OMFPR 16 - Pigmented Lesions (Dr. Menon)
1/227
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
228 Terms
What are the sources of pigment?
- Melanin
- Vascular structures
- Saliva/Mucin
- Cystic fluid
- Foregin material
Are these Non-Melanin or Melanin-Associated pigmented lesions?
- Exogenous
- Endogenous
non-melanin
Are these Non-Melanin or Melanin-Associated pigmented lesions?
- Developmental
- Reactive/Inflammatory
- Infectious
- Autoimmune and immune mediated
- Metabolic/Systemic
- Neoplastic
- Premalignant/malignant
melanin-associated
What type of pigmented lesions are the following?
- Amalgam tattoo
- Graphite and other foreign body tattoos
- Medication-induced pigmentation
exogenous (non-melanin)
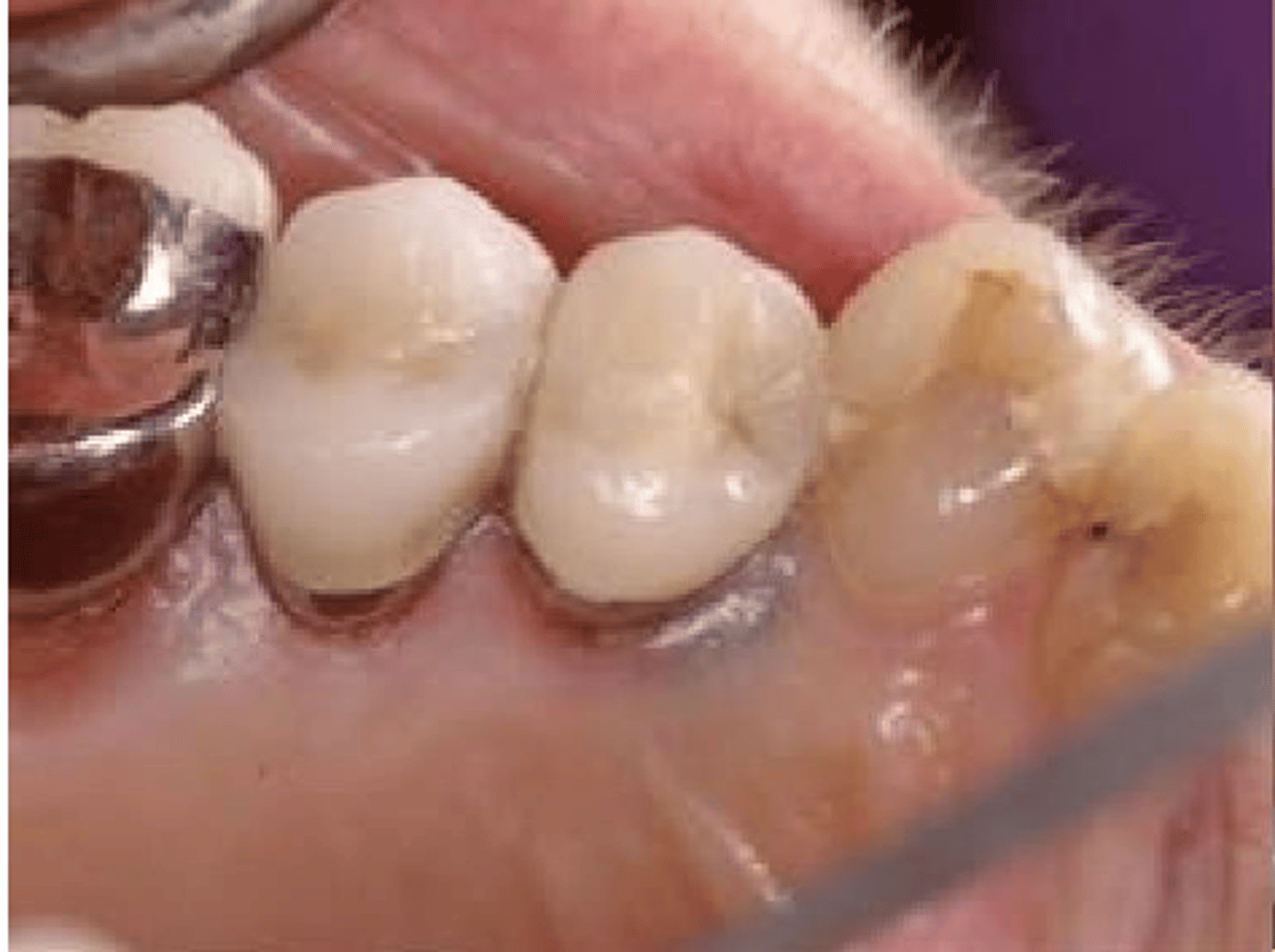
What type of pigmented lesion?
amalgam tattoo
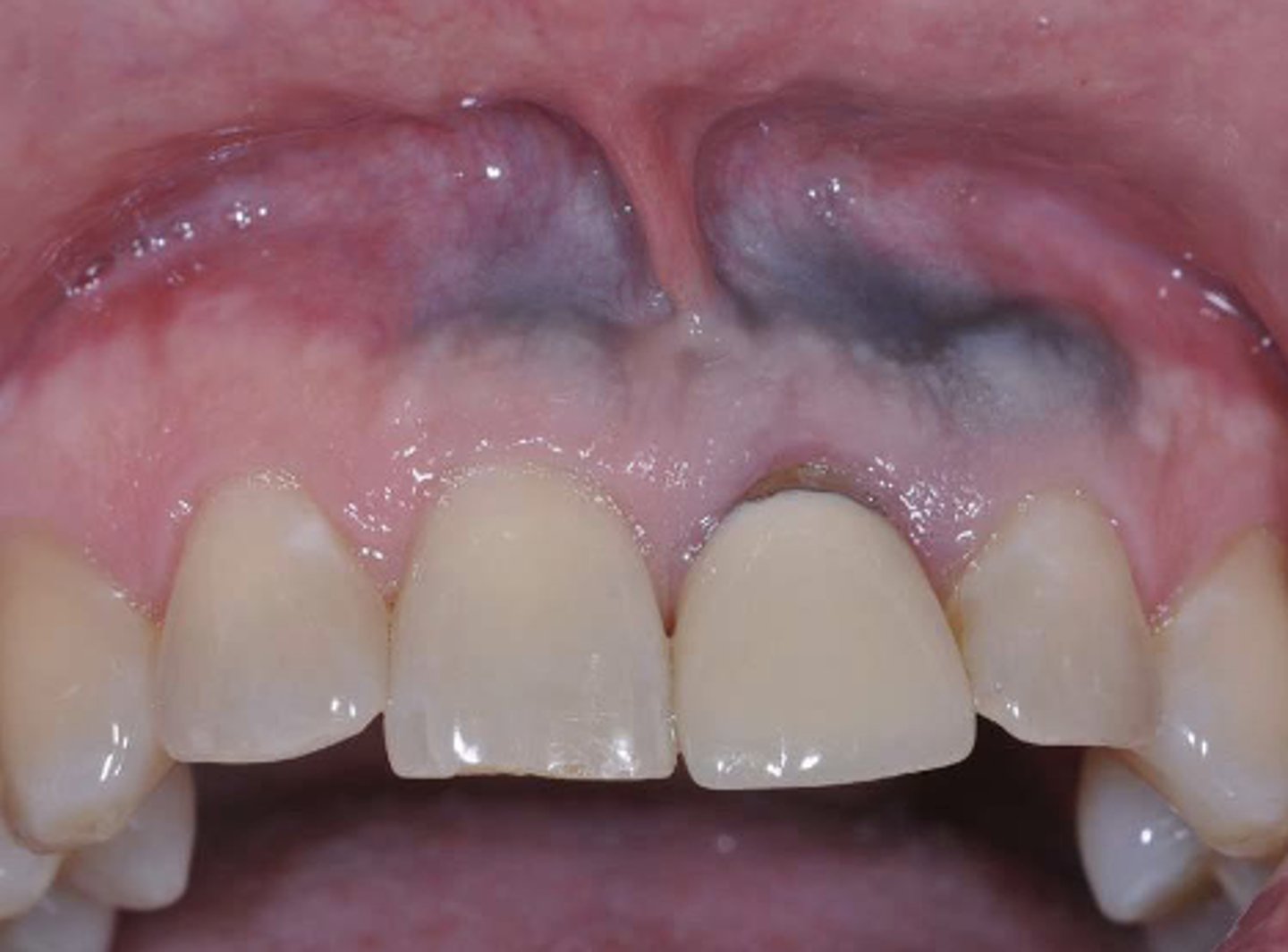
What type of pigmented lesion?
amalgam tattoo
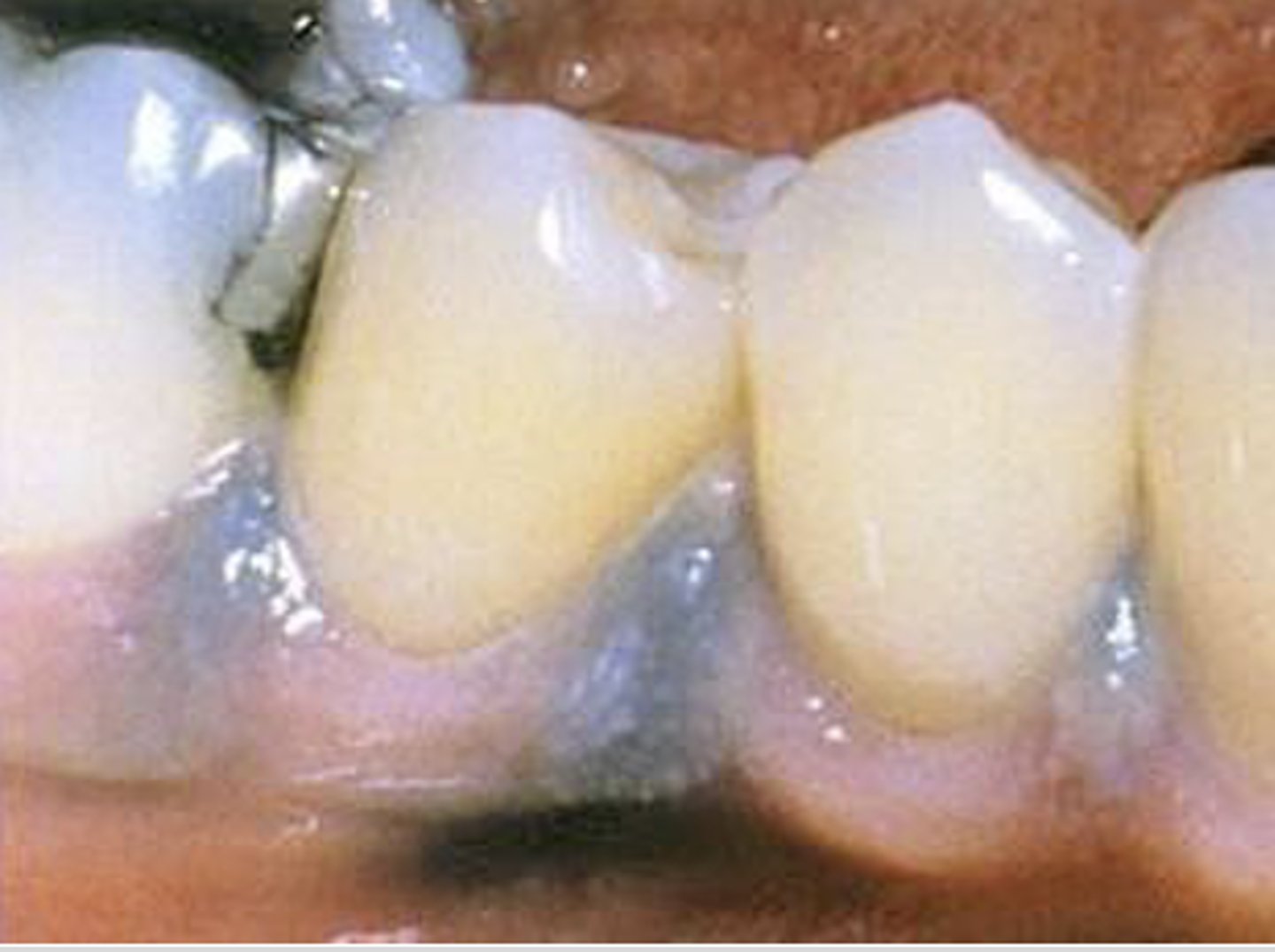
What type of pigmented lesion?
amalgam tattoo
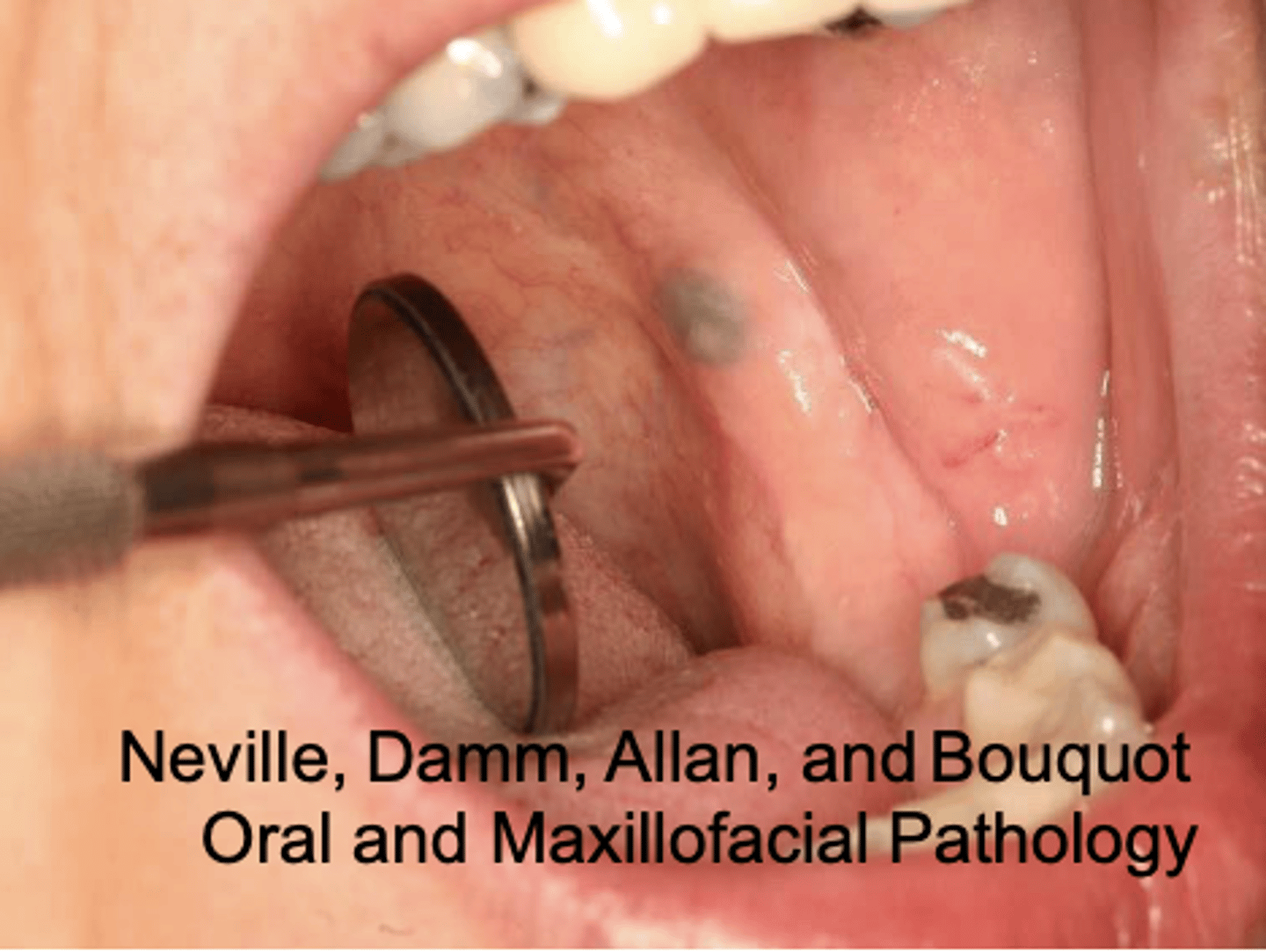
What type of pigmented lesion?
amalgam tattoo
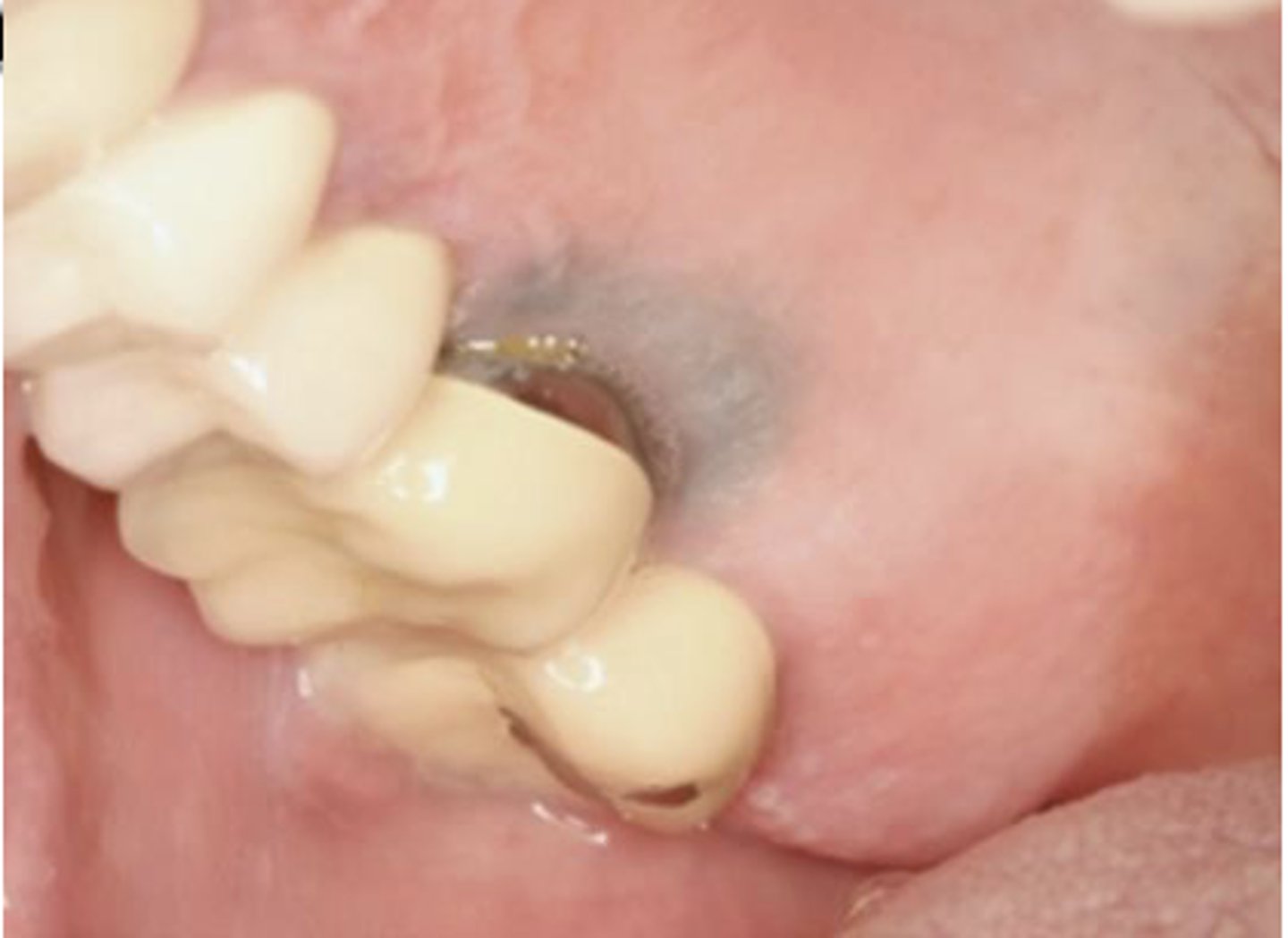
What type of pigmented lesion?
amalgam tattoo
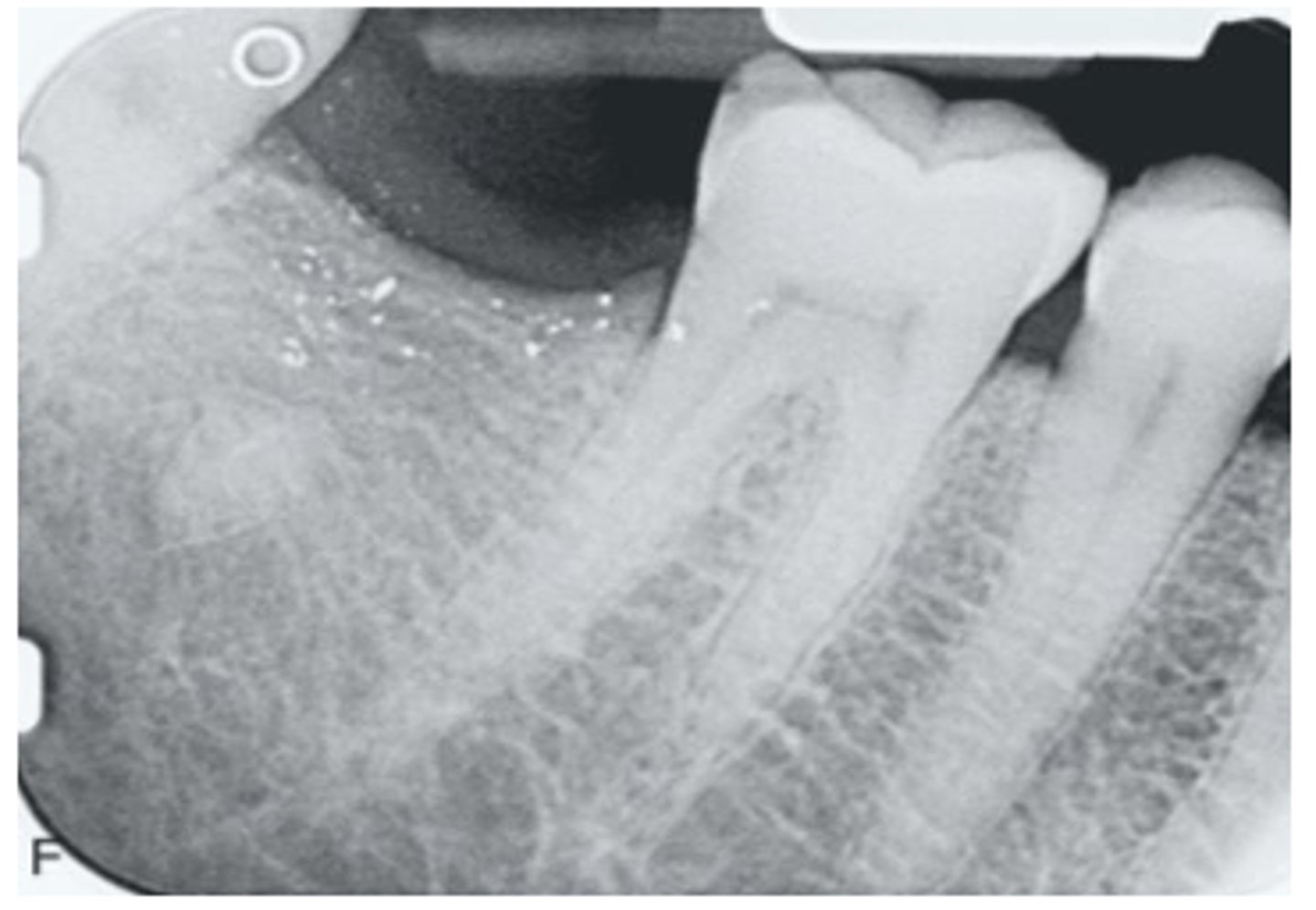
What are these metallic specs?
amalgam tattoos
These are clinical features of what?
- Asymptomatic, localized
- Blue-gray macule
- Localized around areas with amalgam restorations
amalgam tattoos
What is the most common location of amalgam tattoos?
gingiva/alveolar ridge mucosa (50%, then buccal mucosa, then floor of mouth)
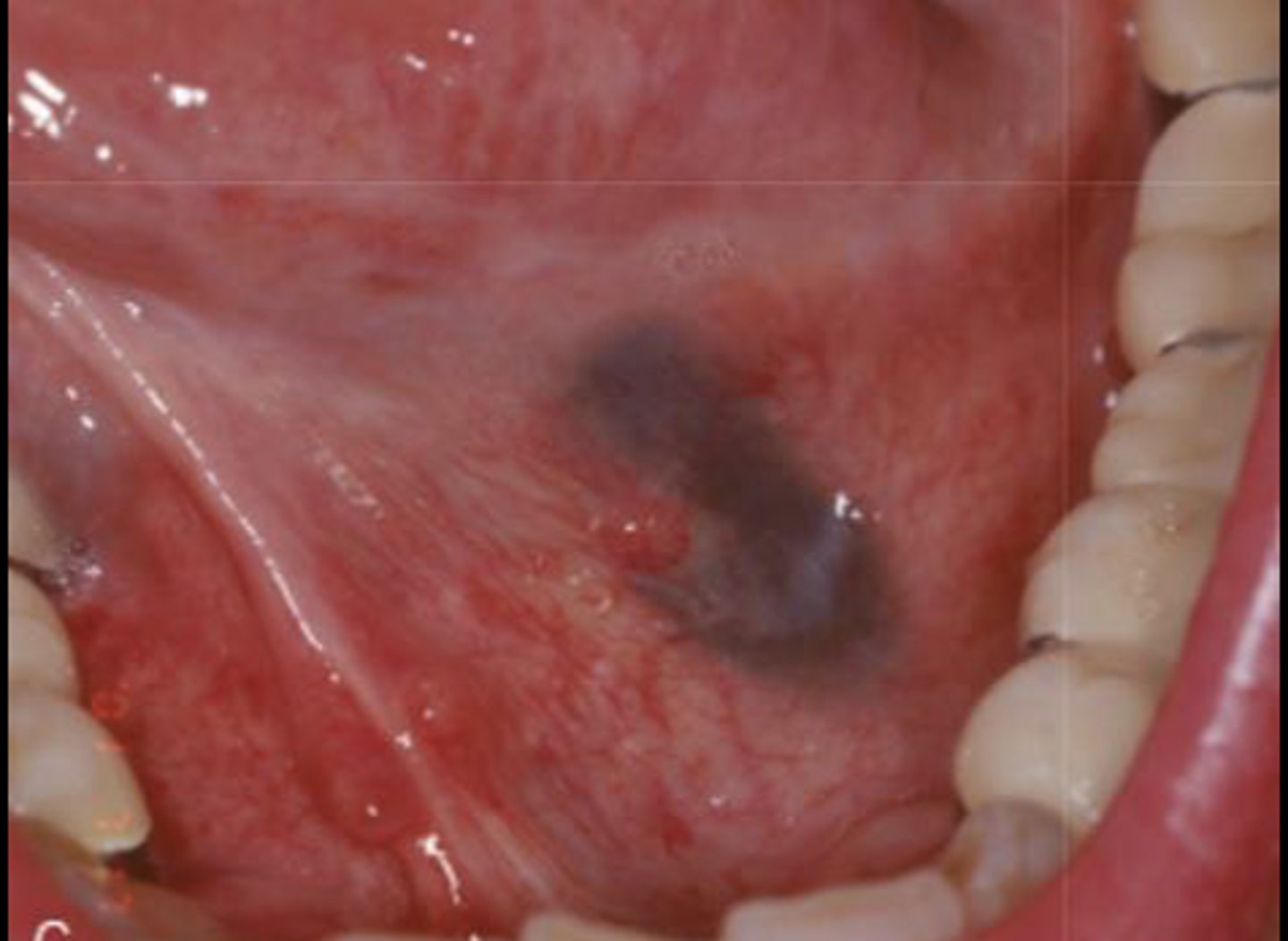
What type of pigmented lesion?
amalgam tattoo
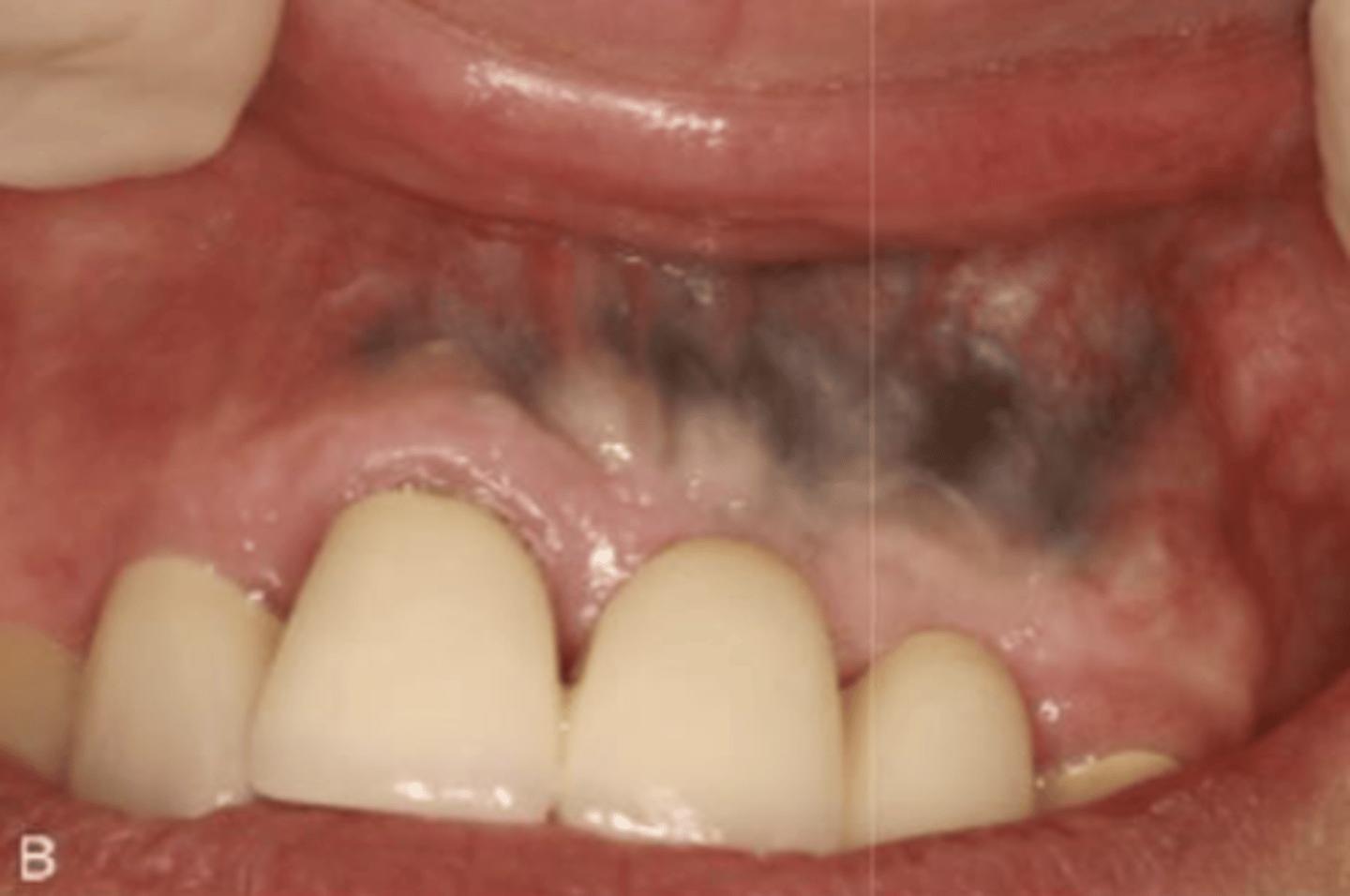
What type of pigmented lesion?
amalgam tattoo
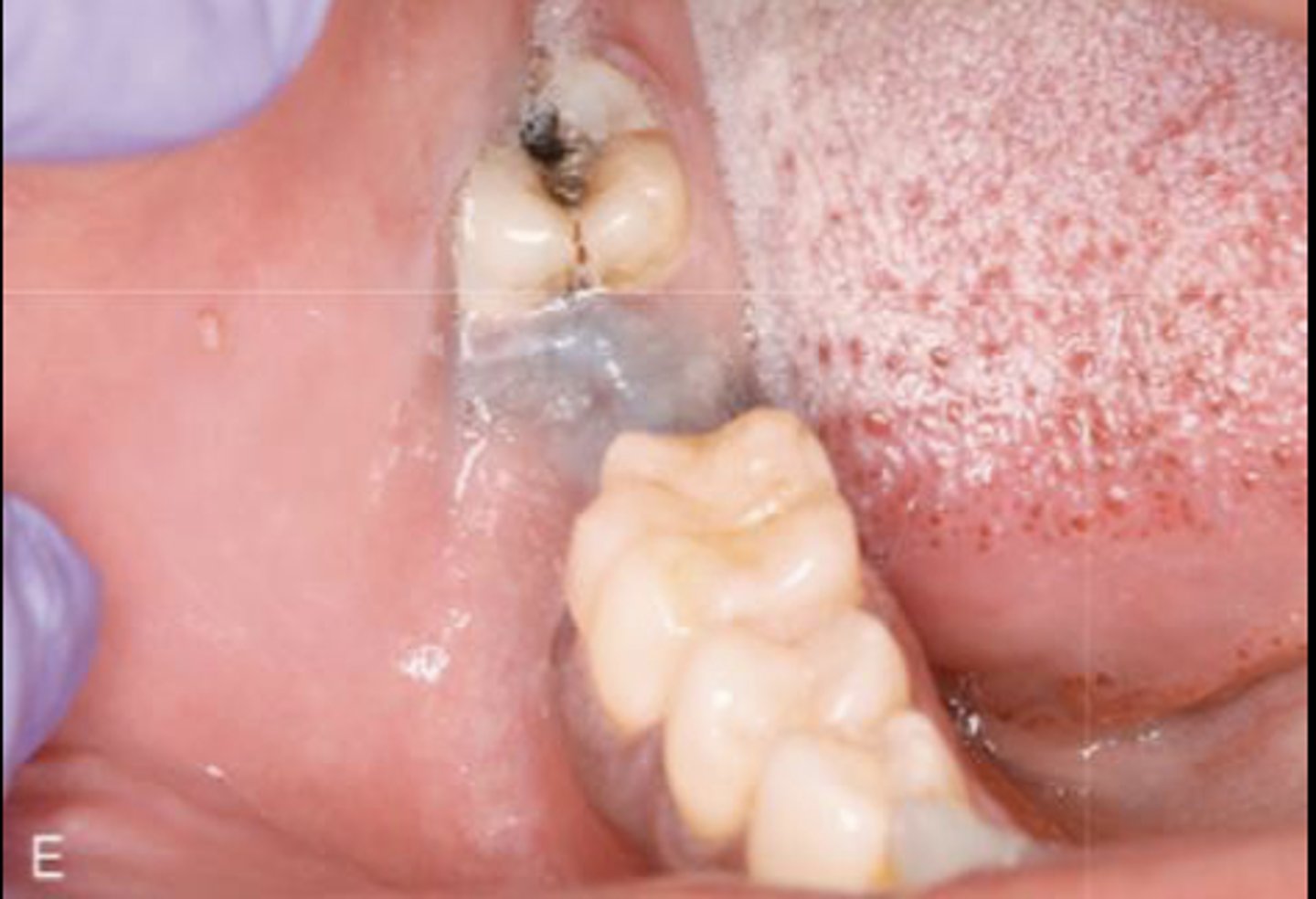
What type of pigmented lesion?
amalgam tattoo
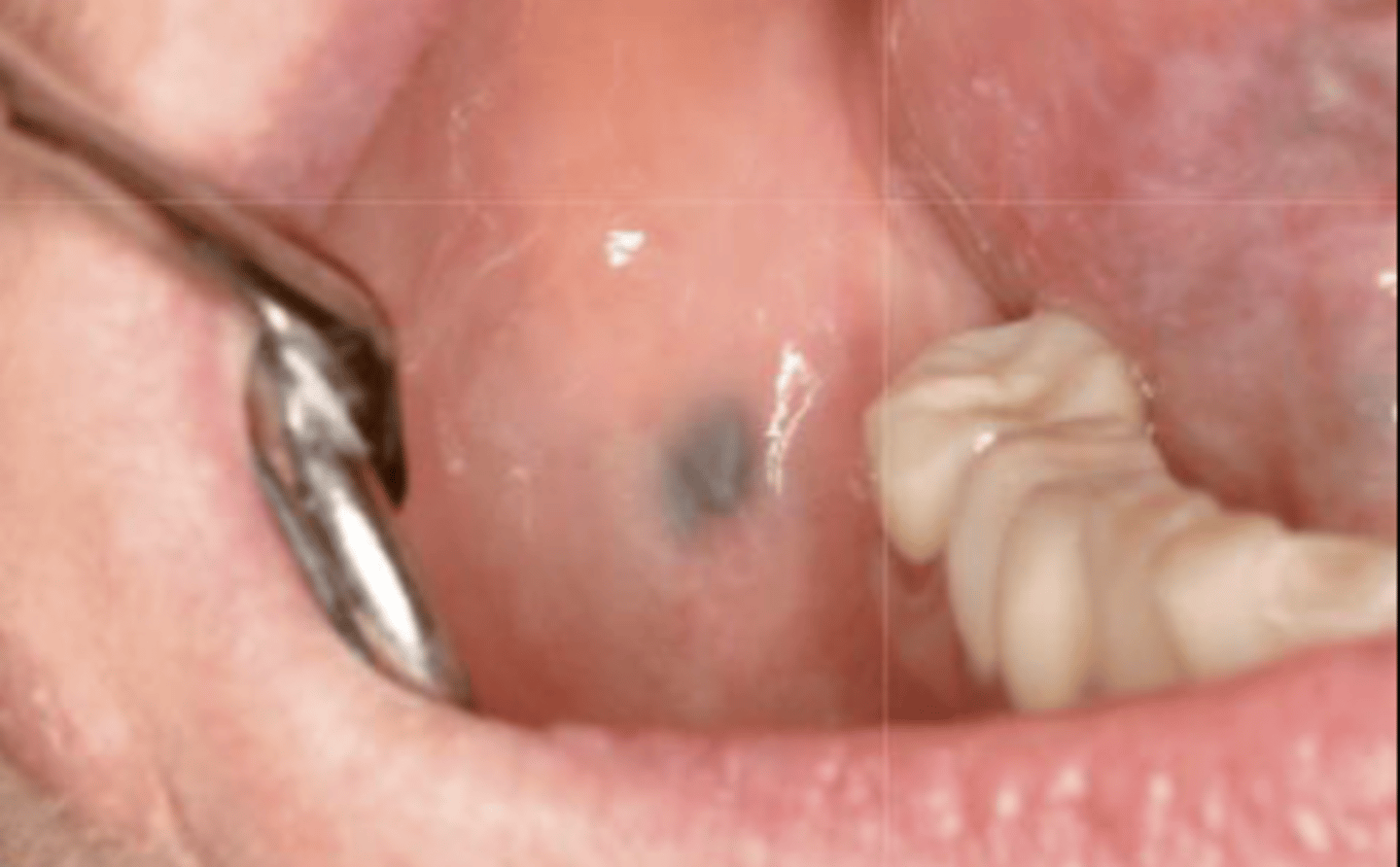
What type of pigmented lesion?
amalgam tattoo
What type of pigmented lesion?
amalgam tattoo
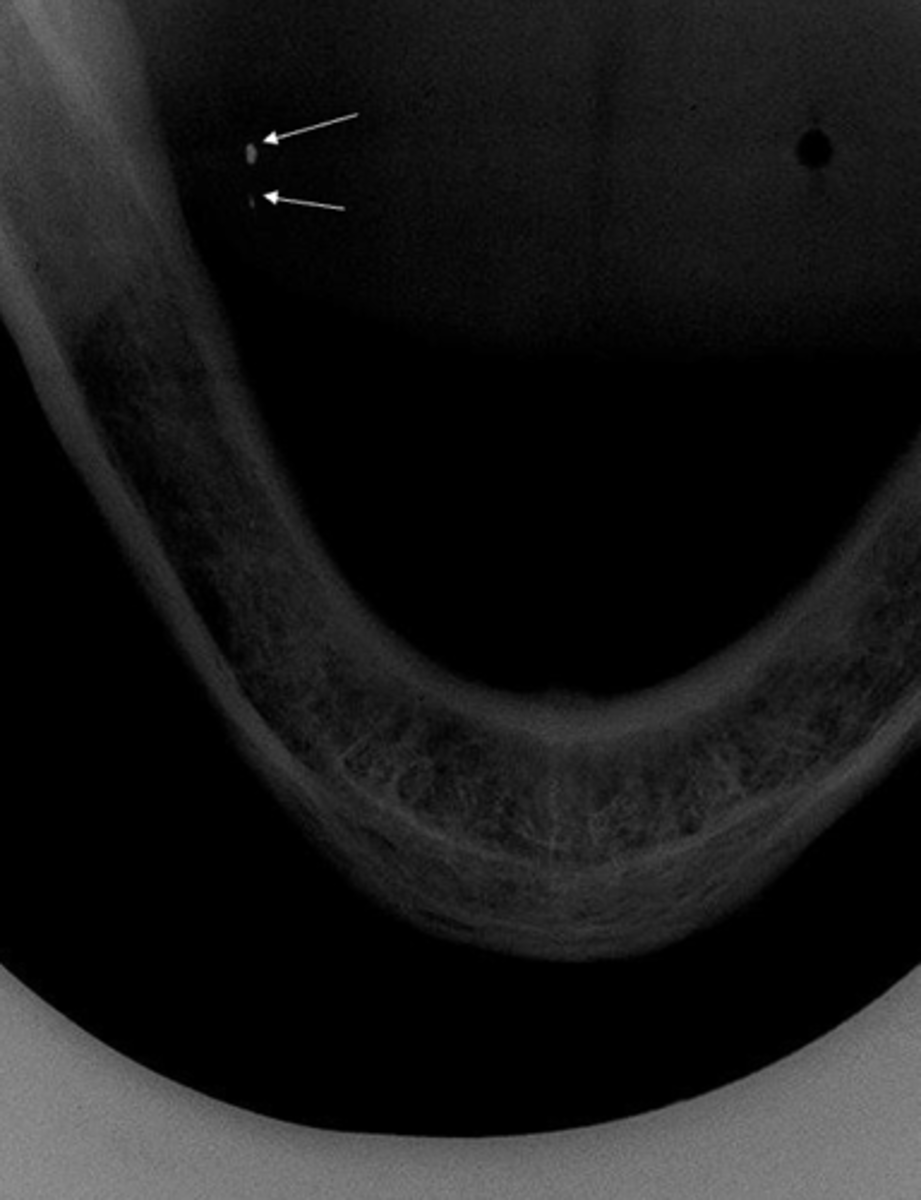
What are the arrows pointing to?
amalgam tattoo

What are the black particles embedded in the purple?
amalgam in scar tissue
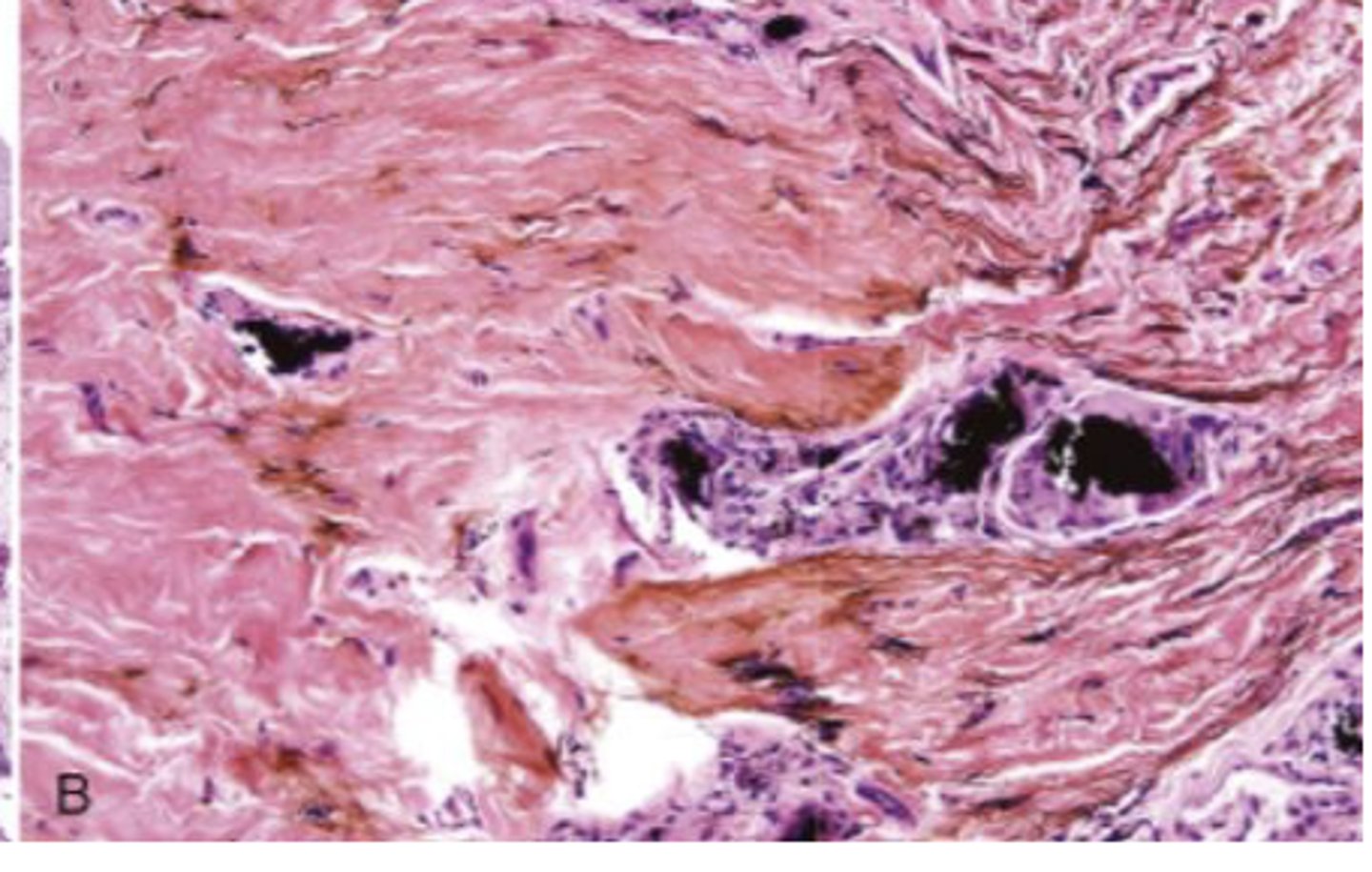
What are the black particles embedded in the purple?
amalgam in scar tissue
These are histopathologic features of what?
- Pigmented fragments
- Staining of reticulin fibers
- Large fragments surrounded by fibrosis
amalgam tattoos
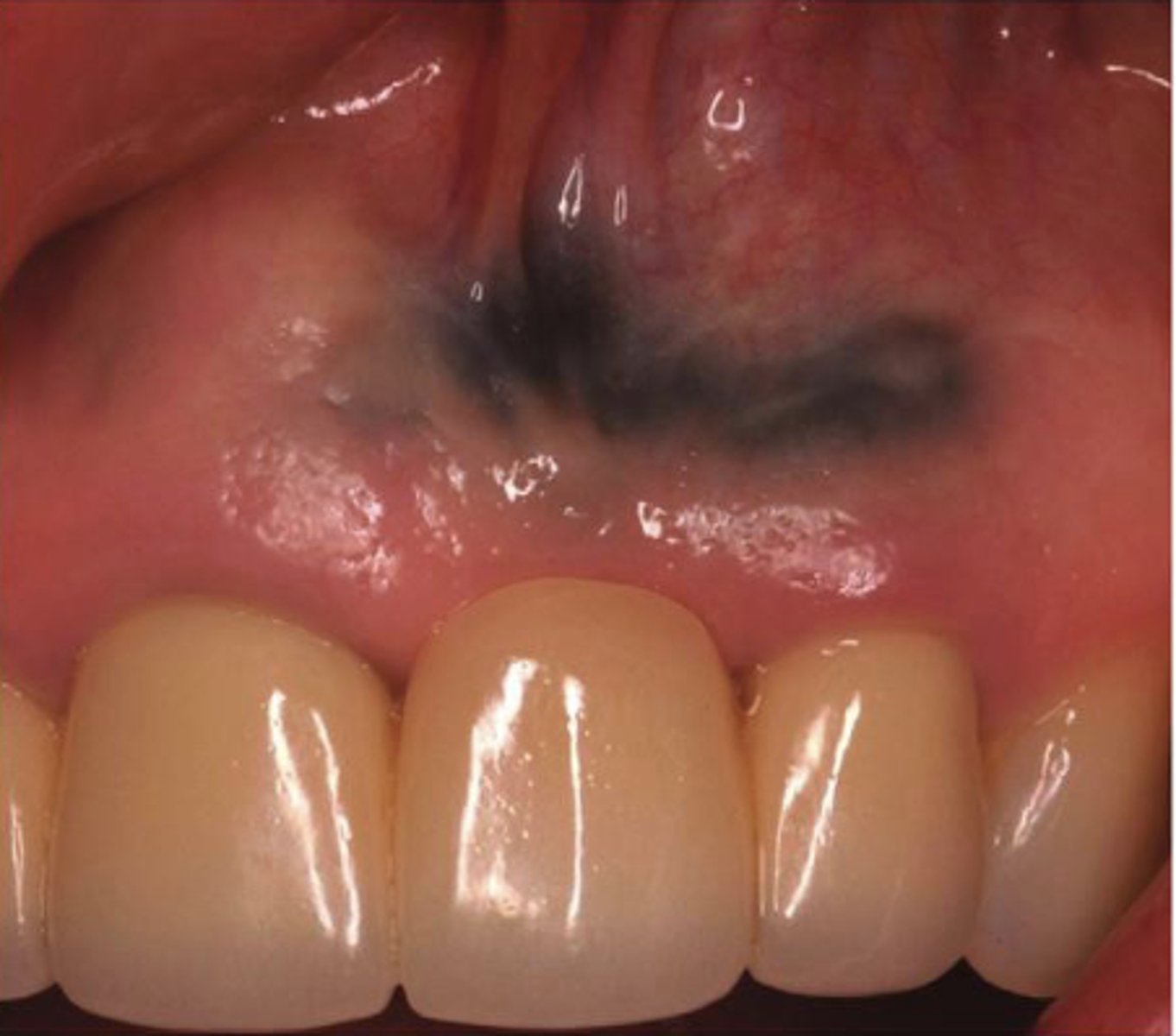
What type of pigmented lesion?
amalgam tattoo
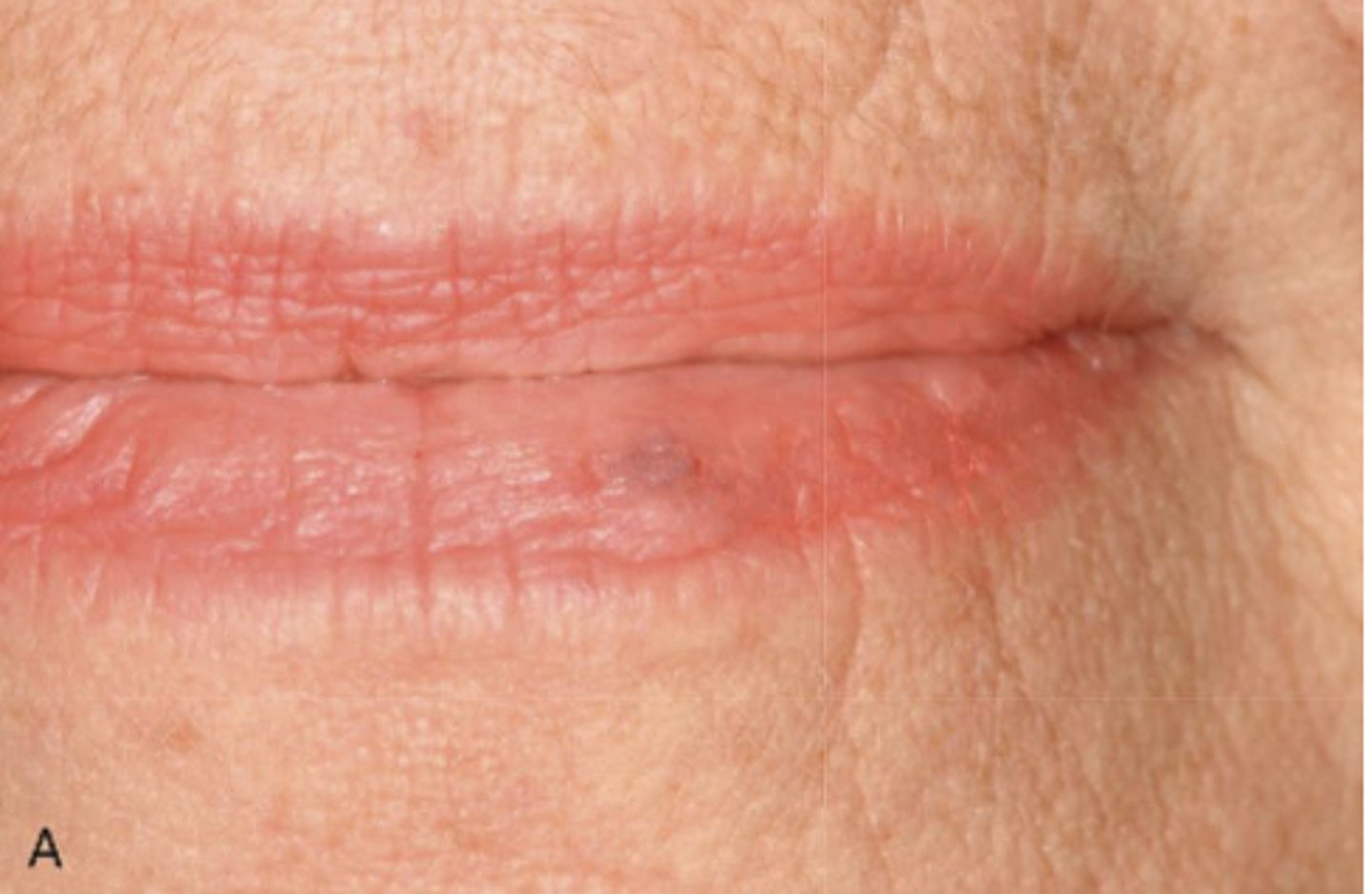
What type of pigmented lesion?
graphite (or other foreign body tattoos)
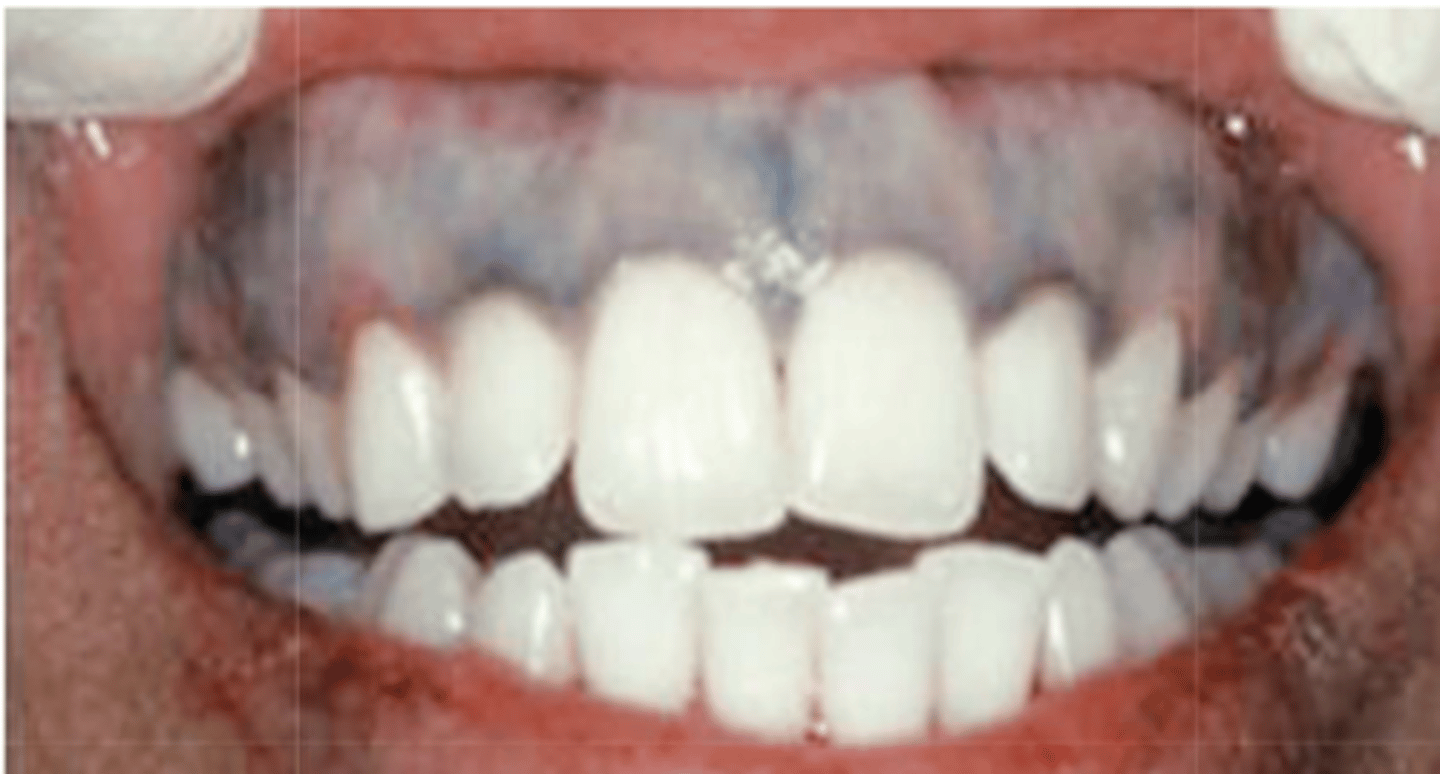
What type of pigmented lesion?
graphite (or other foreign body tattoos)

What type of pigmented lesion?
foreign body tattoo
These are etiopathologies of what pigmented lesion?
- Accumulation of melanin
- Increase in melanin production
- Decrease in melanin clearance
- Accumulation of medication
- Synthesis of special pigments (I.e. Lipofuscin)
- Deposition of iron
medication induced pigmentation
These are clinical features of what pigmented lesion?
- Diffuse, painless, symmetric bluish-gray macule
- Melanonychia and skin lesions
medication-induced pigmentation
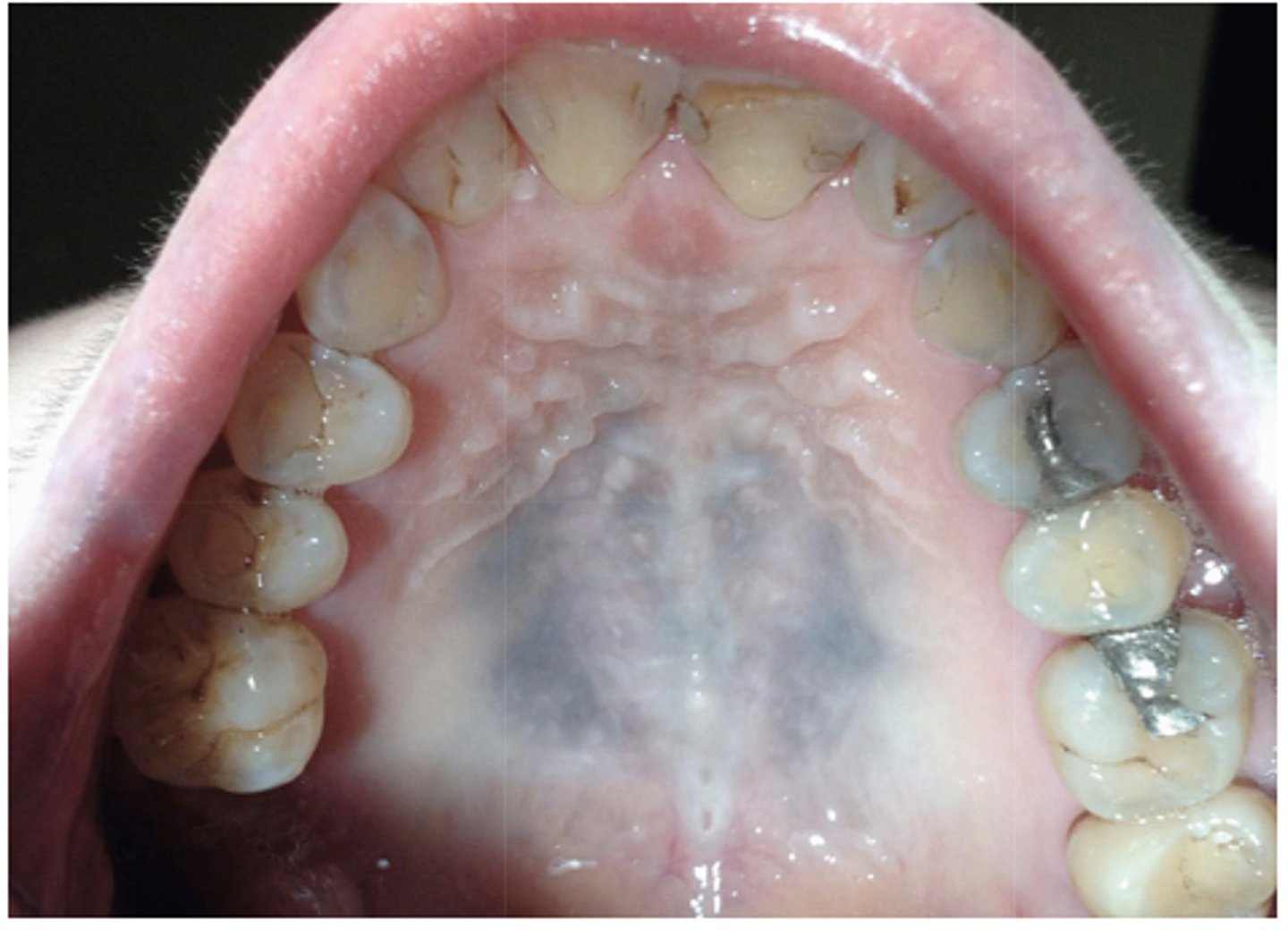
What type of pigmented lesion?
medication-induced pigmentation (typically palatal mucosa)
What medication has the following proposed source of pigmentation?
Hyperproduction of melanin, complex with iron,
or stained bone
Minocycline
What medications have the following proposed source of pigmentation?
Hyperproduction of melanin
- Antimalarials
- Hormones
What medication has the following proposed source of pigmentation?
Chelated metabolites of medication
Clofazamine
What medication has the following proposed source of pigmentation?
Medication/metabolites and/or accumulation of melanin
Tranquilizers
What medication has the following proposed source of pigmentation?
Granules of the metal distributed throughout blood vessels
Heavy metals
What medication has the following proposed source of pigmentation?
Increased production of lipofuscin
Amidorone
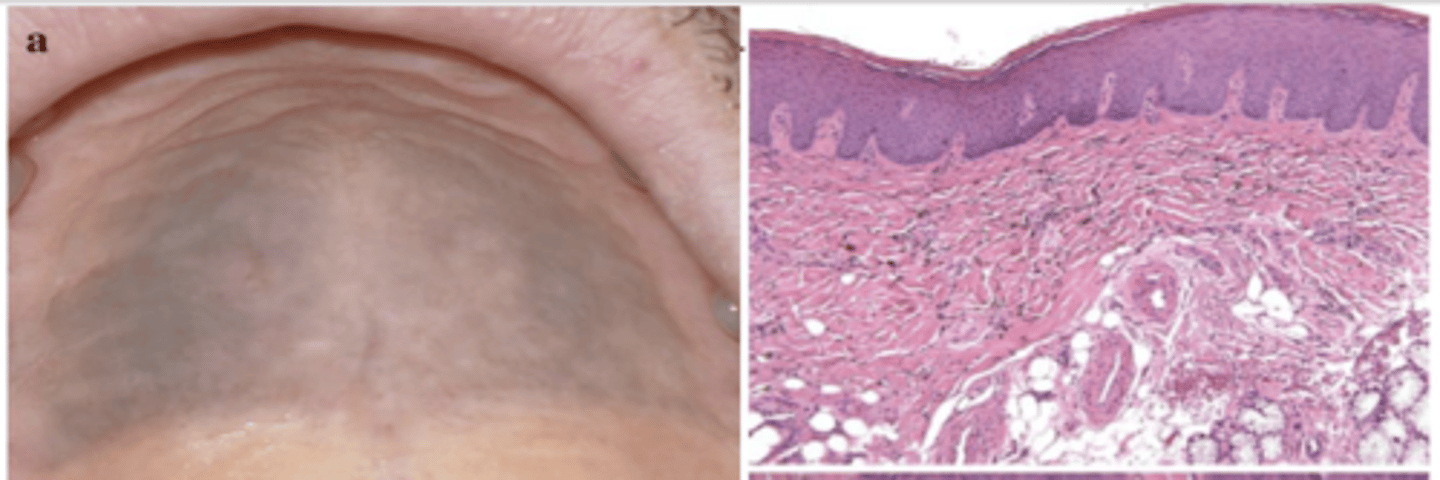
What type of pigmented lesion?
medication-induced (Imatinib-induced hyperpigmentation)
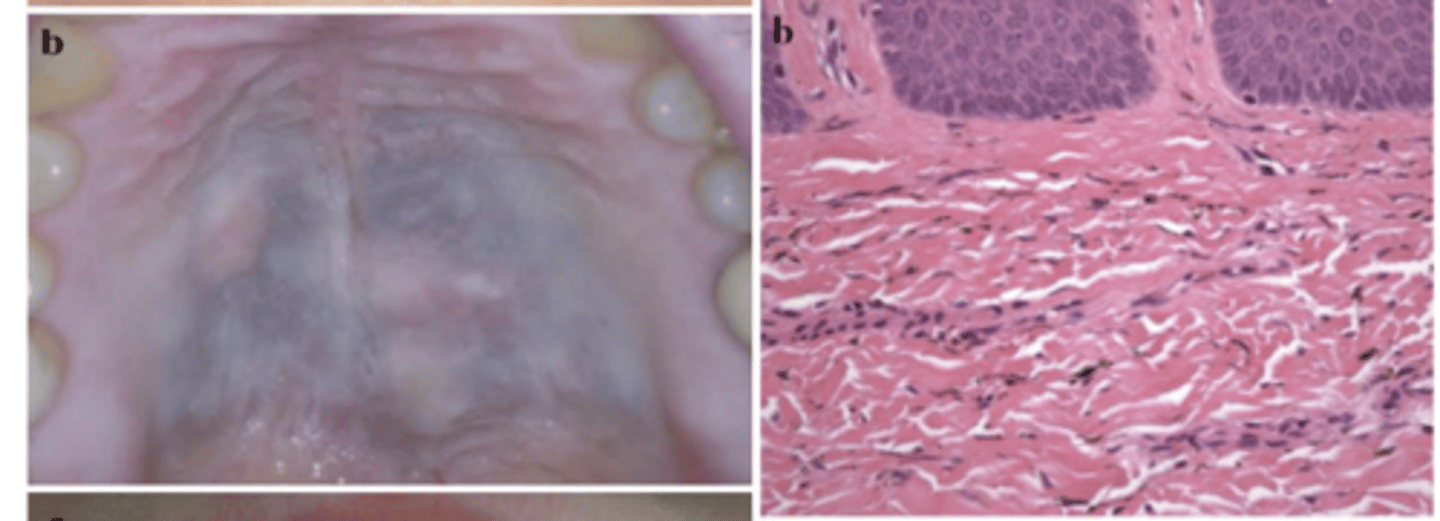
What type of pigmented lesion?
medication-induced (Imatinib-induced hyperpigmentation)
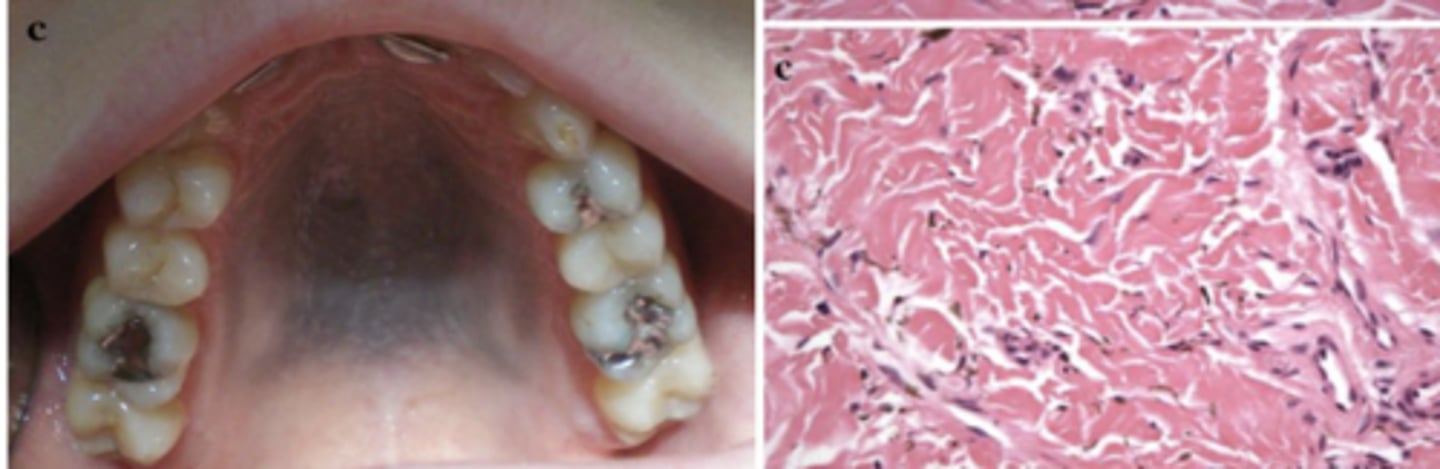
What type of pigmented lesion?
medication-induced (Imatinib-induced hyperpigmentation)
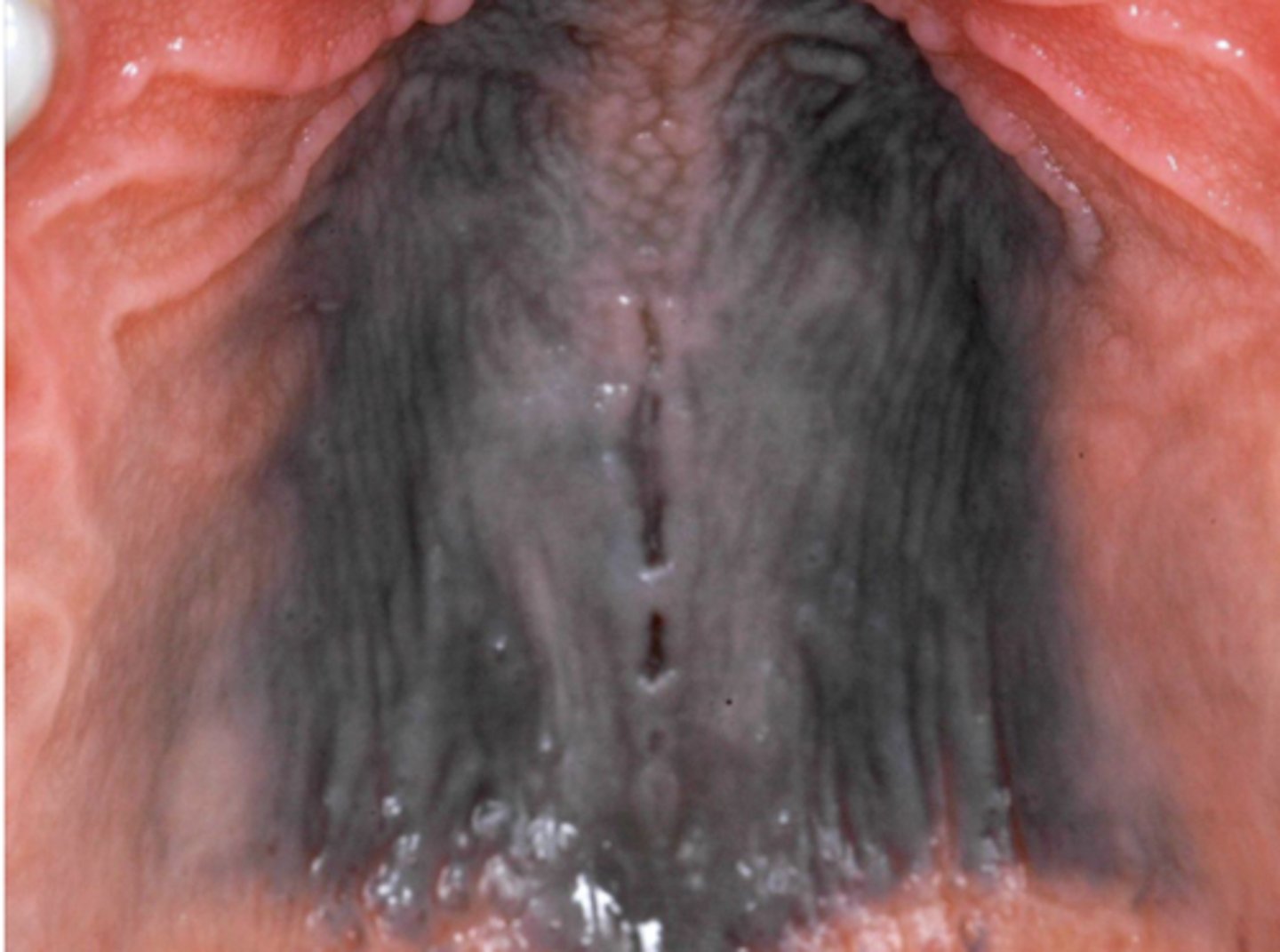
What type of pigmented lesion?
medication-induced
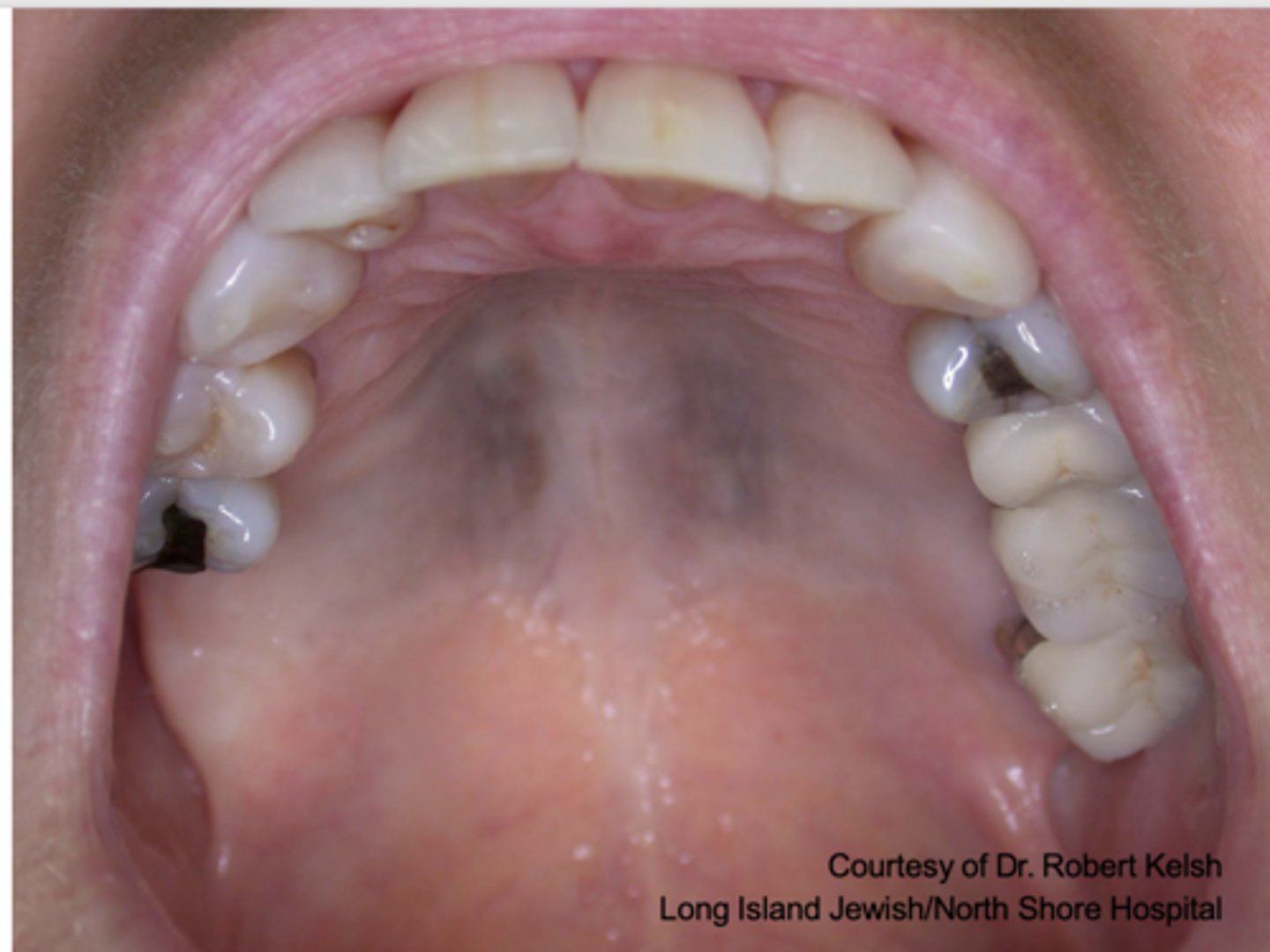
What type of pigmented lesion?
medication-induced

What type of pigmented lesion?
medication-induced
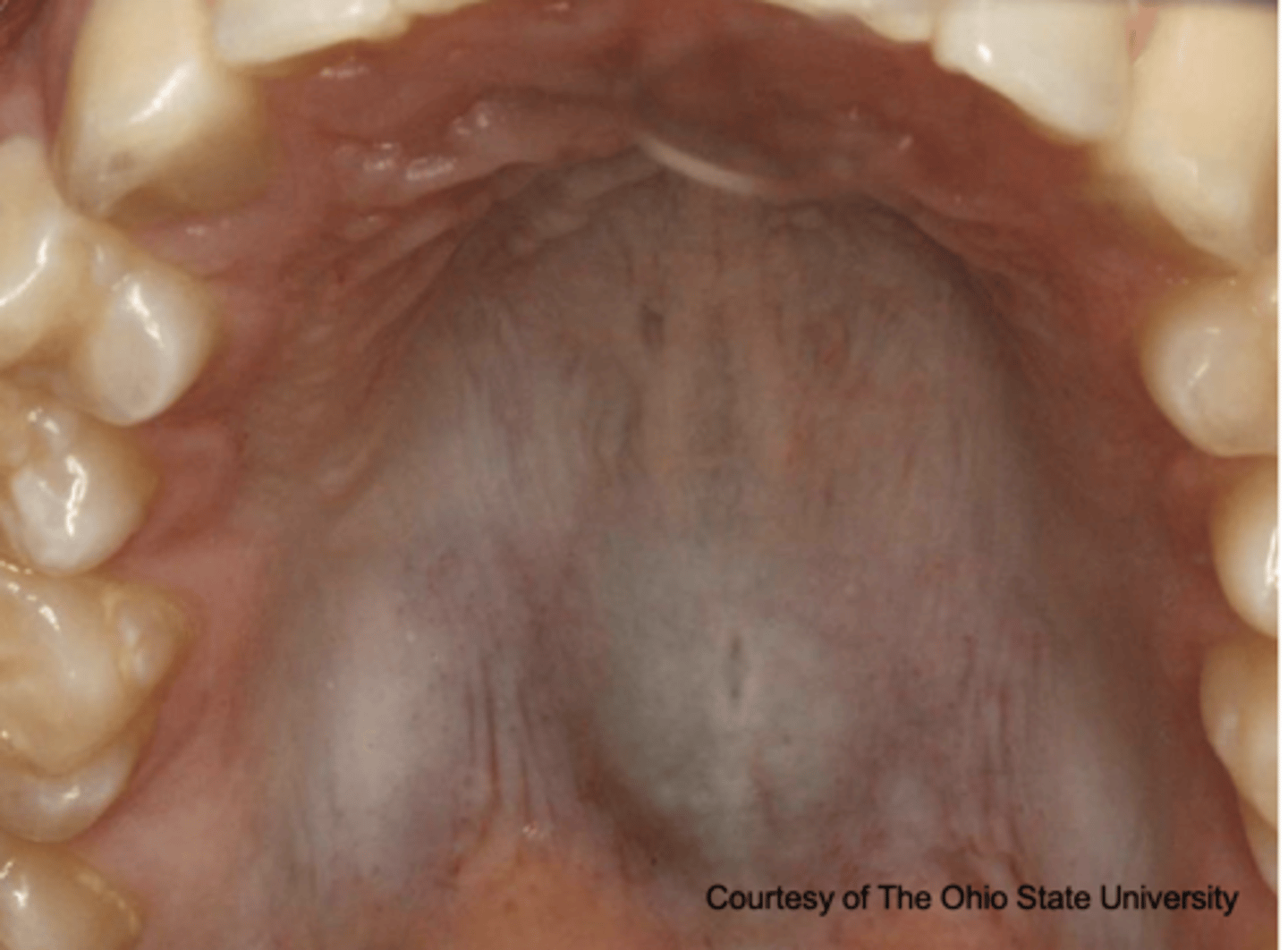
What type of pigmented lesion?
medication-induced
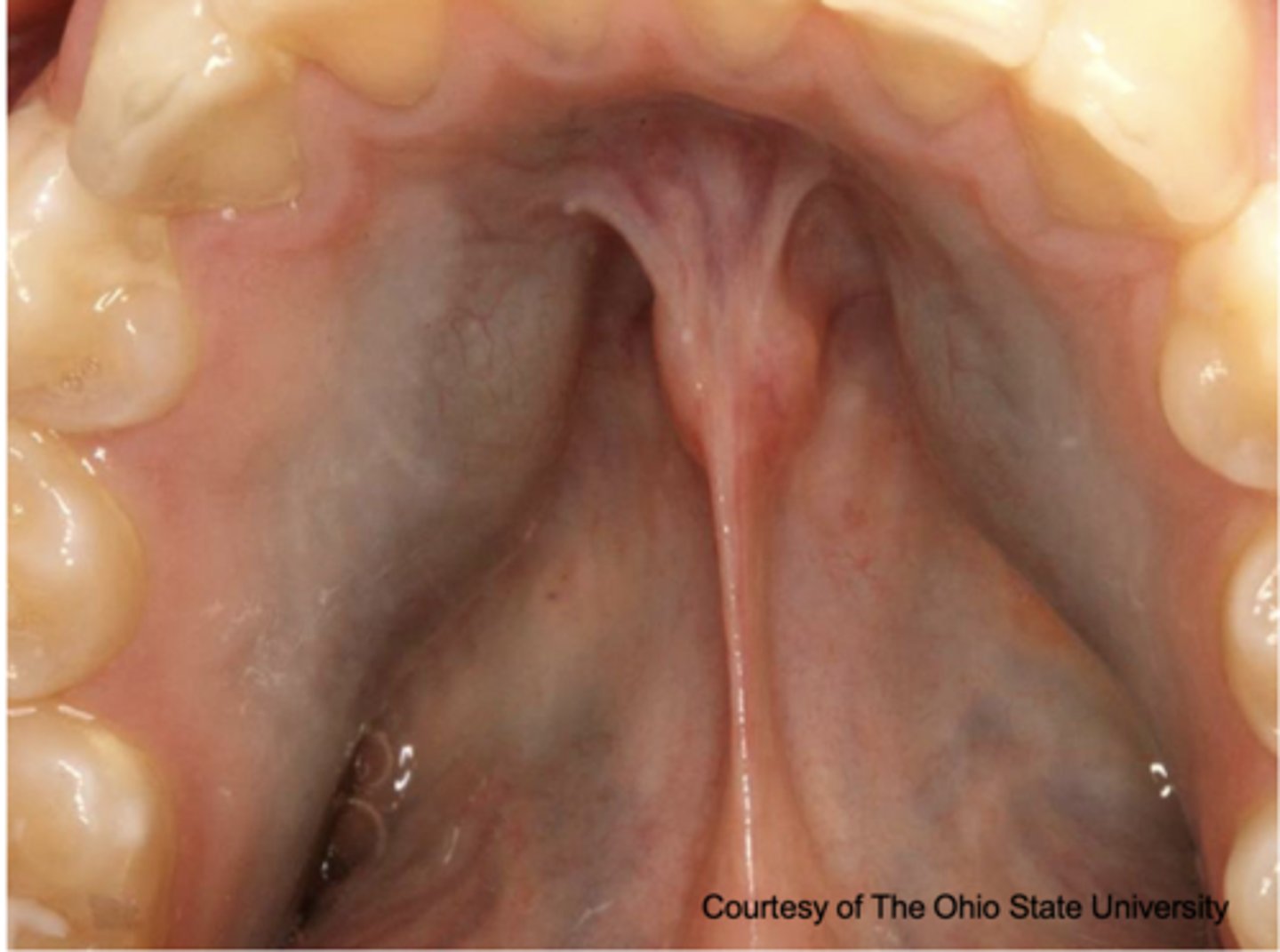
What type of pigmented lesion?
medication-induced
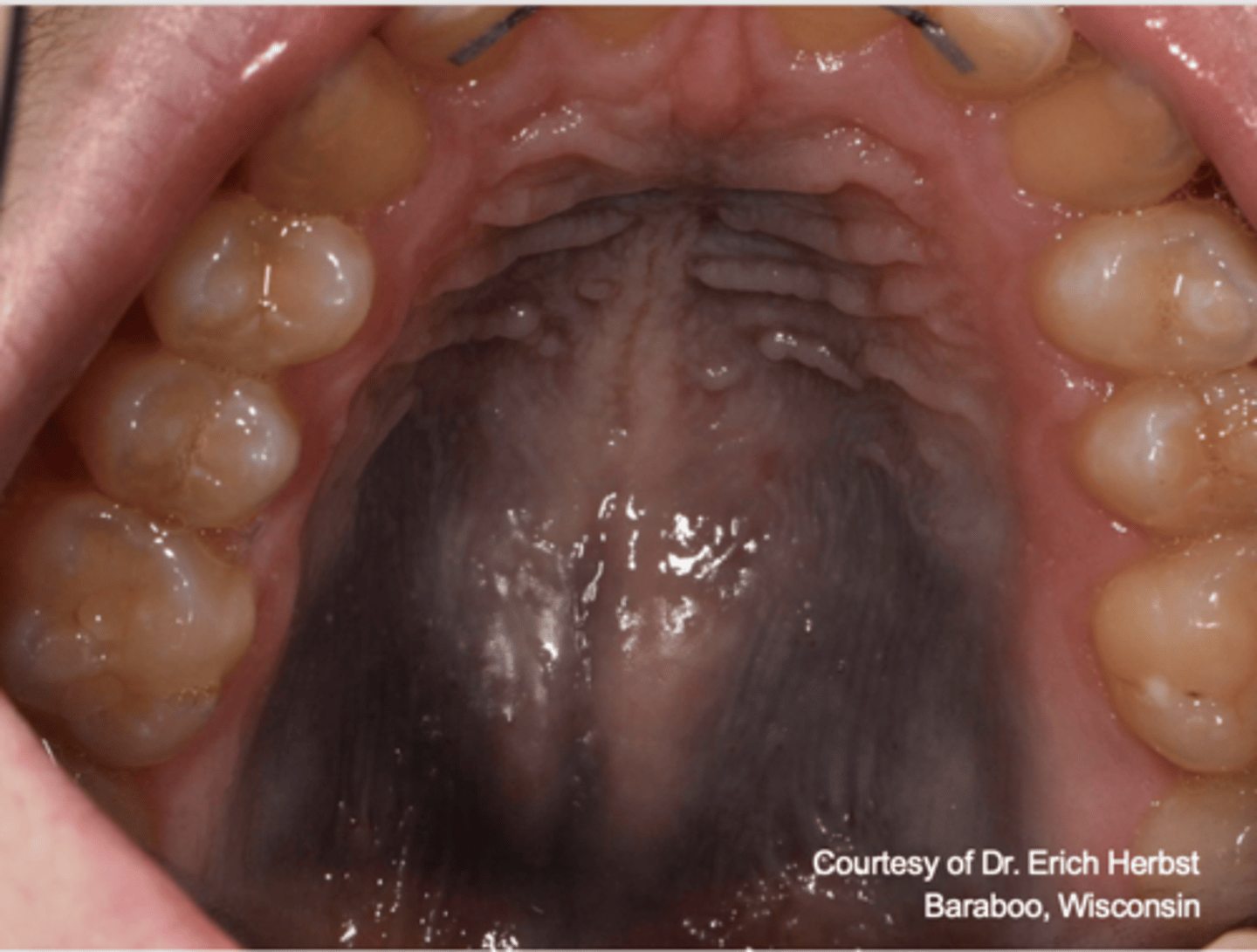
What type of pigmented lesion?
medication-induced
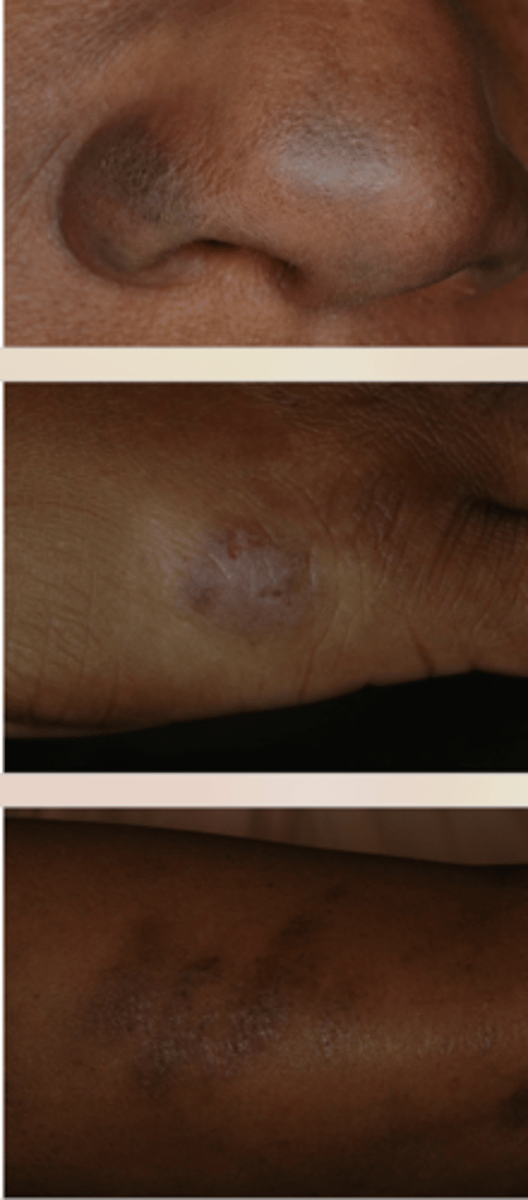
Skin hyperpigmentation can be caused by what?
medication
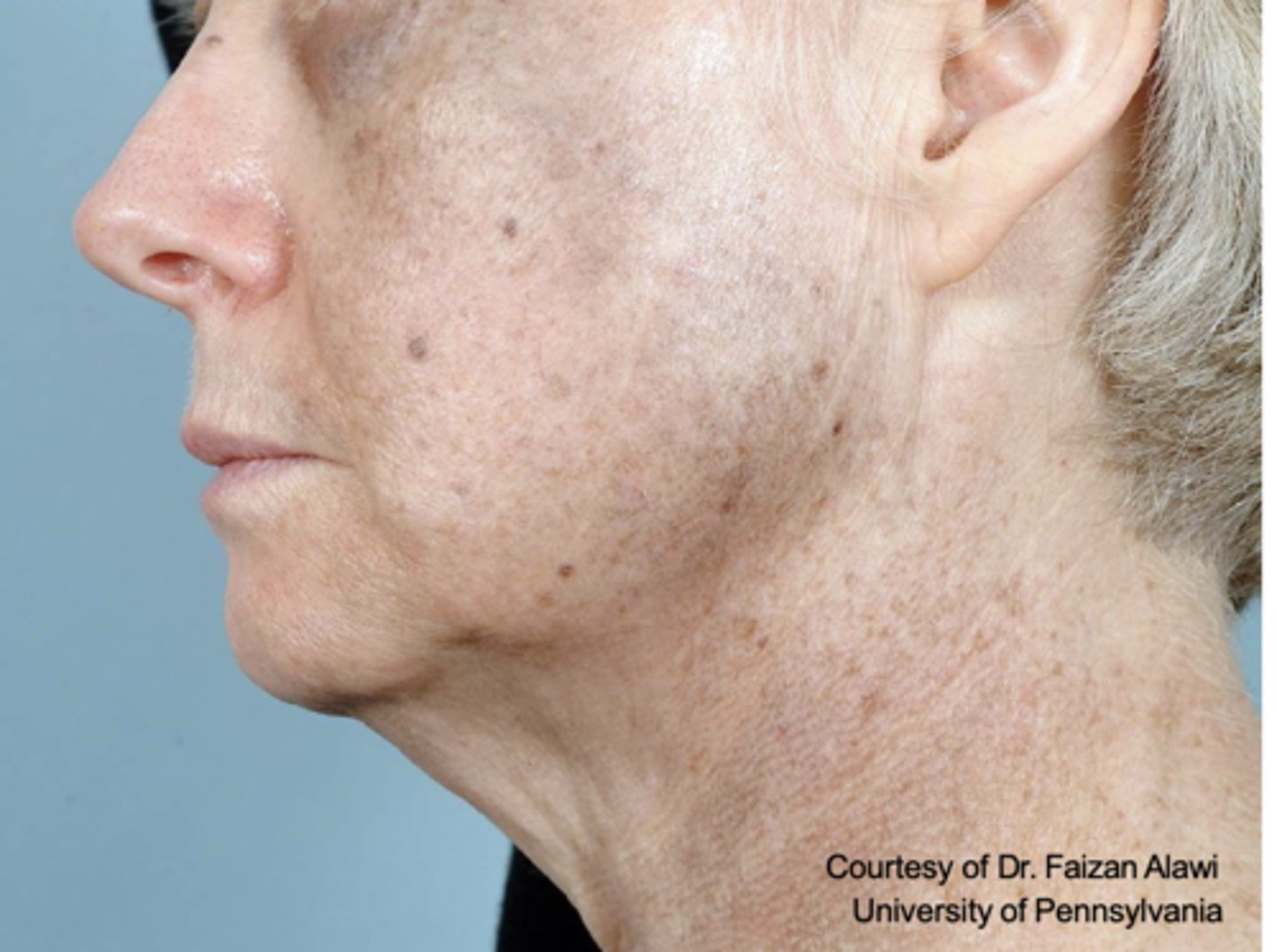
Skin hyperpigmentation can be caused by what?
medication
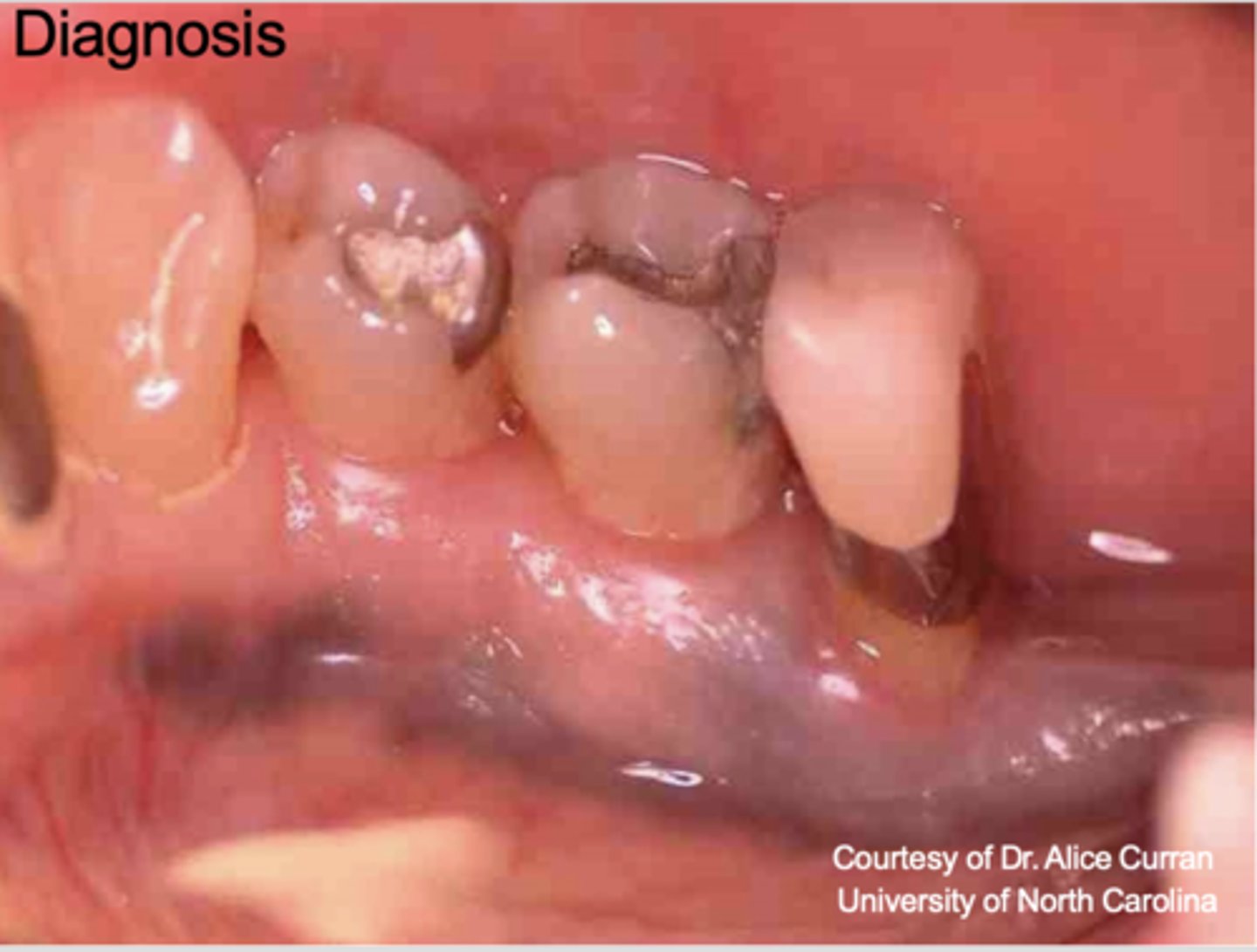
What type of pigmented lesion?
Amalgam tattoo
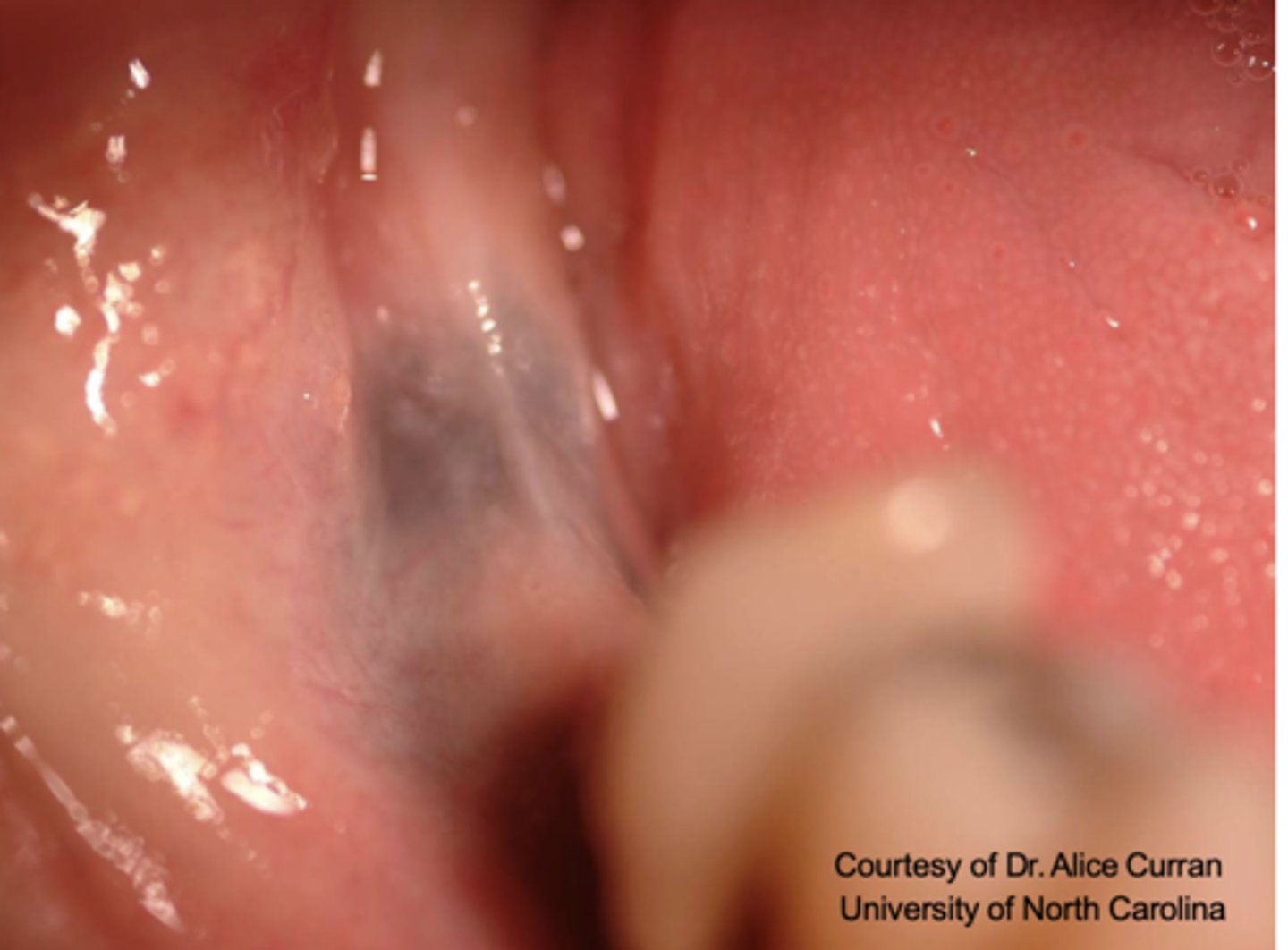
What type of pigmented lesion?
Amalgam tattoo
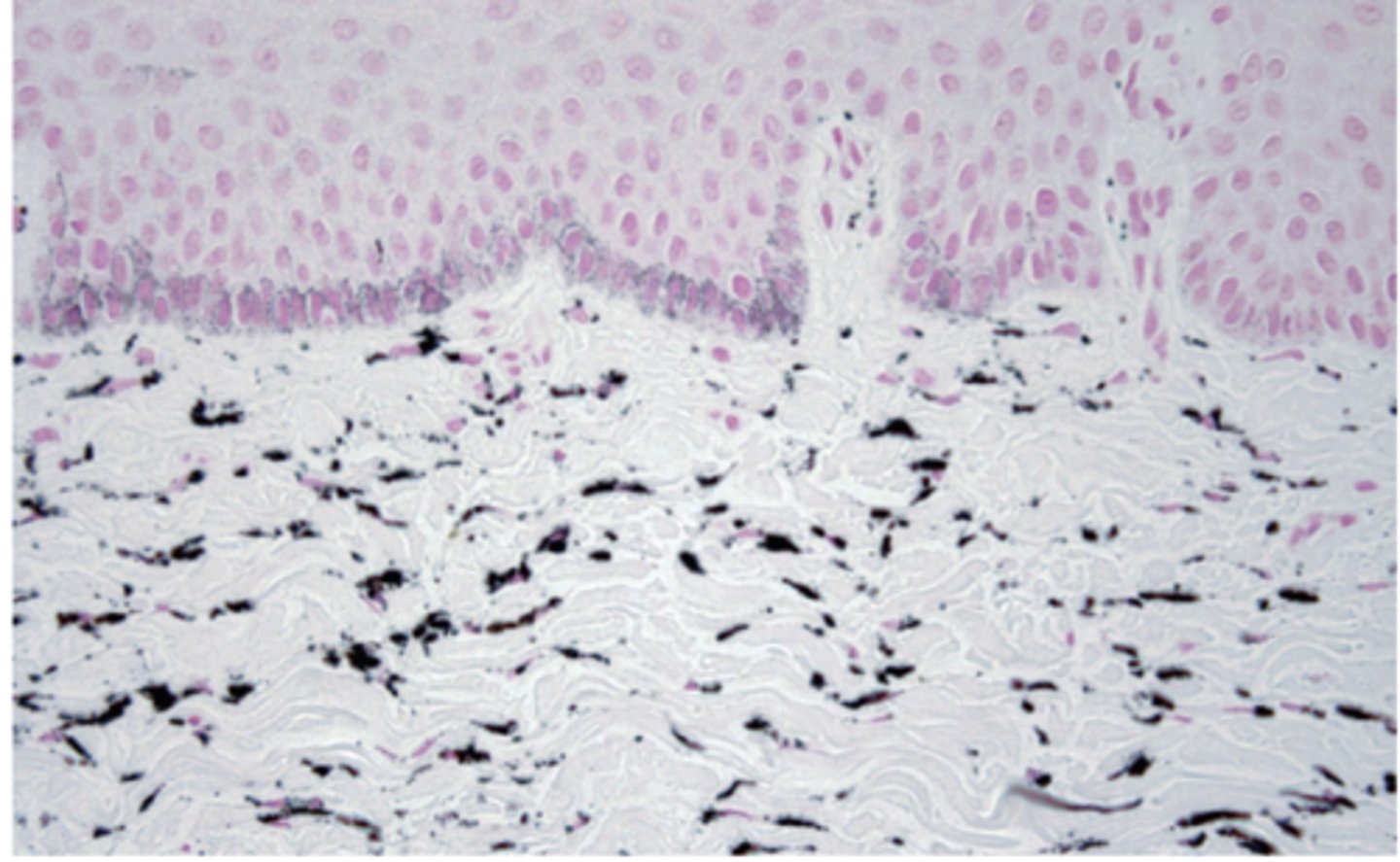
What type of pigmentation has lots of pigmentation in collagen fibers and has melanocytes in basal cells?
medication-induced
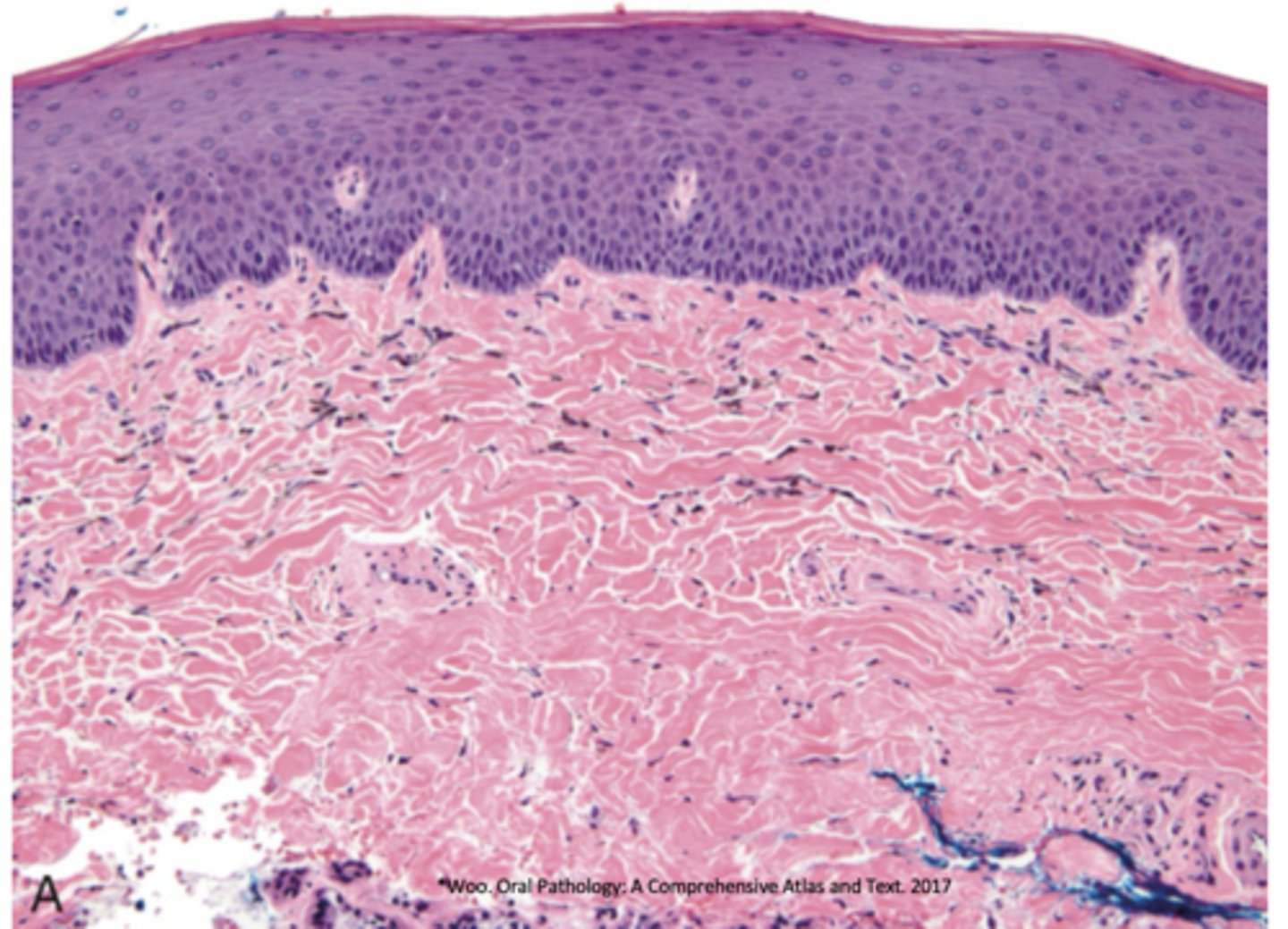
What type of pigmentation has lots of pigmentation in collagen fibers and has melanocytes in basal cells?
medication-induced
The most common medications to cause drug-induced gingival pigmentation include all except:
A. Minocycline
B. Chloroquine
C. Cyclophosphamide
D. Corticosteroids
E. Azidothymidine
D. Corticosteroids (used to treat hyperpigmentation)
These types of metals can cause _________ toxicity
- Lead
- Mercury
- Silver
- Bismuth
- Gold
Heavy metal
What can cause the following?
- Pigmentation of marginal gingiva
- Tongue tremor
- Metallic taste
- Excessive salivation
- Trichotillomania
- Bruxism
heavy metal toxicity

What type of pigmentation?
heavy metal toxicity (Burton line)
The burton line is a line that can show up along the gingival line that is associated with what ?
heavy metal toxicities

What can cause a coated tongue?
- Tea
- Coffee
- Tobacco
- Poor oral hygiene
- Dehydration
What are two types of endogenous (non-melanin associated) pigmented lesions?
- Hemosiderin
- Bilirubin

What type of deposit is shown on this histology?
hemosiderin
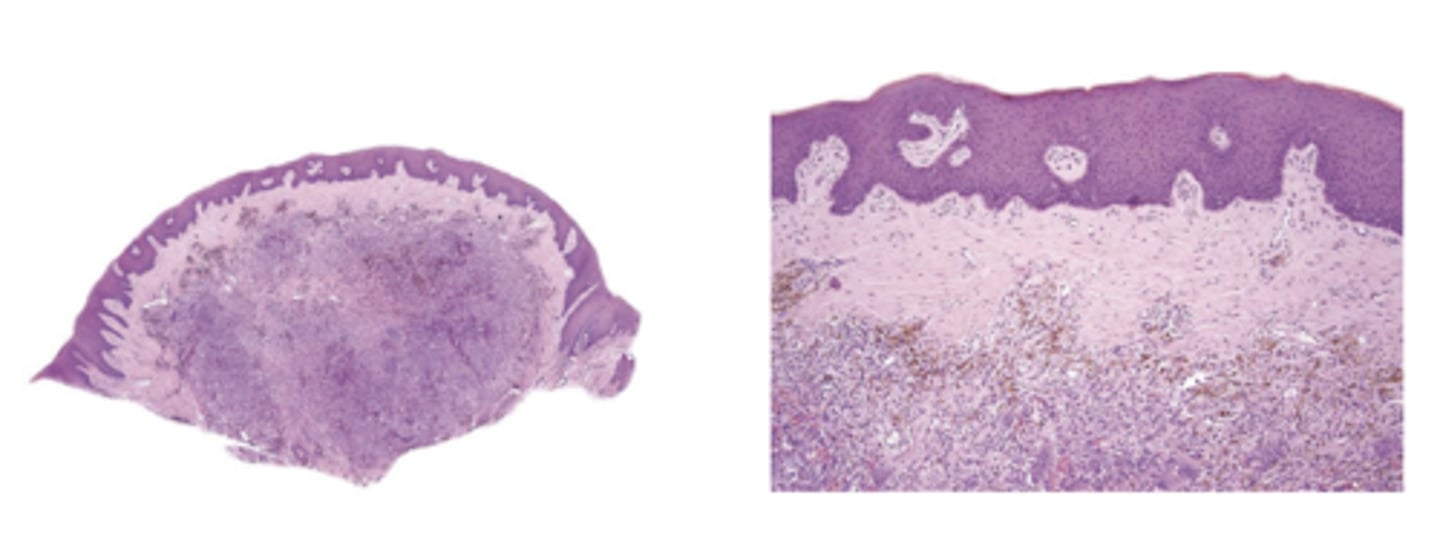
What type of deposit is shown on this histology?
hemosiderin (giant cells)

What type of deposit is shown on this histology?
bilirubin
What cells do melanocytes develop from?
neural crest cells
What are pluripotent cells (melanocytes, neurons and glial cells, adrenal medulla, cardiac cells and craniofacial tissue)?
neural crest cells
What gene is essential for lineage survival, proliferation or to prevent trans- differentiation towards other neural- crest lineages (such as glia and neurons)?
MITF
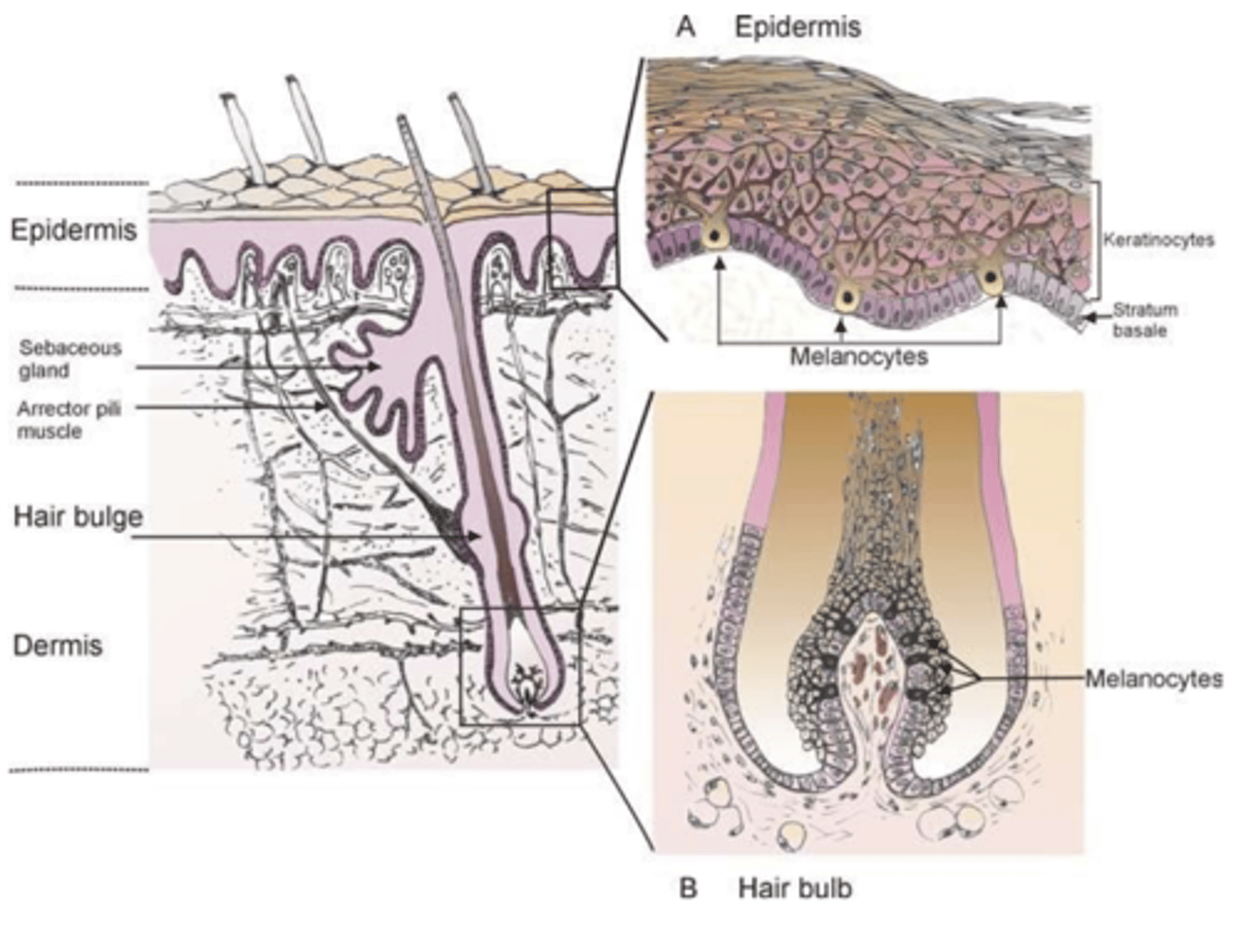
Which layer of the epithelium are melanocytes housed in?
basal layer
Do people of color have more oral mucosa pigmentation?
Yes
Where is the most common location of melanin-associated pigmented lesions?
gingiva
Where is the second most common location of melanin-associated pigmented lesions?
hard palate
Where is the third most common location of melanin-associated pigmented lesions?
buccal mucosa
What is the clinical term for freckles?
Ephelides
When do freckles typically appear?
first decade
Do ephelides (freckles) have male or female predilection?
female
These are clinical features of what?
- Sharply demarcated, uniformly light brown, round-to-oval macule (< 3mm)
- Sun-exposure
ephelides (freckles)

What type of pigmented lesion?
ephelides (freckles)
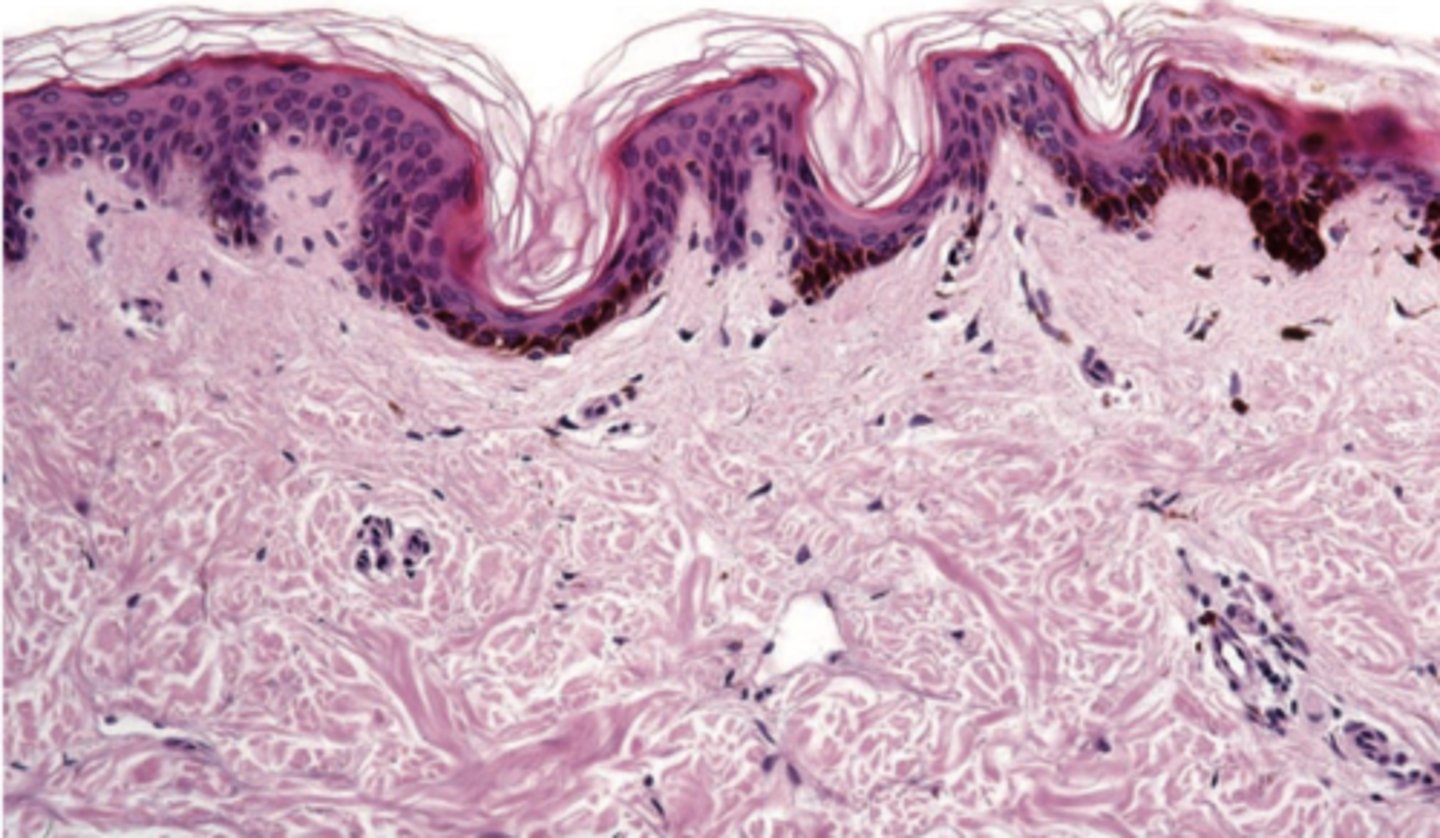
This is histology for what?
ephelides (freckles)
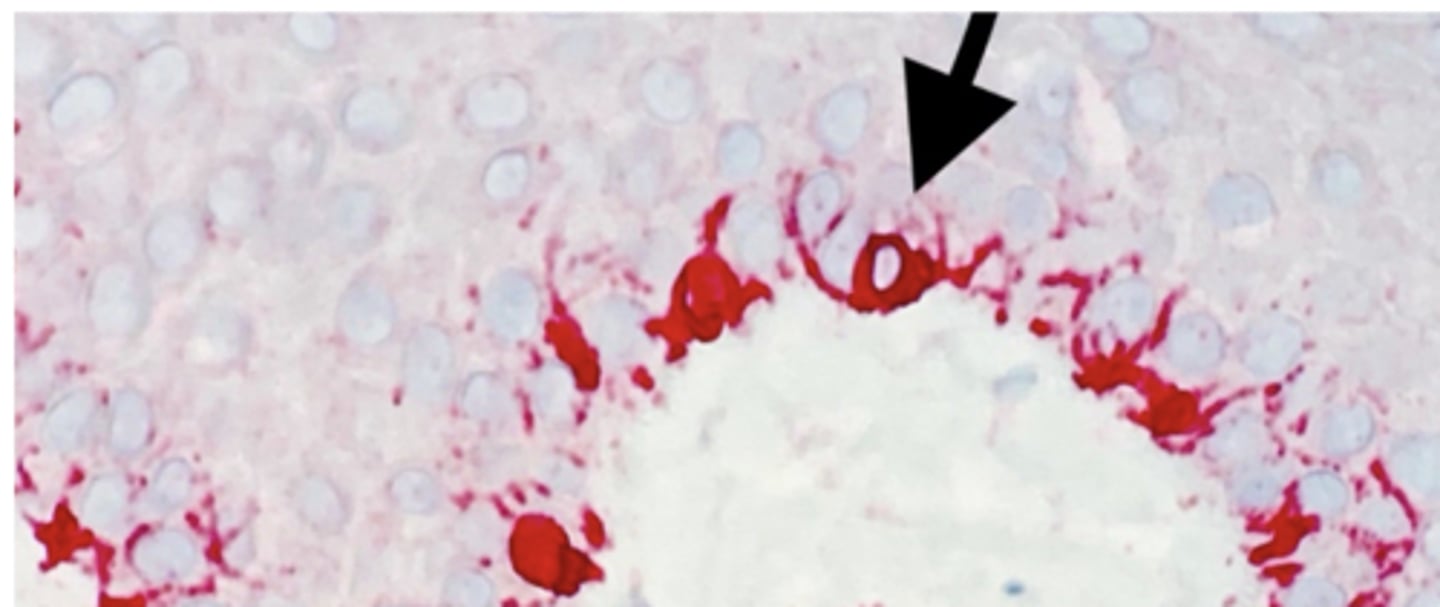
What is the arrow pointing to?
Melanocyte
What layer are melanocytes in?
basal layer
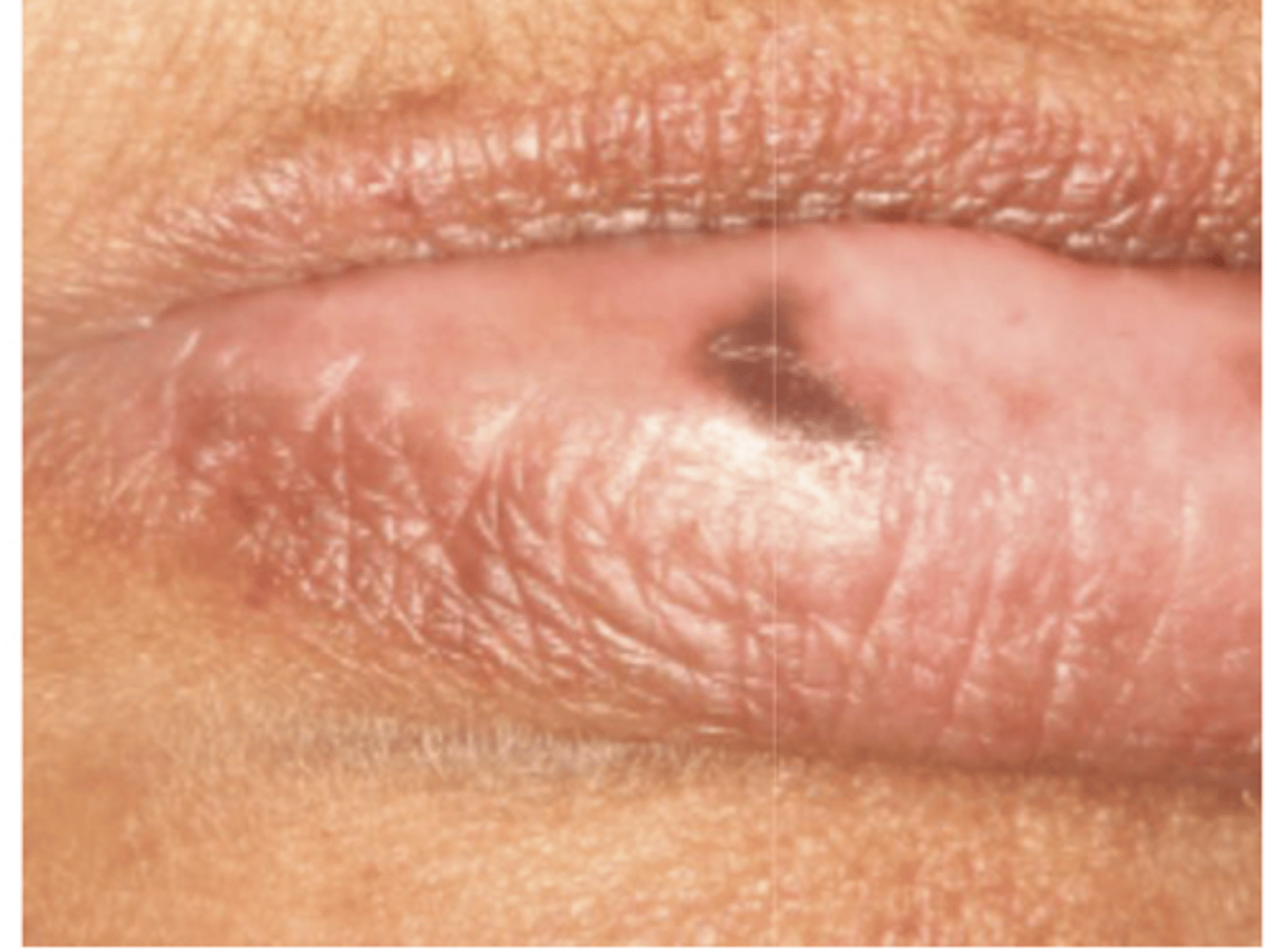
What type of pigmented lesion?
melanotic macule
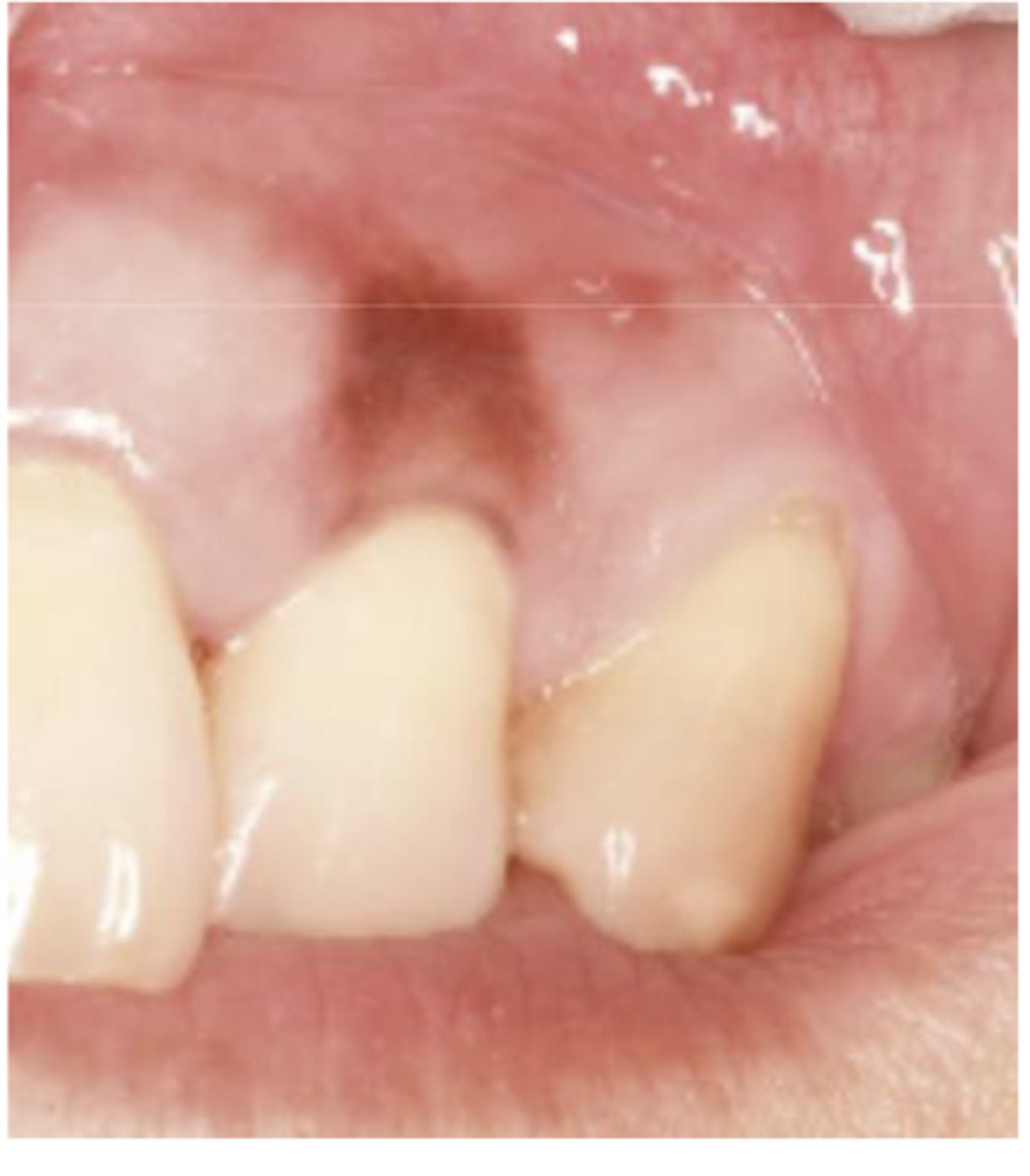
What type of pigmented lesion?
melanotic macule
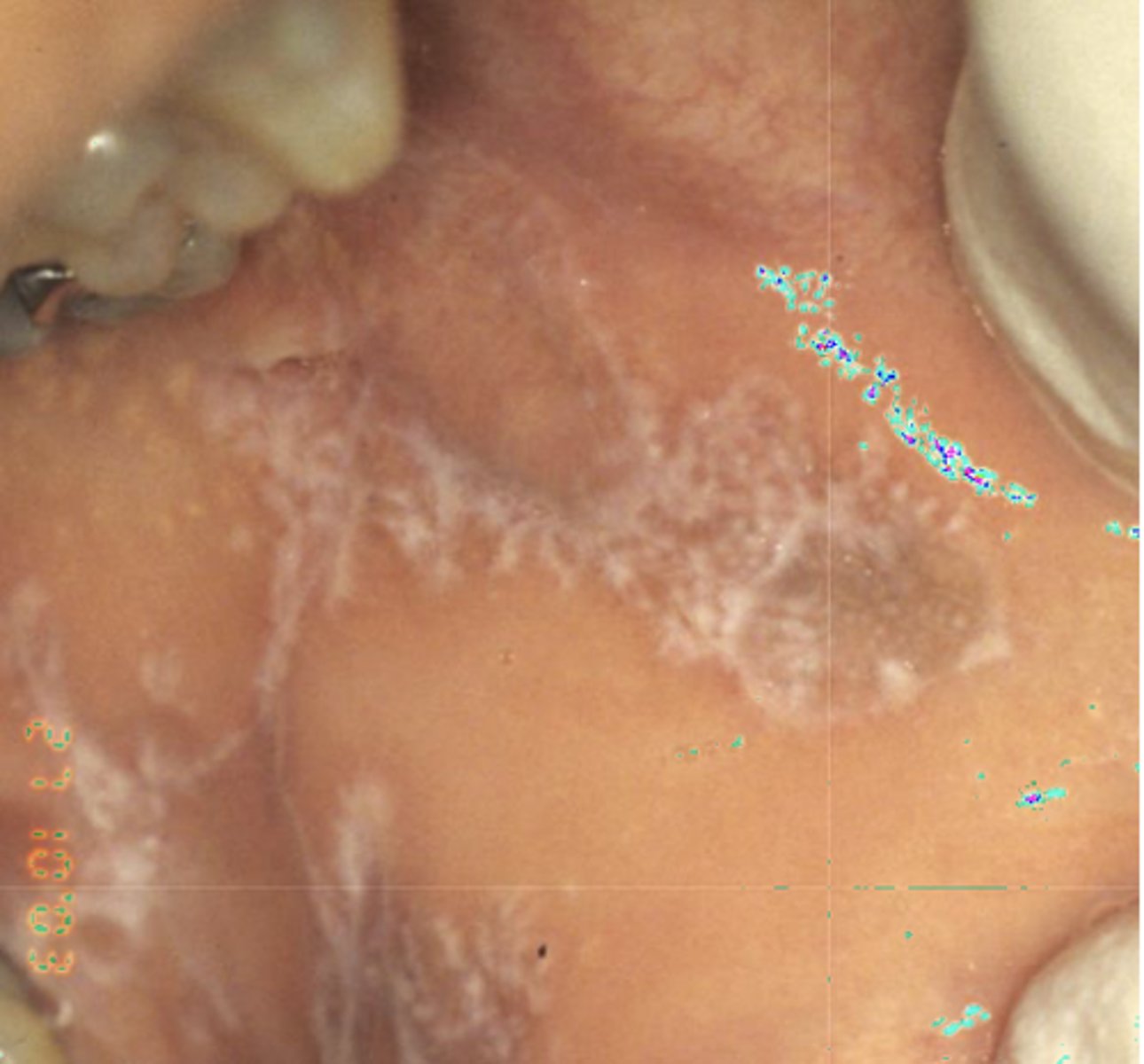
What type of pigmented lesion?
postinflammatory hypermelanosis
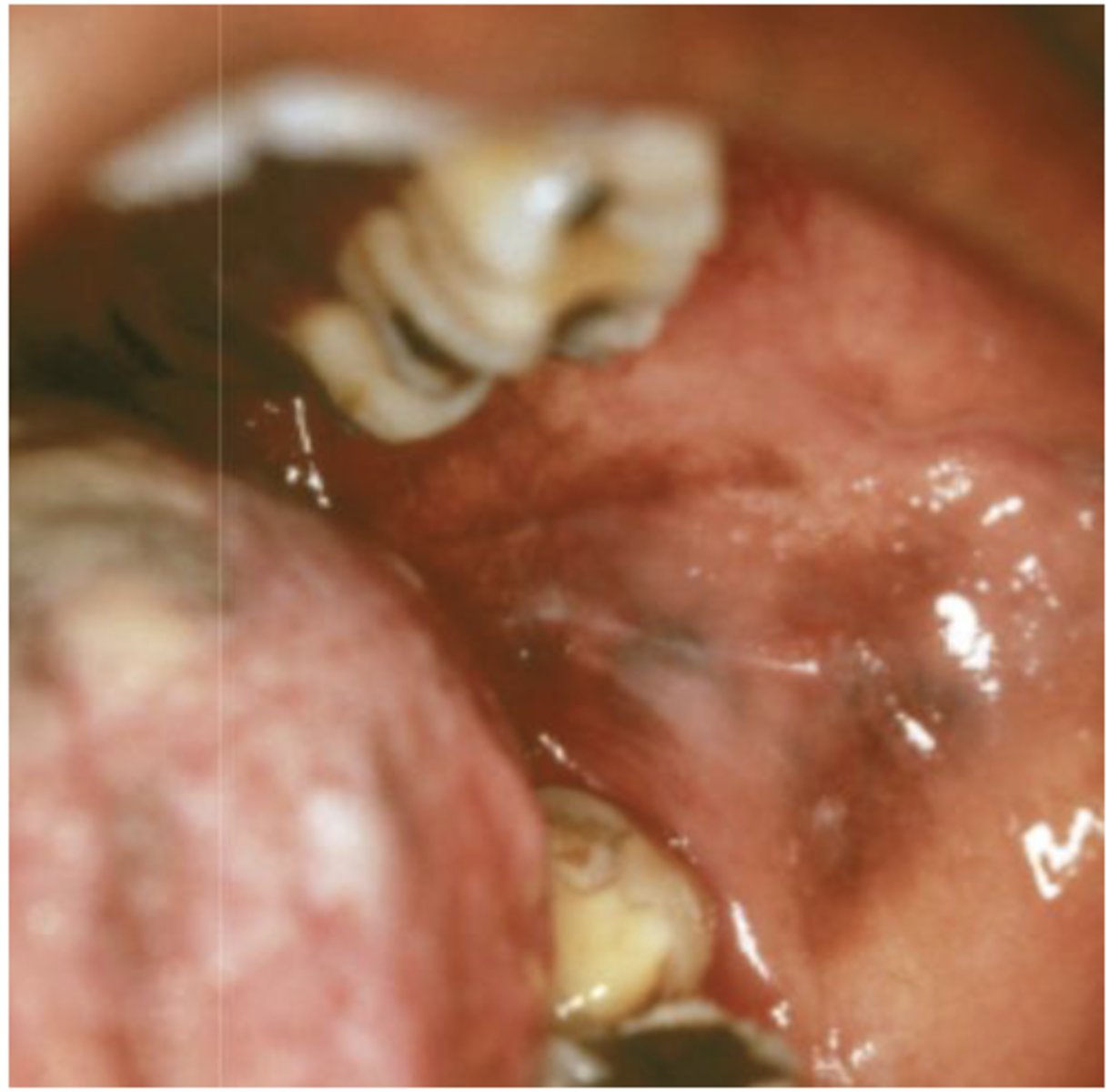
What type of pigmented lesion?
postinflammatory hypermelanosis (eg. smoker's melanosis)
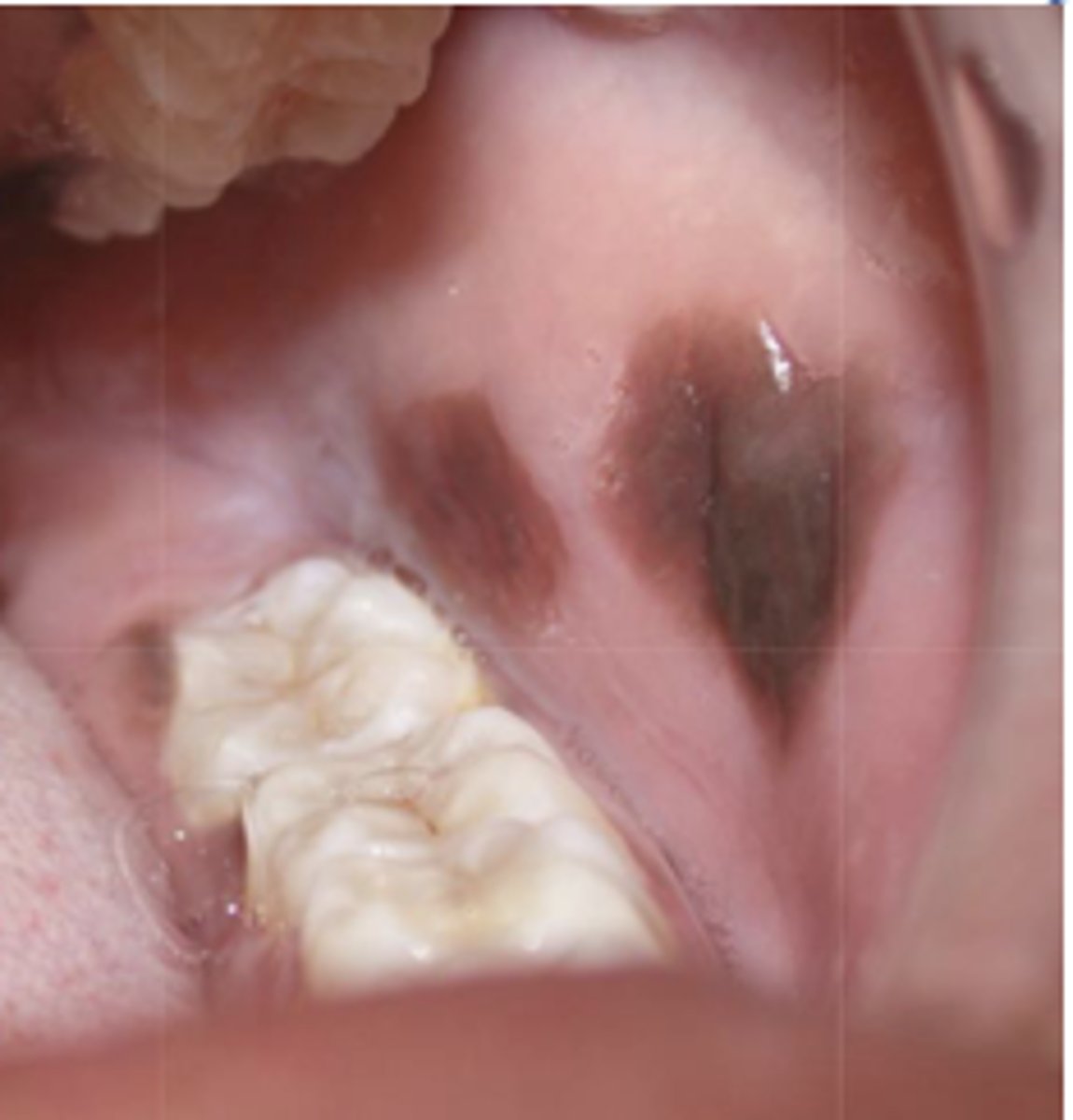
What type of pigmented lesion?
melanocanthosis
When do oral melanotic macules usually appear?
5th decade
Do oral melanotic macule have male or female predilection?
females (2-3:1)
These are characteristics of what pigmented lesion?
- Discrete, solitary (usually), tan to brown painless macule
- Most commonly found on lip mucosa then gingival/palatal mucosa, then buccal mucosa
- If multiple, explore...
oral melanotic macule
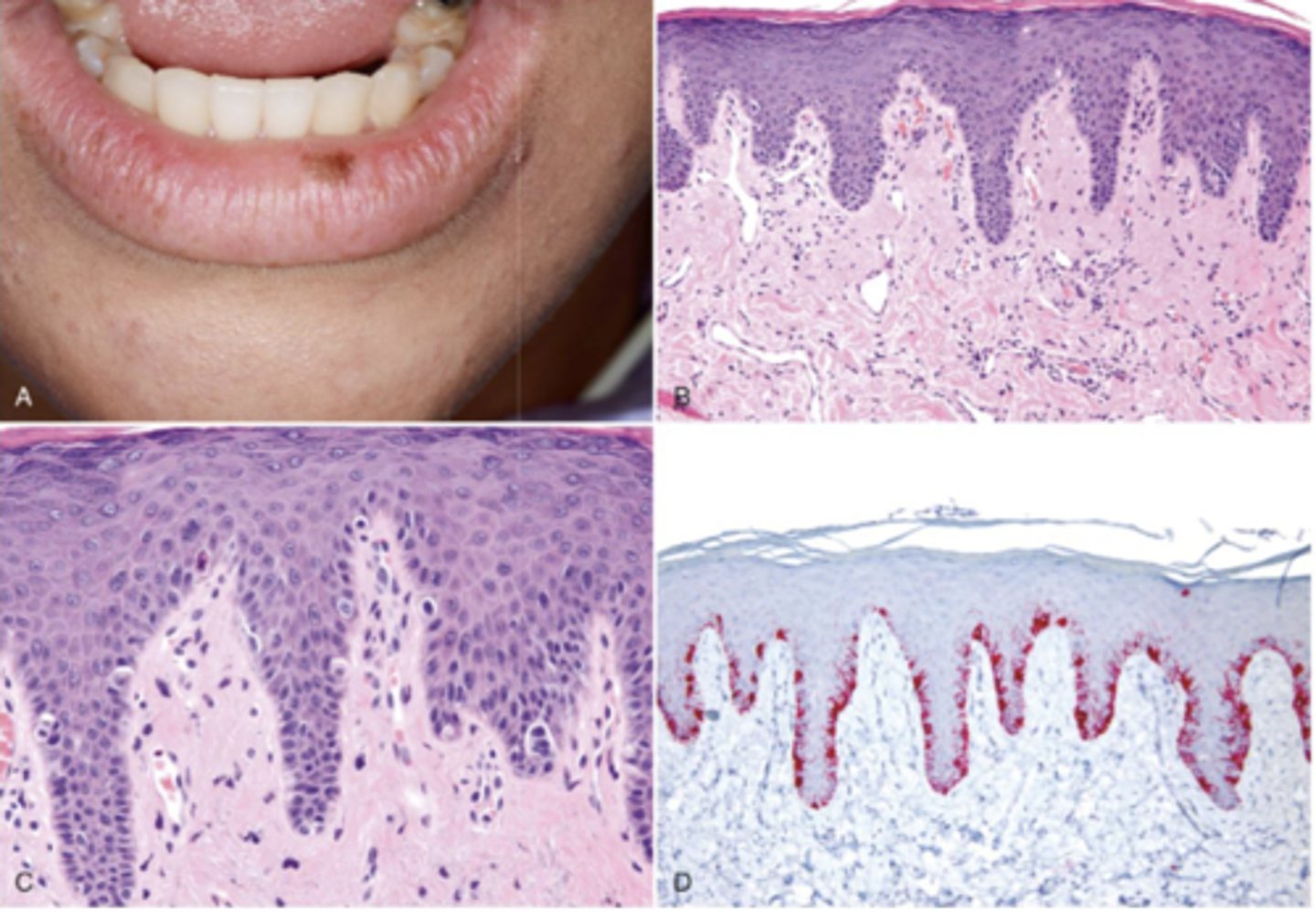
What type of pigmented lesion?
oral melanotic macule
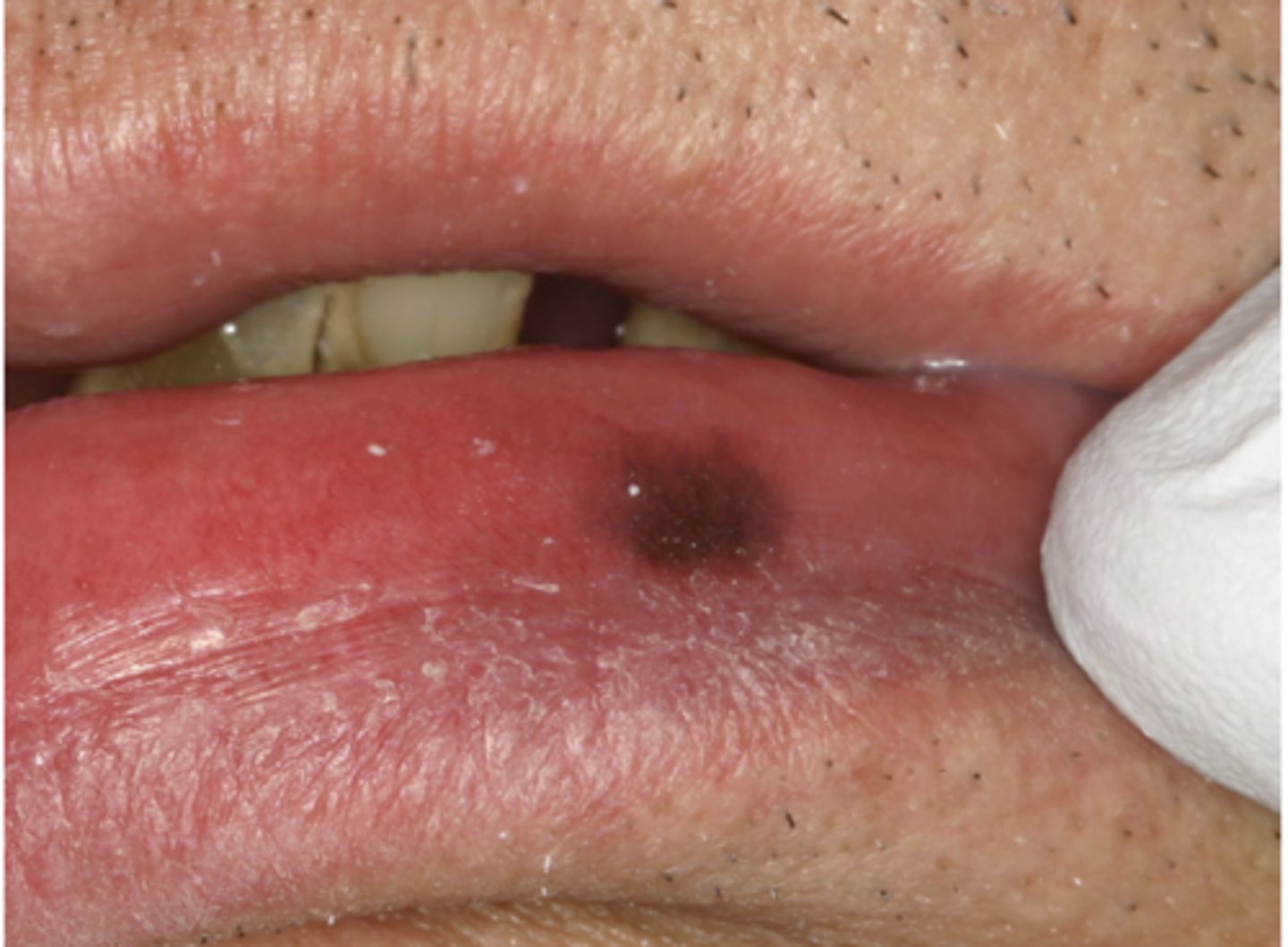
What type of pigmented lesion?
oral melanotic macule
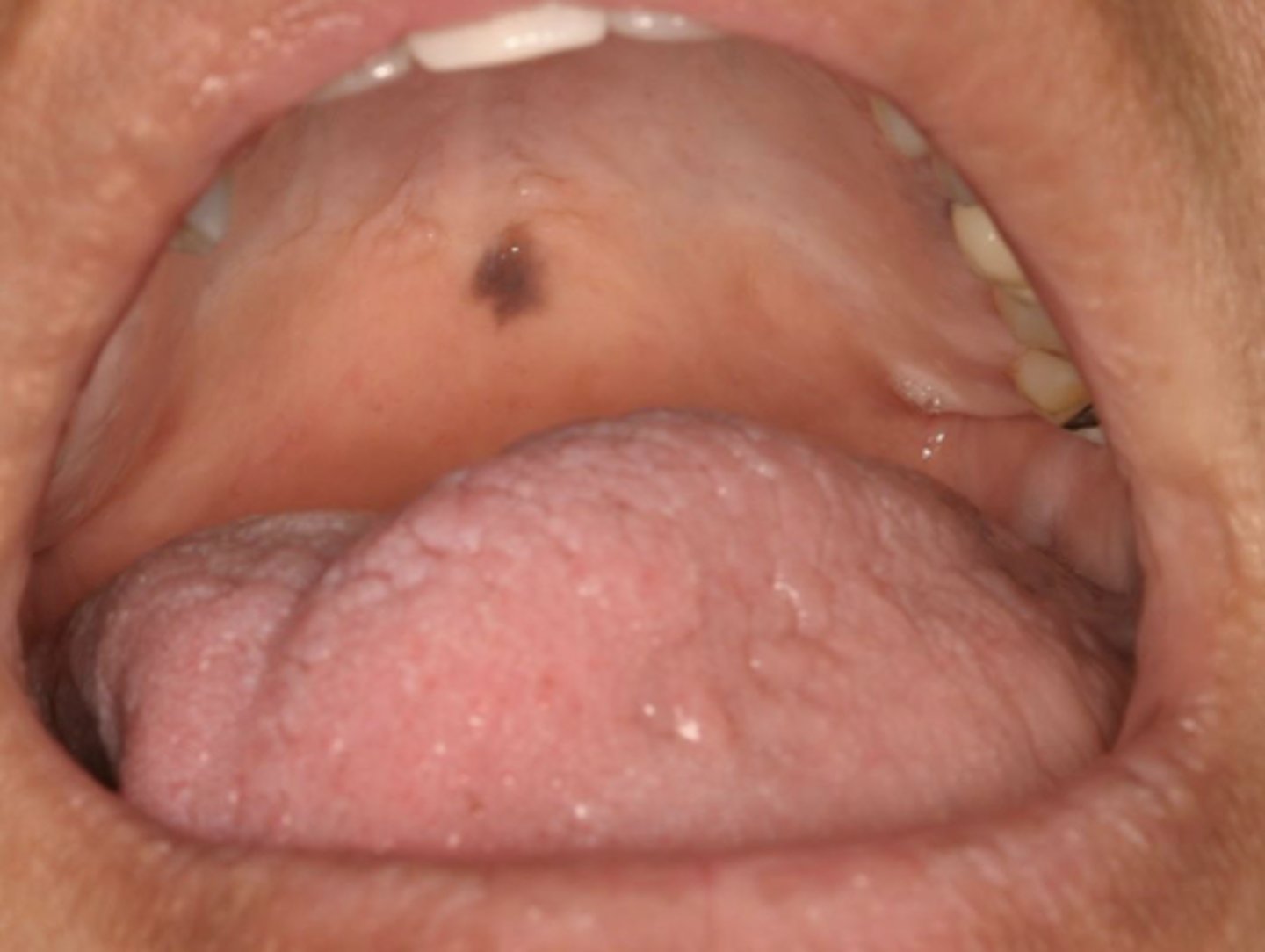
What type of pigmented lesion?
oral melanotic macule
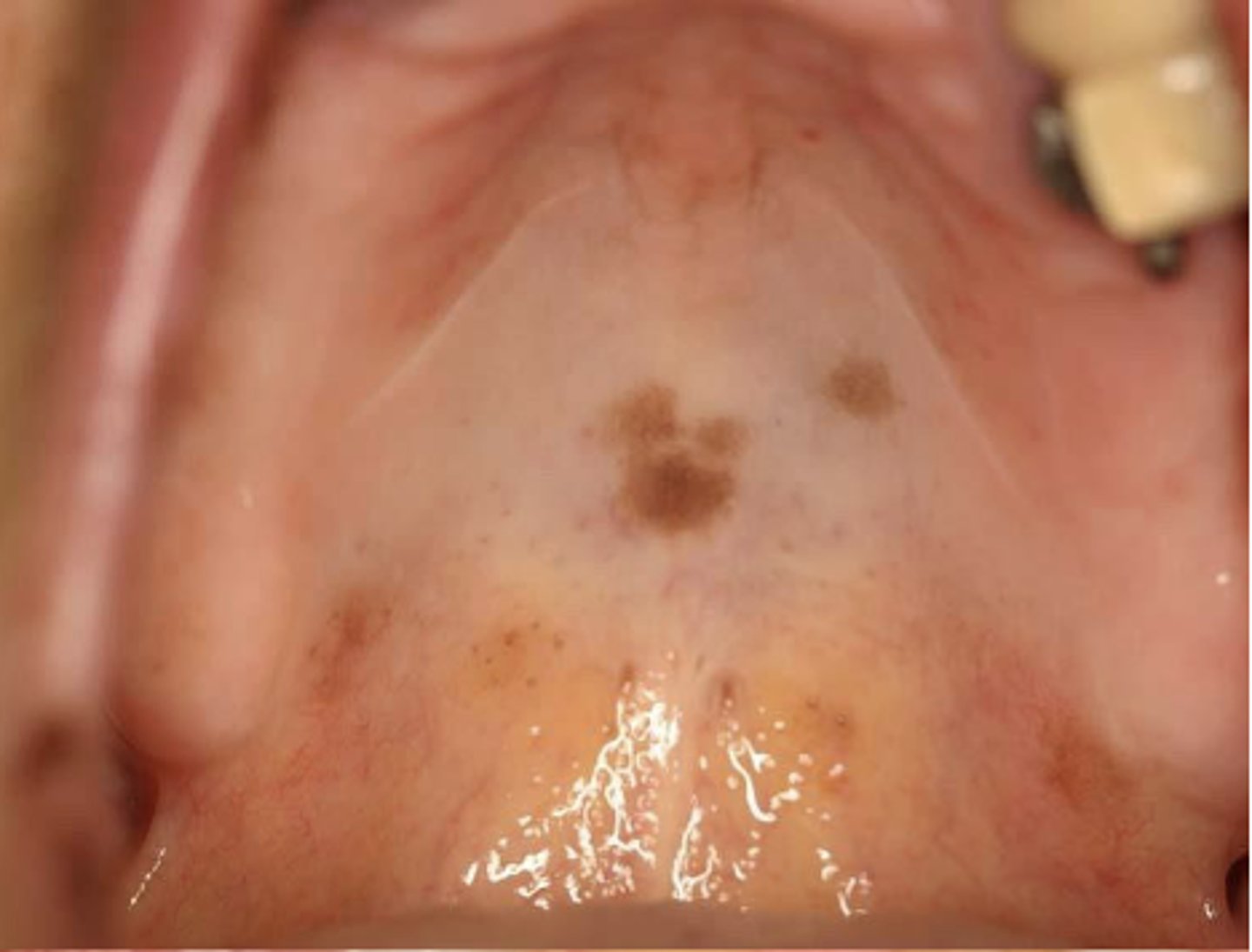
What type of pigmented lesion?
oral melanotic macule
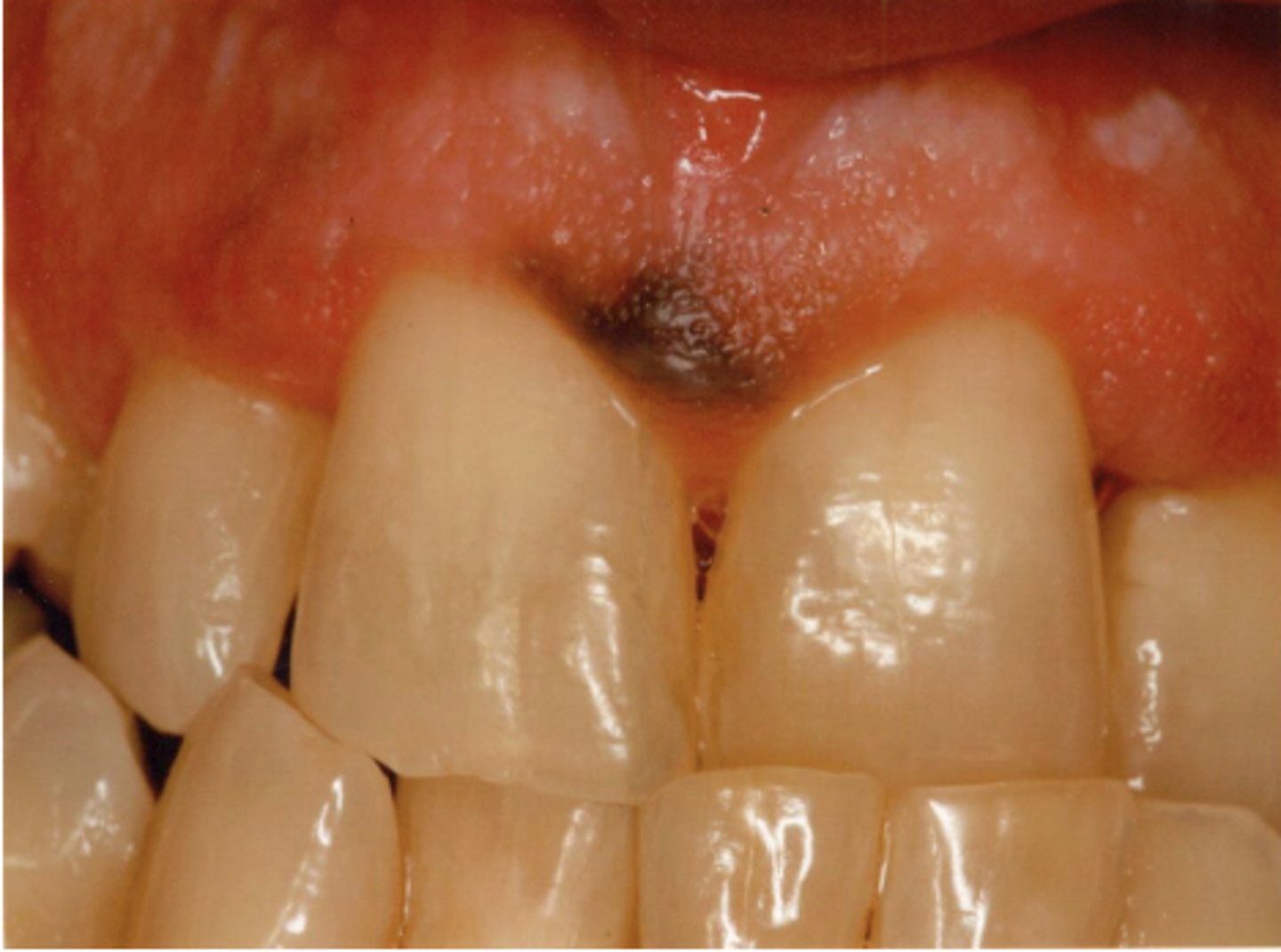
What type of pigmented lesion?
oral melanotic macule (or amalgam tattoo?)
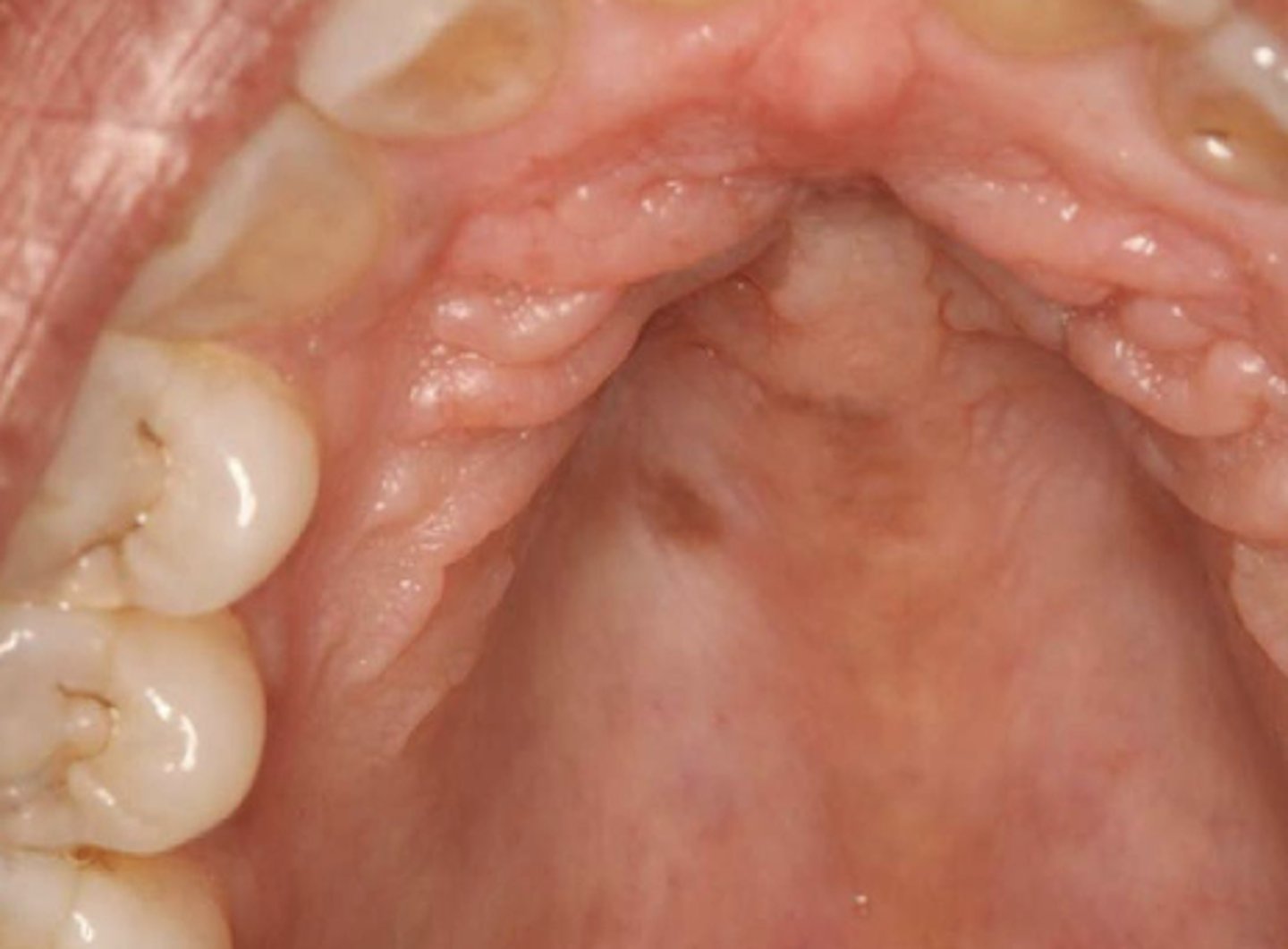
What type of pigmented lesion?
oral melanotic macule

Which type of pigmented lesion has these histopathologic features?
- Increased level of melanin in basal and para-basal layers of epithelium and connective tissue
oral melanotic macule
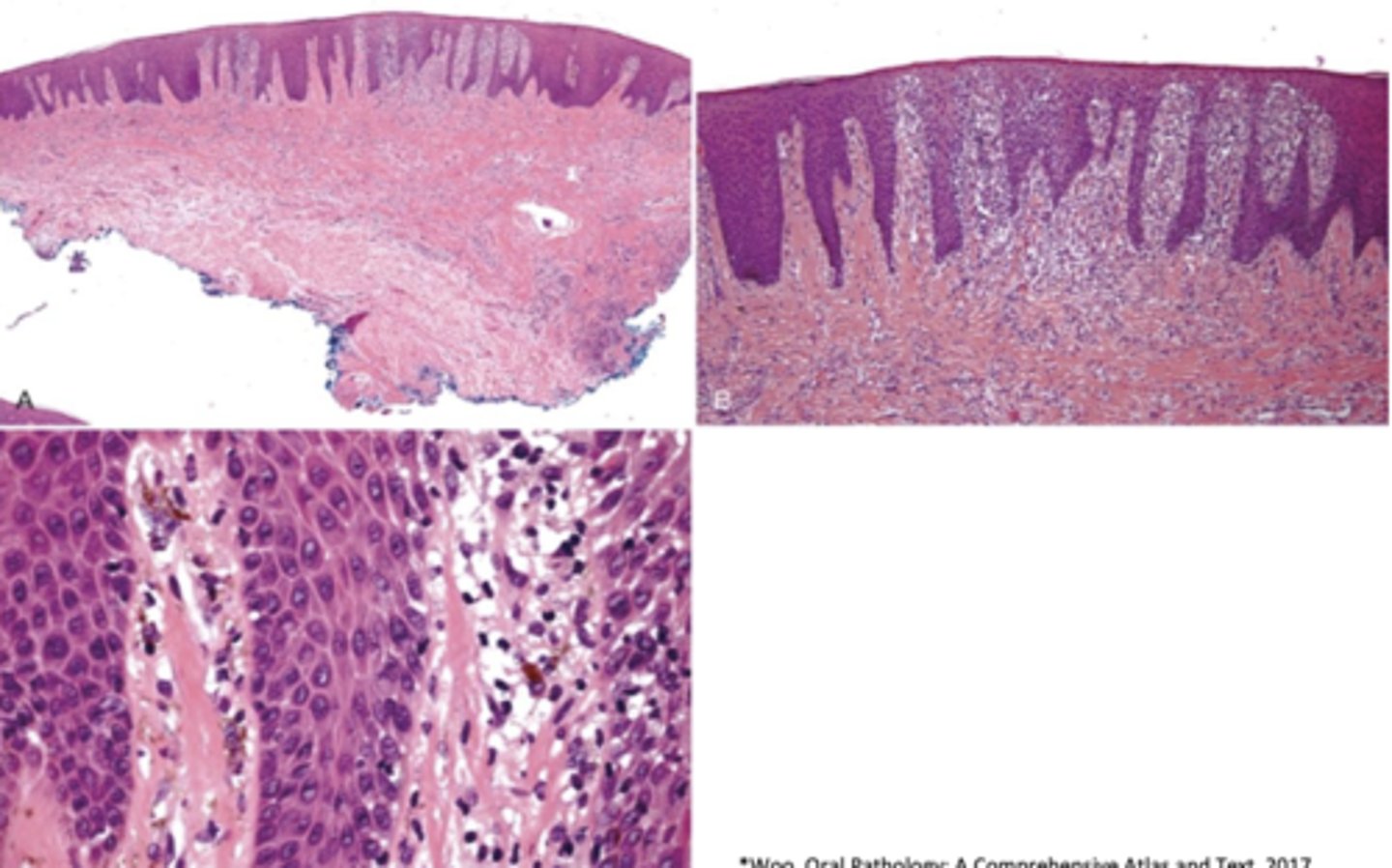
What is a similar type of pigmented lesion to melanotic macules but have inflammation?
post-inflammatory hypermelanosis
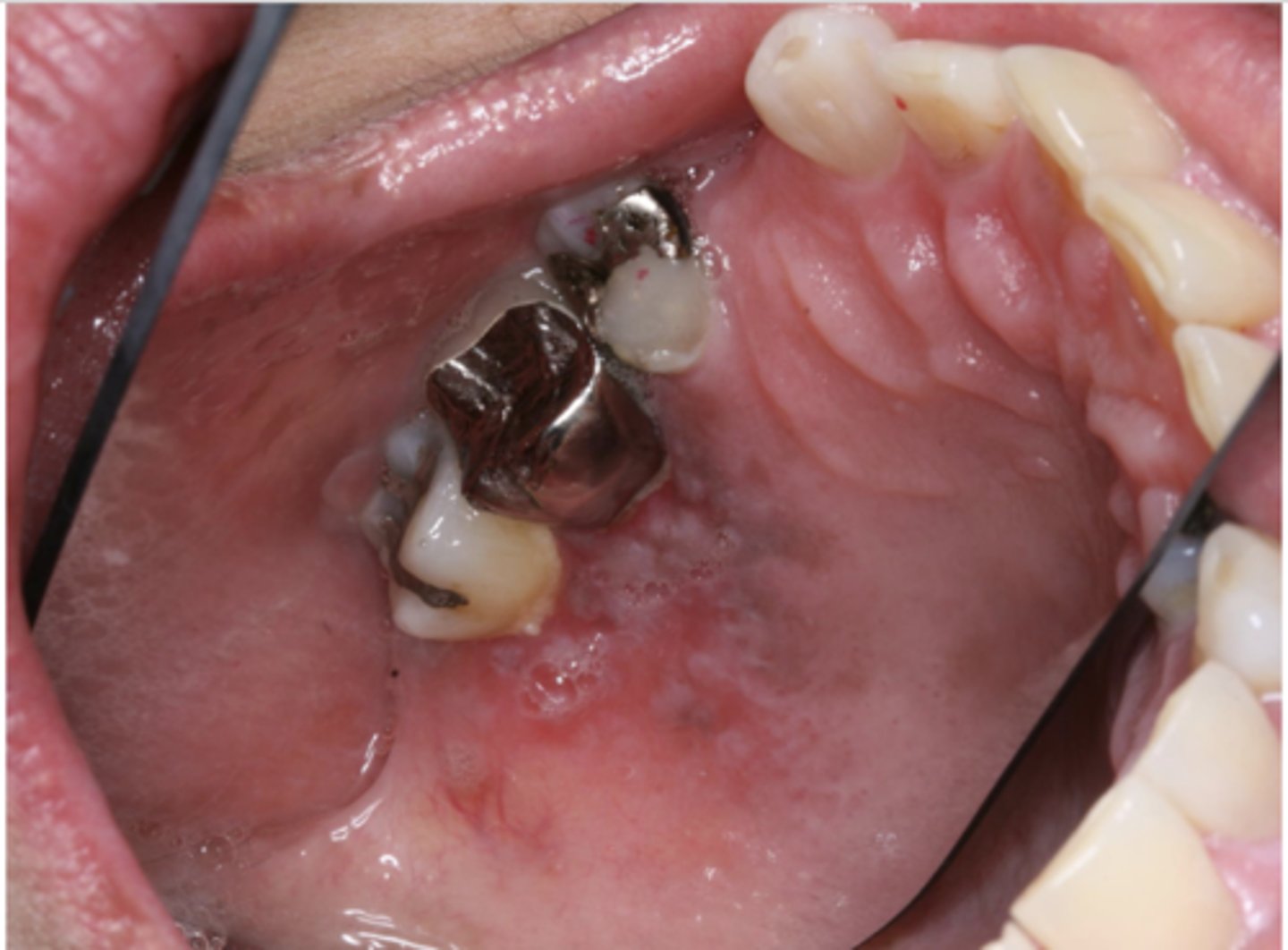
What type of pigmented lesion?
post inflammatory hyperpigmentation
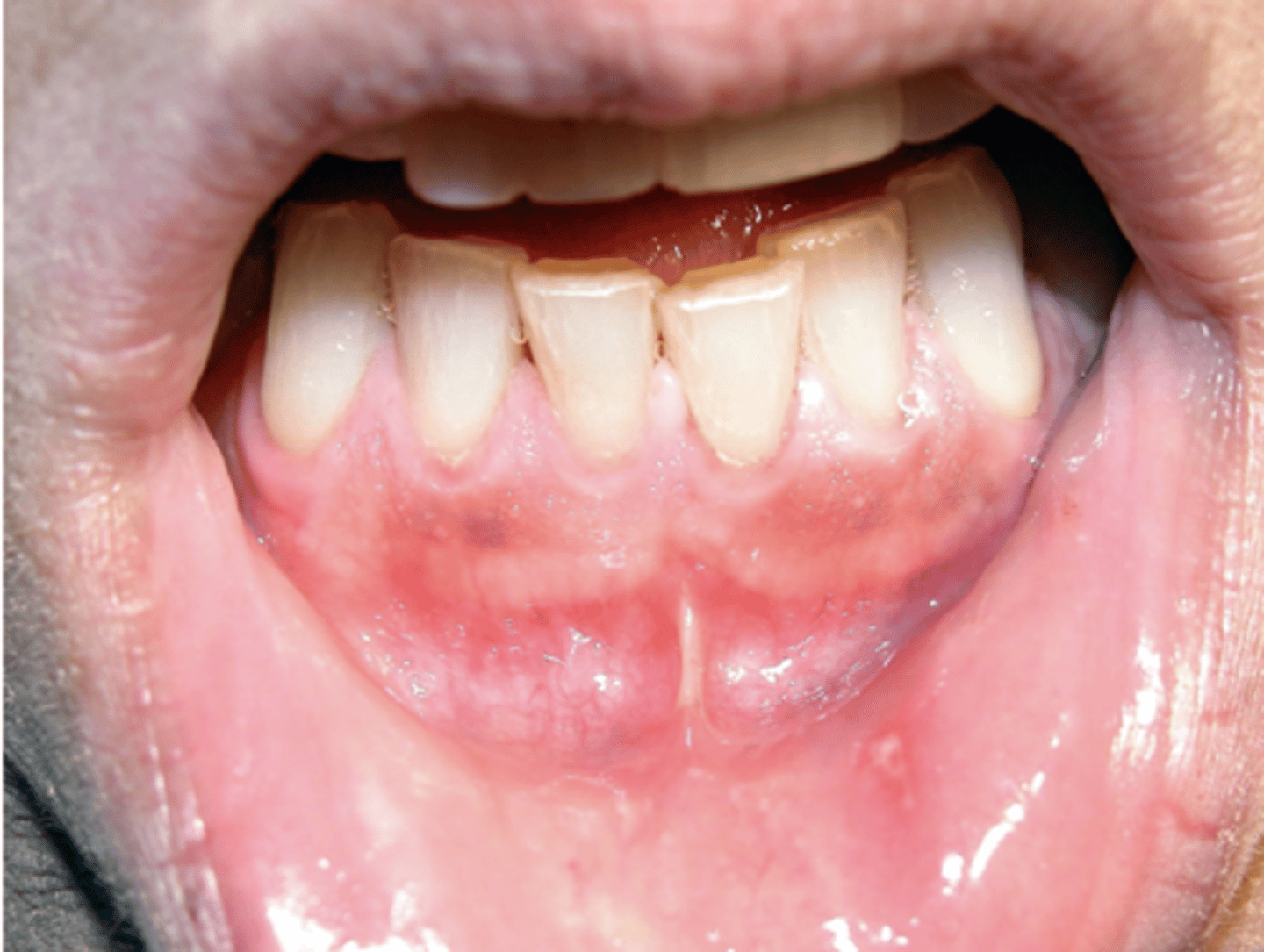
What type of pigmented lesion?
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
- Facial gingiva affected most often
- May be seen in 20% of smokers
smoker's melanosis
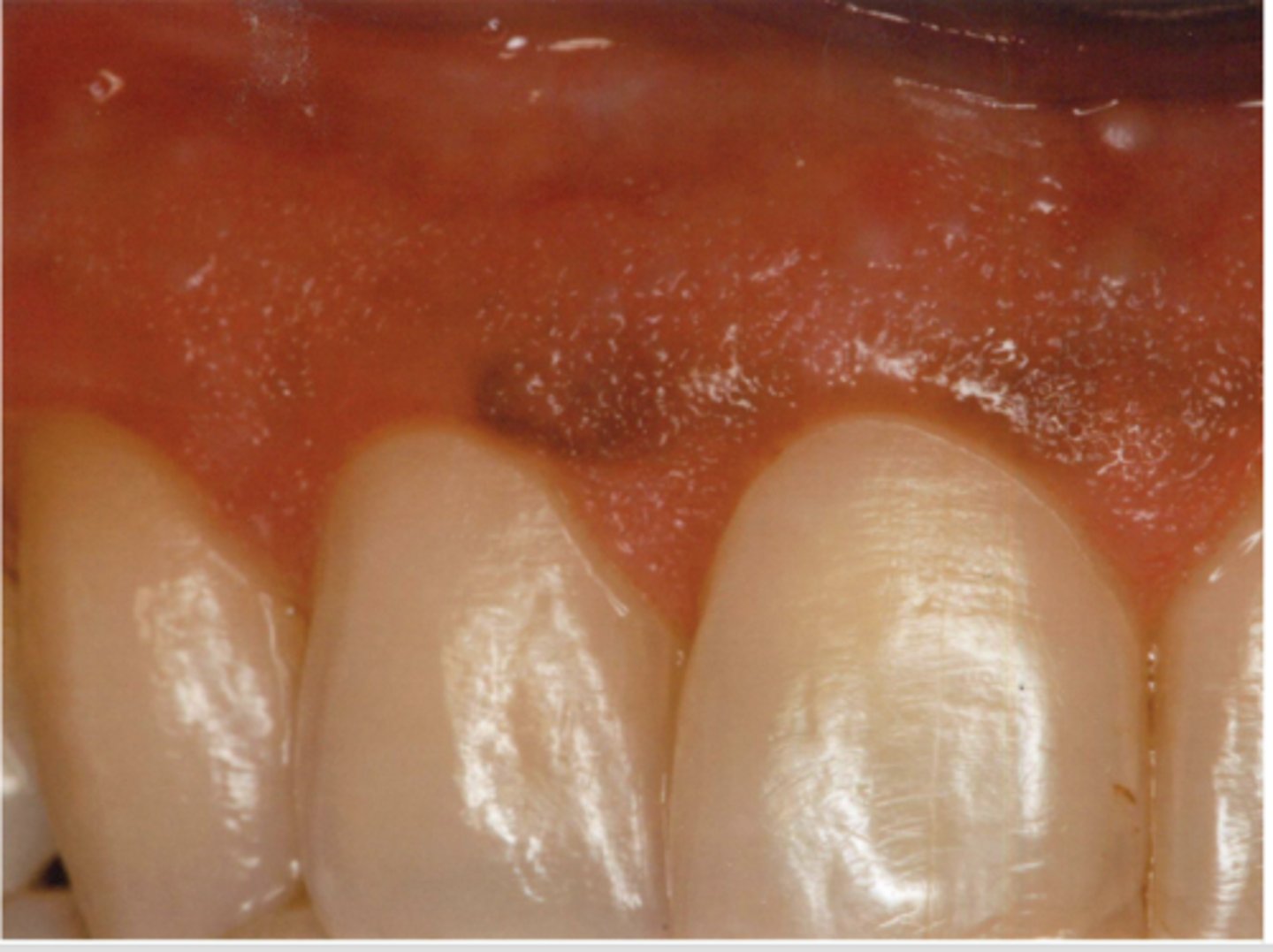
Patient is a smoker. What type of pigmented lesion?
smoker's melanosis
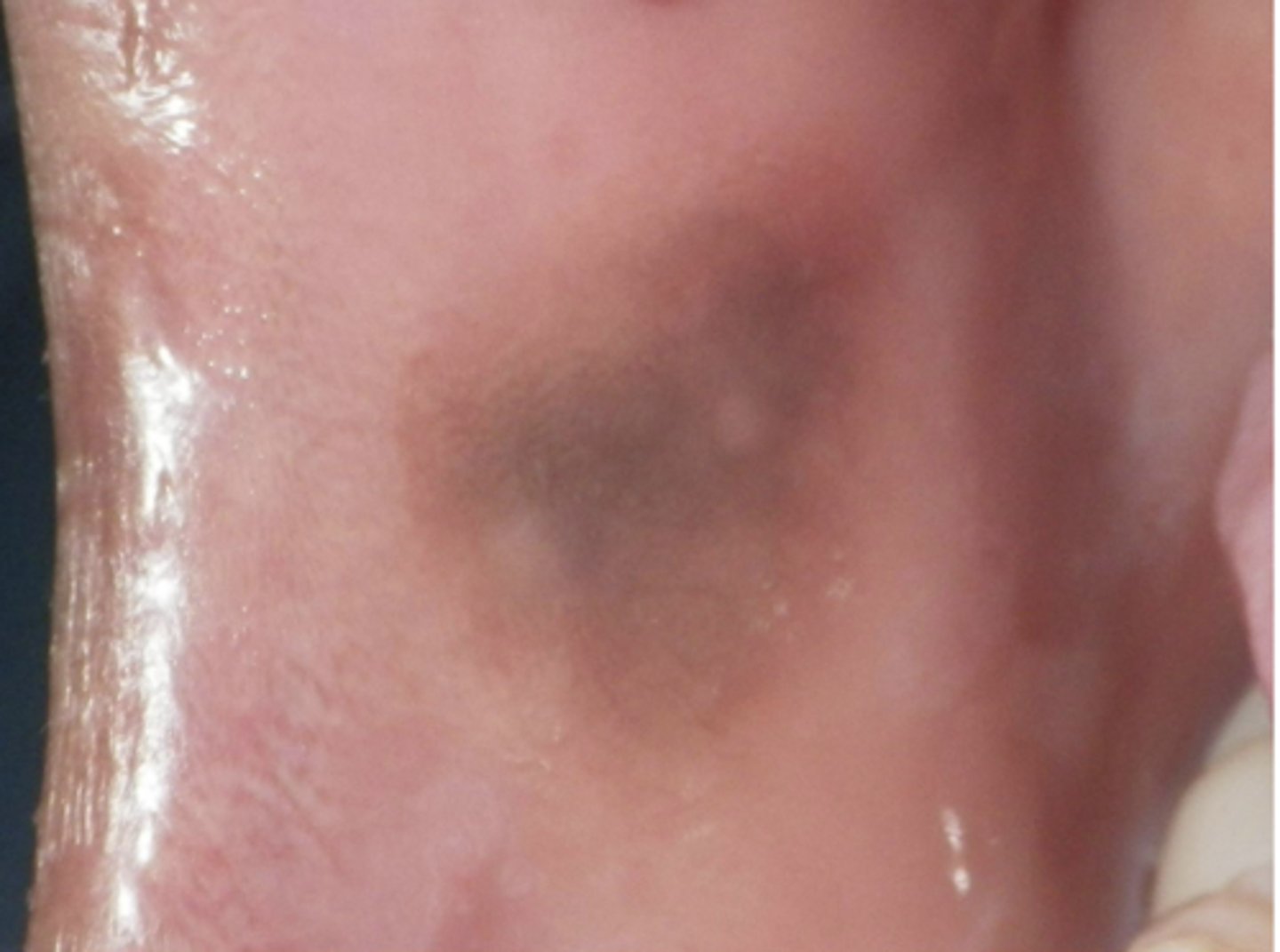
What type of pigmented lesion?
- Rare acquired pigmented lesion(s) of rapid onset
- Reactive?
- May reach several cm in size
oral melanoacanthosis (a.k.a. oral melanoacanthoma)
Oral Melanoacanthosis has a predilection for which ethnic group and which gender?
African American females
Oral Melanoacanthosis usually appears at which age?
3rd-4th decades

What is the differential diagnosis?
45 year-old African American female presented with this asymptomatic lesion for 2 months.
oral melanoacanthosis
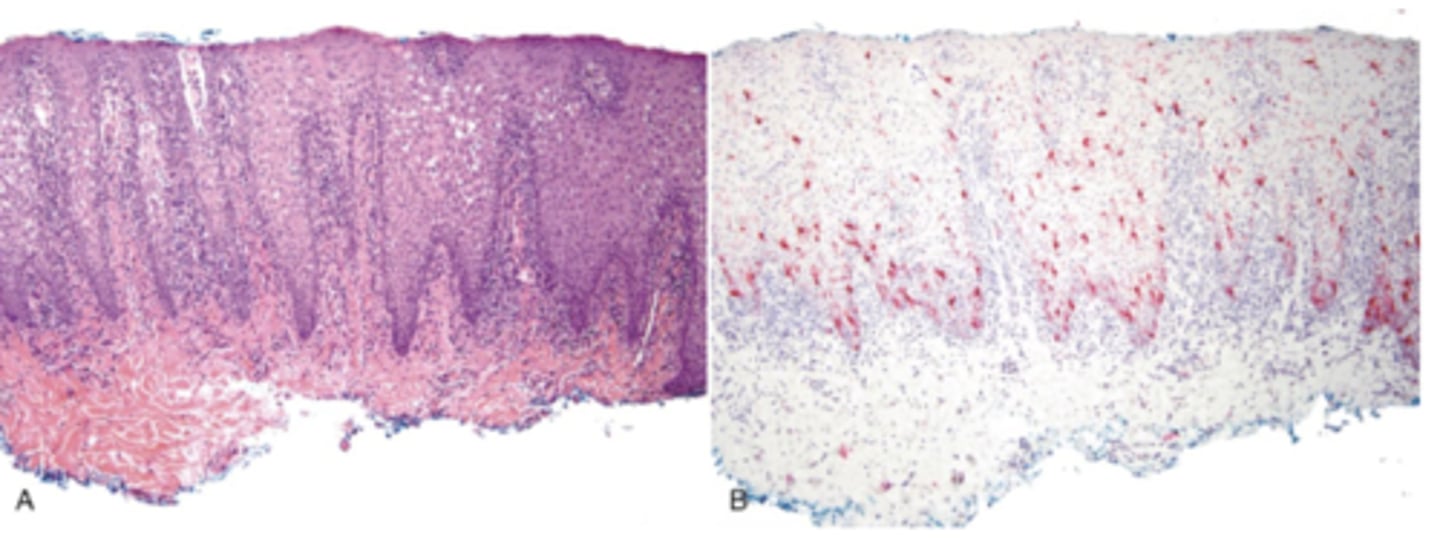
What pigmented lesion has these histopathologic features?
- Dendritic melanocytes throughout epithelium
- Thickened epithelium
- Increase in basal layer melanocytes
- Spongiosis and mild acanthosis
oral melanoacanthosis
What is the treatment of oral melanoacanthosis?
- Biopsy to r/o melanoma
- No further rx required