Magnetic fields
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
In what direction do magnetic field lines go
From north to south
What does the field pattern around a straight, current-carrying wire look like?

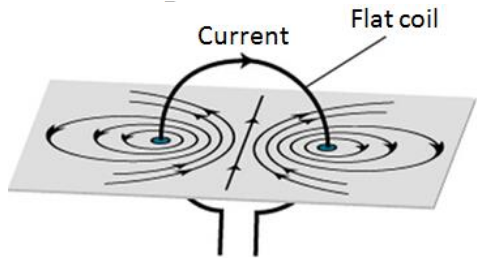
What does the field pattern around a flat coil look like?
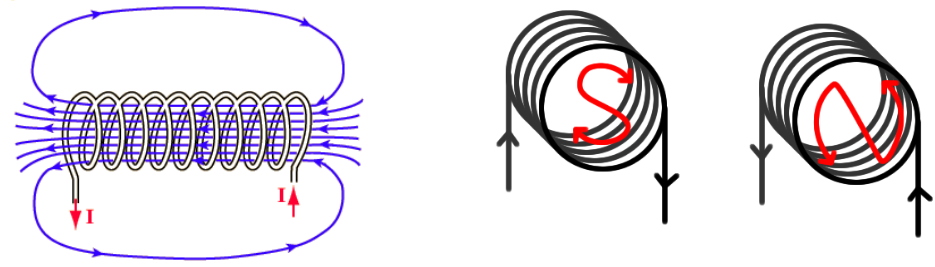
What does the field pattern around a solenoid look like? How do you tell which end is the north and south pole?
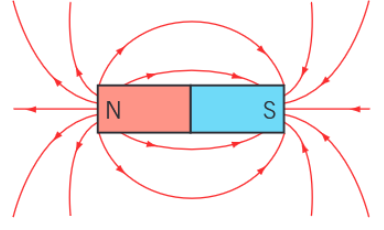
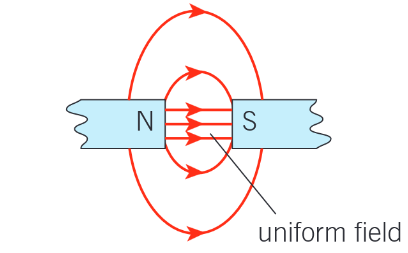
What does the field pattern around a bar magnet look like?
What does the field pattern around 2 bar magnets attracting look like?
What does the field pattern around 2 bar magnets repelling look like?
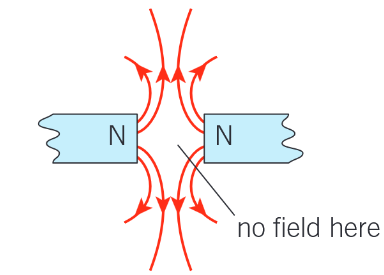
How do you draw a magnetic field line going into a page?

How do you draw a magnetic field line coming out of the page?

How do you draw a wire with current going into a page?

How do you draw a wire with current coming out of the page?

What are the units of magnetic flux density?
tesla (T)
Describe how you can predict the direction a wire carrying a current in a magnetic field will move
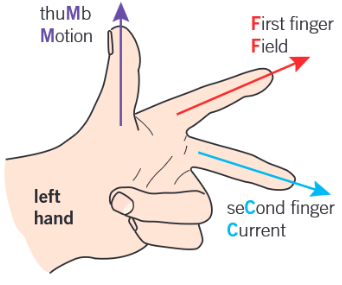
Flemings left hand rule
What is Fleming’s Left Hand rule?
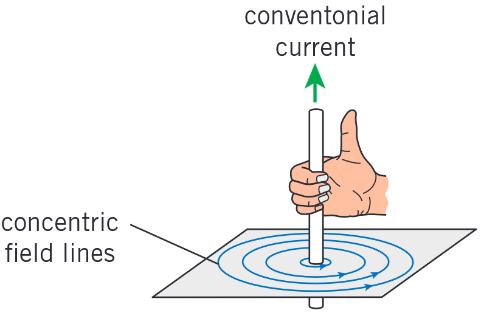
What is Fleming’s right hand grip rule and when is it used?
Used to determine the direction of the magnetic field arround a current-carrying wire
What factors affect the size of the Force on a current carrying wire in a magnetic field?
Strength of magnetic field
current in the wire, I
length L of the wire in the magnetic field
the angle between the magnetic field and the current direction, θ
What equation links the factors that affect the size of the Force on a current carrying wire in a magnetic field, and what is the meaning and unit of each term?
F = BIL sin θ
F is the force experienced by the wire in newtons
B is the magnetic flux density in telsa
I is the current in the wire in amperes
L is the length of the wire in the magnetic field in meters
θ is the angle between the magnetic field and the current direction in degrees
Define magnetic flux density
The strength of a magnetic field
Is Magnetic Flux density a scalar or a vector?
Vector
Define the tesla
1T is the magnetic flux density when a wire carrying a current of 1 A placed perpendicular to the magnetic field experiences a force of 1N per metre of its length.
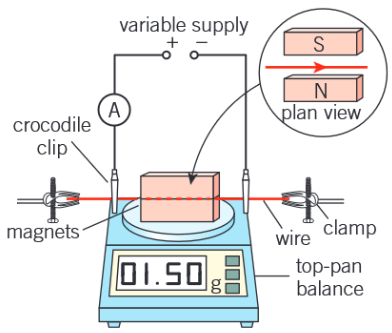
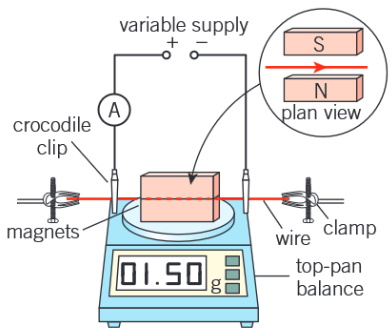
Describe a practical to determine magnetic flux density
The magnets are placed on a top-pan balance and a stiff copper wire is held perpendicular to the magnetic field between the two poles (as shown in diagram)
The length L of the wire in the magnetic field is measured with a ruler.
Using crocodile clips, a section of the wire is connected in series with an ammeter and a variable power supply. The balance is zeroed when there is no current in the wire.
With a current I, the wire experiences a vertical upward force (predicted by Fleming's left-hand rule). According to Newton's third law of motion, the magnets experience an equal downward force, F.
This force F can be calculated from the change in the mass reading, m, using F = mg, where g is the acceleration of free fall
The magnetic flux density B between the magnets can then be determined from the equation B = F/IL
What are the sources of error in the experiment to determine the strength of a magnetic field? What effect would they have on the results? What types of errors are they?
The actual length of the wire feeling a force due to the magnetic field being longer than the magnet. This means the value of L will be smaller than the true value.
The wire wont be perfectly perpendicular to the magnetic field. The size of the mass will read lower if not perpendicular.
These are both systematic errors
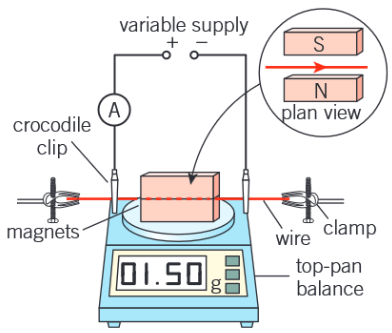
Here are two sources of error in the experiment to determine the strength of a magnetic field:
The actual length of the wire feeling a force due to the magnetic field being longer than the magnet.
The wire not being perpendicular to the magnetic field.
What effect would they have on the value of B obtained?
L and m will both be smaller than true value due to these errors
F= BIL and F = ma so mg = BIL. Rearranging gives m = (BL/g) I. As such gradient of m-I graph is BL/g, so B = gradient × g / L
As such L would cause the value of B to be higher than the true value.
Not being perpendicular would cause the gradient and value of B to be lower than the true value
Describe the direction of flow of conventional current compared to the direction of electron flow?
Opposite to each other:
Convetional is ‘the flow of positive charge’ so goes from positive to negative
Electron flow goes from negative to positive
If electrons are moving as particles, not in a conductor, then which way should you point your second finger when using Fleming’s Left hand rule?
In the direction the electrons are moving
What direction will the force on the electrons be relative to their motion in a uniform magnetic field?
At a right angle to both the direction of motion and the direction of the filed lines
Derive F = Bev from F = BIL
F = BIL
v = L / t so L = vt
I = Q / t
∴ F = B (Q / t) (vt) = BQv
The charge, Q, of electrons and protons is e
∴ F = Bev
If there is a centripetal force provided by the magnetic field show how the radius of the path will change if the particle:
Moves faster
Is more massive
There is a stronger magnetic field.
r = mV / BQ, so:
faster-moving particles travel in bigger circles (r ∝ v)
more massive particles move in bigger circles (r ∝ m)
stronger magnetic fields make the particles move in smaller circles (r ∝ 1/B)
What is the difference between magnetic flux density B, magnetic flux Φ and magnetic flux linkage NΦ?
TBC
Define magnetic flux
The product of the component of the magnetic flux density perpendicular to a given area and that cross-sectional area
What is the equation for magnetic flux?
Φ = BA cos θ
What is the unit of magnetic flux?
Wb (weber)
Define magnetic flux linkage
The product of the number of turns in a coil and the magnetic flux
What is the unit of magnetic flux linkage?
SI unit is weber, but weber-turns is used to distinguish it from magnetic flux
What is electromagnetic induction?
The creation of an electric current in a wire when it is moved through a magnetic field
What is Faraday’s Law?
The magnitude of the induced e.m.f. is directly proportional to the rate of change of magnetic flux linkage (so ε ∝ ΔNϕ / Δt)
What is Lenz’s Law?
The direction of the induced e.m.f. or current is always such as to oppose the change producing it
What equation describes how the flux linkage in the generator coils (of an AC generator) changes as it rotates?
NΦ = B A N cosθ
How does the emf of an AC generator vary with time as the coil rotates?
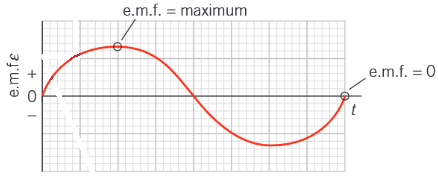
Describe how emf and flux linkage are related to each other through one rotation of the coil in an AC generator
e.m.f = – ∆(NΦ) / ∆t
This equals -1 × gradient of flux linkage against time graph
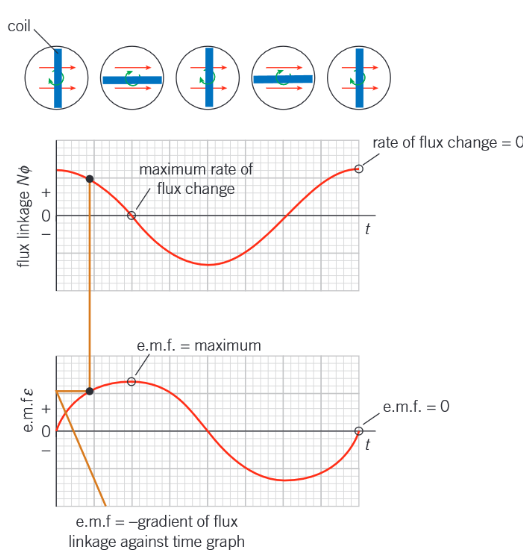
How could you increase the induced emf in the coils of an AC generator?
Increase one of more of the following:
magnetic flux density B
cross-sectional area A of the coil
number of turns N
frequency f of the rotating coil.
How is a varying emf is induced in the secondary coil of a transformer?
An alternating current is supplied to the primary coil. This produces a varying magnetic flux in the soft iron core.
The secondary coil, which is wound round the same core, is linked by this changing flux. The iron core ensures that all the magnetic flux created by the primary coil links the secondary coil and none is lost.
According to Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, a varying e.m.f. is produced across the ends of the secondary coil.
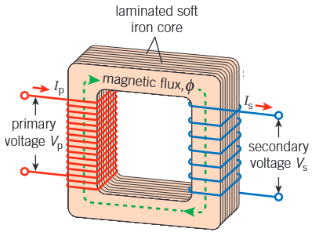
Why do we use transformers?
Transformers are used to change the potential difference
They are used in the national grid to reduce losses due to heat:
Pylons transport electricity at very high voltages
Since power loss ∝ 1/V², a high p.d. will mean a much lower power loss.
State and describe the relationship between the number of turns of coil and the induced emf.
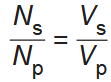
State and describe the relationship between the current and emf in the primary and secondary coils
s and p are flipped for current!!!
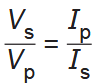
Describe a step up transformer
Transformers that increase voltage, so Vs > Vp
Has more turns on the secondary than on the primary coil
Describe a step down transformer
Transformers that decrease voltage, so Vs < Vp
A step-down transformer has fewer turns on the secondary than on the primary coil