AP Physics Unit13_2: Mirrors
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
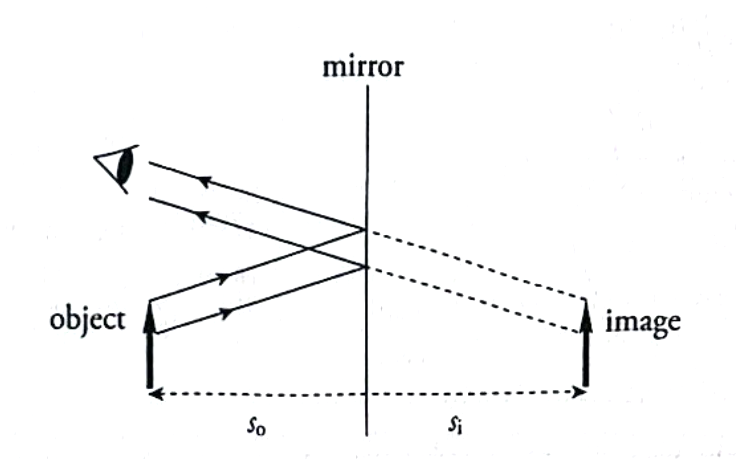
What are the four key properties of images formed by plane mirrors?
Location: Image appears behind the mirror at the same distance as the object is in front (|sᵢ| = sₒ).
Type: Always virtual (light rays don't actually converge behind the mirror).
Orientation: Upright (same vertical direction as the object).
Size: Same height as the object (magnification M = 1).
Key Notes:
Virtual images cannot be projected on a screen.
The mirror equation confirms this: For a plane mirror (f = ∞), sᵢ = -sₒ and M = 1.
Used in everyday mirrors (bathroom mirrors, dressing mirrors).
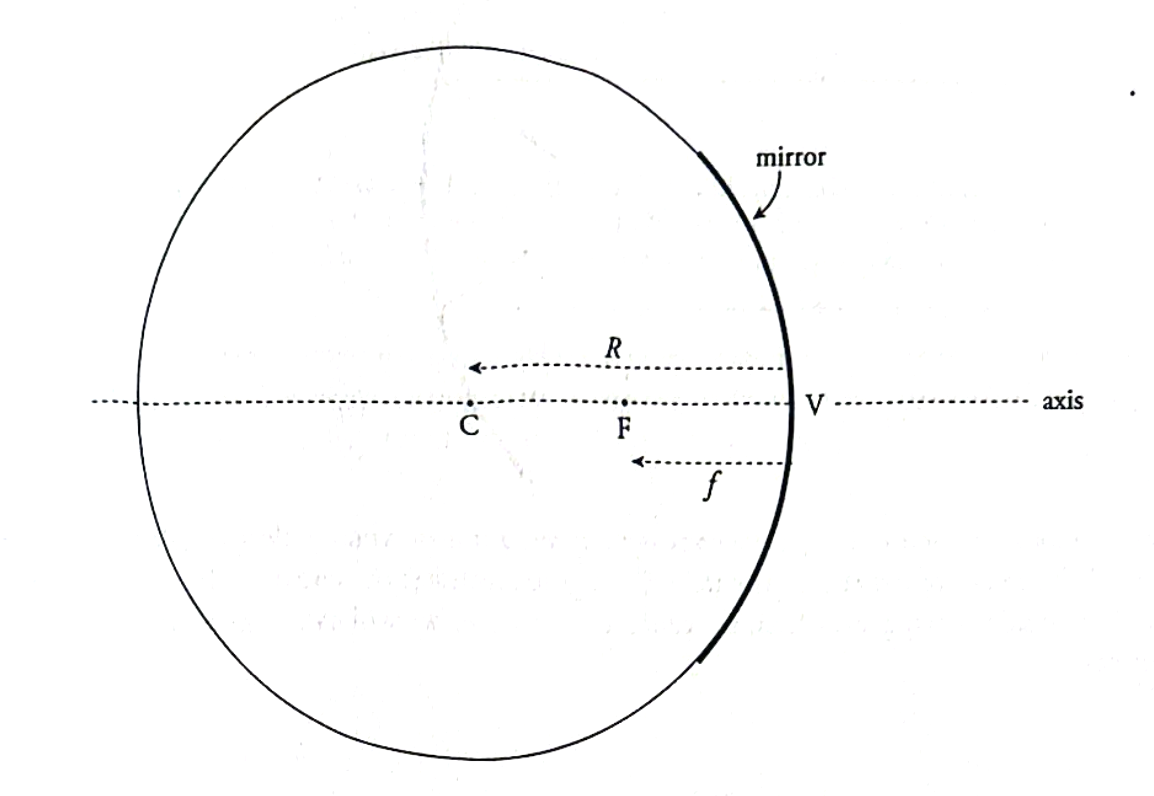
What are the key terms for spherical mirrors (concave & convex)?
Center of Curvature (C): Center of the sphere the mirror is part of.
Radius of Curvature (R): Distance from C to the mirror surface.
Focal Point (F): Where parallel rays converge (concave) or appear to diverge from (convex); f = R/2.
Vertex (V): Geometric center of the mirror surface.
Key Notes:
Concave mirrors:
f is positive (real focus).
Can form real or virtual images depending on object position.
Convex mirrors:
f is negative (virtual focus).
Always form virtual, upright, diminished images.
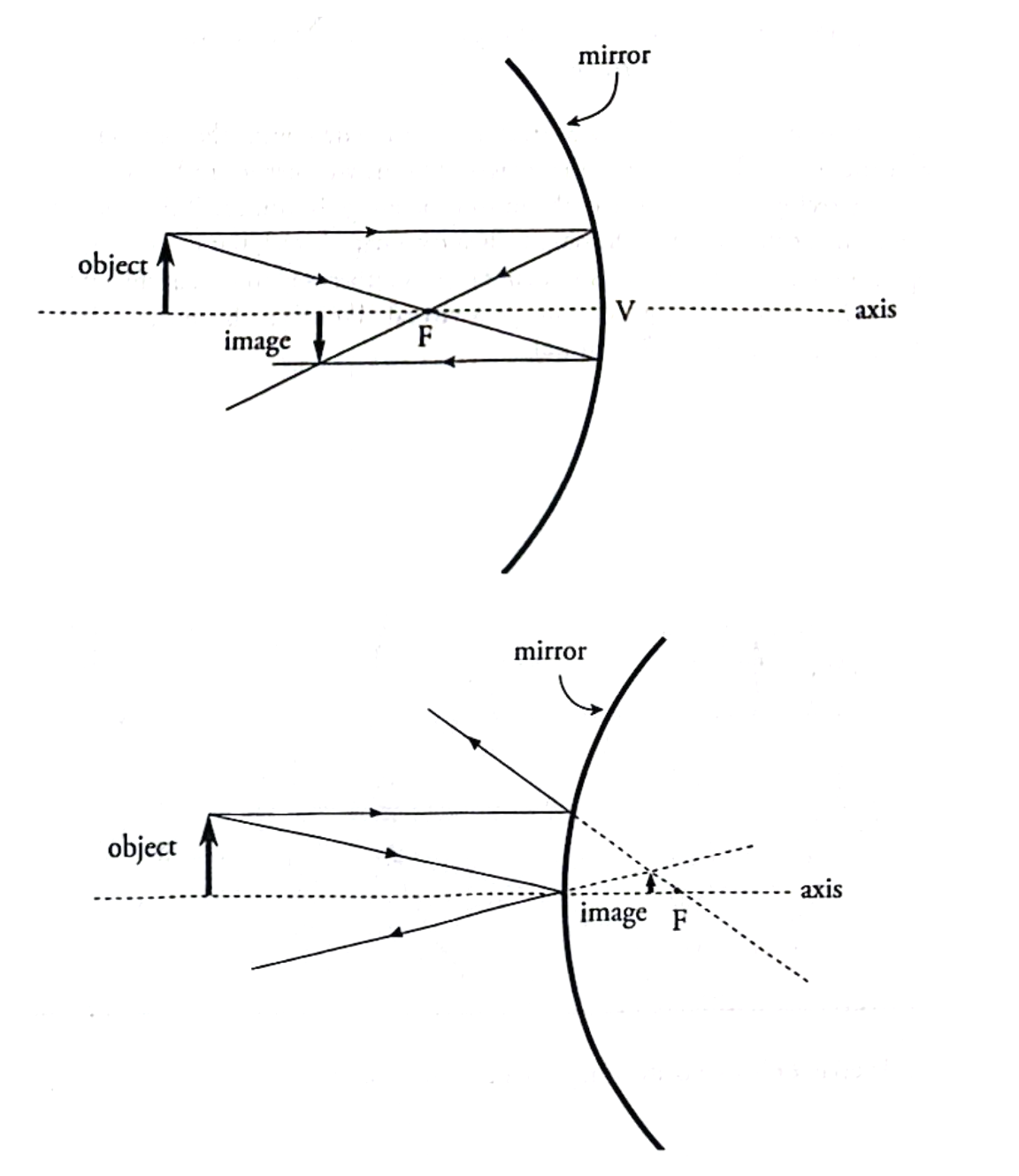
What are the Ray Tracing Rules for concave and convex mirrors?
Concave Mirrors:
Parallel to axis → Through F.
Through F → Parallel to axis.
Through C → Reflects back through C.
Convex Mirrors:
Parallel to axis → Diverges as if from F.
Toward F → Reflects parallel to axis.
Toward C → Reflects back along same path.
Key Notes:
Only two rays are needed to locate an image.
Real images form where rays actually intersect (same side as object).
Virtual images form where rays appear to diverge (opposite side of object).
Mirror Equation & Sign Conventions

How does object position affect images in concave mirrors?
Beyond C: Real, inverted, diminished (|M| < 1).
At C: Real, inverted, same size (M = -1).
Between C and F: Real, inverted, enlarged (|M| > 1).
At F: No image (rays parallel).
Inside F: Virtual, upright, enlarged (M > 1).
Key Notes:
Focal point is the threshold:
Objects outside F → Real images.
Objects inside F → Virtual images.
Example: Makeup mirrors use the "inside F" case for magnification.
Why do convex mirrors always form virtual images?
Mathematical proof:
f is negative, sₒ is positive → Mirror equation forces sᵢ to be negative.
Negative sᵢ → Virtual image.
Ray-tracing proof:
Reflected rays diverge; only virtual images form behind the mirror.
Key Notes:
Always upright and diminished (|M| < 1).
Applications: Security mirrors, side-view car mirrors ("objects are closer than they appear").
Example Problem (Concave Mirror)
An object is placed 30 cm from a concave mirror (f = 10 cm). Find the image properties.

Example Problem (Convex Mirror)
An object is placed 20 cm from a convex mirror (f = -30 cm). Find the image properties.

Key Study Tips
Draw ray diagrams to visualize image formation.
Memorize sign conventions:
sₒ: +, f: + (concave) or - (convex), sᵢ: + (real) or - (virtual).
Check units: Ensure all distances are in the same units (e.g., cm or m).
Need a mnemonic?
"Real Is Inverted" (RII): Real images are always Inverted.
"Convex = Cautious": Convex mirrors make things look smaller (and farther away).