CompTIA Network+ Exam Review
1/439
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
440 Terms
Exam Overview

Clients
Devices that users use to access the network (e.g., workstations, laptops, tablets)
Servers
Provide resources to the network (e.g., email servers, file servers)
Hubs
Older technology connecting devices but not commonly used due to limitations
Switches
Smarter hubs that ensure security and efficient bandwidth utilization
Wireless Access points (WAPs)
Enable wireless devices to connect to a wired network using radio frequency waves
Routers
Connect different networks, make intelligent forwarding decisions based on IP addresses
Firewalls
Security barrier between internal network and the internet, monitor and control traffic
Load Balancers
Distribute network/application traffic across servers, preventing bottlenecks
Proxy Servers
Act as intermediaries between user devices and the internet, enhancing security and privacy
Intrusion Detection System (IDS)
Detect unauthorized access or anomalies
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
Detect and take action to prevent intrusion
Controllers
Manage flow control in software-defined networking (SDN), offering flexibility and efficiency
Network-attached Storage (NAS) Devices
Dedicated file storage systems providing data access to authorized clients
Storage Area Networks (SANs)
High-speed networks for consolidated block-level data storage, enhancing accessibility
Media
Physical materials for data transmission (e.g., copper cables, fiber optic cables)
Wide Area Network (WAN) Links
Connect networks over large areas (e.g., between cities), essential for global connectivity
Key Takeaway
Understanding these network components is crucial for efficient and secure data transmission in information technology, aiding in network design, management, problem-solving, and security implementation
Client/Server Model
■ Utilizes a dedicated server for centralized access to files, scanners, printers, and resources
■ Easy administration and backup due to a central server
Benefits to Client/Server Model
● Centralized administration
● Easier management
● Better scalability
Drawbacks to Client/Server model
● Higher cost
● Requires dedicated hardware and specialized skillset
Peer-to-Peer Model
■ Direct sharing of resources among peers (laptops, desktops)
■ Difficult administration and backup due to dispersed files on different machines
Drawbacks
● Redundancy
● Complex management
● Scalability issues
■ Usefulfor low-cost setups, exemplified by Napster a decade ago
Benefits to Peer-to-Peer Model
● Low-cost
● No specialized infrastructure or hardware
Drawbacks to Peer-to-Peer Model
● Decentralized management
● Poor scalability for large networks
Personal Area Network (PAN)
■ Smallest network type
■ Covers about 10 feet or less
■ Examples are Bluetooth and USB
■ Connection within arm's reach
Local Area Network (LAN)
■ Common in office buildings
■ Limited distance
● Up to 100 meters
● CAT5 cabling
■ Can use WiFi (IEEE 802.11) or Ethernet (IEEE 802.3)
■ Examples include Office, school, and home
Campus Area Network (CAN)
■ Building-centric LAN
■ Spans numerous buildings in an area
■ Covers several miles
■ Examples are College campuses, business parks, military bases
Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
■ Connects locations across the entire city
■ Larger than CAN ● Up to 25 miles
■ Examples are City departments, multiple campuses in a city
Wide Area Network (WAN)
■ Connects geographically disparate internal networks
■ Large geographic coverage
● Across states, countries, or globally
■ Can consist of lease lines or VPNs.
■ Examples are Internet, private connections between offices across the country
Important Standards

Network Topology
■ Refers to the arrangement of elements in a computer network
■ Includes links, nodes, clients, and servers
Diagram Types
■ Physical Topology
● Describes physical cabling and device connections
● Represents real-world layout using floorplans
■ Logical Topology
● Describes how data flows in the network
● Focuses on the logical connection rather than physical placement
Point-to-Point Topology
● Direct connection between two devices
● Simple, reliable for small-scale connections
● Not scalable
● Used in WAN connections for remote offices
Ring Topology
● Circular data path with each device connected to two others
● Unidirectional flow prevents collisions
● Creates a single point of failure situation unless there are redundant connections for failover
● Common in FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Interface) for long-distance fiber optic networks.
Bus Topology

Star Topology

Hub-and-Spoke Topology

Mesh Topology

Infrastructure Mode

Ad Hoc Mode

Wireless Mesh
■ Use Cases for Wireless Mesh
● Post-disaster scenarios
● Humanitarian assistance missions
● Combining microwave, satellite, cellular, and Wi-Fi for reliable and redundant networks
○ Satellite for long distances
○ Microwaves for medium ranges
○ Wireless for short distances

Datacenter
Any facility composed of networked computers and storage that businesses and other organizations use to organize, process, store, and disseminate large amounts of data
Core Layer
● Houses high-performance routers, merging geographically separated networks
● Backbone of the network
Distribution/Aggregation Layer
● Provides boundary definition through access lists and filters
● Defines policies for the network at large
Access/Edge Layer
● Connects endpoint devices using regular switches
● Used to ensure the packets are converted to frames and delivered to the correct end point devices
Collapsed Core
● Network architecture where the core and distribution layers are merged into a single layer
● Creates a two-tiered core
● Simplified architecture for medium to small datacenters
● May not be suitable for larger and more complex networks
Spine and Leaf Architecture
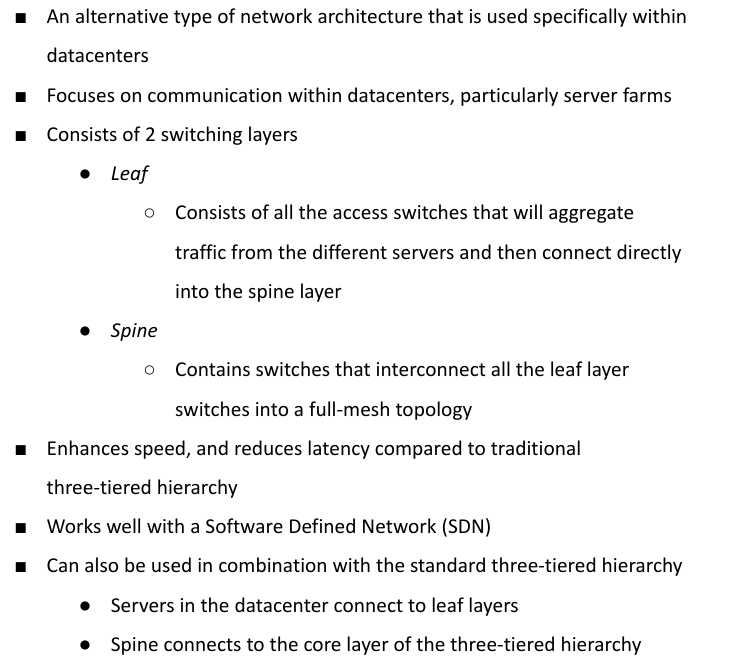
North-South Traffic
● Traffic that enters (Southbound traffic) or leaves (North traffic) data center from a system outside
East-West Traffic
● Dataflow within a datacenter
● Example: In a spine and leaf architecture, all data flow between servers is considered east-west traffic
● Prevalent with SDN, virtualization, and converged networks
Open Systems Interconnect Model (OSI)
■ Developed in 1977 by the International Organization for Standardization
■ OSI is a reference model
● Used to categorize the functions of a network
● Useful for troubleshooting
Layers
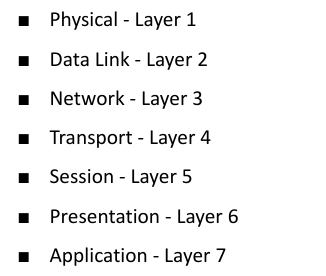
Names of data as it flows through the OSI model

Layer 1 (Physical)
■ First layer of the OSI model where transmission of bits across the network occurs and includes physical and electrical network characteristics
■ Data type occurs as bits
● Binary bits represented as a series of 1s and 0s

Transition Modulation
■ Switching between levels to represent 1 or 0
● Copper Wire (Cat5/Cat6) – Uses voltage (0V for 0, +5V/-5V for 1)
● Fiber Optic Cable– Uses light (on for 1, off for 0)
Connector Standards
■ RJ-45Connector– Used in CAT5/CAT6 cables
■ Wiring Standards
● TIA/EIA-568A
● TIA/EIA-568B
■ Crossover cables– TIA/EIA-568A on one end, and TIA/EIA-568B on the other end
■ Straight-through cables– TIA/EIA-568B on both ends
Asynchronous Communication
● Start and stop bits for out-of-sync data transmission
Synchronous Communication
● Real-time communication using a common time source
Broadband
● Divides bandwidth into separate channels (e.g., cable TV)
Baseband
● Uses all frequency of the cable all the time (e.g., telephone)
Multiplexing
■ Involves taking some limited amount of resource and using it more efficiently
● Allows multiple people to use a baseband connection at the same time
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)
● Allocates dedicated time slots
Statistical Time Division Multiplexing (StatTDM)
● Dynamically allocates time slots based on when people need it
Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM)
● Divides the medium into channels
Data Link Layer (Layer 2)
■ Responsible for packaging bits from Layer 1 into frames and transmitting them across the network
■ Performs error detection and correction, identifies devices using MAC addresses, and provides flow control

MAC Address (Media Access Control Address)
■ A means for identifying a device physically and allowing it to operate on a logical topology ■ A unique 48-bit physical addressing system is assigned to every network interface card (NIC) produced
● Written in hexadecimal numbers
● First 24 bits– identify the manufacturer
● Remaining 24 bits– identify the specific device
■ Crucial for logical topology– identifying devices on the network
Logical Link Control (LLC)
■ Provides connection services and acknowledges message receipt, ensuring controlled data flow
■ Most basic form offl ow control
● Limits data sent by a sender and prevents receiver overwhelm
■ Uses a checksum to detect corrupted data frames
Layer 3 (Network Layer)
■ Concerned with routing and forwarding traffic using logical addresses

IP Variants - common logical addressing schemes

Packet Switching (Routing)
● Data is divided into packets and then forwarded
● Most commonly used method
Circuit Switching
● A dedicated communication link is established between two devices
Message Switching
● Data is divided into messages which may be stored and then forwarded
Route Discovery and Selection

Connection Services at Layer 3
Augment Layer 2 services
■ Involves flow control
● Prevents sender from overwhelming the receiver
Packet reordering
● Ensures data packets arrive and are reassembled in the correct order
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)

Layer 4 (Transport Layer)
■ Dividing line between the upper layers and the lower layers of the OSI model
■ Upper Layers
● Transport
● Session
● Presentation
● Application
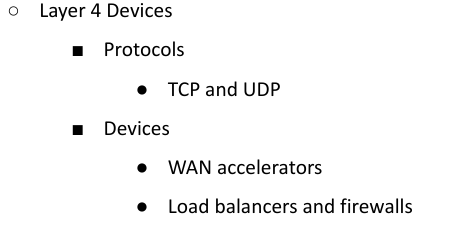
Segments
■ Data Type in Transport Layer
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
● Connection-oriented protocol that is a reliable way to transport segments across the network
● With acknowledgement
● Uses Three-Way Handshake
○ SYN–synchronization
○ SYN-ACK–synchronization- acknowledgement
○ ACK–acknowledgement
● Windowing for flow control
● Used for all network data that needs to be assured to get to its final destination
Segment–datatype for TCP
UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
● A connectionless protocol that is an unreliable way to transport segments (datagram)
● Used for audio and visual streaming
● No three-way handshake and less overhead
● No acknowledgment or retransmission
Datagram–datatype for UDP
Windowing
■ Allows clients to adjust the amount of data in each segment during transmission
■ Optimize throughput and bandwidth
■ Open or close window based on retransmissions
Buffering
■ Occurs when devices allocate memory to store segments if bandwidth is not readily available
■ Buffer
● Temporary storage for segments
■ Prevents overflow by clearing segments
Layer 5 (Session Layer)
■ Manages sessions, ensuring separate conversations to prevent data intermingling

Setting Up Session
■ Checking of user credentials and assigning numbers to sessions to help identify
Maintaining Session
■ Continuous data transfer between parties
■ If connection breaks, it will require re-establishment
■ Includes acknowledgement of data
Tearing Down a Session
■ Ending a session once communication goals are achieved
■ Mutual agreement or one party disconnects
Layer 6 (Presentation Layer)
■ Responsible for formatting data for exchange and securing it through encryption
Data Formatting

Encryption
Using to scramble data in transit to keep it secure and provide data confidentiality
Transport Layer Security (TLS)
● Ensures secure data transfer
● Creates an encrypted tunnel, protecting sensitive information
Control how ASCII Text is displayed on the screen
● HTML
● XML
● PHP
● JavaScript
Different ways of displaying text using ones and zeros
● ASCII
● Unicode
● EBCDIC
Different graphical representations of 1s and 0s
● GIFs
● JPEGs
● TIFFs
● SVGs
● PNGS
1s and 0s formatted to create watchable videos
● MP4s
● MPEGs
● MOV
Scrambles data to provide confidentiality and security during transit and storage
● TLS
● SSL(Secure Sockets Layer)
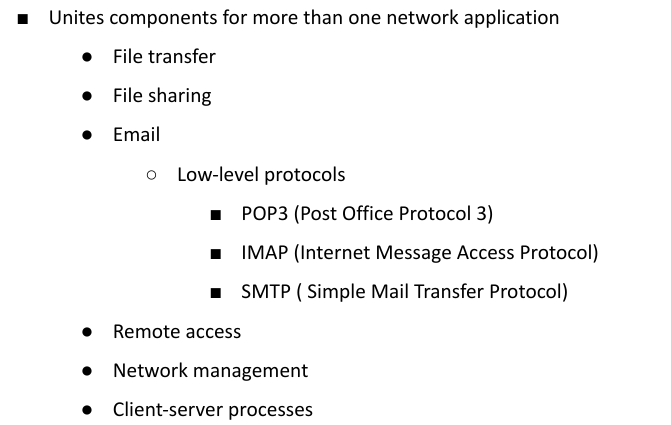
Layer 7 (Application Layer)
■ Provides application-level services where users communicate with the computer
■ Focus on lower-level applications
● File transfer
● Network transfer
Application Services
Service Advertisement
■ Applications send announcements to other devices on the network
■ Devices advertise the services they offer
● Printers and file servers managed by Active Directory
● Self-advertising devices like wireless printers
Email Applications (Layer 7 Protocols)
● POP3
● IMAP
● SMTP
Web Browsing (Layer 7 Protocol)
● HTTPS
● HTTP
Layer 7 Protocol (DNS)
Domain Name Services