Lost Ground - Subsidence, Collapse, Karst, and Thermokarst
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
1
New cards
what is subsidence?
* relatively slow downward movement of land, typically at rates of cm/yr
2
New cards
what is a collapse?
* rapid movement of land, ranging from cm/hr to m/s of material disappearing almost instantaneously
3
New cards
what is a karst?
* topography resulting from dissolution of limestone rocks by water
4
New cards
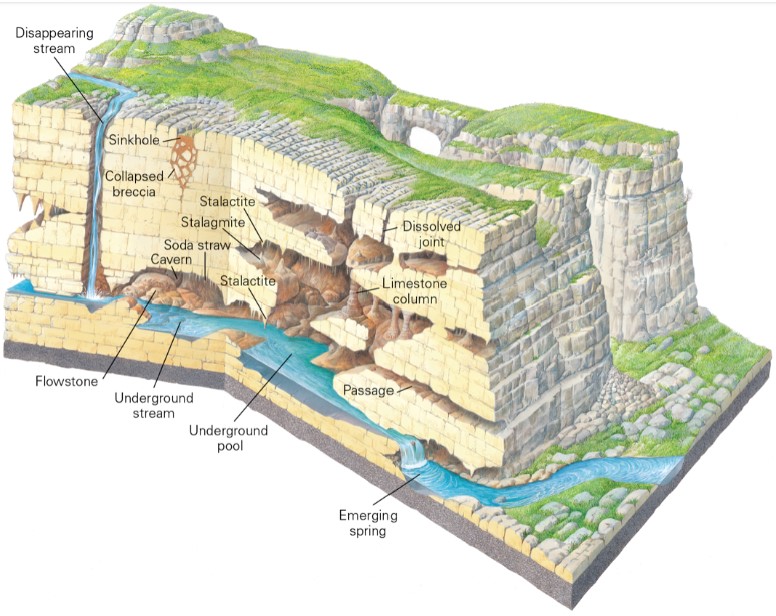
what are some characteristic terrain of karst?
* sinkholes
* ground depression caused by collapse into an underground cavern
* caverns
* large natural underground cave or tunnel
* limestone columns
* can be due to percolation
* ground depression caused by collapse into an underground cavern
* caverns
* large natural underground cave or tunnel
* limestone columns
* can be due to percolation
5
New cards
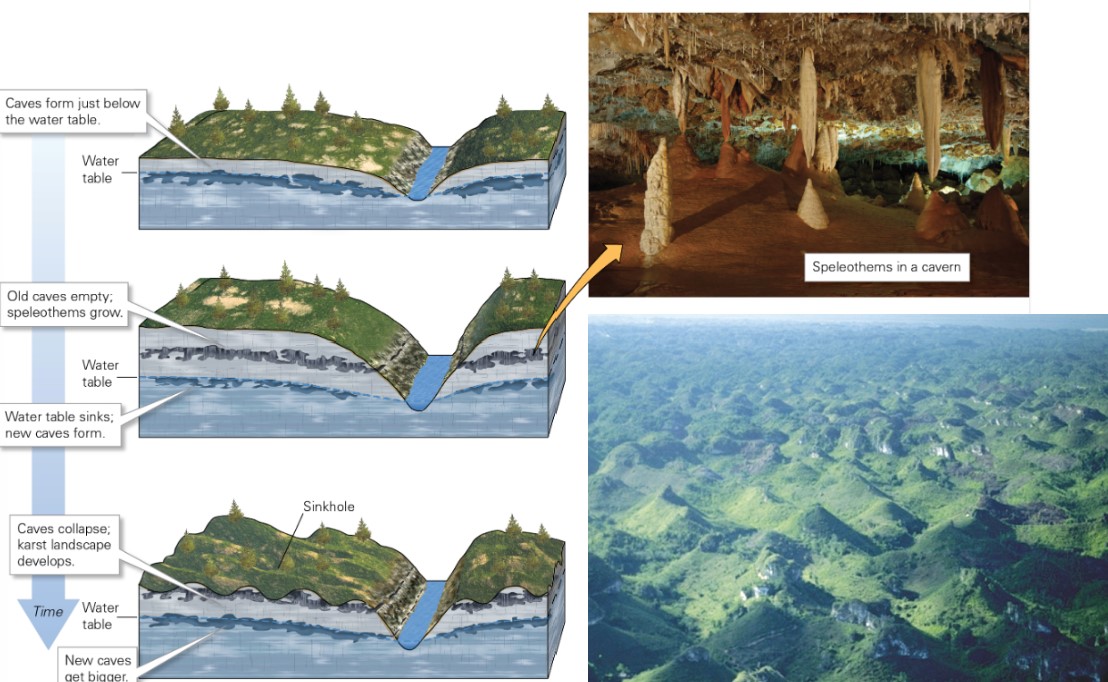
karst
* water flows fastest where water most acidic → at water table
* sometimes top part collapses → sinks
* sometimes top part collapses → sinks
6
New cards
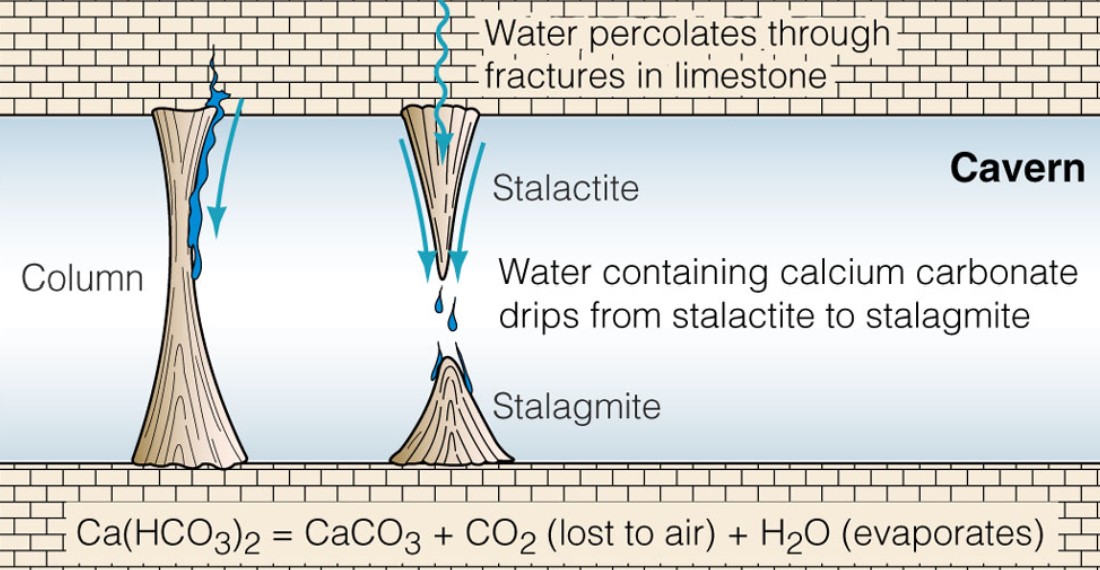
what can we fin in caverns?
* stalactites
* stalagmites
* stalagmites
7
New cards
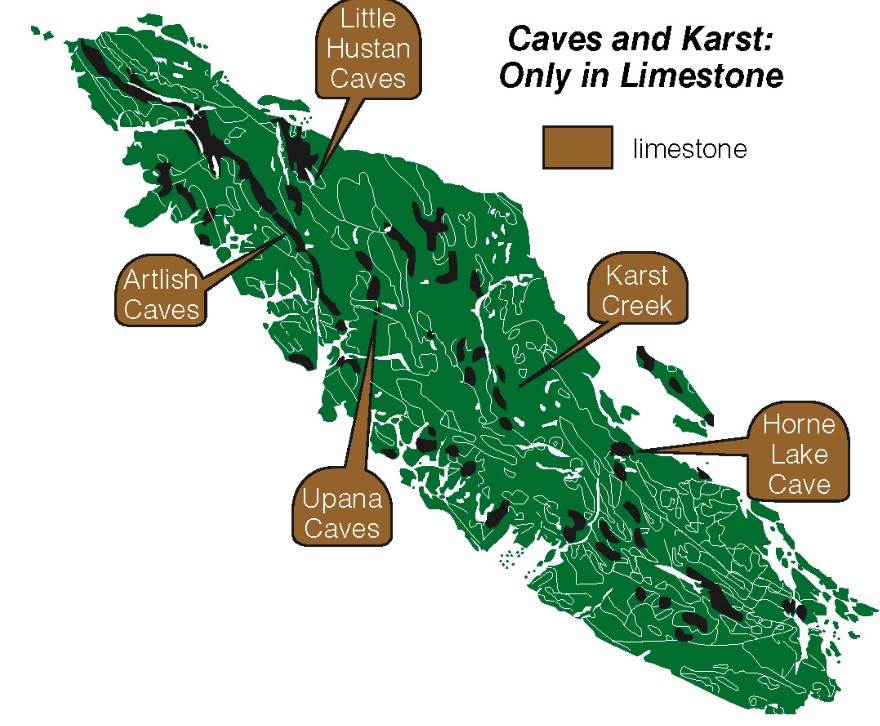
cavern and karst examples?
* limestone cavern in Kentucky, USA
* Mammoth Cave National Park
* Eramosa Karst, Hamilton ON
* BC is conc in belt where limestone occurs near the surface
* Mammoth Cave National Park
* Eramosa Karst, Hamilton ON
* BC is conc in belt where limestone occurs near the surface
8
New cards
what are collapse sinkholes?
* formed when weak rock overlying a cavern collapses
* water holds up struct, so when water table drops → can fall
* also when top is heavy (from building and heavy rainfall)
* these r the most dangerous kinds of sinkholes
* water holds up struct, so when water table drops → can fall
* also when top is heavy (from building and heavy rainfall)
* these r the most dangerous kinds of sinkholes
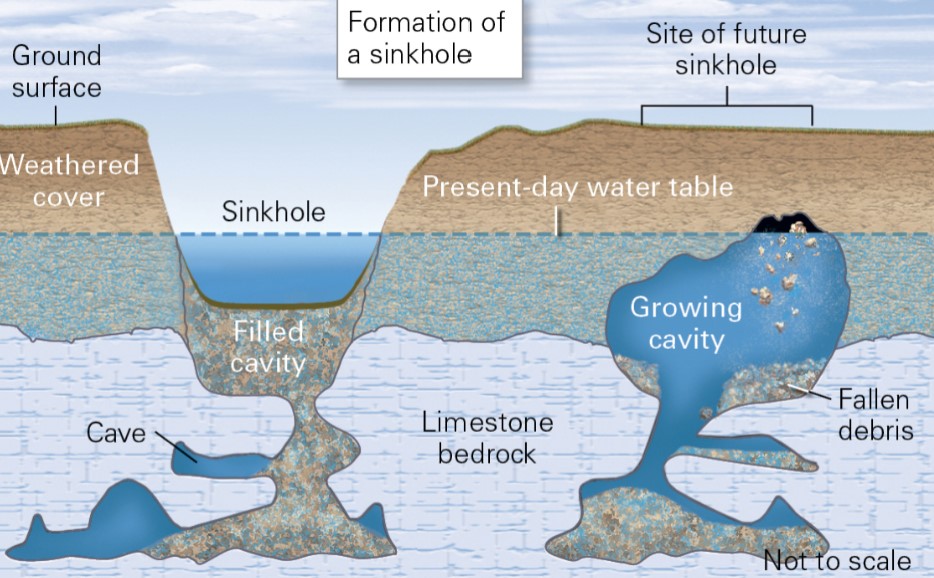
9
New cards
what is a dissolution sinkhole?
* depression formed from dissolution of rock at the ground surface
* leads to more economic damage
* leads to more economic damage
10
New cards
what is a cover-subsidence sinkhole?
depression formed when loose sediment at the surface washes into caverns or voids below
11
New cards
climate factors for karst?
* rainfall
* water is the driving force behind dissolution
* temperature
* limestone and dolostone dissolve more readily in cold water
* vegetation:
* plants can make water more acidic = rocks dissolve more readily
* soil type
* influences the permeability of land surface
* water is the driving force behind dissolution
* temperature
* limestone and dolostone dissolve more readily in cold water
* vegetation:
* plants can make water more acidic = rocks dissolve more readily
* soil type
* influences the permeability of land surface
12
New cards
karst topography in Minerve, France

13
New cards
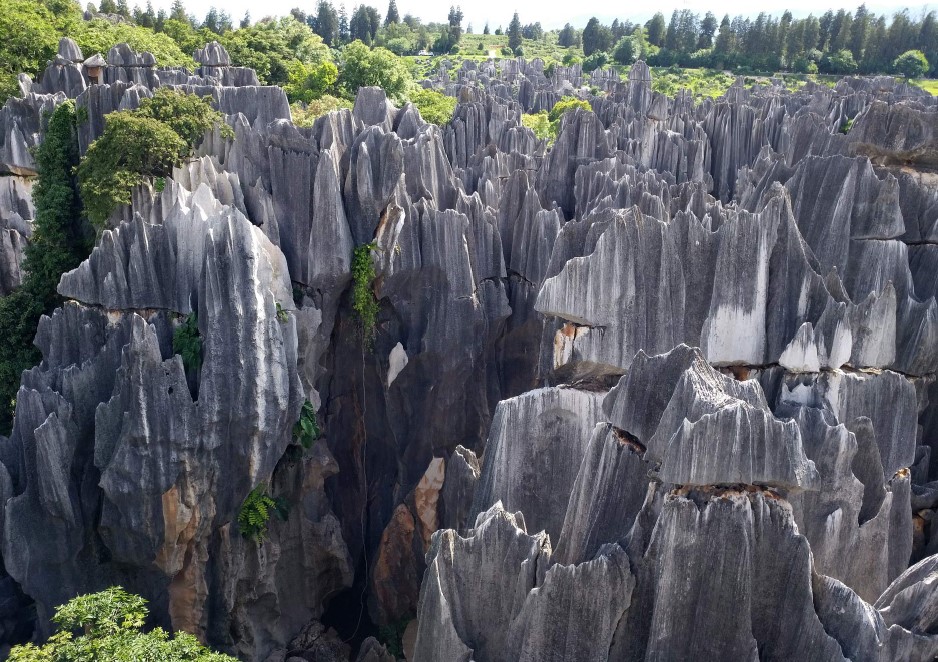
extreme Karst weathering in Stone Forest, south of Kunming, China

14
New cards
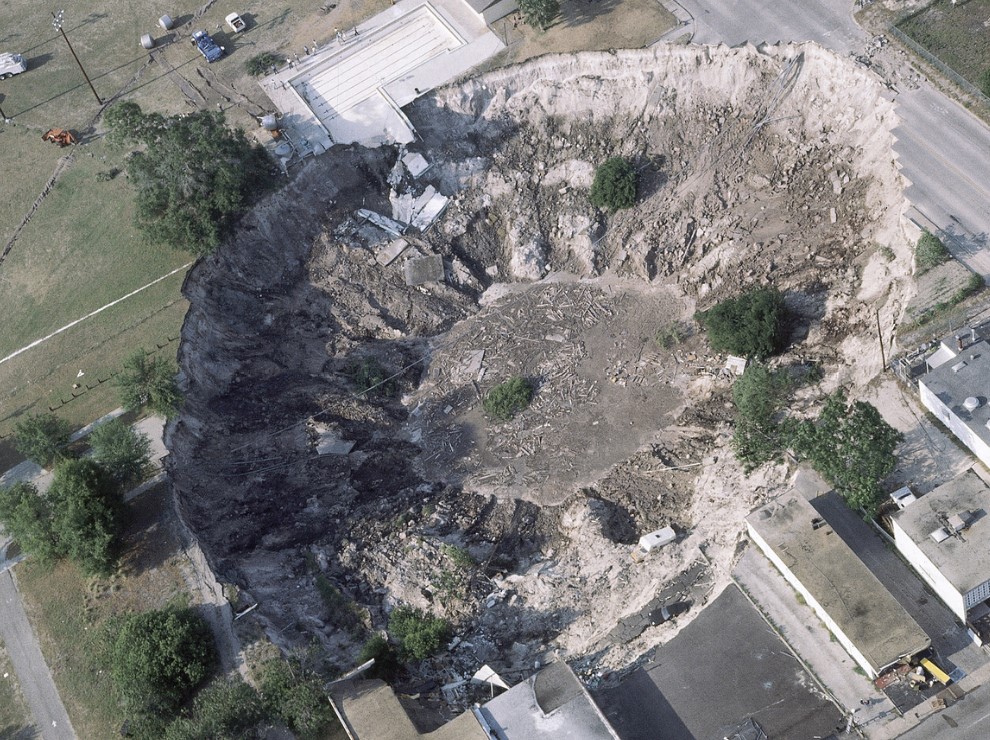
winter park, Florida, sinkhole; 1981

15
New cards
large sinkhole opened under this house in Sebring, Florida, leaving it buckled in the middle and full of water
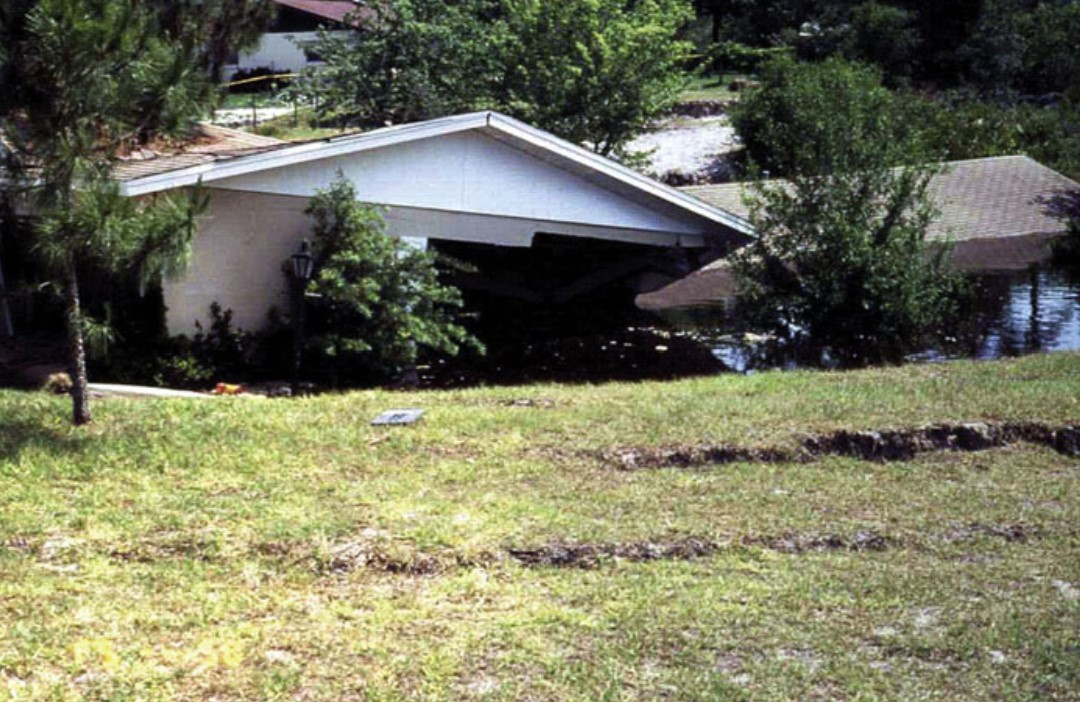

16
New cards
Guatemala, 2010 - sinkhole caused by floodwaters from tropical storm Agatha; 20m wide and 30 stories deep
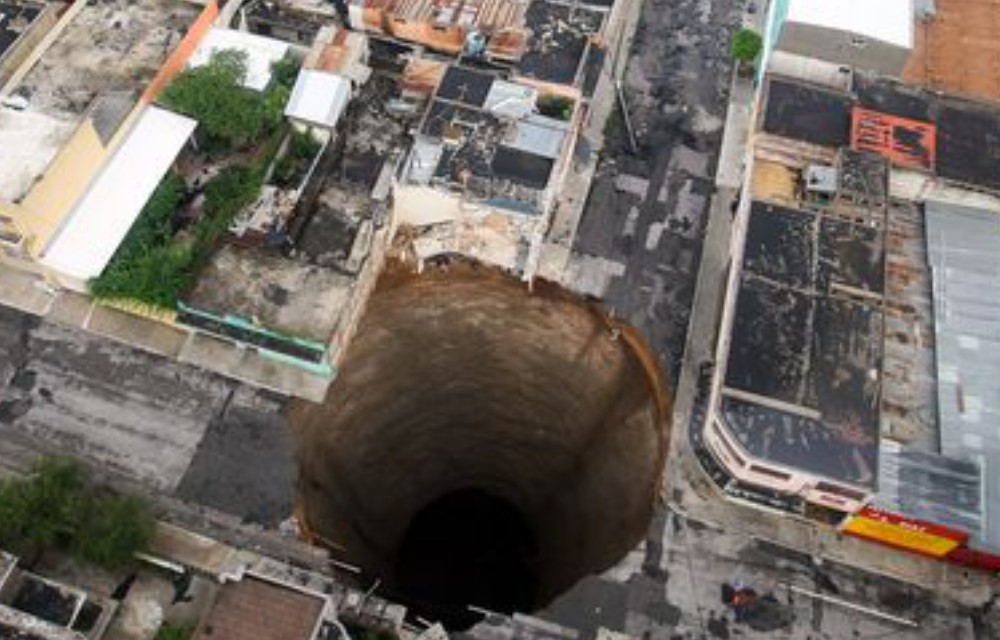

17
New cards
what is subsidence?
* the settling of the ground in response to:
* extraction of groundwater
* can also cause irreversible permanent reduction in aquifer porosity, permeability & storage
* extraction of oil
* drying of peat
* extraction of groundwater
* can also cause irreversible permanent reduction in aquifer porosity, permeability & storage
* extraction of oil
* drying of peat
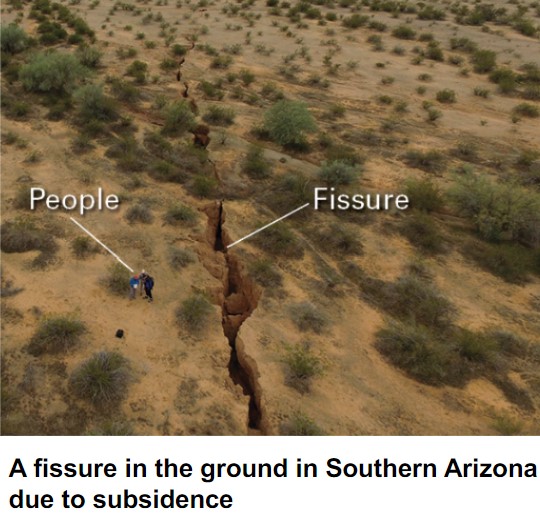
18
New cards
what happens when groundwater is extracted in relation to subsidence?
* pore spaces collapses, and the ground subsides
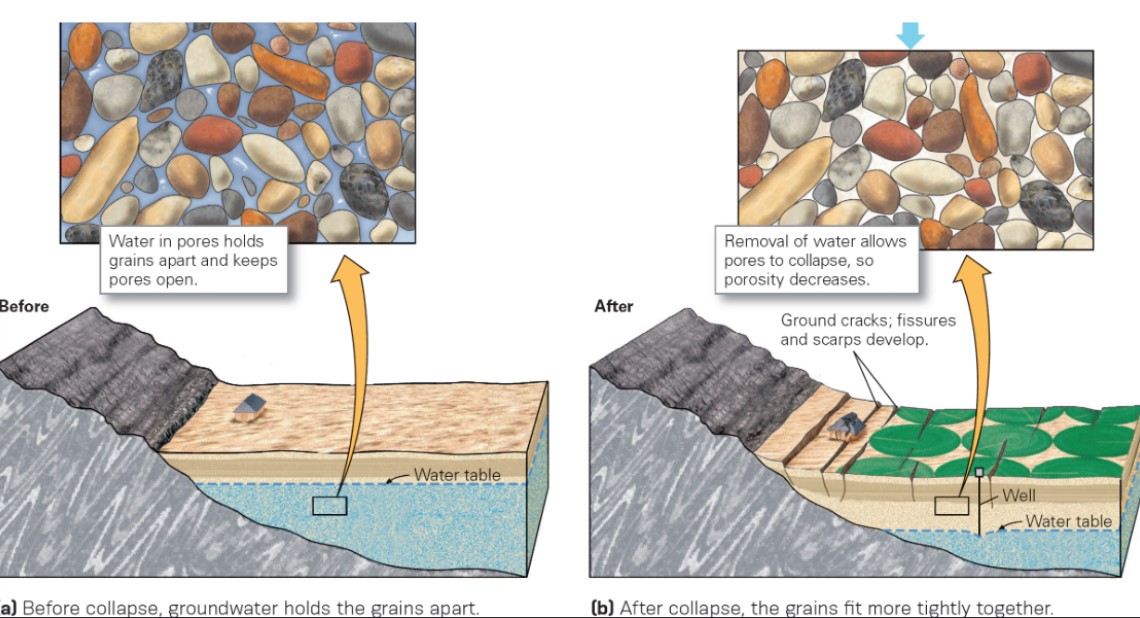
19
New cards
Groundwater pumping in Santa Clara, California (green) and land subsidence (brown)
\
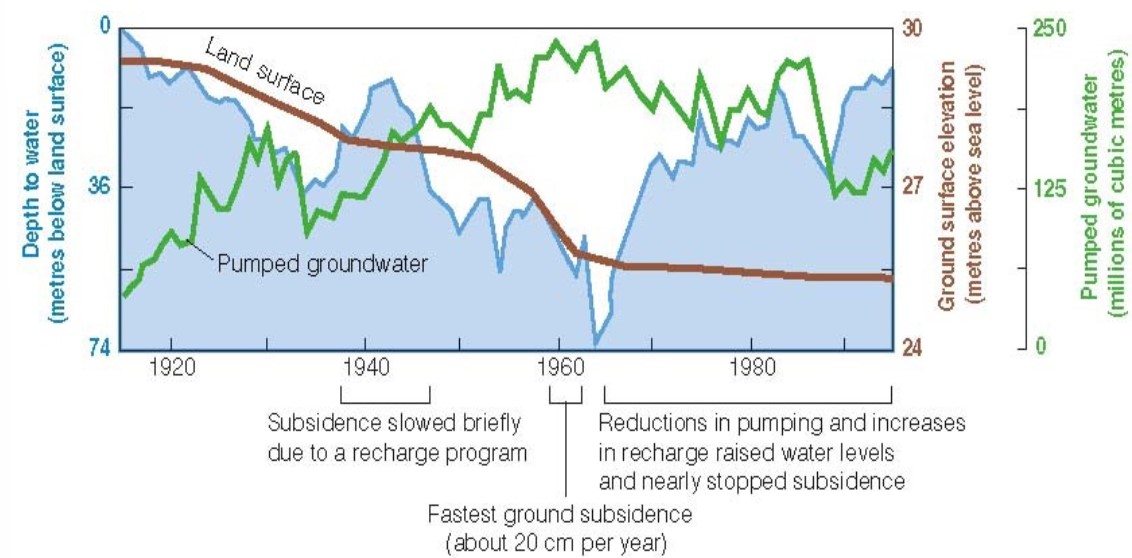
20
New cards
what is subsidence is semi-arid Sacramento-San Joaquin caused by?
* groundwater pumping for crop irrigation
* decomposition or organic matter in the sediments from agricultural activities
* decomposition or organic matter in the sediments from agricultural activities

21
New cards
what has subsidence in Mexico city caused?
* buildings to wrap → caused by groundwater extraction to support pop
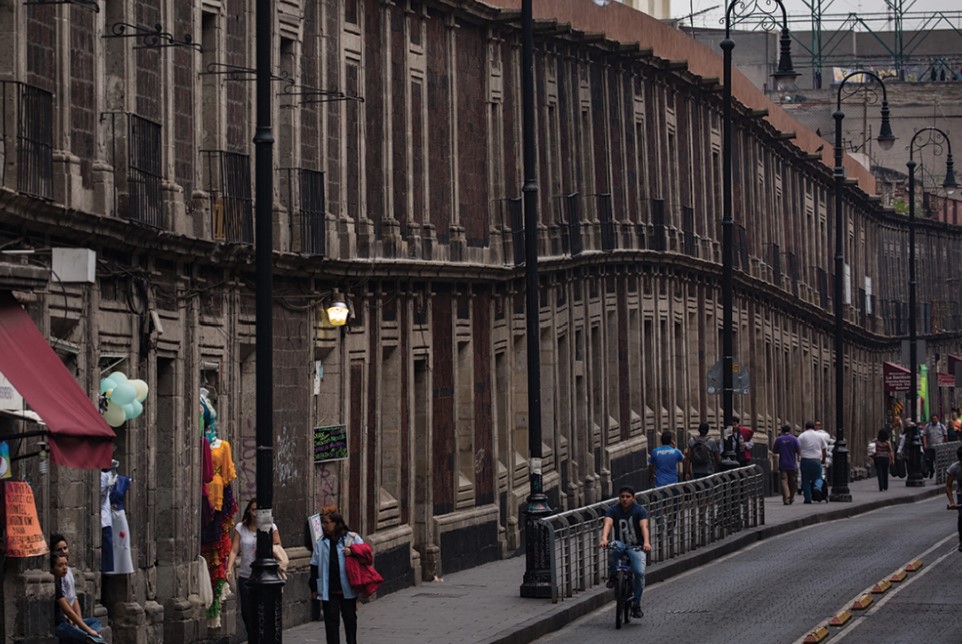

22
New cards
reason for leaning tower of Pisa leaning?
* built on marine clay that is spreading apart
23
New cards
what is subsidence of the Mississippi delta caused by?
* oil and gas extraction
24
New cards
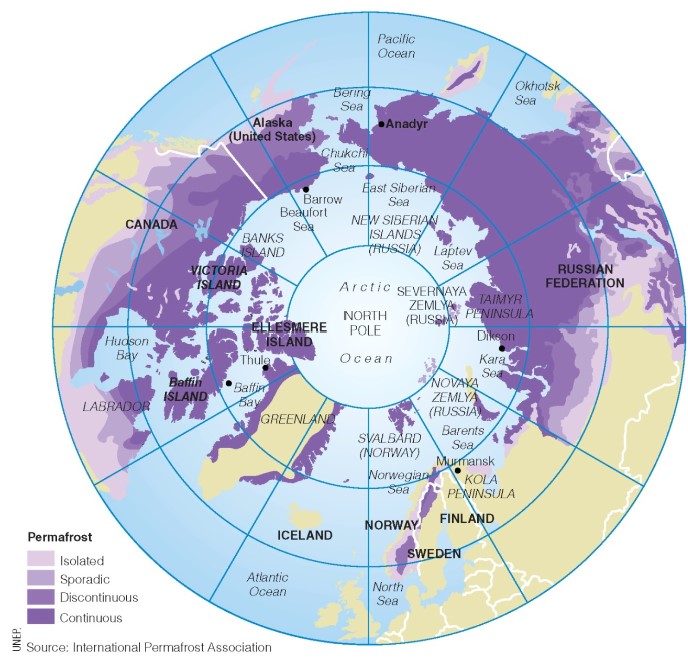
what is permafrost?
* ground that remains frozen (below 0 C) for at least 2 consecutive yrs
25
New cards
what is interstitial ice?
* ice that crystallizes in pores between grains of sediment
* picture: Mudflow formed by melting interstitial ice in permafrost, Mackenzie River near Inuvik, Northwest Territories
* picture: Mudflow formed by melting interstitial ice in permafrost, Mackenzie River near Inuvik, Northwest Territories
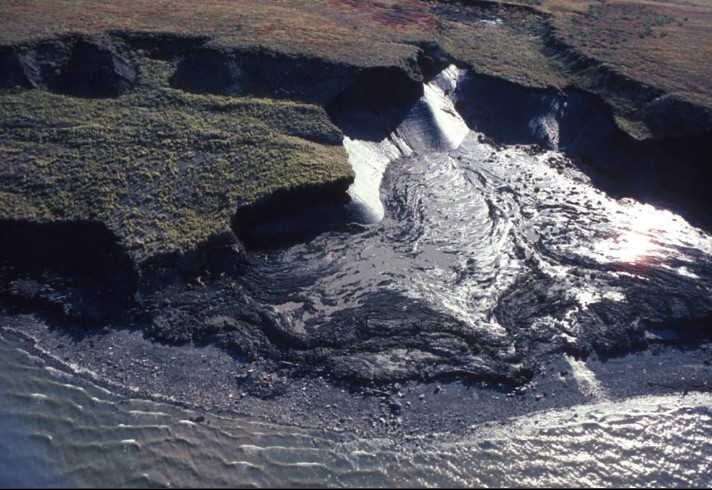

26
New cards
what is segregated ice?
* lenses of pure ice dev in permafrost sediment
* pic: southern Banks Island, Northwest Territories
* pic: southern Banks Island, Northwest Territories
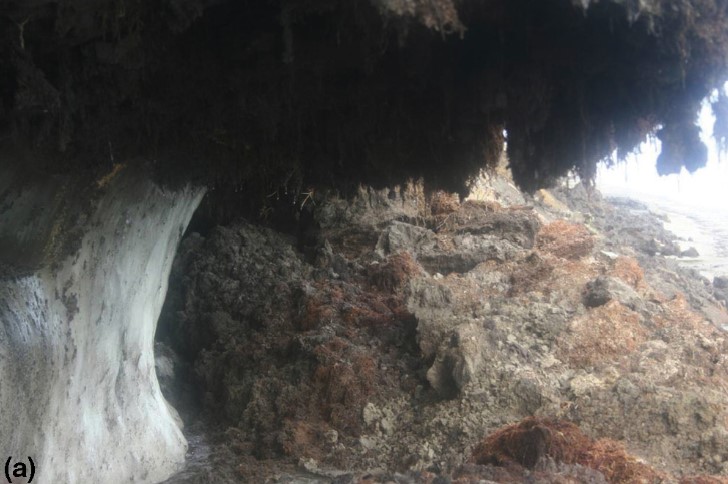

27
New cards
what is an ice wedge?
* wedge-shaped accumulation of ice in permafrost regions; formed from freeze-thaw cycles

28
New cards
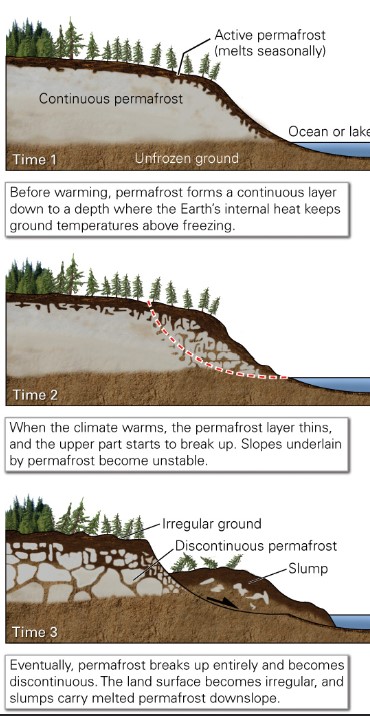
what is permafrost (interstitial and segregated ice) melting caused by?
* land subsidence
* slumping
* mudflows
* slumping
* mudflows
29
New cards
As segregated ice lenses melt, they trigger mudflows and result in erosion.
Sachs Harbour area, Banks Island, Northwest Territories
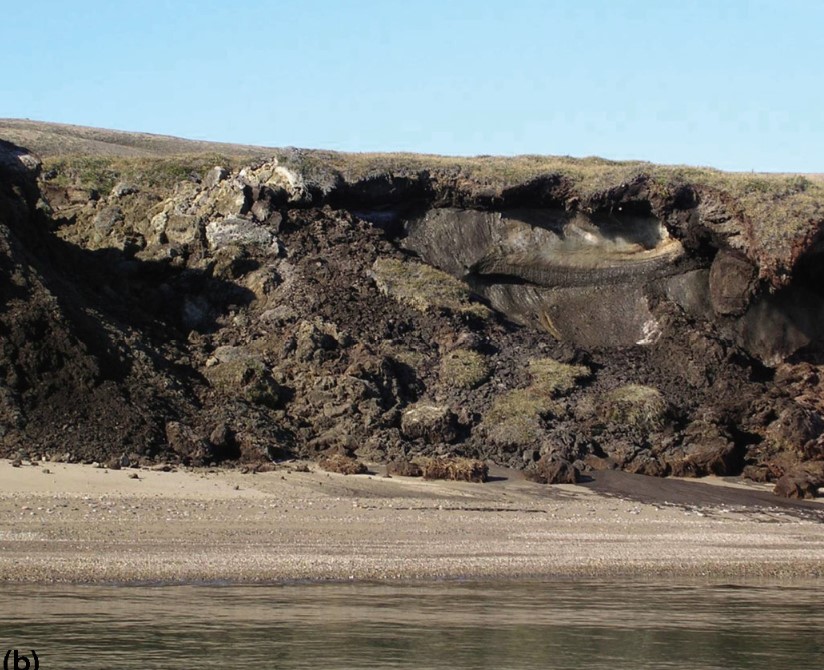

30
New cards
Evidence of Permafrost melting in Drew, Point, Alaska
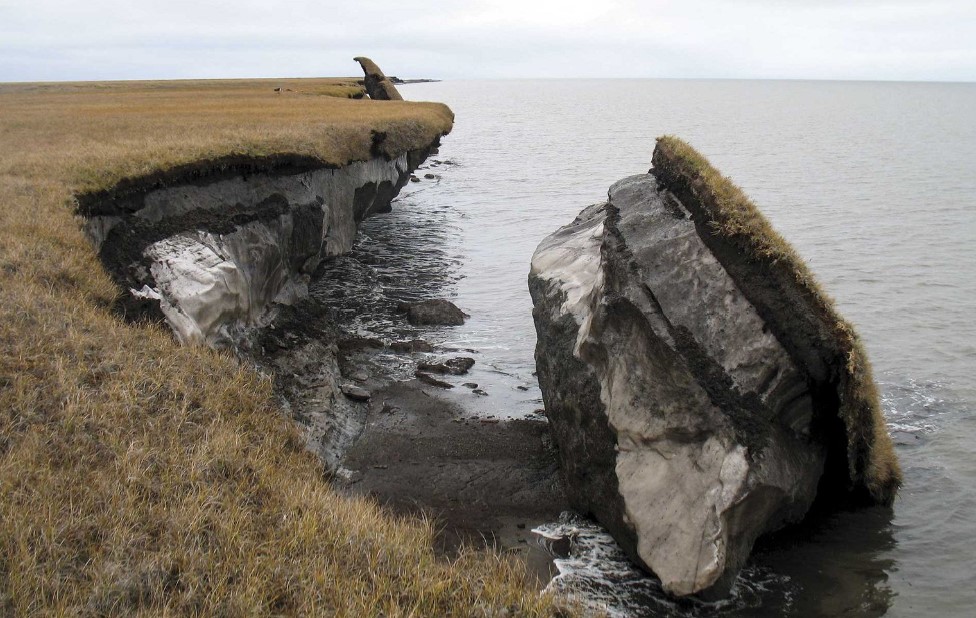

31
New cards
An eroding thermokarst shoreline, Pelly Island, NWT

32
New cards
This oil pipeline in northern Alberta was constructed across discontinuous permafrost. To keep the oil flowing, the pipeline was heated and the heat melted the underlying permafrost.
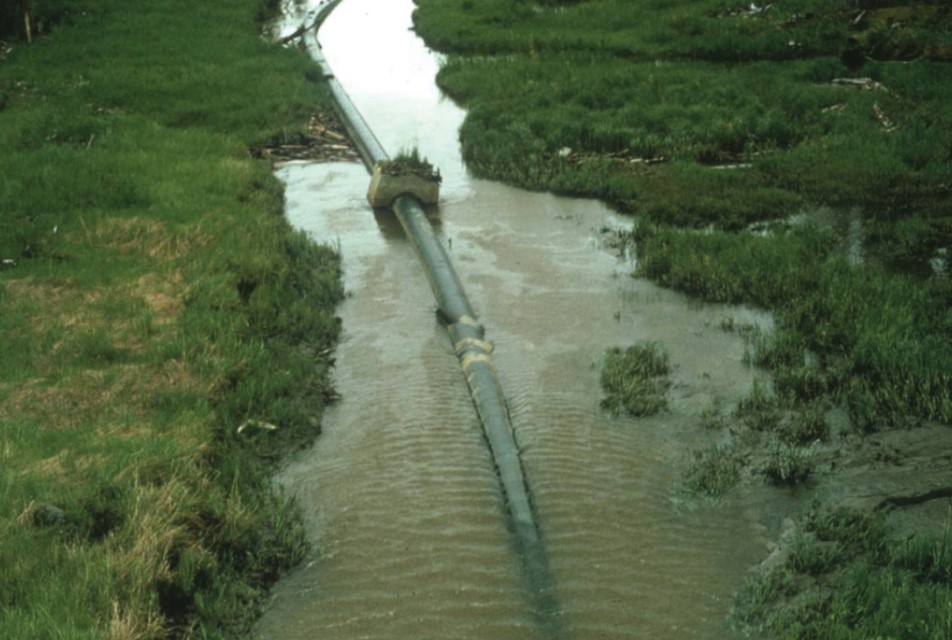

33
New cards
Permafrost melting has caused this house to sink
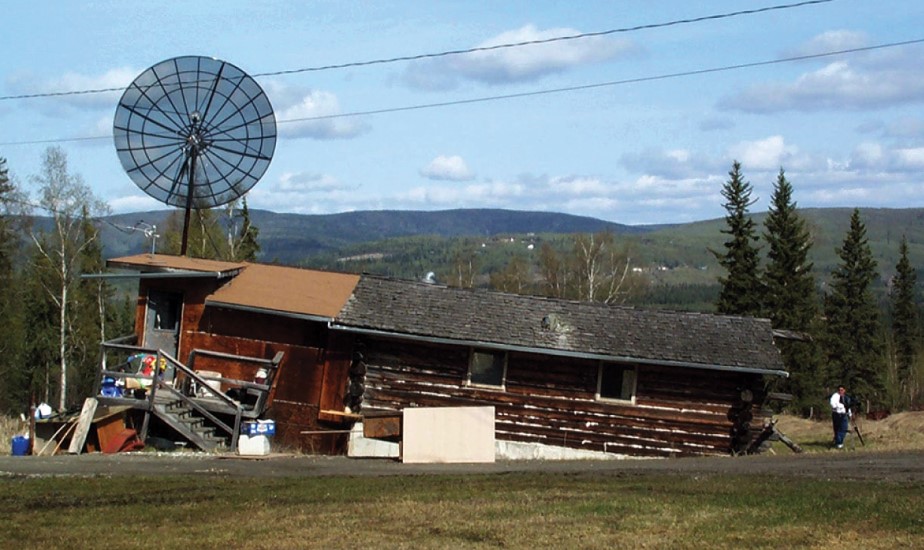

34
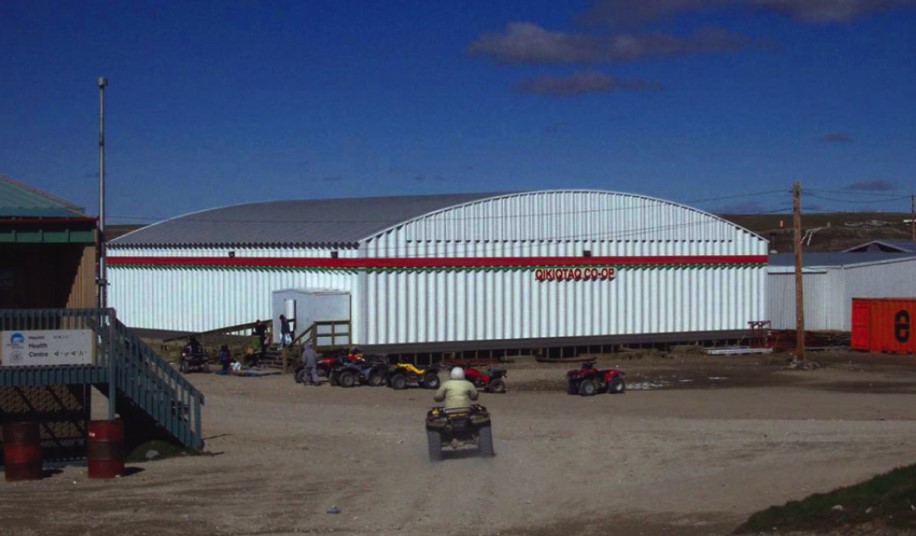
New cards
he community Qikiqtaq Co-op (centre), the community health centre (left) and other buildings in Gjoa Haven, Nunavut, are elevated above the ground to isolate their heat from the underlying permafrost

35
New cards
what is a thermokarst?
* karst-like landscape in permafrost terrain caused by melting of permafrost under increasing temperatures
* NOT related to limestone
* NOT related to limestone
36
New cards
causes of thermokarst?
* warming climate
* erosion along coastlines and rivers when ice-rich sediment is exposed
* heating of ground surface
* vegetation removal
* erosion along coastlines and rivers when ice-rich sediment is exposed
* heating of ground surface
* vegetation removal
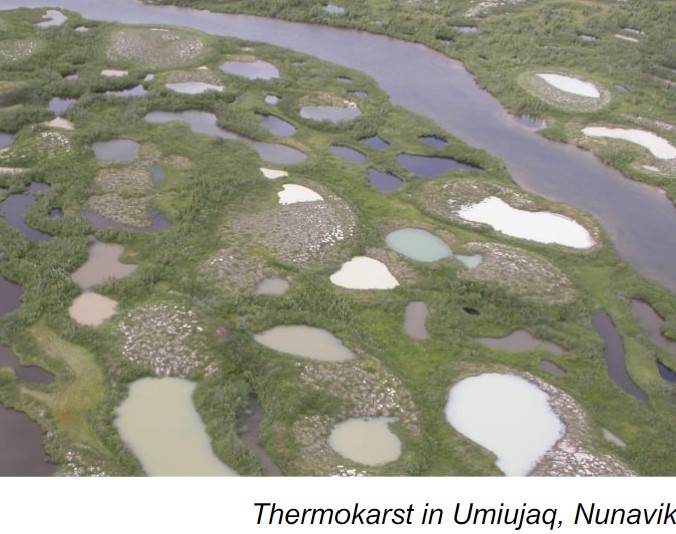

37
New cards
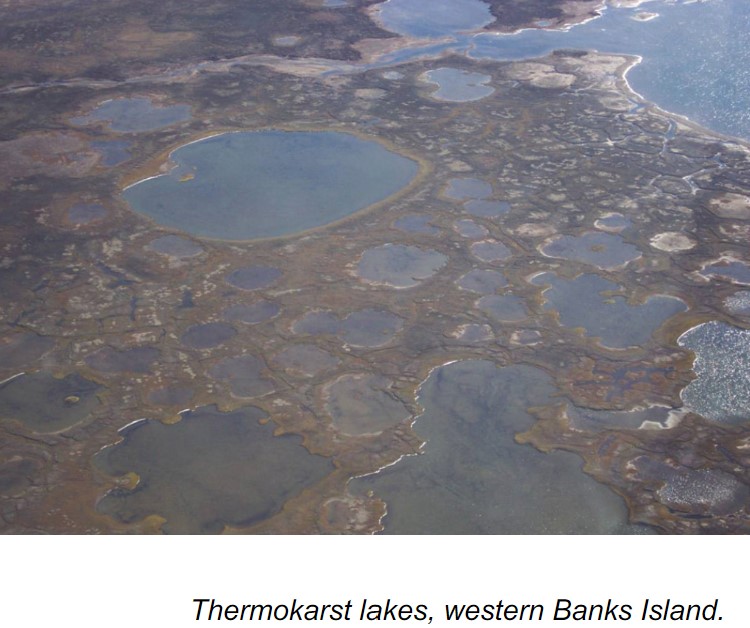
what are thermokarst lakes?
* circular, oval or square lakes from by thermokarst melting

38
New cards
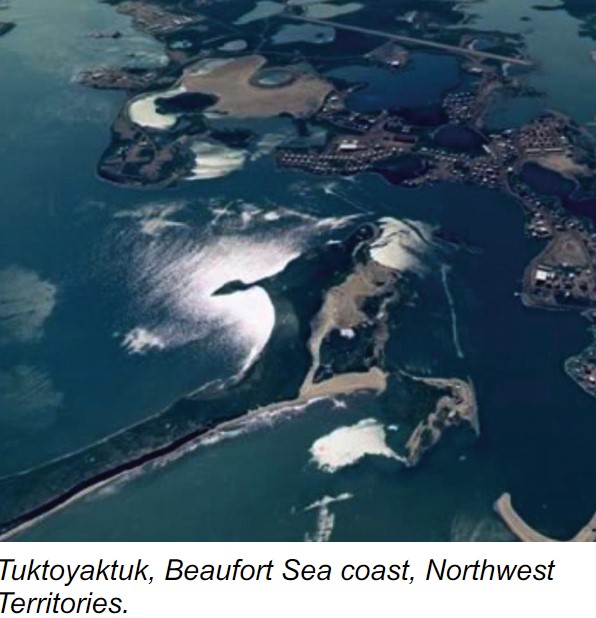
Tuktoyaktuk, Northwest Territories
* Community that is the most northerly point in Canada accessible by road
* Highest point is 25 metres above sea level
* Flooding and land loss
* caused by:
* Rising Sea Levels
* Coastal Erosion (1 metre a year since 1980)
* Thermokarst Activity → dev of thermokarst terrain
* Highest point is 25 metres above sea level
* Flooding and land loss
* caused by:
* Rising Sea Levels
* Coastal Erosion (1 metre a year since 1980)
* Thermokarst Activity → dev of thermokarst terrain
