IB Biology ECOLOGY
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1
New cards
species
a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring
2
New cards
What do members of a species have in common?
-Similar characteristics
- ability to interbreed and produce fertile offspring
-different gene pools than other organisms
- a common phylogeny
- ability to interbreed and produce fertile offspring
-different gene pools than other organisms
- a common phylogeny
3
New cards
Hybrids
The offspring of two similar but different species
4
New cards
Autotrophs/ PRODUCERS
synthesize organic molecules from inorganic molecules, usually through the process of photosynthesis - PRODUCERS
5
New cards
Heterotrophs/ CONSUMERS
Must obtain their organic molecules from other organisms
6
New cards
Detrivores
eat non-living irganic matter
7
New cards
Saprotrophs / DECOMPOSERS
digest their food externally by secreting digestive enzymes ono living or non-living organic matter and absorb the nutriens
8
New cards
community
a group of populations living and interacting with each other in the same area
9
New cards
population
a group of the species living in the same area
10
New cards
ecosystem
a system formed by the interaction of a community of organisms with their physical environment
11
New cards
abiotic factors (of an ecosystem)
non-living components of the environment
12
New cards
biotic factors(of an ecosystem)
living components of the environment
13
New cards
Describe the nutrien cycle
1. producers take inorganic compounds and transform them into organic compounds
2. consumers eat the producers
3. complex molecues found in the producers are digested into smaller monomers
4. consumer dies, its cells are broken down by the digestive enzymes of decomposers and the nutriens are returned to the soil
2. consumers eat the producers
3. complex molecues found in the producers are digested into smaller monomers
4. consumer dies, its cells are broken down by the digestive enzymes of decomposers and the nutriens are returned to the soil
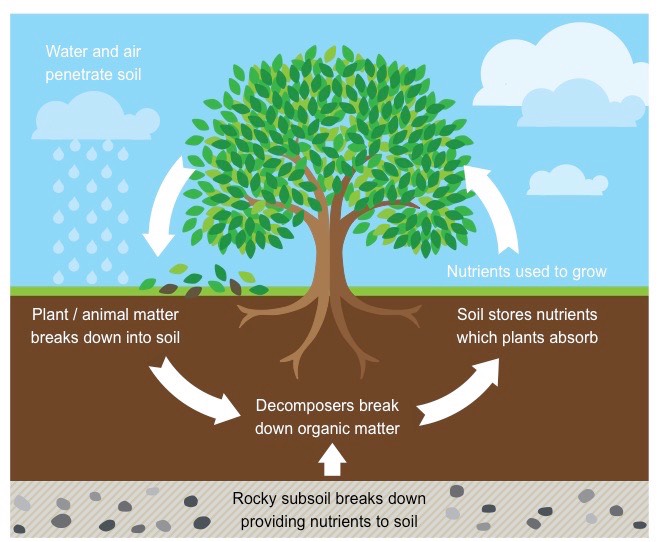
14
New cards
photosynthesis energy conversion formula
H20+CO2--->C6H12O6+O2
15
New cards
cellular respiration energy conversion furmula
C6H12O6--->CO2+H2O+ATP+HEAT
16
New cards
energy flow
the process of passing energy from one organism to another through feeding
17
New cards
food chain
a sequence showing the feeding relationships and energy flow between species
18
New cards
peat
a type of water logged soil that contains large amounts of partially decomposed matter
19
New cards
Desribe peat formation
1. dead organisms are covered in water
2.the weight of the water causes the air outt creating an anaerobic environment
3. microorganisms which would decompose the dead matter die off
4. energy-rich compounds are compressed and preserved
2.the weight of the water causes the air outt creating an anaerobic environment
3. microorganisms which would decompose the dead matter die off
4. energy-rich compounds are compressed and preserved
20
New cards
Ecology
a science about interactions between organism and their envirnoment
21
New cards
3 requirements for sustainability in ecosystems
1. nutrien availability
2. detoxification of waste products
3.energy availability
2. detoxification of waste products
3.energy availability
22
New cards
carbon cycle
a biochemical cycle whereby carbon is exchanged between differents spheres of the Earth
23
New cards
greenhouse gases
absorb and emit long-wave radiation, trapping and holding heat within the atmosphere