Superior and Posterior Mediastinum
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
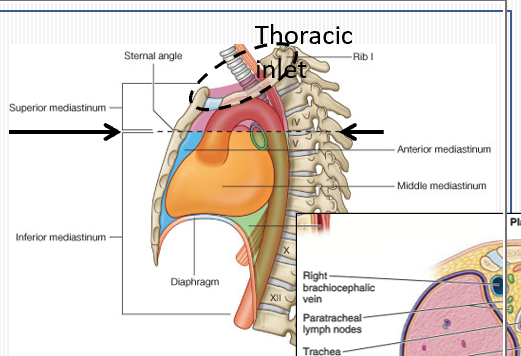
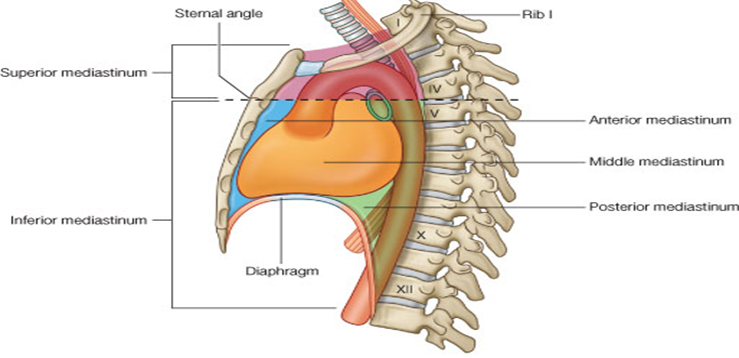
What are the superior mediastinum boundaries?
From thoracic inlet to transverse plane at sternal angle (T4–T5), between mediastinal pleura laterally.
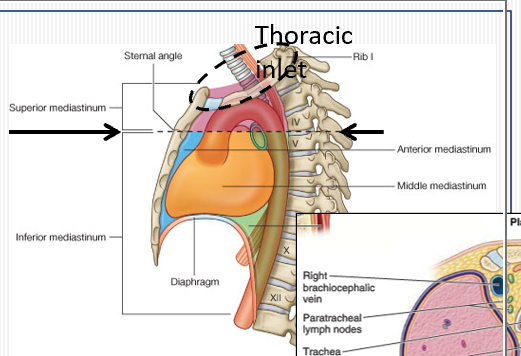

What are the anterior and posterior borders of the superior mediastinum?
Anterior: manubrium; Posterior: vertebral bodies T1–T4.

Name the key contents of the superior mediastinum.
Thymus, great vessels (SVC, brachiocephalic veins, aortic arch + branches), trachea, esophagus, thoracic duct, vagus & phrenic nerves, lymph nodes.
Where is the thymus located and what is its function?
In the anterior superior mediastinum, posterior to manubrium; site of T-lymphocyte maturation and immune education, regresses after puberty.
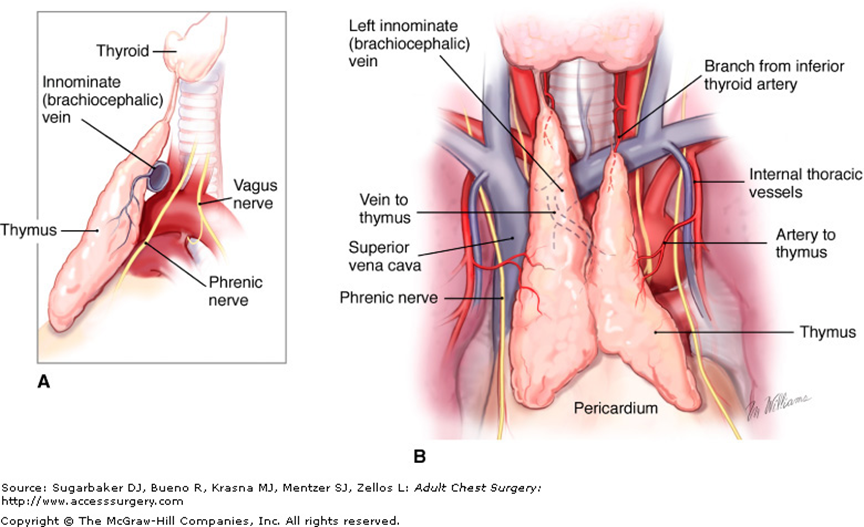
How do the brachiocephalic veins form?
Union of each internal jugular and subclavian vein; left and right merge to form SVC at right first costal cartilage.
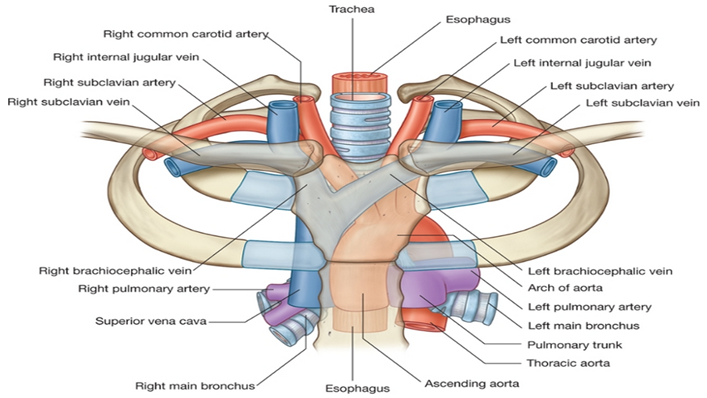
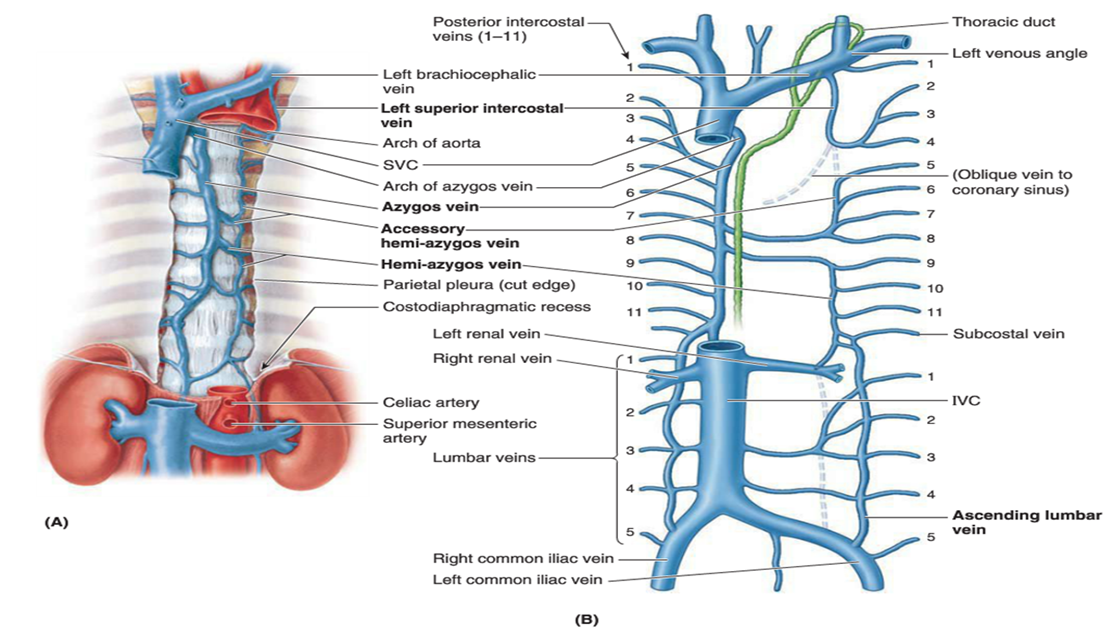
Where does the arch of the azygos vein drain?
Into the SVC just before it enters the pericardial sac.
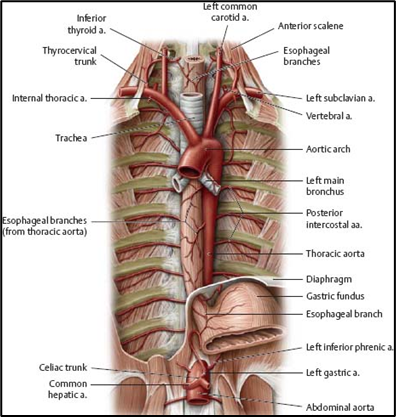
What are the branches of the aortic arch?
Brachiocephalic trunk (→ right subclavian & right common carotid), left common carotid, left subclavian arteries.
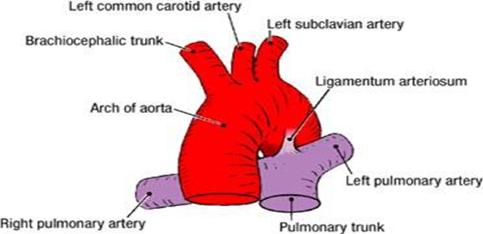
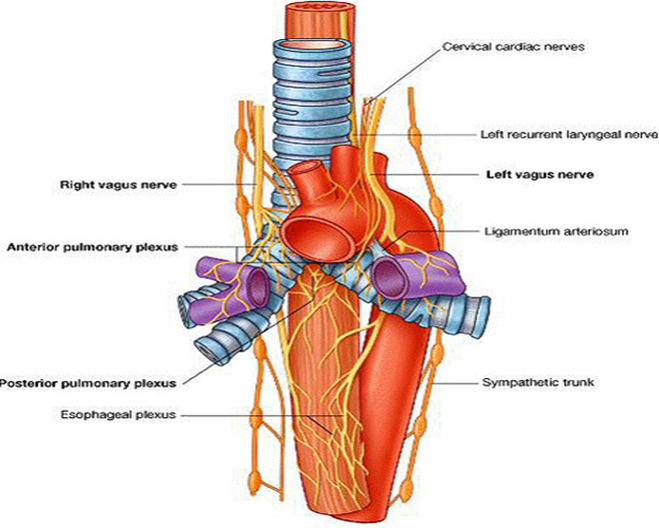
How does the left vagus nerve course over the aortic arch?
Descends anterior to the arch, gives off left recurrent laryngeal branch under ligamentum arteriosum, then contributes to cardiac and esophageal plexuses.
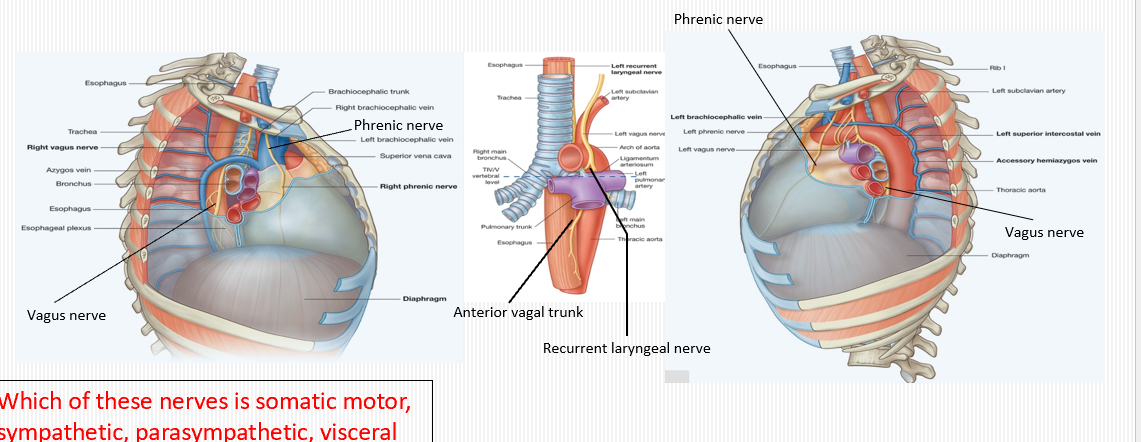

Where does the phrenic nerve run in the superior mediastinum?
Descends along the pericardium, anterior to the root of the lung, between mediastinal pleura and fibrous pericardium to innervate the diaphragm.
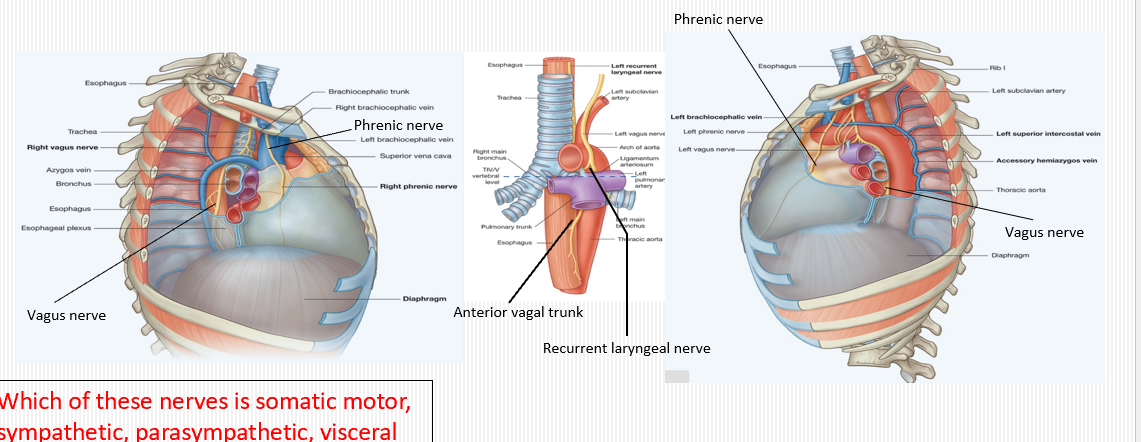

What is the role of the vagus nerve in the thorax?
Provides parasympathetic innervation to heart (slows heart rate) and bronchi (bronchoconstriction) and sensory to visceral pleura/esophagus.
What is the role of the phrenic nerve in the thorax?
Motor and sensory to the diaphragm; sensory to fibrous pericardium, mediastinal pleura, and diaphragmatic pleura/peritoneum.
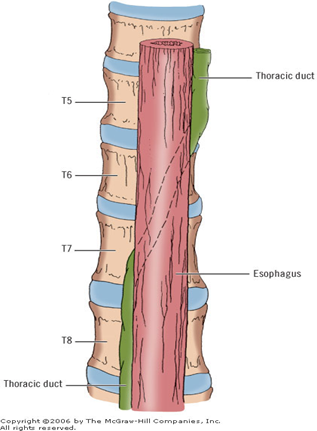
Where is the thoracic duct located in the superior mediastinum?
Posterior to esophagus, between azygos vein (right) and aorta (left), drains into left venous angle.
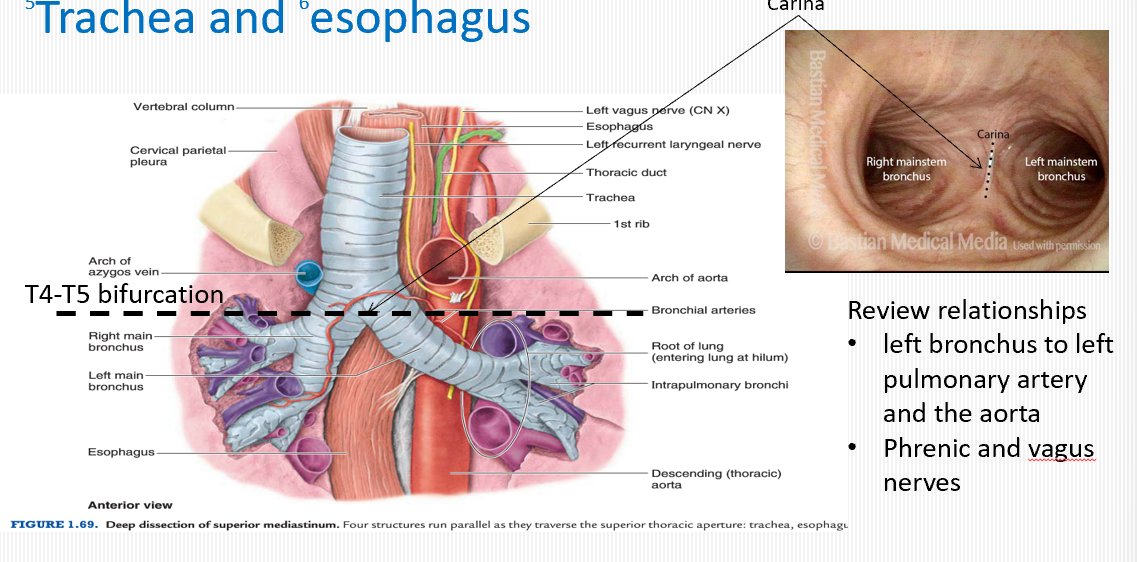

What region does the thoracic duct drain?
Lymph from both lower limbs, abdomen, left thorax, left head & neck, left upper limb.
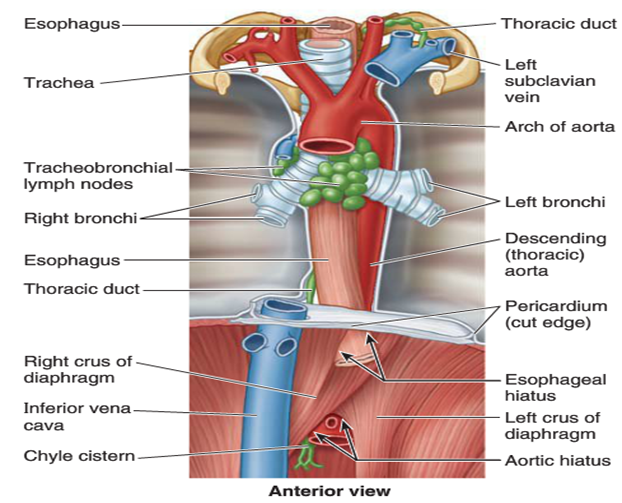
Define the posterior mediastinum boundaries.
Superior: T4–T5 plane; Inferior: diaphragm; Anterior: pericardium and roots of lungs; Posterior: vertebral bodies; Lateral: mediastinal pleura.
Name the key contents of the posterior mediastinum. (two candy canes and three waterfowl)
Descending thoracic aorta, esophagus, thoracic duct, azygos and hemiazygos veins, sympathetic trunks, splanchnic nerves.(Two candy canes: Aortic arch and Arch of azygos; and Three waterfowl: Esophagoose, Azygoose, Vagoose)
How does the descending aorta lie in the posterior mediastinum?
Along left side of vertebral bodies, posterior to root of left lung.
Describe the azygos vein system on the right side.
Azygos vein ascends along right vertebral bodies, arches over right lung root into SVC; receives right posterior intercostals.
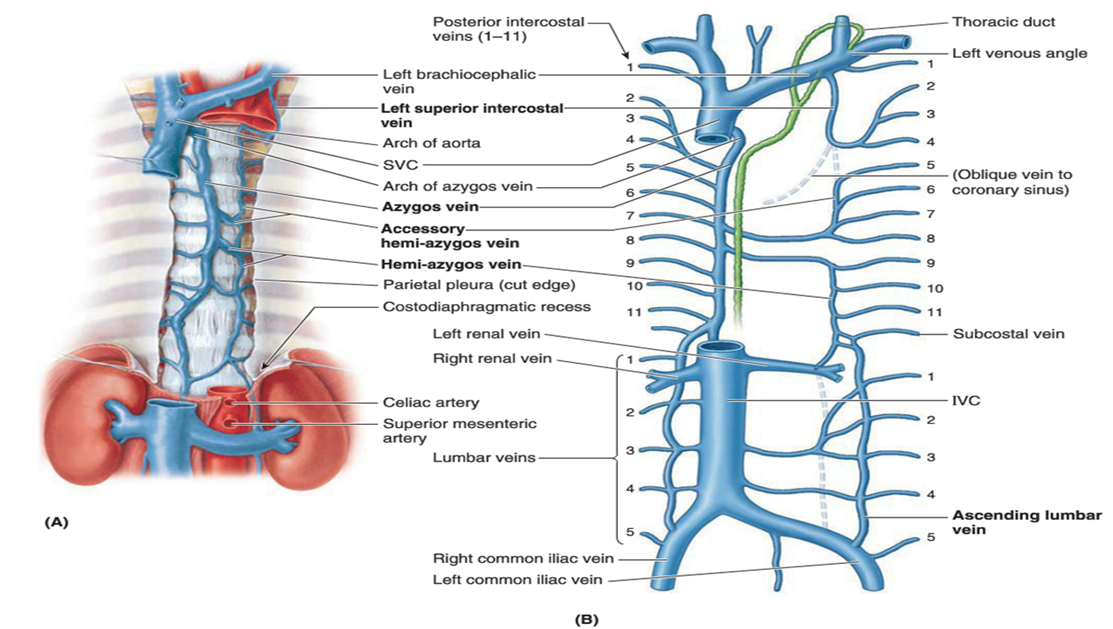
Describe the azygos system on the left side.
Hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos veins collect left posterior intercostals, cross midline to drain into azygos.
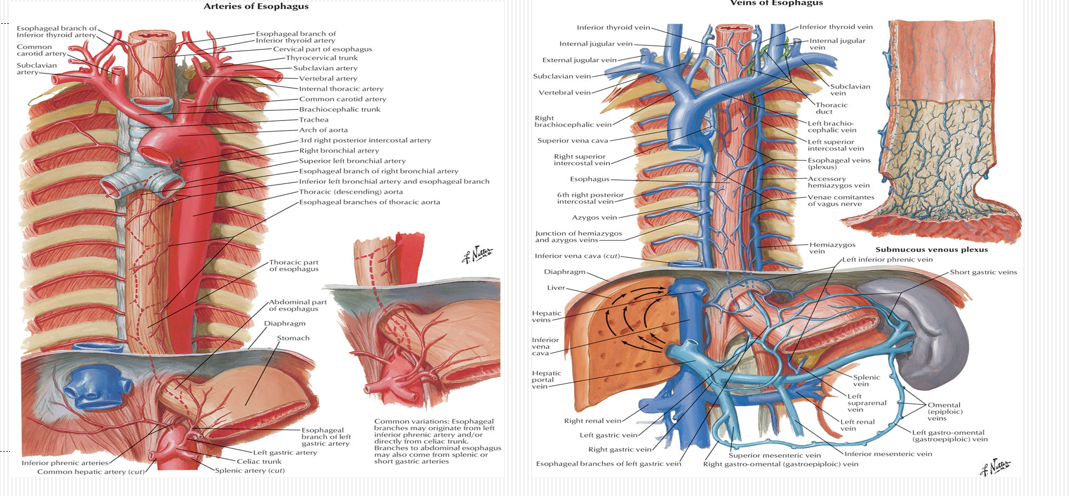
What is the esophageal blood supply and drainage?
Esophageal arteries from aorta and inferior thyroid; venous drainage to azygos on right and hemiazygos + left gastric on left.

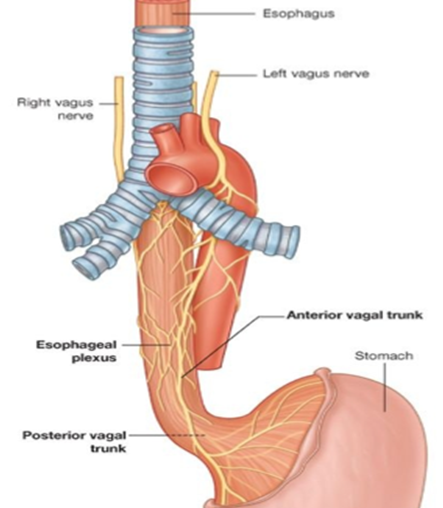
How is the esophagus innervated?
Vagal trunks form esophageal plexus (parasympathetic) plus thoracic splanchnic fibers (sympathetic) and visceral sensory fibers.
Where does the thoracic duct cross to the left side?
At T5 vertebral level posterior to esophagus and anterior to vertebral bodies, then arches to left venous angle.
What are the components of the sympathetic trunk in the mediastinum?
Chain ganglia adjacent to vertebral bodies from T1–T12, giving off cardiac and splanchnic branches.
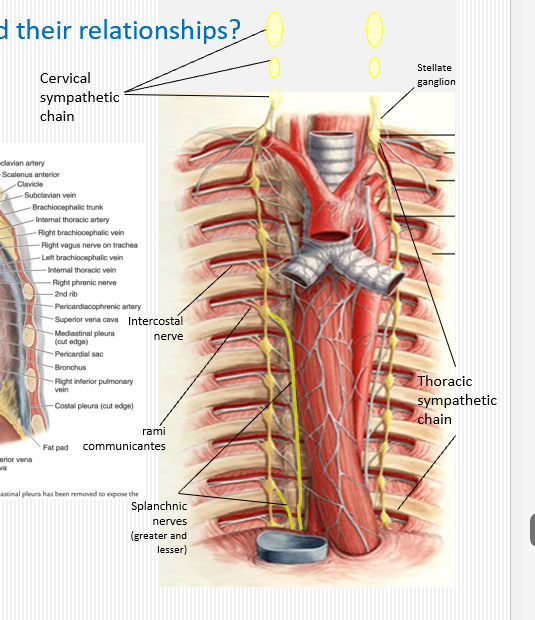

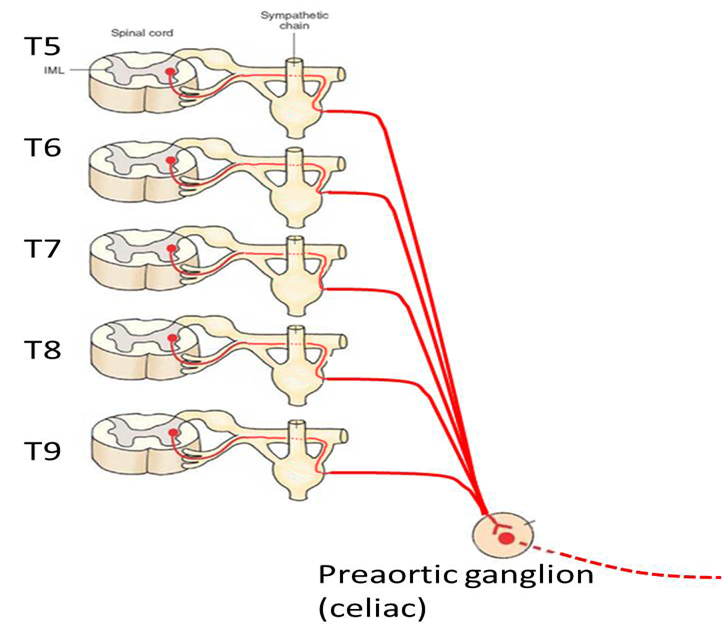
What do the thoracic splanchnic nerves innervate?
T5-T9; Preganglionic sympathetic fibers to abdominal prevertebral ganglia (celiac, superior mesenteric, inferior mesenteric).
How do the phrenic and vagus nerves differ in function?
Phrenic = somatic motor/sensory to diaphragm and pericardium; Vagus = visceral parasympathetic to heart, lungs, gut, and sensory to thoracic organs.
What somatic(skeletal muscle) structures traverse the mediastinum?
Phrenic nerves (C3–C5), intercostal nerves, sympathetic chain.
What autonomic(smooth muscle) structures traverse the mediastinum?
Vagus nerves, sympathetic trunks, thoracic splanchnic nerves, cardiac and pulmonary plexuses.
How is lymph drained from posterior mediastinal structures?
Collected into posterior intercostal and esophageal lymph nodes → thoracic duct.
What is a chylothorax?
Leakage of lymph (chyle) into pleural cavity due to thoracic duct injury or obstruction.
Name two clinical implications of mediastinal anatomy.
Mediastinitis risk in esophageal rupture; nerve injury (vagus, phrenic) in surgery causing bradycardia or diaphragmatic paralysis.
How do superior and posterior mediastinum differ in visceral contents?
Superior houses great vessels and thymus; posterior houses conduit structures (esophagus, aorta, duct) and autonomics.
What landmark separates superior from inferior mediastinum?
The transverse thoracic plane at the sternal angle (T4–T5).