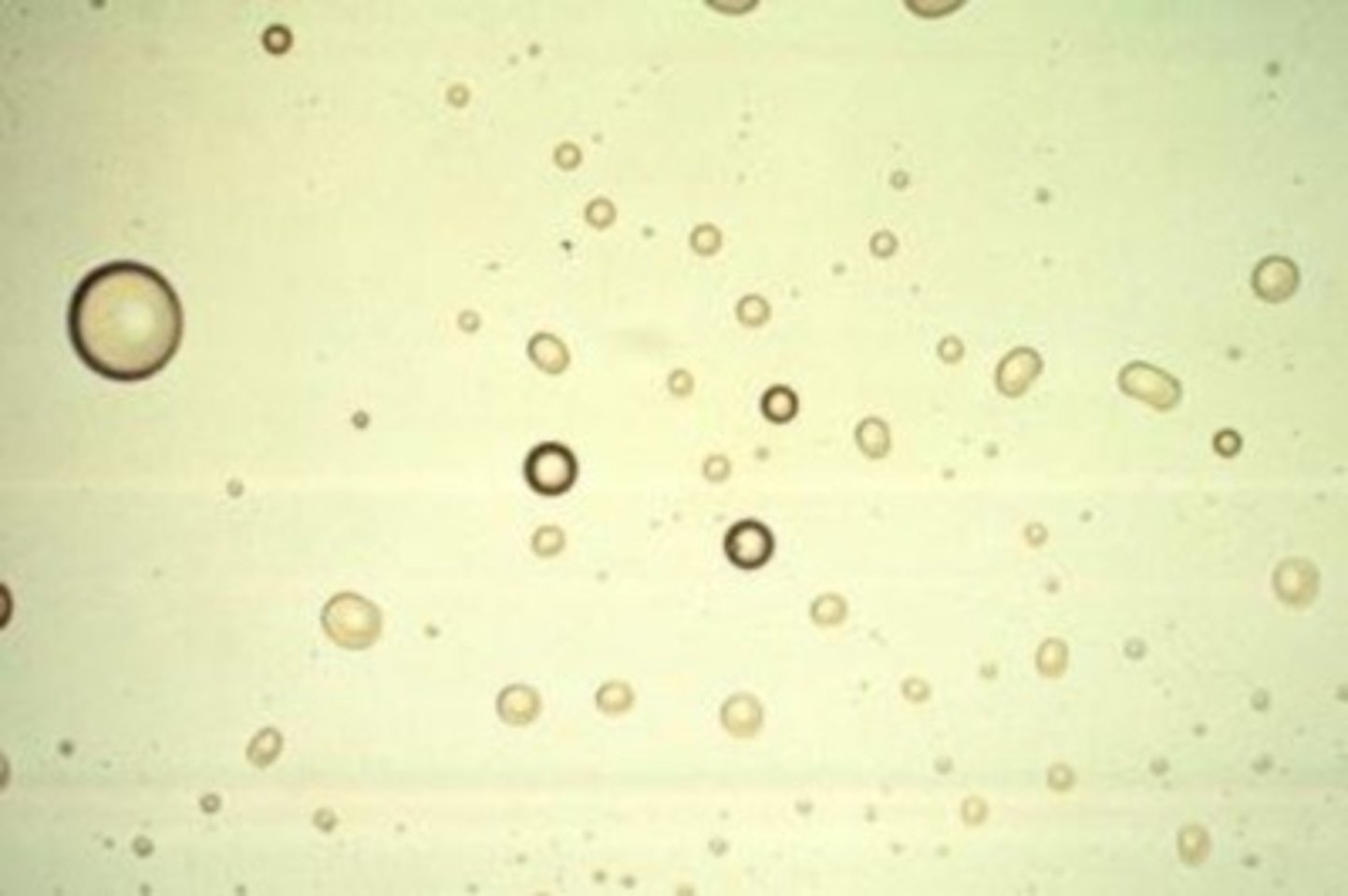
Air Bubbles
artifacts

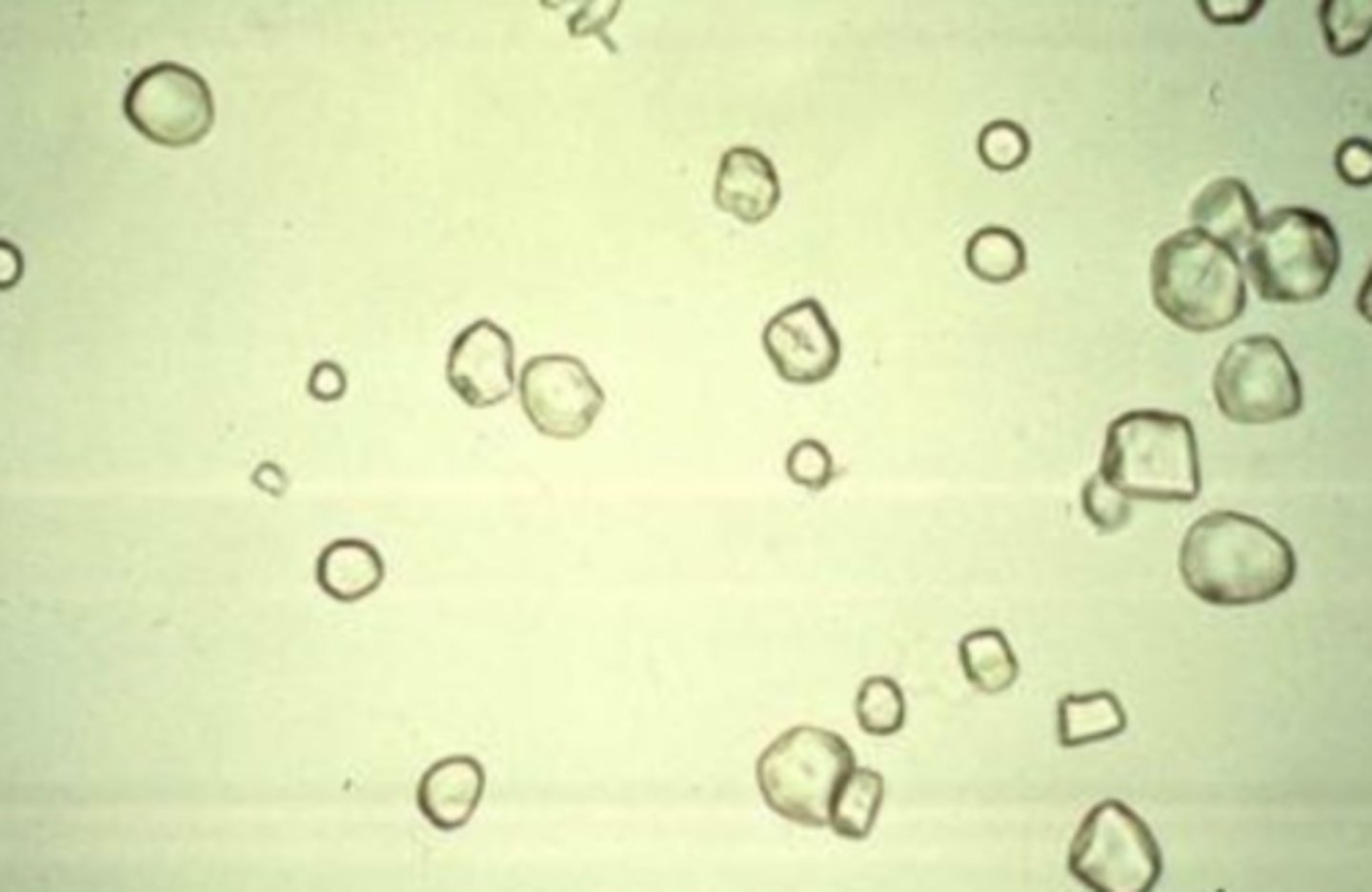
Starch Granules
artifacts
Fibers
artifact
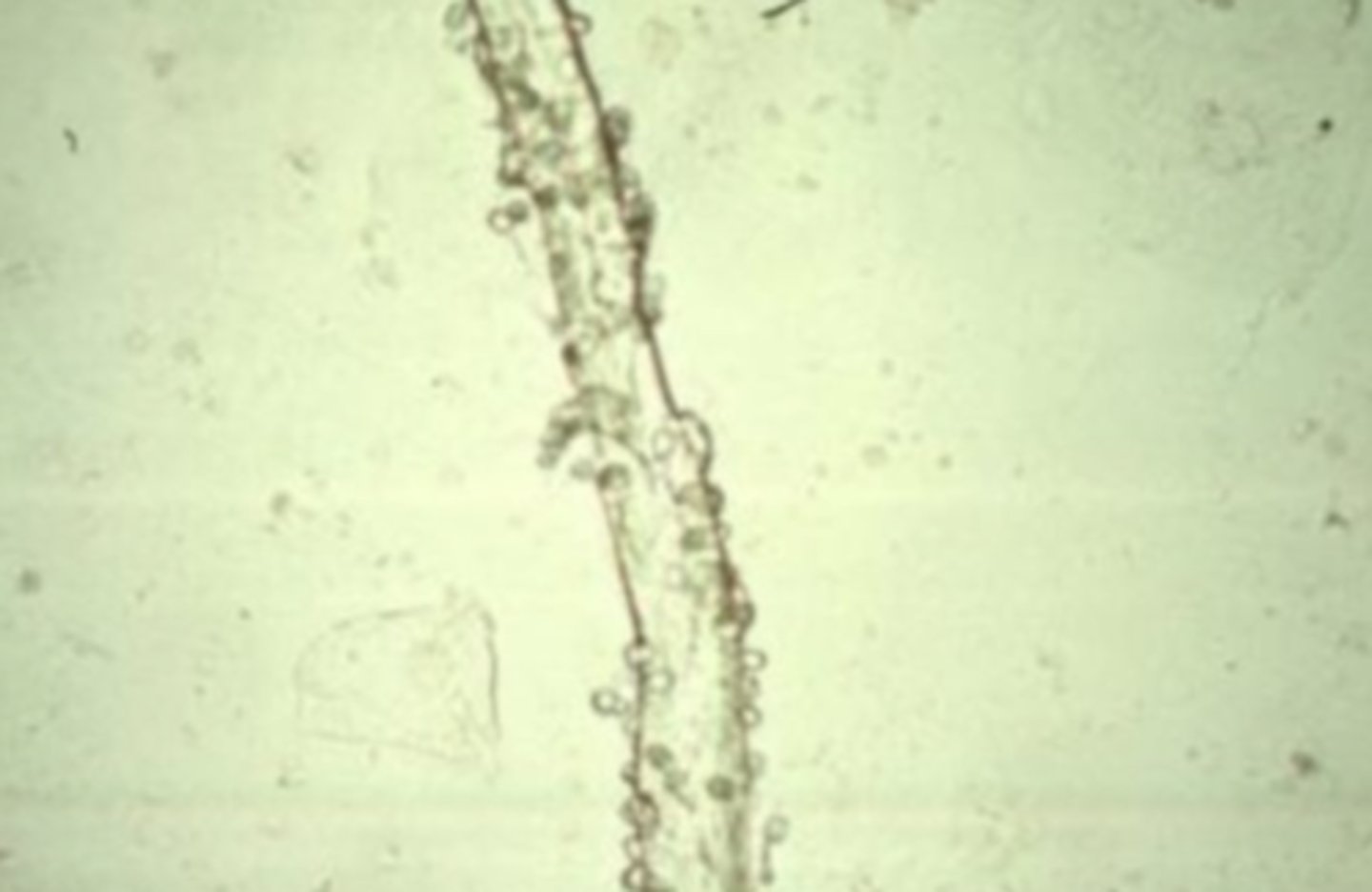
Sperm
have a characteristic oval body with a long, thin tail and are 50 microns long
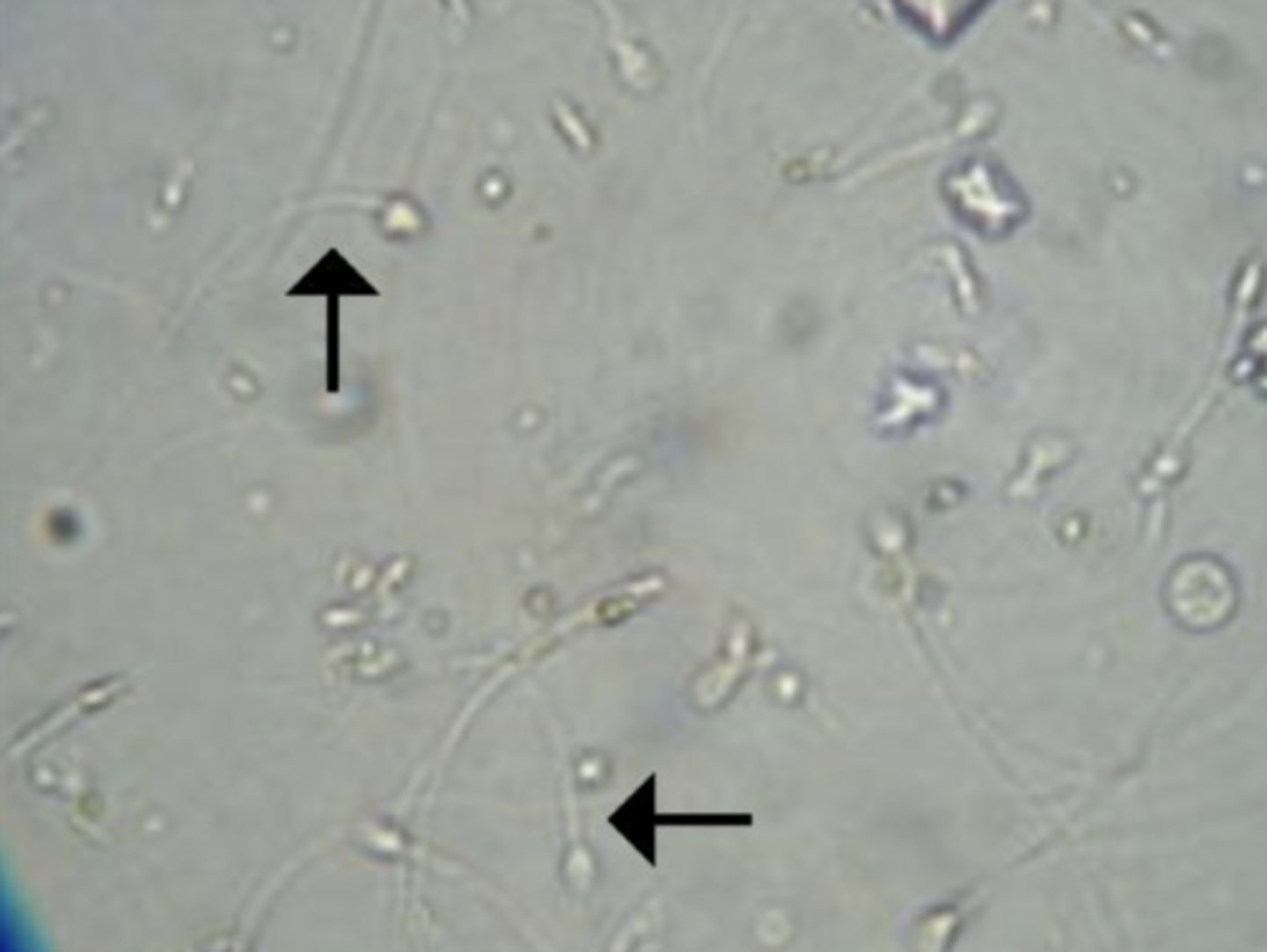
Mucus Threads
semi-transparent under brightfield microscopy and could be mistaken for hyaline casts. They are ribbon-like strands with poorly defined edges, pointed or split ends, and longitudinal striations.