kinesology test 3
1/316
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
317 Terms
how many vertbrae and spinal nerves in the vertebral column
24 vertebrae, 31 paris of spinal nerves
how are abdominal muscles linked
fascia and tendinous bands, do not attach from bone to bone
what do the small muscles of the head, verebral column, and throax do
assist in spinal stabilization or respiration
how many of each type of vertebrae are there
7 cervicle
12 thoracic
5 lumbar
9 fused (5 scarum, 4 coccyx)
what are the 3 curves of the moveable spin, how do they curve and what do they do
thoracic curves posteriorly (kyphotic)
cervical and lumbar curve anteriorly (lordotic)
spinal curves enable it to abdorb blows and shocks
why do the vertebrae increase in size from cervical to lumbar
lower back having to support more weight
what are the first two cervical vertebrae and what do they do
atlas is first, axis is second. They allow for extensive rotary movements of head to side as well as forward and backward
what does the cervical vertebral foramen house
spinal cord
transverse process project out
laterally
spinous process project out
poseriorly
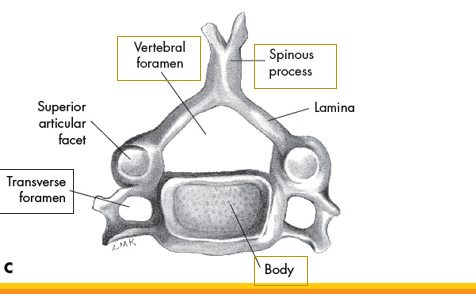
what vertebrae is this
cervicle
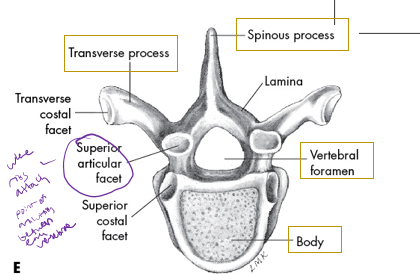
what vertebrae is this
thoracic
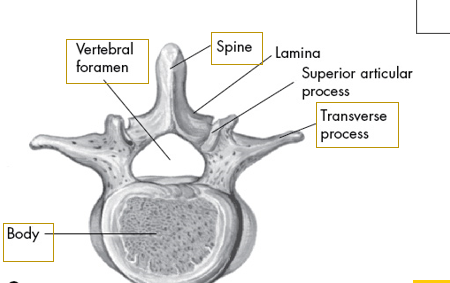
what vertebrae is this
lumbar
how many true, false, and floating ribs
7 true
5 false (3 attach indirectly to sternum, 2 floating ribs)
where to ribs attach
poteriorly to thoracic vertebrae
what is the most superior joint called
atlantooccipital joint
how is atlantoocipital joint formed
occipital condyles of skull sitting on articular fossa of the first vertebrae
movement allowed at the atlantooccipital joint
capital flexion and extension
what hoint is between atlas (c1) and axis (c2)
atlantoaxial joint
atlantoaxial joint actions and joint type
cervical rotaion (most occurs here)
piviot-type (trochoid) joint
what is the most mobile joint of any two vertebrae
atlantoaxial joint
what are vertebral articulations classified as and what type of joint
arthroidial, gliding-type joint
where are the gliding motions between the vertebrae located
between superior and inferior articular processes of facets joints
name the two parts of the invertebral disk and what they are composed of
annulus fibrosus: outer rim of dense fibrocartilage
nucleus pulposus: central gelatinous, pulpy substance
the compressed elastic material in invertebral disks allows compression in what direction
all directions along with torsion
with aging, injury, or improper use, what happens to invertebral disks
less resilent, weakened annulus fibrosus
what is herniated nucleus pulposus
herniated or slipped disk, nucleus protruding through annulus resulting from substaintial weakening combined with compression. Puts pressure on spinal nerve root, causing radiating pain, tingling, numbness, and/or weakening in lower extremity.
what part of the spine is most movable
cervical and lumbar, slight thoracic movement
lordosis
increased anterior curve )extension) of lumbar and cervical vertebrae
kyphosis
increased posterior curve (flexion) or thoracic curve
scoliosis
lateral curvature or sideward deviations of spine (plus rotation)
cervical region movements
flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation
lumbar spine including trunk movment
flexion, extension, lateral flexion, rotation
spinal flexion
◦anterior movement of spine; in cervical region the head moves toward chest; in lumbar region the thorax moves toward pelvis
spinal extension
return from flexion or posterior movement of spine; in cervical spine, head moves away from chest; thorax moves away from pelvis
Lateral flexion (left or right)
sometimes referred to as side bending; head moves laterally toward shoulder & thorax moves laterally toward pelvis
Reduction
return movement from lateral flexion to neutral
Spinal rotation (left or right)
rotary movement of spine in transverse plane; chin rotates from neutral toward shoulder & thorax rotates to one side
what is the largest muscle of the spinal column
erector spinae, extends on each side of spinal column from pelvic region to cranium
what is the erector spinae divided into
spinalis(medial), longissimus(middle), iliocostalis(lateral)
what are the largest muscles of the cervicle and head movements
sternocleidomastoid and splenius muscles
what are the large abdominal muscles
Rectus abdominus, external oblique abdominal, internal oblique abdominal & quadratus lumborum
what abdominal wall mucles attach into an aponeurosis (fasicia)
external oblique abdominal, internal oblique abdominal & transversus abdominus
what muscles are of inner core and how to activate
◦Diaphragm, transversus abdominus, lumbar multifidus & pelvic floor muscles which attach to bony ring of pelvis
◦Activating these muscles requires a level of focus & concentration
what are outercore muscles and how to activate
◦rectus abdominus, external obliques, internal obliques & erector spinae
◦Exercised in a variety of means including but not limited to sit-ups, V-sit-ups, crunches, curl-ups, abdominal twists, prone extensions, superman exercises, etc.
what are the 3 anteror vertebral muscles that flex the head and upper cervical spine
•longus capitis, rectus capitis anterior & rectus capitis lateralis
◦All are flexors of head & upper cervical spine
sternocleidomastoid orgin, inerstion, action
•Origin: Manubrium & superior, medial clavicle
•Insertion: Mastoid Process
Action: •Both Sides: Extension of head at atlantoocciptal joint and neck flexion.
•Opposite Rotation
Same Side Lateral Flexion
diaphragm action and what happens as it contracts and flattens
◦Responsible for breathing during quiet rest
◦As it contracts & flattens, thoracic volume is increased & air is inspired to equalize the pressure
◦When larger amounts of air are needed, as in exercise, other thoracic muscle have a more significant role in inspiration
scalene muscle action
•muscles elevate first 2 ribs to increase thoracic volume
external intercostals action
further expand the chest
internal intercostals action
contract to force expiration
multifidus general orgin, insertion, action
spinous process superior vertebrae→ transverse process inferior vertebrae
Action: Bilateral = Extension
Contralateral Rotation & Lateral Flexion
Lumbar spine stabilization (with TrA and pelvic floor)
erector spinae muscles action
•Extension, Lateral Flexion, Rotation of spine and head
•Anterior pelvic tilt, Lateral Flexion of Pelvis
quadratus lumborum muscle orgin, insertion, action
•Origin: Posterior lip of iliac crest
•Insertion: 12th rib and Lumbar 1-4
•Stabilizes Pelvis and Lumbar Spine
•Lumbar extension, lateral flexion
•Pelvic lateral flexion and anterior tilt
what are the muscles of the abdominal wall
•Rectus abdominus
•External oblique abdominal
•Internal oblique abdominal
•Transverse abdominus
rectus abdominis orgin, insertion, action
Origin: Crest of pubis
Insertion: Cartilage of ribs 5, 6, 7, and xiphoid process
Action: Lumbar Flexion
Posterior Pelvic Tilt
Weak opposite lateral flexion
external oblique orgin, insertion, action
Origin: Borders of lower 8 ribs
Insertion: Anterior Iliac crest
Action: Lumbar Flexion
Posterior Pelvic Tilt
Lumbar lateral flexion,
rotation, pelvic rotation
internal oblique, orgin, insertion, action
Origin: Iliac Crest, Lumbar Fascia
Insertion: Costal Cartilages of Ribs 8, 9, 10
Action: Lumbar Flexion
Posterior Pelvic Tilt
Lumbar lateral flexion,
rotation, pelvic rotation
transversus abdominis orgin, insertion, action
Origin: Inguinal ligament à iliac crest àinner surface of the costal cartilage of lower 6 ribs à lumbar fascia
Insertion: Pubic crest and iliopectineal line, aponeurosis of linea alba
Forced expiration by pulling abdominal wall inward
Stabilization!
muscles of cervical flexion
sternocleidomastoid
muscles of cervicle extension
erector spinae
muscles of cervical lateral flexion
sternocleidomastoid
erector spinae
cervical rotation
sternocleidomastoid
muscles of lumbar flexion
rectus abdominis
external oblique abdominal
internal oblique abdominal
muscles of lumbar extension
erector spinae
multifidi
muscles of lumbar lateral flexion
erector spinae
external oblique abdominal
internal oblique abdominal
muscles of lumbar rotation
rectus abdominus
external oblique abdominal
internal oblique abdominal
what does acetabulofemoral refer to
hip joint
why is the hip joint relativly stable
bony architecure, strong ligaments, large supportive muscles
hip joint function
weight bearing and locomotion
what type of joint is the hip bone
ball and socket
head of femur connects with_______
acetabulum of pelvic girdle
right and left pelvic bone joined together posteriorly by_________
sacrum
name the 3 pelvic bones
ilium, ischium, and pubis
longest bone in the body
femur
sacroiliac motion
minimal oscillating type movements
acetabulofemoral joint reinforced by
extreamly strong and dense ligametous capsule, esecially anteriorly
function of labrum
lines periphery of the acetabulum to enhance stability and provide some shock absorption
hip flexion
movment of femur straight anteriorly toward pelvis
hip extension
movement of femur straight posteriroly away from the pelvis; sometimes referred to as hyperextension
hip abduction
movement of femur laterally to side away from midline
hip adduction
movment of femur medially toward midline
hip external rotation
rotary movement of femur laterally around its longitudinal axis away from midline; lateral rotation
hip internal rotation
◦rotary movement of femur medially around its longitudinal axis toward midline; medial rotation
anterior pelvic tilt
anterior movement of upper pelvis; iliac crest tilts forward in a sagittal plane; anterior tilt; downward rotation
posterior pelvic tilt
◦anterior movement of upper pelvis; iliac crest tilts forward in a sagittal plane; anterior tilt; downward rotation
Left lateral pelvic flexion
◦in frontal plane left pelvis moves inferiorly in relation to right pelvis; either left pelvis rotates downward or right pelvis rotates upward; left lateral tilt
•Right lateral pelvic flexion
◦in frontal plane right pelvis moves inferiorly in relation to left pelvis; either right pelvis rotates downward or left pelvis rotates upward; right lateral tilt
•Left transverse pelvic rotation
◦in horizontal plane pelvis rotates to body's left; right iliac crest moves anteriorly in relation to left iliac crest, which moves posteriorly
•Right transverse pelvic rotation
◦in horizontal plane pelvis rotates to body's right; left iliac crest moves anteriorly in relation to right iliac crest, which moves posteriorly
what does the hip and lumbar do due to anterior pelvic tilt
hip flexion, lumbar extension
when posterior pelvic tilt what does hip and lumbar do
hip extension, lumbar flexion
sagittal plane movments of hip, lumbar, pelvis
•Anterior pelvic tilt
◦hip flexion
◦lumbar extension
• Posterior pelvic tilt
◦hip extension
◦lumbar flexion
in left lateral pelvic flexion what does left hip, right hip, and lumbar duo
•Left lateral pelvic flexion
◦Left hip abduction
◦Right hip adduction
◦Right Lumbar lateral flexion
ir right lateral pelvic flextion what does right and left hip and lumbar do
•Right lateral pelvic flexion
◦Right hip abduction
◦Left hip adduction
Left Lumbar lateral flexion
movments of fronal plane of hip, pelvis, and lumbar
•Left lateral pelvic flexion
◦Left hip abduction
◦Right hip adduction
◦Right Lumbar lateral flexion
• Right lateral pelvic flexion
◦Right hip abduction
◦Left hip adduction
◦Left Lumbar lateral flexion
left pelvic rotation right, left hip and lumbar movements
•Left pelvic rotation
◦Right hip external rotation
◦Left hip internal rotation
◦Right lumbar rotation
right pelvic rotation, left and right hip and lumbar movement
•Right pelvic rotation
◦Left hip external rotation
◦Right hip internal rotation
◦Left lumbar rotation
transverse plane hip, pelvis, and lumbar movements
•Left pelvic rotation
◦Right hip external rotation
◦Left hip internal rotation
◦Right lumbar rotation
• Right pelvic rotation
◦Left hip external rotation
◦Right hip internal rotation
◦Left lumbar rotation
lower cross syndrome
Facilitated “tight” thoracolumbar extensors and iliopsoas
Inhibited “weak” abdominals and glutes
Increased lordosis
Anterior pelvic tilt
External rotation