APUSH Unit 2: Heimler's History Review, Heimler's History: APUSH Unit 1, APUSH Period 1 Review (1491-1607), American Colonial History: Native Tribes, European Motives, and Key Events
1/292
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
293 Terms
Why did the French want to explore the Americas?
Wanted a water route that passed through that would give them access to trade in Asia. They were distracted with their European war so they were not completely devoted to colonization.
Who was Samuel de Champlain? What did he do?
Established the first permanent French settlement, Quebec.
What made French settlements different from other European ones?
The French had a much greater interest in trade than in conquest (fish and fur trade especially). Relatively few French colonizers came. They wanted vast trading networks with the Native Americans.
What were French trading relations like with the Ojibwe?
The French fostered alliances with them, cultural alliances occurred. The French introduced iron and farming tools.
Who was Henry Hudson? What did he do?
The Dutch also wanted a water-based passage through the Americas. They sent Henry Hudson to find it. He sailed up a river and claimed that portion of the country for the Dutch. That colony would become New Amsterdam.
What were the Goals of the Dutch in their colonization?
Mainly economic, the establishment of New Amsterdam became a trading hub.
How did Dutch colonizers differ from the Spanish?
The Dutch differed from the Spanish: although proudly protestant, they felt no need to convert natives to their belief.
What economic reasons led English people to explore America?
The English economy had drastically changed since the Columbian exchange and noble wealth began to diminish. Nobles were seeking new economic opportunities elsewhere. Furthermore, the peasantry also experienced hardship because their land was disappearing due to the enclosure movement (took land from everyone held in common and sold it to private parties).
What religious reasons led English people to explore America?
Pursuit of religious freedom was a massive incentive.
How did the English settle in America?
Set out in family groups to establish new homes - far different from the French and the Dutch. For a period, the English peacefully coexisted with the natives, but that then gave way to tension and violence. The English expelled the native populations rather than subjugating them.
What was the first British colony established? How was it funded?
Jamestown, funded by a joint-stock company, its purpose was to profit.
What is a joint-stock company?
A joint-stock company was not state-sponsored, but private. In order to pay for exploration, investors pooled together money and shared the financial risk.
What was discovered in 1612?
The cultivation of tobacco. John Rolfe began to experiment with tobacco planting.
How was labor done in these colonies?
Indentured servitude: signed a seven-year labor contract where they worked to pay off their settlement fee
What was a consequence of the discovery of tobacco?
Increased demand for tobacco required more land to plant it, and the way to acquire this land was to encroach on the land of the Native Americans. This caused tension.
Who was William Berkeley?
Governor of the colony, colonists called upon him and he decided their cause was not worth his effort. This led to Bacon's Rebellion.
What was Bacon's Rebellion?
Resentful of Indian violence and Berkeley's neglect, Bacon led other poor farmers on an attack on Native Americans and Berkeley's land as well.
What were the consequences of Bacon's Rebellion?
Planters began to fear more uprisings may occur so they looked for new labor. Enslaved people from Africa then began to replace indentured servants
What were the New England colonies like?
Settled by Pilgrims, paved the way for an influx of Puritan settlers (those unhappy with the Church of England).
What was the key reason Pilgrims came to America?
When they first left England, many went to Holland where they had pure religious freedom. The problem was that, as farmers, they had difficulty cultivating land, which is why they would inevitably move to America. Thus, they went for economic reasons and not religious reasons.
How did New England colonists migrate? What did they do democratically?
Largely as family groups, not for profit but to establish a society and family economies. Many died originally due to diseases but then they were able to establish a thriving economy centered on agriculture. Created the Mayflower Compact, which organized their government on the model of a self-governing church organization.
What were British Southern Atlantic colonies like?
The Caribbean was warm for most of the year, so long growing seasons existed. Tobacco and sugarcane became cash-crops.
What would the growth of sugarcane lead to?
The growth of sugarcane would cause a spike in the demand for enslaved people, leading the majority of the population or Barbados to be black. In response, the planter elites created slave codes which strictly regulated enslaved people and established them as property, or "chattel".
What were the middle colonies like?
Developed an export economy based on cereal crops. These colonies had a diverse population that overtime, became increasingly unequal.
What hierarchy existed in the middle colonies?
Urban merchants at the top, then artisans, then unskilled laborers/unemployed people, and at the bottom were enslaved africans.
Who was William Penn
A Quaker and Pacifist, founded Pennsylvania.
What was Pennsylvania like?
Religious freedom for all, mostly negotiated with the Indians.
What was a similarity in all the British colonies?
Fairly democratic governance. It was difficult to govern these colonies overseas so Britain let the colonies figure out their own governance.
What was the House of Burgesses?
A representative assembly within Virginia with the power to levy taxes on the population and pass laws.
What was Triangular Trade?
Merchants followed a generally three-part journey. As an example: merchants would start in England with rum, and would then go to West Africa for enslaved laborers for whom demand was spiking in the Americans, these enslaved laborers would go through middle passage to the West Indies, those slaves were traded for sugarcane, where they traded sugarcane for rum.
What was the Slave Trade Act?
The British Parlaiment passed the Slave Trade Act in 1800, which limited the number of slaves on a ship.
What was mercantilism? What was its goal?
The dominant economic system in Europe at this point. In the mercantilist world view, there was a fixed amount of wealth in the world, measured by gold and silver. The main goal of this system was to maintain a favorable balance of trade. Nations wanted more exports than imports.
Why was the establishment of colonies a benefit of mercantilism?
It gave mercantilists power to materials not in their own countries. Those colonies could become markets for their manufactured goods.
What were the Navigation Acts?
Required merchants to engage in trade with English colonies exclusively in English ships and also certain valuable trade items were required to pass exclusively through British ports where they were taxed. This was done to ensure that the British would have maximum gold and silver arriving.
How would trans-atlantic trade shape the economy?
Generated massive wealth for the elites of society, it would transform American seaports into thriving urban centers. This would cause a consumer revolution in North America.
What was the consumer revolution?
Societal status became more tied to financial success and a refined lifestyle.
What were Spanish interactions with Native Americans like originally?
The Spanish re-ordered people based on their ancestry with the Caste System. The Spanish disliked the Native Americans. The Spanish established Sante Fe as the capital of New Mexico in 1610. The Spanish employed brutal methods to convert Pueblos into Christianity which led to the Pueblo Revolt.
How did Spanish and British interactions with Native Americans differ?
The Spanish conquered areas with large existing empires, forcing present Native Americans to become part of the encomienda system. When the British showed up, they settled in places with no large empires and thus no large labor force that they could enslave. The English colonists initially coexisted peacefully with Native Americans, borrowing things from each other. The Spanish subjugated American Indians while the English forced them out.
What led to Metacom's War? What was Metacom's War?
The British encroachment on Native American land. Metacom, or King Philip, saw that the more the British settlers encroached, the more it would destroy their ancestral way of life, and therefore they should be sent away. King Philip led a rebellion, burning fields and killing colonists. In response, the British called upon the Mohawk Indians who ambushed and killed Metacom.
How did the French interact with the Native Americans?
The French were much less invasive. They saw the Natives as trade partners and military allies, leading them to maintain positive relations. The French also did not settle into colonial society, but instead established trading posts in order to facilitate the lucrative fur trade in the regions.
Why were Europeans not worried about the Native Americans?
Their cultures were so diverse and they sometimes lived in warring groups, leading Europeans to not worry about a unified resistance from them.
What were the reasons for the need for slaves in America?
The increased demand for colonial agricultural goods and the shortage of indentured servants to perform said agricultural labor.
How did Bacon's Rebellion lead to a reliance on African slavery?
White elites were worried about future alliances and uprisings between enslaved Africans and indentured servants, so they began to rely more fully on African slavery.
What was the enslaved African population like in New England?
In New England, their farms were generally smaller and had less enslaved Africans in comparison. All major port cities had a large number of enslaved people
What was the enslaved African population like in the Chesapeake colonies?
Higher amount of enslaved people needed for the emerging plantation system.
Where was the greatest population of enslaved Africans?
The British West Indies. The further south you go, the more of a reliance.
What is chattel slavery?
Race-based slavery.
What rules did slave laws create?
Legally defined African laborers as chattel (property), slavery was made a perpetual institution that was passed from one generation to the next, these laws would become harsher and harsher.
What slave resistance occurred?
Most enslaved people did not resign to their fate but actually found ways to resist this dehumanizing institution. Covertly, they secretly practiced cultural customs from their homeland, maintained belief systems, spoke native languages, kept naming practices from home, and damaged crops/tools. Overtly, they began to start rebellions.
What was the Stono Rebellion?
A small group of enslaved men stole weapons from a store and proceeded to kill the white owners of that store. Rebellions like these prove that the plantation owners were not being merciful when they enslaved people
What was the Enlightenment? Why did it expand to America?
A European movement that emphasized rational thinking over tradition and religious revelation. It emerged in America due to the robust print culture that allowed for a spread of ideas.
Who was John Locke?
Wrote the Two Treatises of Government, this awakened colonists to the ideas of natural rights.
What are natural rights?
The idea that humans, simply by virtue of existing, have rights to life, liberty, and property - given to them by a creator and not by a creator.
What is a social contract?
A social contract between the people and their government - the power to govern was in the hands of the people and they willingly gave that power to the government which would protect those rights. If the government did not respect their given power, the people had every right to revolt.
What was a result of Enlightenment thinking in the americas?
American colonies had confidence in the authority of biblical revelation. This would allow for the Great Awakening.
What was the Great Awakening?
A group of preachers were lamenting this loss of faith in the biblical revelation, and they were known as new light clergy. They were influenced by pietism, which emphasized the heart over the head in spiritual matters. The Great Awakening was a massive religious revival and generated an intense Christian devotion and enthusiasm.
What two men were vital to the Great Awakening? What did they do?
Jonathan Edwards: a New England Minister and scholar who preached sermons that combined enlightenment ideas with intense religious fervor. Lit the fire of the Great Awakening
George Whitfield: had been part of the Methodist revival in England. Spread the message of God’s salvation by grace to all the colonies. People flocked to hear him preach because he was such a powerful preacher.
What were social consequences to the Great Awakening?
New light preachers tended to emphasize the democratic tendencies in the bible. Preachers gave colonists biblical ballast to resist the tyranny of wealthy colonial officials. This environment led to lasting changes in the attitude of colonies towards the colonial authority. Many colonies formed self-governing structures.
What did Enlightenment thinkers and the Great Awakening lead to?
Ideas of liberty, rights, and democratic government. The Great Awakening created a movement that truly bounded American society together, teaching them to resist threats to democracy.
What is Anglicanization?
Colonists were becoming more British like.
What is an example of growing mistrust on both sides of the Atlantic?
The practice of impressment was the practice of seizing men and forcing them to serve in the royal navy. In 1747, Britain was fighting King George's War, and George ordered a general impressment of men and Americans rioted.
How were tribes in the Americas described?
Diverse, as they did many different things and had different ways of life.
Some farmed, created cities, were nomads, etc.
Who were the Aztecs? Where did they live? What are some characteristics of their society?
Civilization in Mexico (at its peak had 300,000 people).
Capital city at Tenochtitlan.
Had written language, complex irrigation systems, and human sacrifice.
Who were the Mayans? Where did they live? What are some characteristics of their society?
Civilization in Yucatan Peninsula Mexico
Had large cities, complex irrigation systems, and large stone temples for rulers/gods.
Who were the Inca? Where did they live? What are some characteristics of their society?
Civilization in Andes Mtns of Peru (at height ruled 16 million people and covered 350,000 square miles.
Had fertile mountain valleys and irrigation systems that were great for farming.
Which crop did the Aztecs, Mayans, and Inca grow? How did this affect their society?
Maize.
This supported them economically, socially, politically, this was their cash crop that made their civilization grow.
What are the similarities of the civilizations of the Aztecs, Mayans, and Inca?
All located in Central/South America and Mexico.
Maize was the cash crop.
All had complex cities, irrigation systems, writing, and lots of technological advancements along with great infrastructure.
Who were the Pueblo? Where did they live? What are some characteristics of their society?
Lived in present day Arizona and New Mexico.
Sedimentary farmers that built their homes in the open and in sides of cliffs (remember Pueblo National Park).
Highly organized society.
Maize
Corn
Where was maize popular?
Present day Mexico northward to Southwest
How did maize transform society?
Less emphasis on hunting and gathering, increase in population, est. permanent villages with socially diverse societies
What was the main type of lifestyle in the Great Plains and the Great Basin?
Hunting and gathering because of the aridity and lack if natural resources
Arid
Dry
What type of lifestyle was found in the Northeast, Mississippi River Valley and along the Atlantic?
A mix of agricultural and hunter gatherer economies that favored the development of permanent villages.
What is an example of a society being influenced by the economy?
The Iroquois were a matriarchal society because they were hunter gatherers. Women oversaw the crops and community affairs while the men were off hunting.
What were the societies of the Northwest and California based on?
Hunting, gathering and foraging
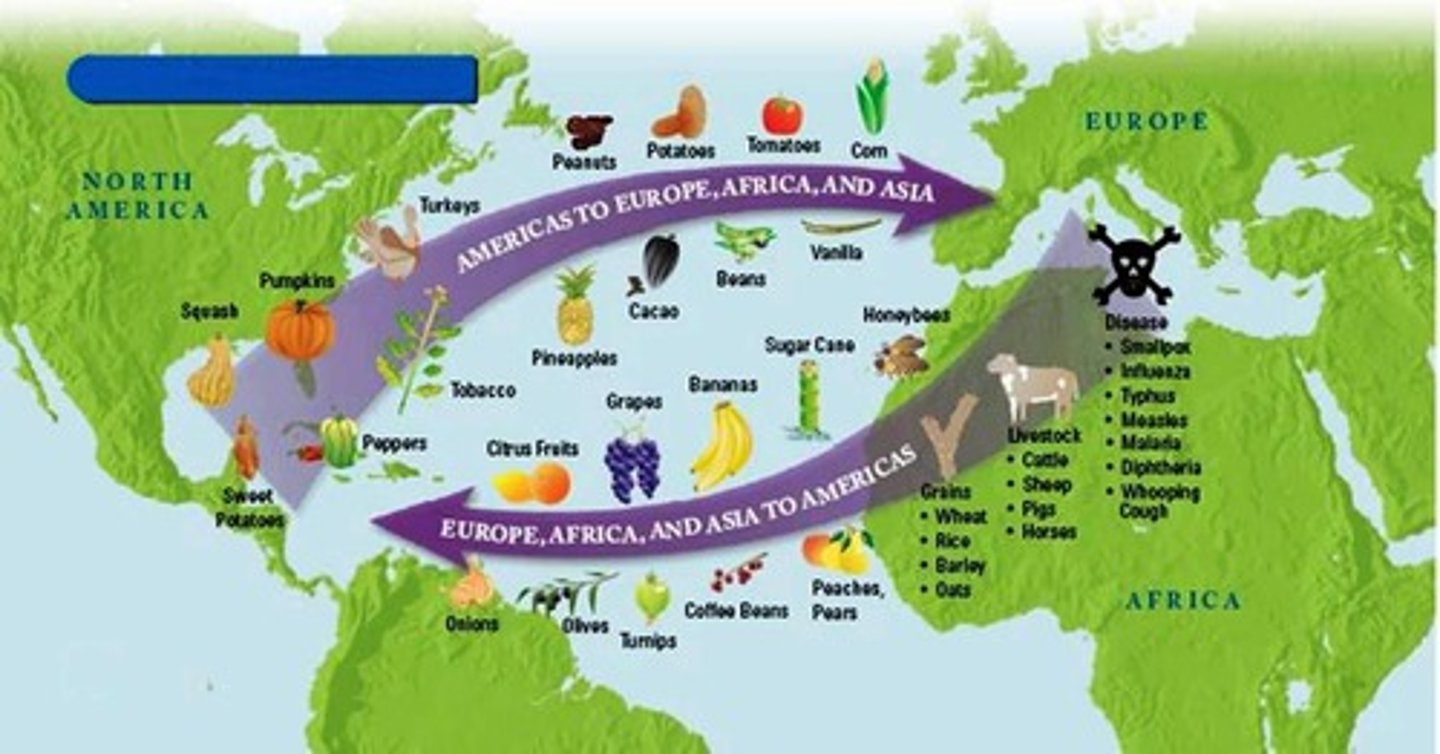
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, cultures, resources, languages, diseased and ideas between the Americas, Europe and Africa.
What triggered European nations' efforts to explore and conquer the New World?
3 gs: gold, glory (fame), god
Christopher Columbus
Italian mariner who in 1492 sailed west across the Atlantic Ocean in search of the Indies.
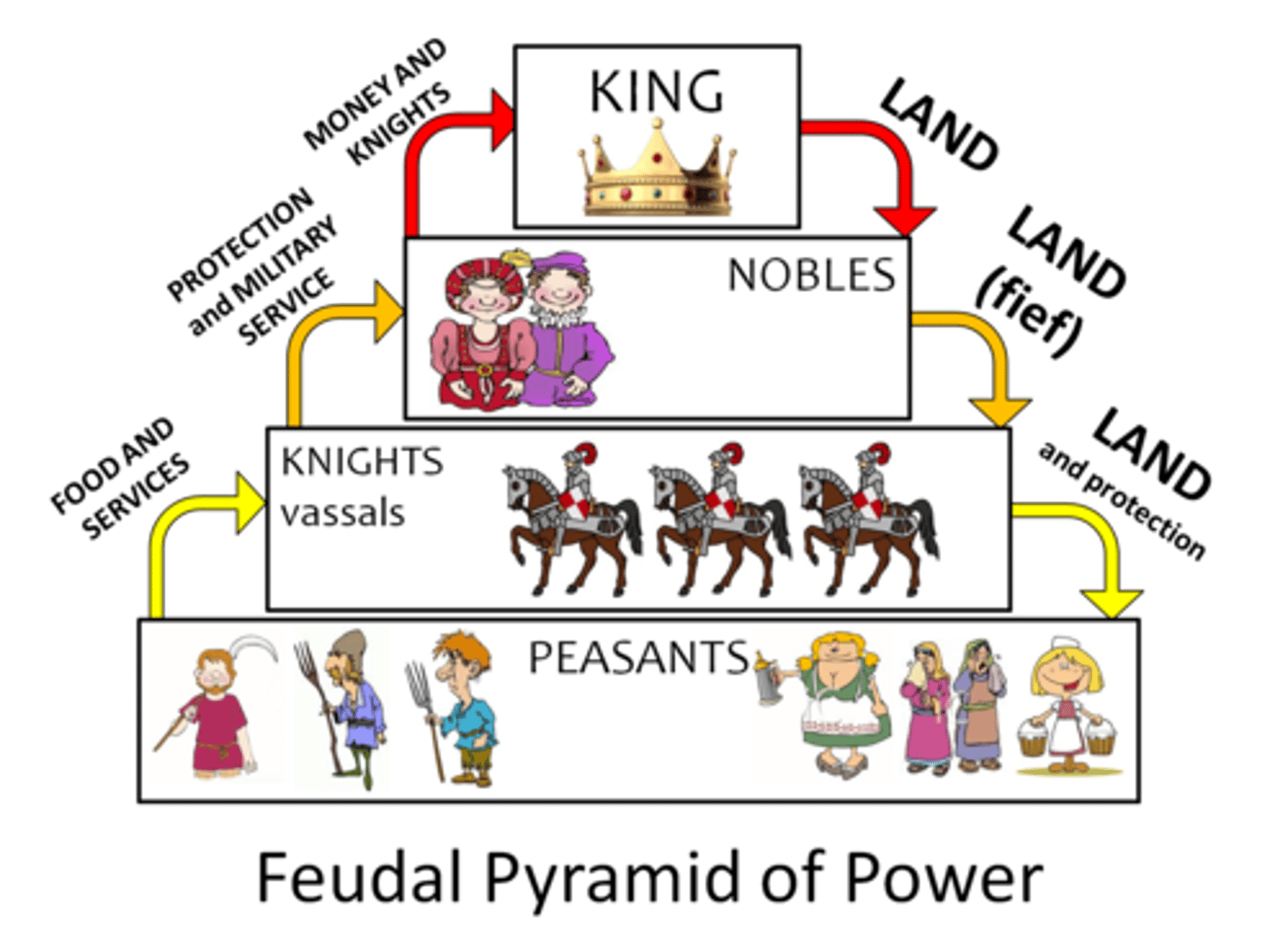
Feudalism
Political and economic system in medieval Europe, in which lesser lords received lands from powerful nobles in exchange for service.
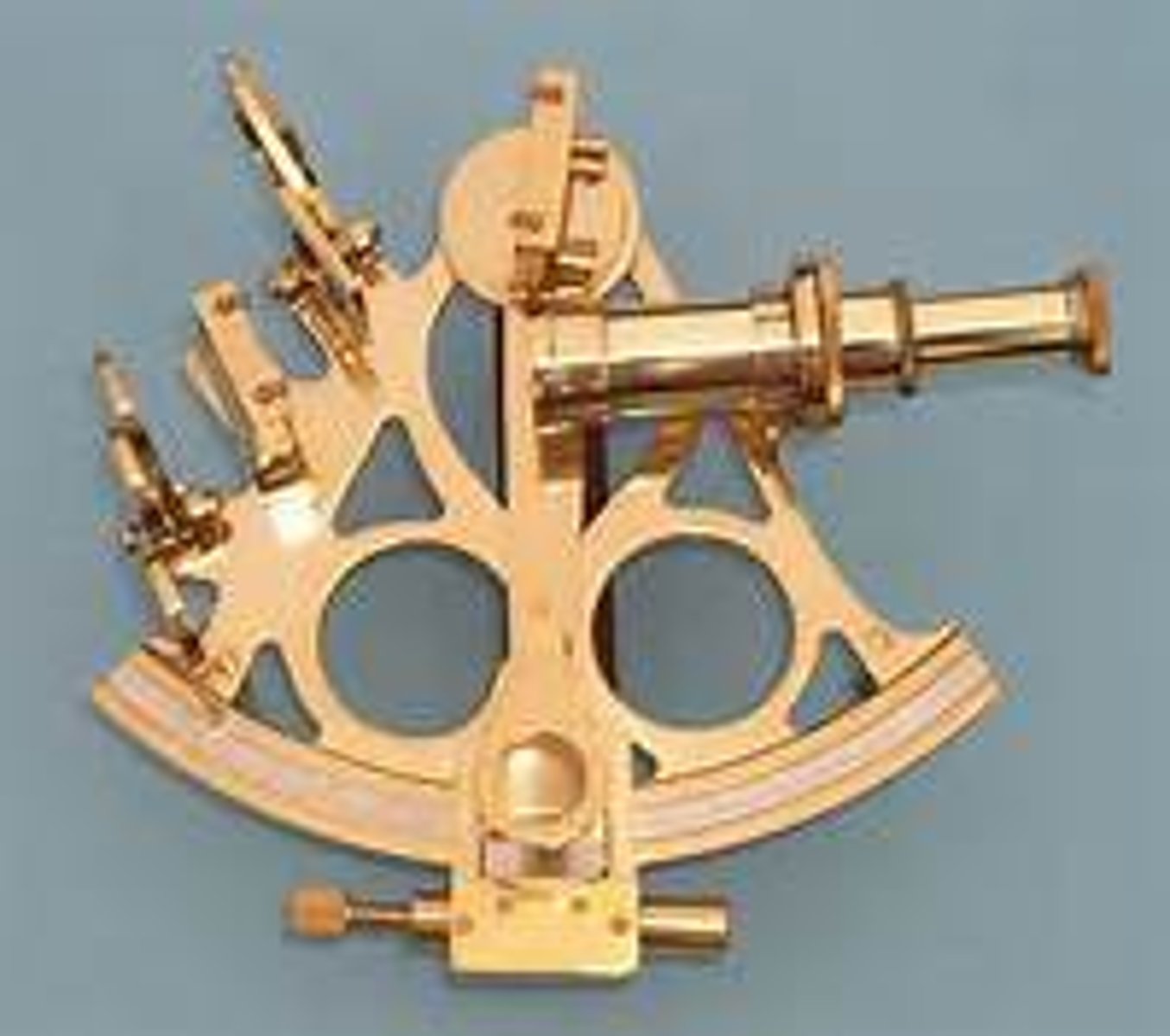
Sextant
A piece of technology that could be used to find the exact position on earth that allowed for more precise sailing.

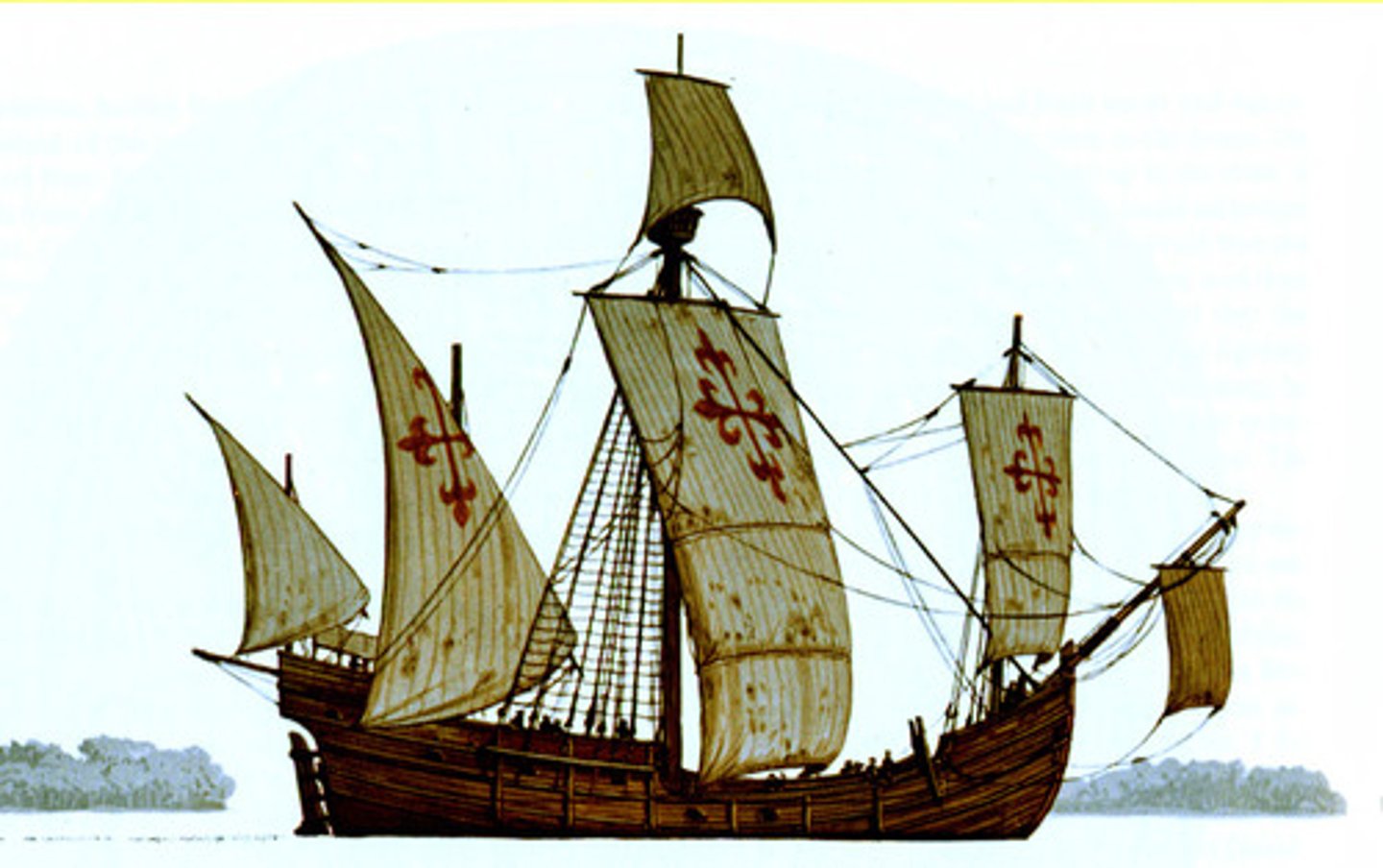
Caravel ship
Developed by the Portuguese that allowed for faster travel.

Joint Stock Company (with an example)
People would pool their money to raise money for explorations and would share the profits and losses of colonies. Ex. Jamestown in 1607

True or False: Spanish exploration and conquest of the Americas were accompanied by the deadly diseases and killed up to 90% of natives in some places.
True
How did the introduction of horses impact life on the Great Plains?
1) Some tribes became horse nomads
2) Hunting became more important as ranges increased
3) More frequent contact with other tribes caused an increased likelihood of competition and conflict
4) Wealth was sometimes measured by ones horses
5) could carry larger loads

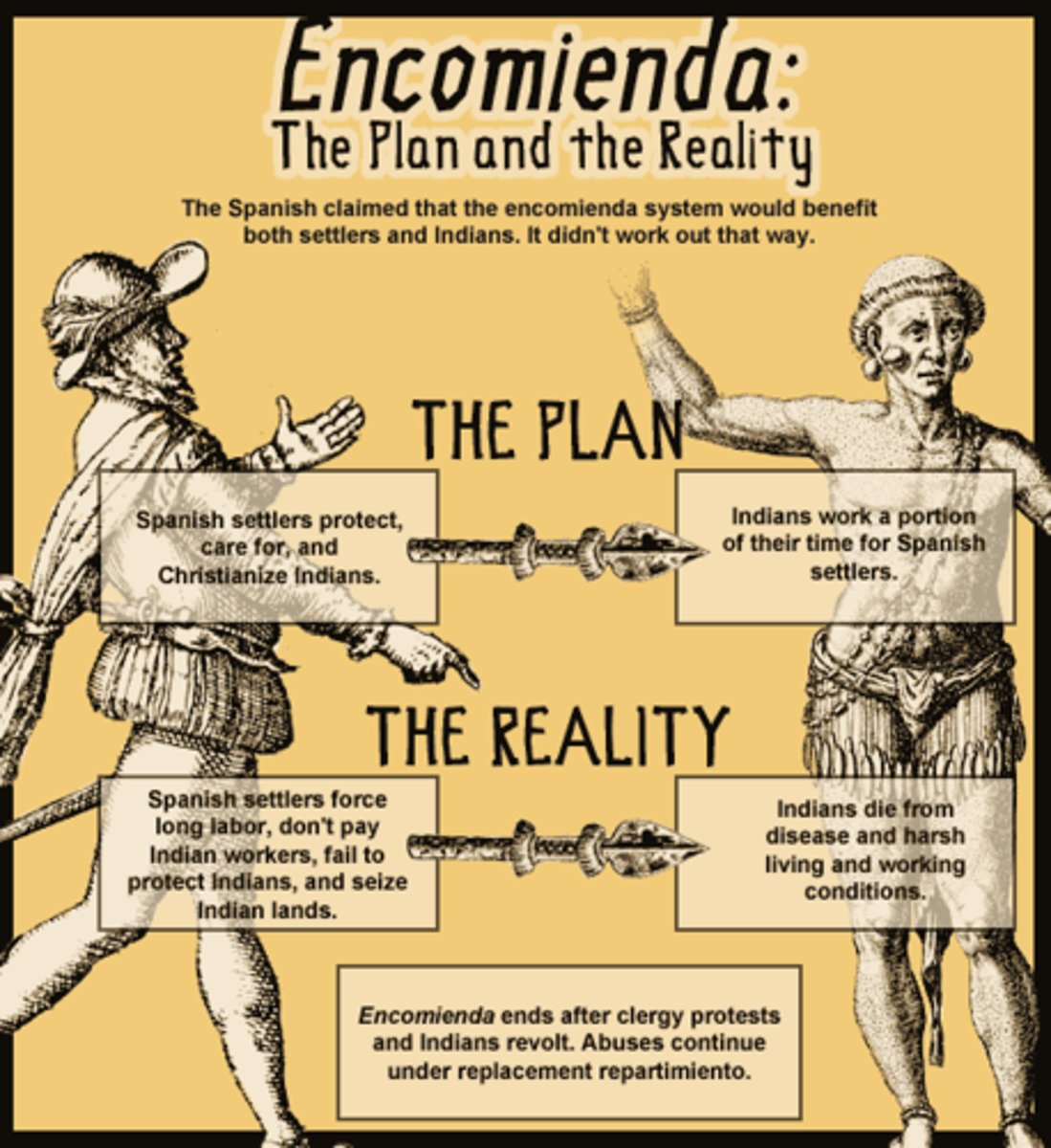
Encomienda System
Native American labor was marshaled (arranged, assembled) on plantations or in mines. It was later replaced by African slave labor.
When did the Atlantic slave trade being and by whom?
~1526 by the Portuguese
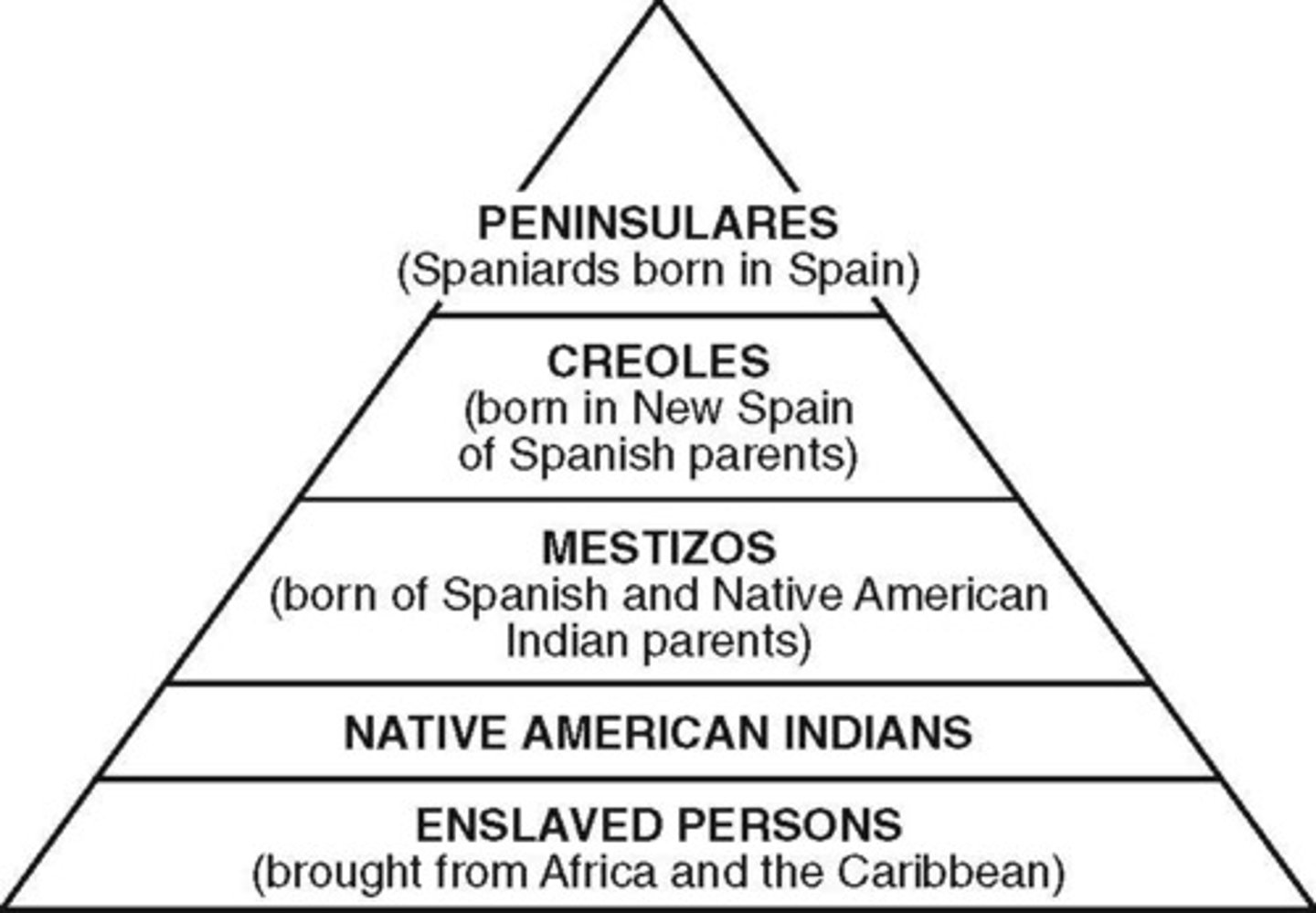
Caste System
Europeans from Europe (Peninsulares), Europes born in Central America (Creoles), Mixed (Mestizo, mulatos)
True or False: Columbus was the first European to America.
False, the Vikings were there first.
Black Legend
Propaganda to challenge the treatment of natives by the Spanish in the colonies.
Juan de Sepulveda
Advocated for the harsh treatment of natives and stated that slavery was justified in Christianity.
Bartoleme de Las Casa
Advocated for better treatment of natives and contributed to the Black Legend.

What were some ways that poor treatment of Africans and Natives was justified?
Racism, religious (spread of Christianity), seen as barbaric
Protestant Reformation 1517-1685
Started by Martin Luther's 95 Theses it was the challenging of Catholicism and the beginning of Protestant Christianity.

Hacienda
A great farm or ranch
Hernando Cortes
The leader of the Spanish conquistadors, he invaded and destroyed the Aztecs
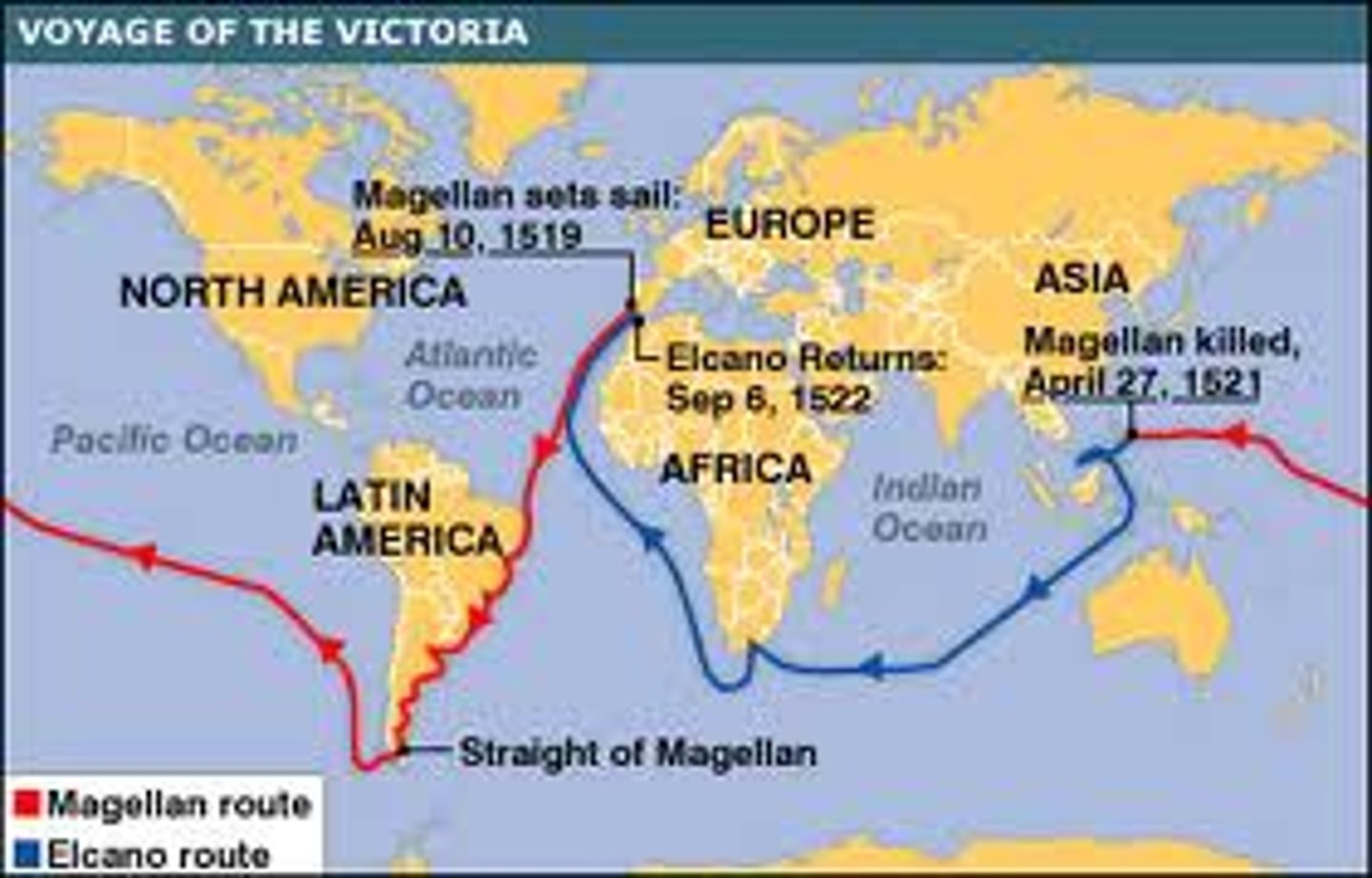
Ferdinand Magellan
Portuguese seaman, who in the employ of Spain set out to find passage through or around South America, and consequently led the first voyage around the globe.
Amerigo Vespucci
Italian explorer who first suggested that South America was a new continent.
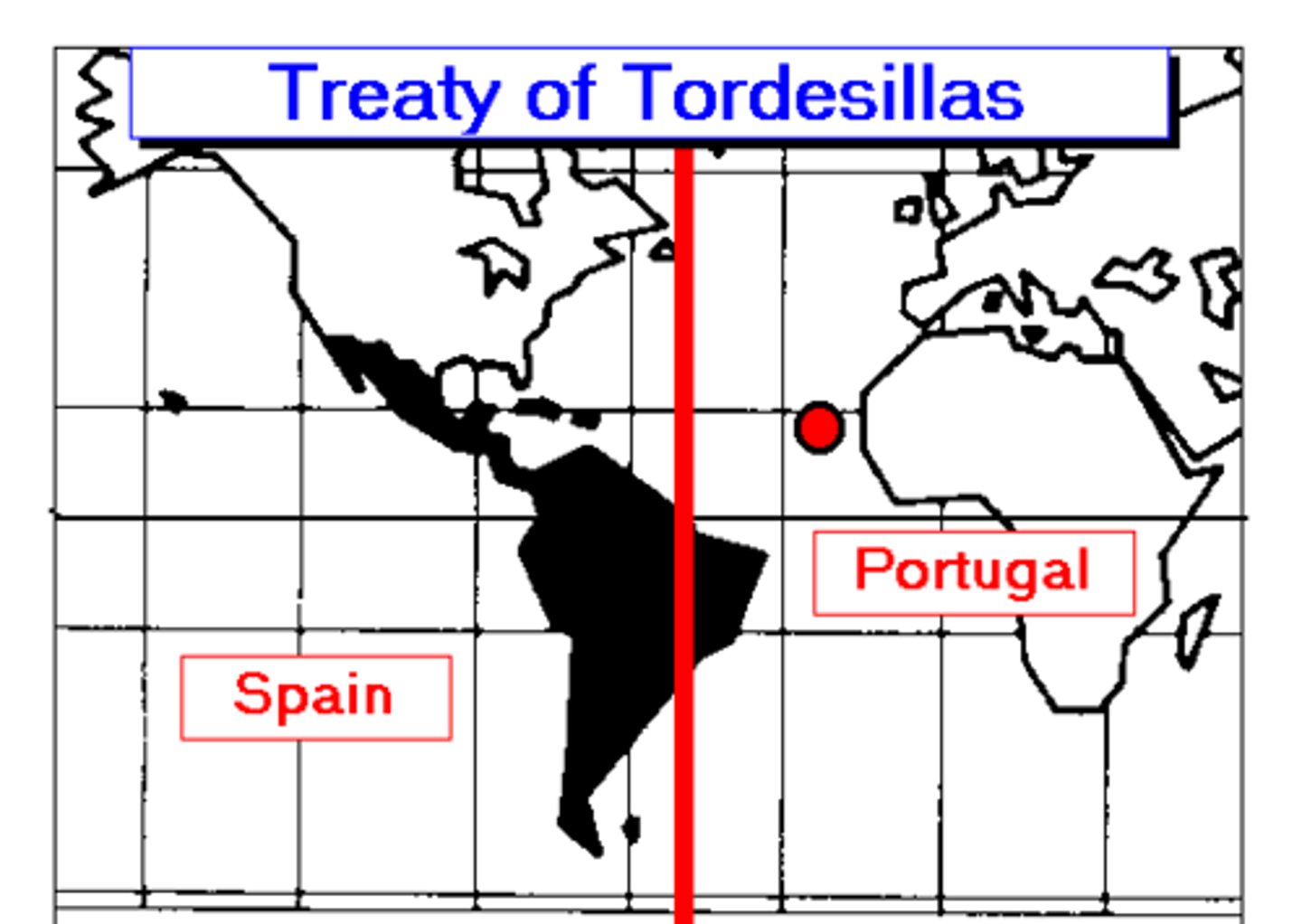
Treaty of Tordesillas
Treaty between Spain and Portugal defining the Spanish claim on exploration and settlement west of the Cape Verde Islands in 1494.
Reniassance
Period in European history from 12th C AD through the 16th C AD distinguished by its spirit of inquiry and return to secular learning.