BIOL 1107 Exam 2
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Which of the following are involved in synthesizing lagging strands but not leading strands during DNA replication?
A. Helicases
B. DNA polymerase
C. Okazaki fragments
D. Primases
C
DNA ligase _____
A. Releases the tension created by twisting the DNA molecule during replication
B. Makes a DNA strand complementary to the template strand
C. Separates the two strands of a DNA molecule
D. Makes a RNA strand complementary to the template strand
E. Joins separate strands of DNA to form a continuous strand
F. Prevents DNA strands from forming base pairs
E
Primase _____
A. Releases the tension created by twisting the DNA molecule during replication
B. Makes a DNA strand complementary to the template strand
C. Separates the two strands of a DNA molecule
D. Makes a RNA strand complementary to the template strand
E. Joins separate strands of DNA to form a continuous strand
F. Prevents DNA strands from forming base pairs
D
T or F: Mutations can have negative, neutral, or positive effects on protein function?
A. True
B. False
A
If one gene has all five mutations described below, which would be the most impactful?
A. Frameshift in exon 3 from a single deletion
B. Promoter mutation that does not affect transcription
C. Missense in exon 5 that changes GLU to VAL
D. Intron mutation that does not influence RNA splicing
E. Nonsense mutation in exon 2 resulting in stop codon
E
Match the description to the type of mutation
The protein has not changed
A. Missense
B. Frameshift
C. Silent
D. Nonsense
C
Match the description to the type of mutation
The protein has one incorrect amino acid
A. Missense
B. Frameshift
C. Silent
D. Nonsense
A
Match the description to the type of mutation
Changes several amino acids beyond the site of mutation
A. Missense
B. Frameshift
C. Silent
D. Nonsense
B
Match the description to the type of mutation
Causes the protein to be too short
A. Missense
B. Frameshift
C. Silent
D. Nonsense
D
Which mutation is likely to cause several amino acids in the protein that is produced to be wrong or missing? (select all that apply)
A. Silent
B. Nonsense
C. Frameshift
D. Missense
B&C
T or F? Telomerase makes strands longer by performing reverse transcription, in that it converts RNA into DNA
A. True
B. False
A
Sister chromatids are considered to be:
A. Two different chromosomes
B. Similar but not identical copies of the same chromosomes
C. Identical copies of the same chromosome that remain physically attached to each other
D. Identical copies of the same chromosome that have moved to separate daughter cells
C
T or F? The separation of sister chromatids happens during interphase?
A. True
B. False
B
T or F? Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell during metaphase.
A true
B false
A
Separation of sister chromatids is characteristic of which stage of mitosis?
A. Prometaphase
B. Metaphase
C. Anaphase
D. Telophase
C
Which of the following are reasons why a cell would grow and divide?
A. Organism growth
B. Replacement of worn-out cells
C. Wound healing
D. All of the above
D
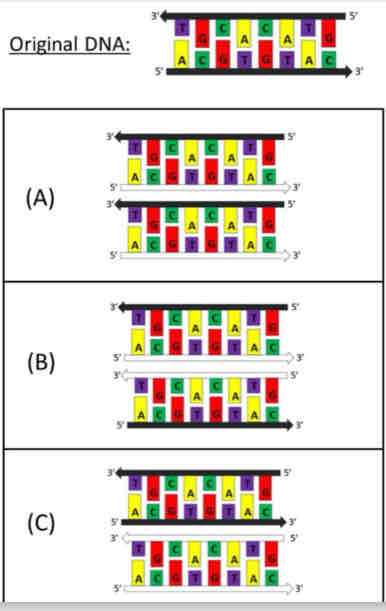
The DNA piece illustrated is labeled black. If this DNA is replicated in conditions where any new DNA gets labeled white, what picture illustrates the resulting pieces of DNA?
A, B, C?
B
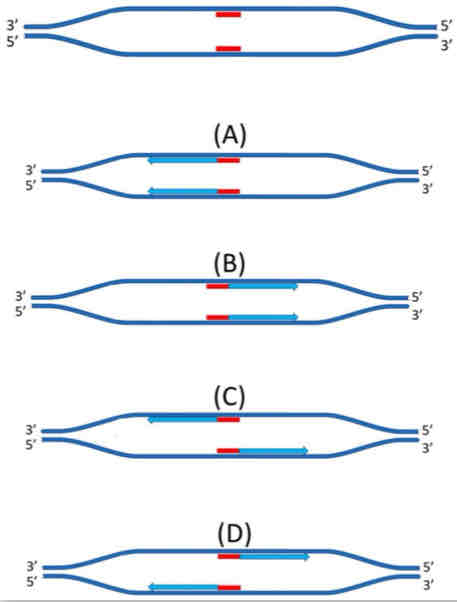
The diagram illustrates the beginning of a replication bubble. Two RNA primers are illustrated in red. Which of the pictures best illustrates how the two primers would be elongated by DNA polymerase?
A, B, C, D
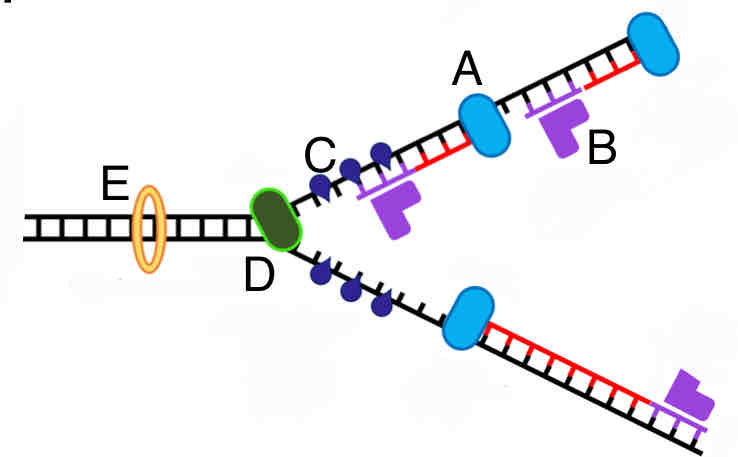
What replication enzyme is labeled A in the picture?
A. RNA primase
B. DNA polymerase
C. Topoisomerase
D. Single strand binding proteins
E. Helicase
B
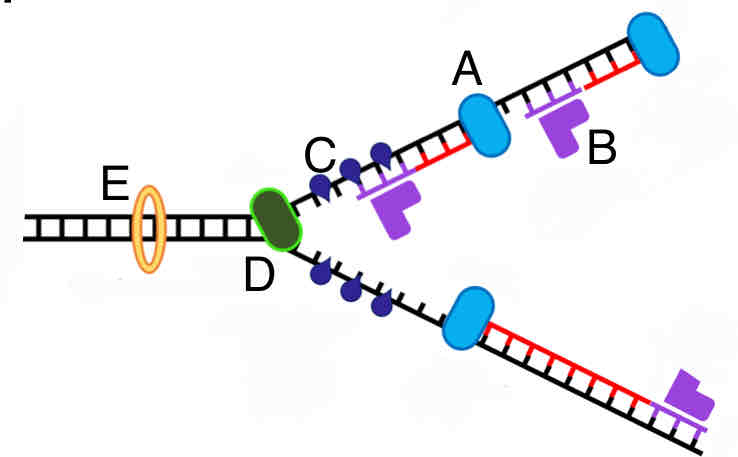
What replication enzyme is labeled B in the picture?
A. RNA primase
B. DNA polymerase
C. Topoisomerase
D. Single strand binding proteins
E. Helicase
A
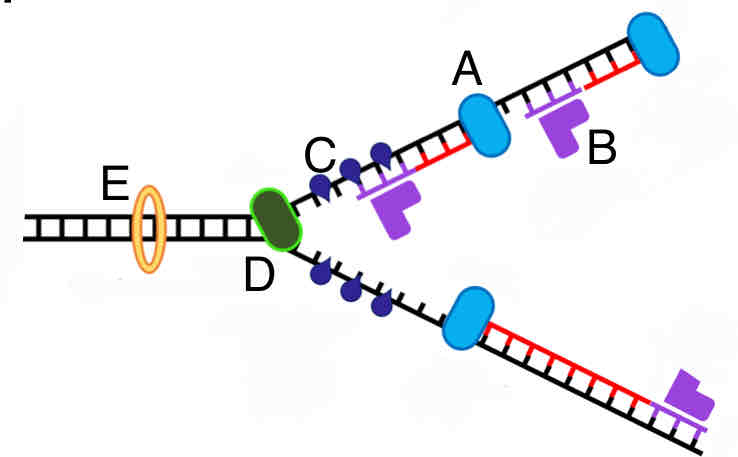
What replication enzyme is labeled C in the picture?
A. RNA primase
B. DNA polymerase
C. Topoisomerase
D. Single strand binding proteins
E. Helicase
D
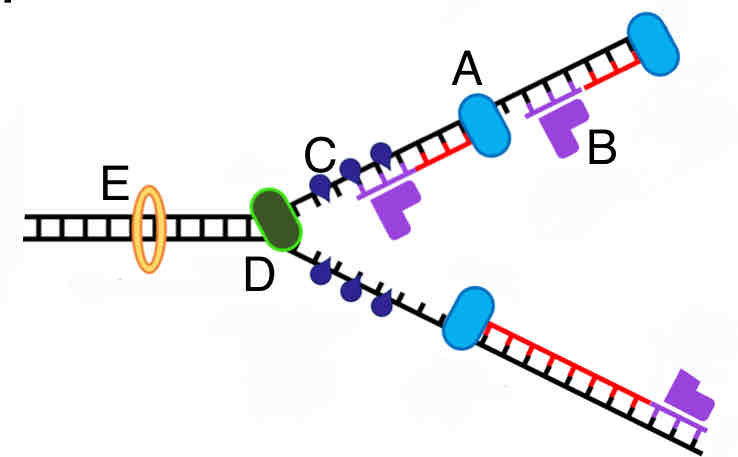
What replication enzyme is labeled D in the picture?
A. RNA primase
B. DNA polymerase
C. Topoisomerase
D. Single strand binding proteins
E. Helicase
E
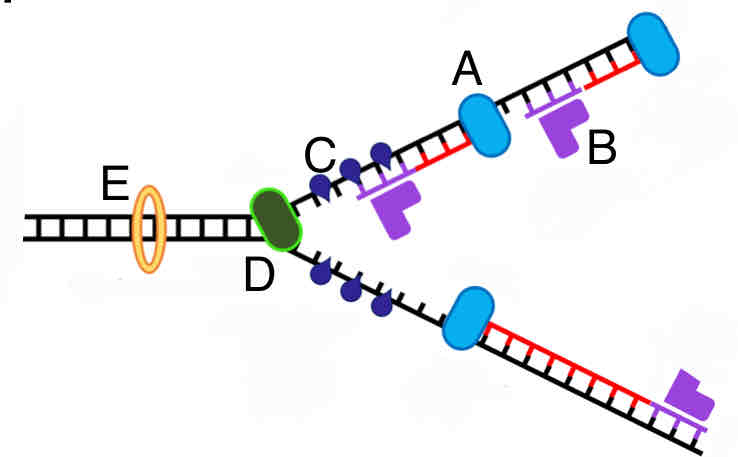
What replication enzyme is labeled E in the picture?
A. RNA primase
B. DNA polymerase
C. Topoisomerase
D. Single strand binding proteins
E. Helicase
C
What is the primary function of helicase in DNA replication?
Unwinds and separates two strands
What is the primary function of topoisomerase in DNA replication?
Keeps the DNA strand from getting tangled and broken from twisting.
What is the primary function of the single strand binding proteins in DNA replication?
Keep the DNA strands open, prevent hydrogen bonding
What is the primary function of RNA primase in DNA replication?
Makes short complimentary RNA sequences for DNA polymerase to use
What is the primary function of DNA polymerase in DNA replication?
Builds a new DNA strand that is complimentary to the old ones. Hopes for each of the original strands.
What happens in prophase?
Chromosomes condense, microtubule spindles start to form
What happens in Prometaphase?
Nuclear membrane disassembles, spindles attach to chromosomes at kinetochore
What happens in metaphase?
Chromosomes line up in the middle of cell, sister chromatids for each chromosome face opposite sides of the cell
What happens in Anaphase?
Sister chromatids separate and move to opposite sides of the cell
What happens in Telophase
Nuclear membranes reform, chromosomes condense again
What happens in Cytokinesis?
Cell divides into two daughter cells
What happens in the G1 checkpoint?
The cells checks for favorable conditions, asks if it should prepare to divide? Does it have the energy? Is there damage?
What happens at the G2 checkpoint?
Checks that all chromosomes were replicated and there is no damage. Asks if the DNA is copied fully and correctly?
What happens at the M checkpoint?
Checks if the sister chromatids are correctly attached to spindles in metaphase. Asks if the chromosomes are lined up correctly?
What happens in DNA polymerase proofreading?
DNA polymerase inserts an incorrect base about once every 100,000 bases. DNA polymerase can detect if an improper hydrogen bonds form and correct errors.
What happens in post-replication mismatch repair?
A multi-protein mislaid recognition and removal system works on newly synthesized DNA strand cutting out fragments of DNA from the new strand that include mispaired bases.